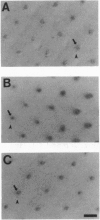
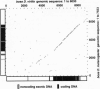
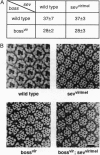
Abstract
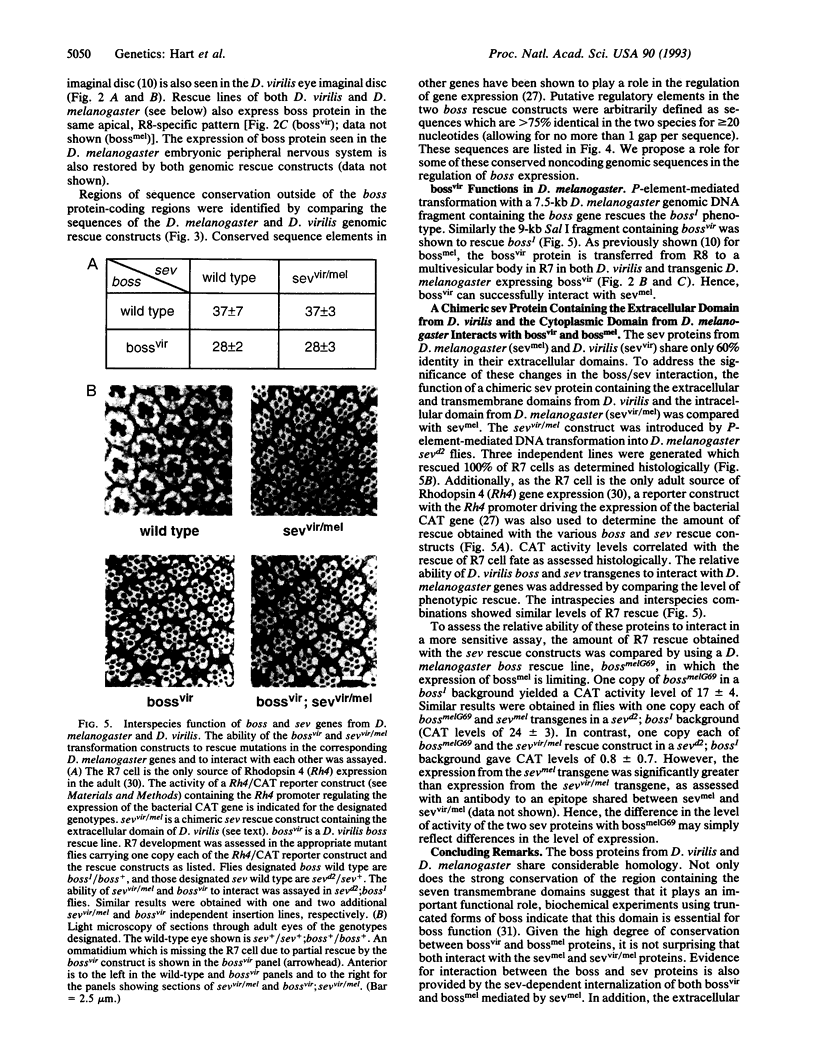
An inductive interaction between the sevenless (sev) transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor and the bride of sevenless (boss) transmembrane ligand is required for the development of the R7 photoreceptor neuron in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. The boss protein is proposed to contain a large N-terminal extracellular domain, seven transmembrane segments, and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail. The boss protein from Drosophila virilis (bossvir) retains strong amino acid identity with loss from D. melanogaster (bossmel): 73% identity in the N-terminal extracellular domain and 91% identity in the seven-transmembrane domain, including the cytoplasmic tail. By using P-element-mediated DNA transformation, the bossmel and bossvir genes were shown to rescue the D. melanogaster boss1 mutation. The expression of bossvir protein in D. melanogaster is indistinguishable from that of bossmel protein. Noncoding sequences which may regulate boss expression were identified based on their conservation during evolution. The predicted sev protein from D. virilis (sevvir) was previously shown to be 63% identical to sev from D. melanogaster (sevmel). A chimeric gene, (sevvir/mel), encoding the extracellular domain of sevvir and the cytoplasmic domain of sevmel rescues the D. melanogaster sevd2 mutation through interaction with either bossvir or bossmel.
Full text
PDF

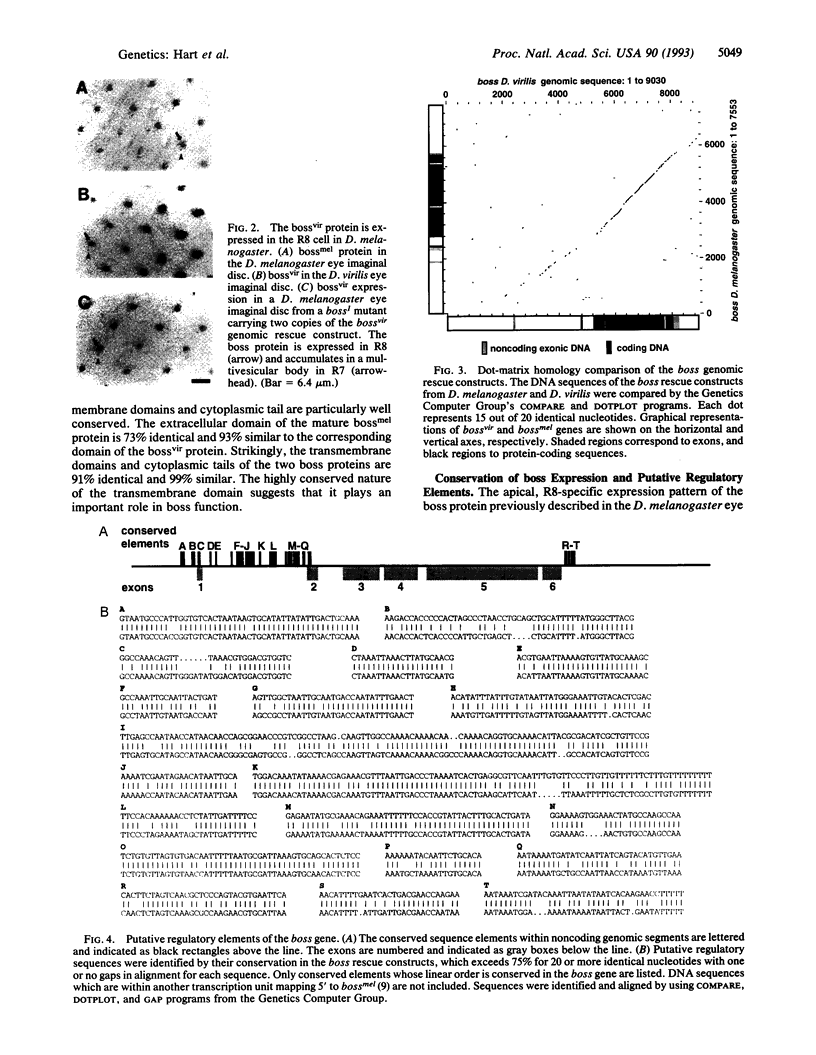

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee U., Renfranz P. J., Hinton D. R., Rabin B. A., Benzer S. The sevenless+ protein is expressed apically in cell membranes of developing Drosophila retina; it is not restricted to cell R7. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Hafen E. Control of photoreceptor cell fate by the sevenless protein requires a functional tyrosine kinase domain. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Wilson A. C. Molecular evolution in Drosophila and the higher Diptera II. A time scale for fly evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02100622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Lila T., Michael W. M., Hackett D., Rubin G. M. Analysis of the enhancer element that controls expression of sevenless in the developing Drosophila eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6853–6857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagan R. L., Krämer H., Hart A. C., Zipursky S. L. The bride of sevenless and sevenless interaction: internalization of a transmembrane ligand. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90442-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of cis-acting requirements of the Rh3 and Rh4 genes reveals a bipartite organization to rhodopsin promoters in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):444–463. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. A., Stark W. S., Walker J. A. Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):415–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart A. C., Krämer H., Van Vactor D. L., Jr, Paidhungat M., Zipursky S. L. Induction of cell fate in the Drosophila retina: the bride of sevenless protein is predicted to contain a large extracellular domain and seven transmembrane segments. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1835–1847. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart A. C., Krämer H., Zipursky S. L. Extracellular domain of the boss transmembrane ligand acts as an antagonist of the sev receptor. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):732–736. doi: 10.1038/361732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., Heberlein U., Rubin G. M. The homeo domain protein rough is expressed in a subset of cells in the developing Drosophila eye where it can specify photoreceptor cell subtype. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):712–727. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Cagan R. L., Zipursky S. L. Interaction of bride of sevenless membrane-bound ligand and the sevenless tyrosine-kinase receptor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):207–212. doi: 10.1038/352207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael W. M., Bowtell D. D., Rubin G. M. Comparison of the sevenless genes of Drosophila virilis and Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5351–5353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mismer D., Rubin G. M. Analysis of the promoter of the ninaE opsin gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):565–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Jones K., Zuker C., Rubin G. A second opsin gene expressed in the ultraviolet-sensitive R7 photoreceptor cells of Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01558.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi R., Güssow D. H., Jones P. T., Winter G. Cloning immunoglobulin variable domains for expression by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3833–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinke R., Zipursky S. L. Cell-cell interaction in the Drosophila retina: the bride of sevenless gene is required in photoreceptor cell R8 for R7 cell development. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Dodson G. S., Laverty T. R., Rubin G. M. Ras1 and a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor perform crucial steps in signaling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):701–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Rubin G. M. Structure and activity of the sevenless protein: a protein tyrosine kinase receptor required for photoreceptor development in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8333–8337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Rubin G. M. Structure and activity of the sevenless protein: a protein tyrosine kinase receptor required for photoreceptor development in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8333–8337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Bowtell D. D., Hafen E., Rubin G. M. Localization of the sevenless protein, a putative receptor for positional information, in the eye imaginal disc of Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Cell fate in the Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):264–275. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Sevenless: a cell-specific homeotic mutation of the Drosophila eye. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4736.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vactor D. L., Jr, Cagan R. L., Krämer H., Zipursky S. L. Induction in the developing compound eye of Drosophila: multiple mechanisms restrict R7 induction to a single retinal precursor cell. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1145–1155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]