Abstract
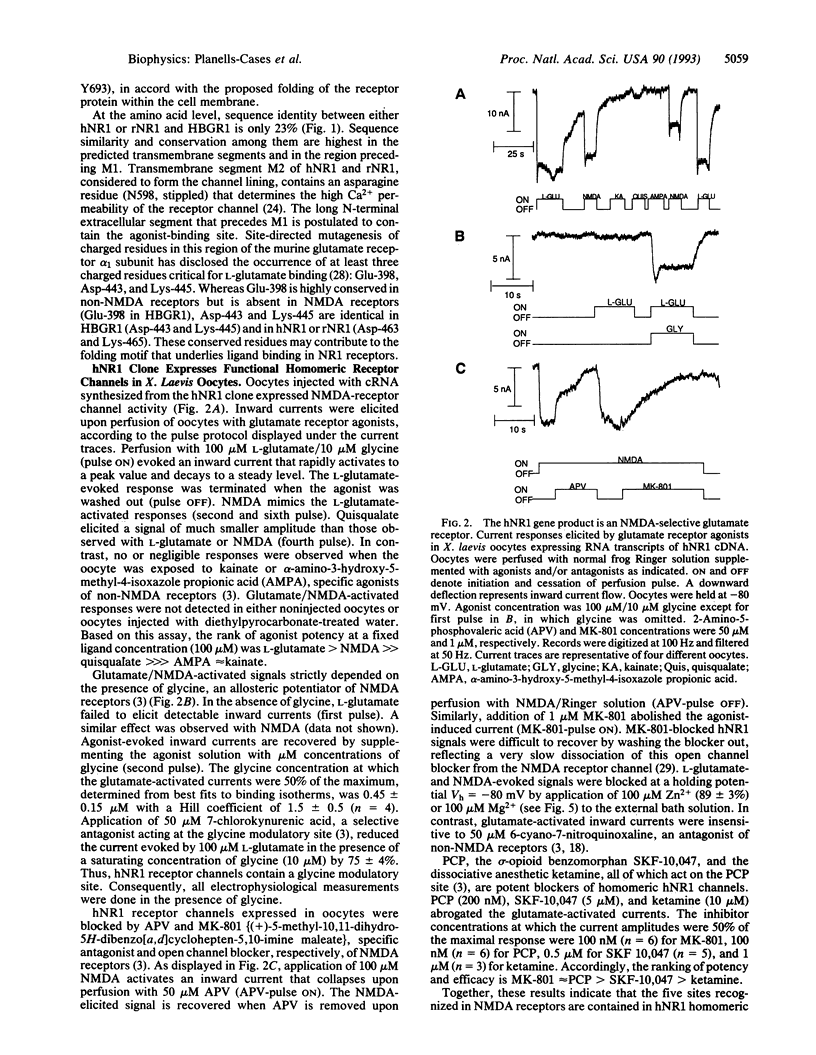
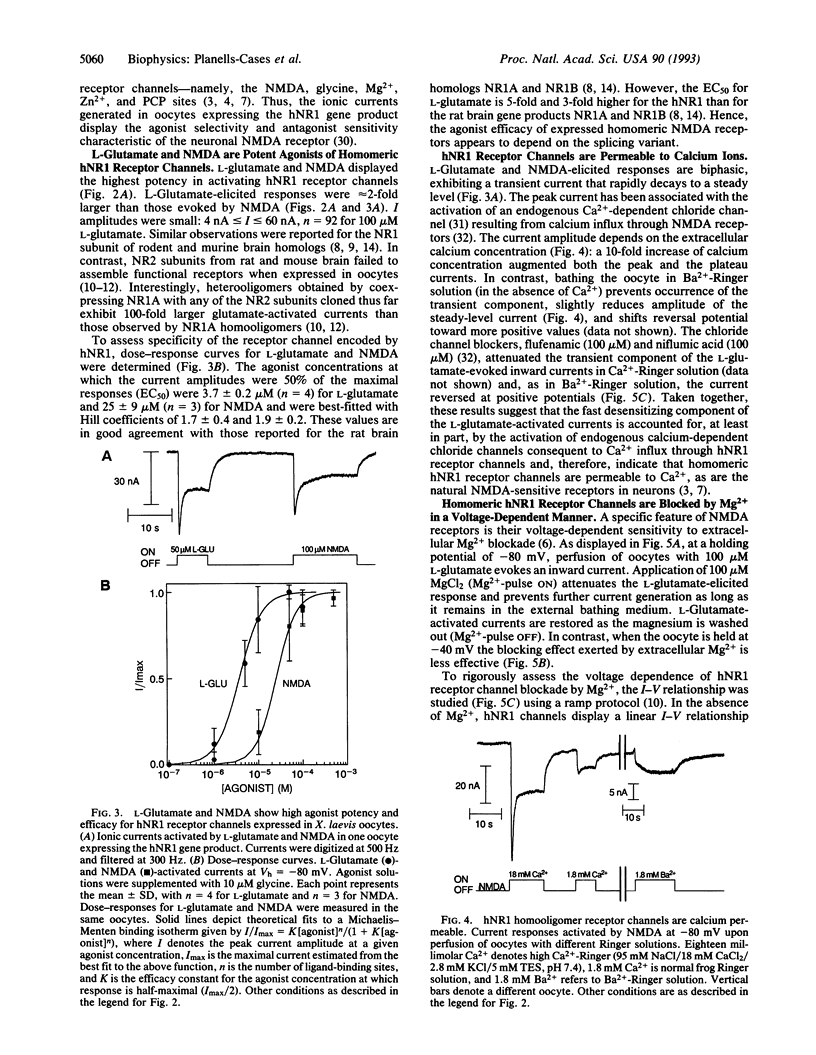
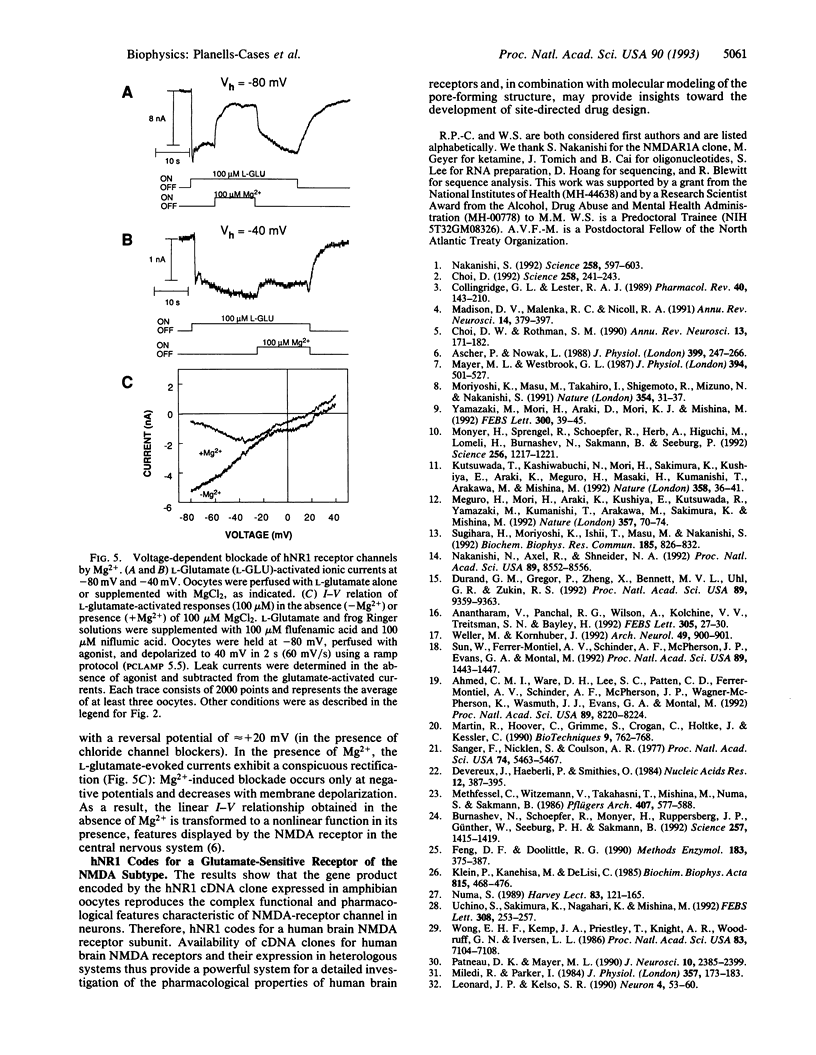
A cDNA encoding a full-length N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit 1, hNR1, was isolated from a human brain cDNA library. The hNR1 cDNA encodes an open reading frame of approximately 2.7 kb that shares high homology with the rat brain NMDA receptor subunit 1 and the mouse zeta 1 subunit. The hNR1 sequence, however, diverges from the rodent and murine homologs near the C terminus, suggesting that they represent alternatively spliced messages of the same gene. Oocytes injected with cRNA synthesized from the hNR1 cDNA express glutamate and NMDA-activated currents in the presence of glycine. Currents are blocked by the NMDA-receptor-specific antagonists 2-amino-5-phosphovaleric acid and 7-chlorokynurenate, and the open channel blockers MK-801 and phencyclidine, by Mg2+ ions in a voltage-dependent manner, and by Zn2+. Expressed hNR1 homomeric receptor channels exhibit the high Ca2+ permeability characteristic of neuronal NMDA receptors. Therefore, the cDNA clone hNR1 codes for a human brain NMDA receptor subunit cognate to the rodent and murine brain NR1 subunits.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Ware D. H., Lee S. C., Patten C. D., Ferrer-Montiel A. V., Schinder A. F., McPherson J. D., Wagner-McPherson C. B., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A. Primary structure, chromosomal localization, and functional expression of a voltage-gated sodium channel from human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8220–8224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantharam V., Panchal R. G., Wilson A., Kolchine V. V., Treistman S. N., Bayley H. Combinatorial RNA splicing alters the surface charge on the NMDA receptor. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 22;305(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80648-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Ruppersberg J. P., Günther W., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1415–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1382314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Bench to bedside: the glutamate connection. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):241–243. doi: 10.1126/science.1357748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Rothman S. M. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:171–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Lester R. A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):143–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand G. M., Gregor P., Zheng X., Bennett M. V., Uhl G. R., Zukin R. S. Cloning of an apparent splice variant of the rat N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NMDAR1 with altered sensitivity to polyamines and activators of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9359–9363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsuwada T., Kashiwabuchi N., Mori H., Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Araki K., Meguro H., Masaki H., Kumanishi T., Arakawa M. Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):36–41. doi: 10.1038/358036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. P., Kelso S. R. Apparent desensitization of NMDA responses in Xenopus oocytes involves calcium-dependent chloride current. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90443-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. Mechanisms underlying long-term potentiation of synaptic transmission. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:379–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Hoover C., Grimme S., Grogan C., Höltke J., Kessler C. A highly sensitive, nonradioactive DNA labeling and detection system. Biotechniques. 1990 Dec;9(6):762–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meguro H., Mori H., Araki K., Kushiya E., Kutsuwada T., Yamazaki M., Kumanishi T., Arakawa M., Sakimura K., Mishina M. Functional characterization of a heteromeric NMDA receptor channel expressed from cloned cDNAs. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):70–74. doi: 10.1038/357070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monyer H., Sprengel R., Schoepfer R., Herb A., Higuchi M., Lomeli H., Burnashev N., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1217–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):31–37. doi: 10.1038/354031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N., Axel R., Shneider N. A. Alternative splicing generates functionally distinct N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8552–8556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):597–603. doi: 10.1126/science.1329206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S. A molecular view of neurotransmitter receptors and ionic channels. Harvey Lect. 1987;83:121–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Structure-activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2385–2399. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara H., Moriyoshi K., Ishii T., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structures and properties of seven isoforms of the NMDA receptor generated by alternative splicing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):826–832. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91701-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun W., Ferrer-Montiel A. V., Schinder A. F., McPherson J. P., Evans G. A., Montal M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and functional expression of human brain glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchino S., Sakimura K., Nagahari K., Mishina M. Mutations in a putative agonist binding region of the AMPA-selective glutamate receptor channel. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81286-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Kornhuber J. N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists, schizophrenia, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1992 Sep;49(9):900–901. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530330018007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki M., Mori H., Araki K., Mori K. J., Mishina M. Cloning, expression and modulation of a mouse NMDA receptor subunit. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 23;300(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80160-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



