Abstract
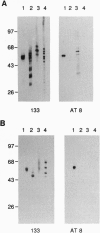
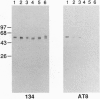
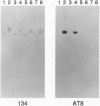
Tau is a neuronal phosphoprotein whose expression is developmentally regulated. A single tau isoform is expressed in fetal human brain but six isoforms are expressed in adult brain, with the fetal isoform corresponding to the shortest of the adult isoforms. Phosphorylation of tau is also developmentally regulated, as fetal tau is phosphorylated at more sites than adult tau. In Alzheimer disease, the six adult tau isoforms become abnormally phosphorylated and form the paired helical filament, the major fibrous component of the characteristic neurofibrillary lesions. We show here that Ser-202 (in the numbering of the longest human brain tau isoform) is a phosphorylation site that distinguishes fetal from adult tau and we identify it as one of the abnormal phosphorylation sites in Alzheimer disease. The abnormal phosphorylation of tau at Ser-202 in Alzheimer disease thus recapitulates normal phosphorylation during development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreadis A., Brown W. M., Kosik K. S. Structure and novel exons of the human tau gene. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10626–10633. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernat J., Mandelkow E. M., Schröter C., Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Steiner B., Berling B., Meyer H., Mercken M., Vandermeeren A., Goedert M. The switch of tau protein to an Alzheimer-like state includes the phosphorylation of two serine-proline motifs upstream of the microtubule binding region. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1593–1597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butner K. A., Kirschner M. W. Tau protein binds to microtubules through a flexible array of distributed weak sites. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):717–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Olesen O. F., Jakes R., Goedert M. The microtubule binding repeats of tau protein assemble into filaments like those found in Alzheimer's disease. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 7;309(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel D. N., Hyman A. A., Cobb M. H., Kirschner M. W. Modulation of the dynamic instability of tubulin assembly by the microtubule-associated protein tau. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1141–1154. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes G., Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Döring F., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Goris J., Dorée M., Mandelkow E. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase transforms tau protein into an Alzheimer-like state. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Lennon A. M., Fellous A., Mareck A., Pierre M., Nunez J. Heterogeneity of microtubule-associated proteins and brain development. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Cohen E. S., Jakes R., Cohen P. p42 MAP kinase phosphorylation sites in microtubule-associated protein tau are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A1. Implications for Alzheimer's disease [corrected]. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 2;312(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81418-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Crowther R. A., Garner C. C. Molecular characterization of microtubule-associated proteins tau and MAP2. Trends Neurosci. 1991 May;14(5):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R. Expression of separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4225–4230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Cairns N. J., Crowther R. A. Tau proteins of Alzheimer paired helical filaments: abnormal phosphorylation of all six brain isoforms. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90117-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):393–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Walker J. E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P. A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5827–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P., Schein J. D., Binder L. I. Hydrofluoric acid-treated tau PHF proteins display the same biochemical properties as normal tau. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M., Morishima-Kawashima M., Takio K., Suzuki M., Titani K., Ihara Y. Protein sequence and mass spectrometric analyses of tau in the Alzheimer's disease brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17047–17054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W., Martin D. W., Jr Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Takamatsu M., Tomizawa K., Omori A., Takahashi M., Arioka M., Uchida T., Imahori K. Tau protein kinase I converts normal tau protein into A68-like component of paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10897–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemaru K., Takio K., Miura R., Titani K., Ihara Y. Fetal-type phosphorylation of the tau in paired helical filaments. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1667–1675. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Bakalis S., Neve R. L. Developmentally regulated expression of specific tau sequences. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1389–1397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Yen S. H. Structural stability of paired helical filaments requires microtubule-binding domains of tau: a model for self-association. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90169-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang E., Szendrei G. I., Lee V. M., Otvos L., Jr Immunological and conformation characterization of a phosphorylated immunodominant epitope on the paired helical filaments found in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91264-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledesma M. D., Correas I., Avila J., Díaz-Nido J. Implication of brain cdc2 and MAP2 kinases in the phosphorylation of tau protein in Alzheimer's disease. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 17;308(2):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81278-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Cowan N., Kirschner M. The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.3122323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Neve R. L., Kosik K. S. The microtubule binding domain of tau protein. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1615–1624. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q. The disordered neuronal cytoskeleton in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Oct;2(5):653–656. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90034-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken M., Vandermeeren M., Lübke U., Six J., Boons J., Van de Voorde A., Martin J. J., Gheuens J. Monoclonal antibodies with selective specificity for Alzheimer Tau are directed against phosphatase-sensitive epitopes. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;84(3):265–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00227819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Hamada Y., Kawaguchi M., Honda T., Kondo J., Ihara Y. A distinct form of tau is selectively incorporated into Alzheimer's paired helical filaments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1221–1226. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92240-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder H. M., Ingram V. M. Two novel kinases phosphorylate tau and the KSP site of heavy neurofilament subunits in high stoichiometric ratios. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3325–3343. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03325.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szendrei G. I., Lee V. M., Otvos L., Jr Recognition of the minimal epitope of monoclonal antibody Tau-1 depends upon the presence of a phosphate group but not its location. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Feb 1;34(2):243–249. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490340212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohyama T., Lee V. M., Rorke L. B., Trojanowski J. Q. Molecular milestones that signal axonal maturation and the commitment of human spinal cord precursor cells to the neuronal or glial phenotype in development. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Aug 15;310(3):285–299. doi: 10.1002/cne.903100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille H., Drewes G., Biernat J., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments and antiparallel dimers formed from microtubule-associated protein tau in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):573–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Mirra S. S., Pollock N. J., Binder L. I. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4040–4043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]