Abstract
The FLT3 kinase represents an attractive target to effectively treat AML. Unfortunately, no FLT3 targeted therapeutic is currently approved. In line with our continued interests in treating kinase related disease for anti-FLT3 mutant activity, we utilized pioneering synthetic methodology in combination with computer aided drug discovery and identified low molecular weight, highly ligand efficient, FLT3 kinase inhibitors. Compounds were analyzed for biochemical inhibition, their ability to selectively inhibit cell proliferation, for FLT3 mutant activity, and preliminary aqueous solubility. Validated hits were discovered that can serve as starting platforms for lead candidates.
Keywords: FLT3, Kinase inhibitor, AML, Ligand efficiency, Computer aided drug discovery
1. Introduction
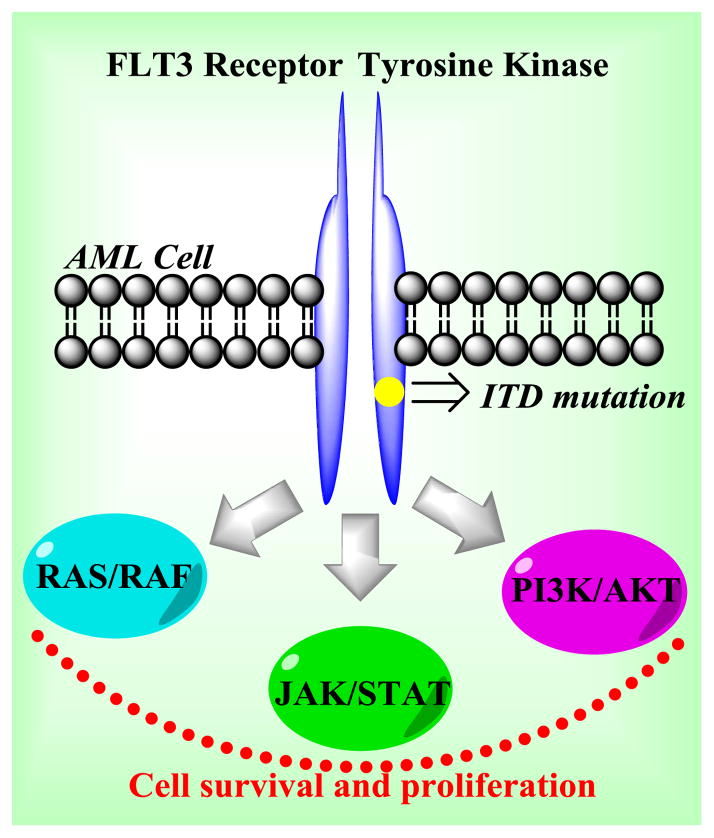
FLT3 (Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3) is a member of the class III family of cytokine receptor tyrosine kinases [1]. FLT3 signaling produces pro-survival and growth signals in cells and is important for the normal development of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells [2]. Pathological activating mutations in the FLT3 kinase represent the most common genetic alteration in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), occurring in approximately one third of all cases, and are associated with a poor prognosis [3]. The most common FLT3 gain of function alterations are FLT3-ITD (internal tandem duplication) mutations, which typically occur in the juxtamembrane (JM) domain-coding sequence of FLT3 [4]. The ITD event produces constitutive ligand-independent activation of FLT3 [5]; therefore, the catalytic regulation of FLT3 is compromised leading to autophosphorylation and continuous activation of the RAS/RAF, JAK/STAT, and PI3K/AKT pathways (Fig. 1) [6]. FLT3-ITD mutations are present in about 20–25% of all AML patients [7]. An additional 5–10% of AML patients have activating point mutations in the FLT3 kinase domain.
Fig. 1.
In AML, the FLT3 receptor tyrosine kinase becomes constitutively active and stimulates RAS/RAF, JAK/STAT, and PI3K/AKT pathways. This modifies the apoptotic signaling axis, which causes cell survival and proliferation.
The growing body of evidence that suggests FLT3 activity is essential for a large population of AML has sparked enormous therapeutic interests. A number of tyrosine kinase (TK) inhibitors have been tested as FLT3 inhibitors [8–25]. TK inhibitors such as cabozantinib [8], sorafenib [9–12], sunitinib [12–14], ponatinib [15–17], crenolanib [18–21], and quizartinib [22,23] have all displayed FLT3 activity, and crenolanib [24] and quizartinib [25] are currently undergoing FDA trials. Issues with current FLT3 inhibitors stem from problems with poor pharmacokinetic and toxicity profiles and also vulnerability to drug-resistant mutations [24–26]. Crenolanib has displayed significant drawbacks in a phase II solid tumor trial because of issues with hepatic toxicity and a poor pharmacokinetic (PK) profile, requiring the drug to be administered three times daily; [24], leading to modest clinical activity to date. Quizartinib cannot be dosed at a high enough concentration to inhibit secondary kinase domain mutations because of dose-limiting myelosuppression [26]. Although numerous kinase inhibitors have displayed FLT3 activity, issues with toxicity, poor drug properties, and vulnerability to drug-resistant mutation have caused unfavorable therapeutic profiles with no agent achieving FDA approval.
In our continued effort to develop novel kinase inhibitors for human disease [27,28], we identified novel FLT3 validated hits with low molecular weights and high ligand efficiency (LE) [29] values utilizing an innovative synthetic methodology [30,31]. While the compounds are not as active as known FLT3 inhibitors, low molecular weights (MW), high LE values, and rapid synthesis permit the hit compounds to serve as exceedingly flexible starting points to develop FLT3 lead candidates. Further, the inhibitors are based upon the imidazopyridine core, which is a unique heterocycle for FLT3 inhibition. Herein we discuss the identification of novel imidazopyridine FTL3 inhibitors using innovative synthetic methodology in combination with computer aided drug discovery (CADD).
2. Results and discussion
2.1. Virtual library generation
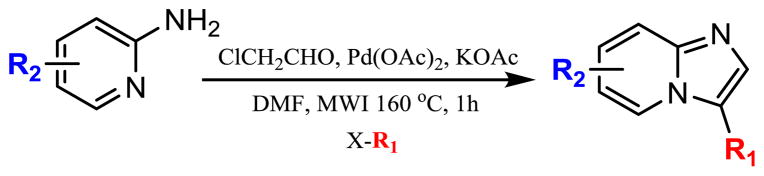
Recently, a new synthetic methodology has been developed that permits the rapid generation of imidazopyridine analogs that appear to have kinase-inhibitor functionality (Scheme 1) [30]. A virtual library was constructed around the synthesis using a select compound (Table 1; 1) along with additional compounds (Tables 1–3) and were utilized to help identify potential kinase inhibitors (Table 1). In total, the virtual library contained about 50 structures that could be synthesized utilizing this novel, one-pot synthesis. The overarching goal was to exploit rapid synthetic diversity with help from computer aided drug discovery (CADD) to expeditiously evaluate the usefulness of imidazopyridine-based kinase inhibitors.
Scheme 1.
Novel multi-component reaction (MCR) that generates functionally constrained, imidazopyridine analogs in a one-pot synthesis.
Table 1.
FLT3 computational screening results with select analogs from the virtual library.

| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmpd | Predicted ΔG (kcal/mol) | Predicted LEa | MW (g/mol) |
| 1 | −8.6 | 0.48 | 239 |
| 2 | −8.6 | 0.54 | 228 |
| 3 (17) | −10 | 0.50 | 276 |
LE (ligand efficiency) was calculated from the equation, LE = (− ΔG)/N, where ‘ΔG’ is the predicted computational affinity, and ‘N’ is the amount of non-hydrogen atoms.
Table 3.
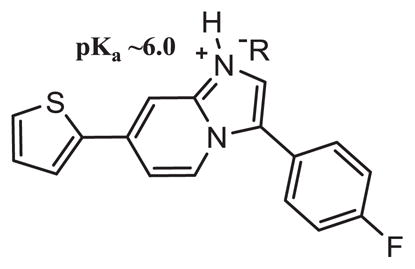
Aqueous solubility of compound 17 with various complexing acids (−R). The pKa of 17 is predicted around 6.0, which is similar to Ambien® (zolpidem).
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Acid (−R) | Acid pKa | Aqueous solubility (mg/mL)a |
| Free-basea | / | <0.080 |
| Acetic acid | 4.7 | <0.080 |
| HCl | −7.0 | <0.080 |
| pTSA | −2.8 | ~0.25 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 3.5 | <0.080 |
| Stearic acid | 4.7 | <0.080 |
| 2-thiobarbituric acid | 3.9 | <0.080 |
| L-ascorbic acid | 4.1 | <0.080 |
| Salicylic acid | 2.9 | <0.080 |
| Oxalic acid | 1.2 | ~0.50 |
| Benzoic acid | 4.2 | <0.080 |
25 °C with 0.2 μM filtered, deionized water at pH 7.
2.2. Computer aided drug discovery (CADD)
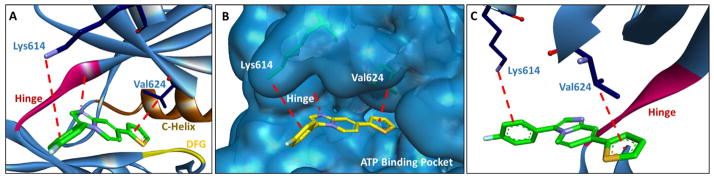
Using AutoDock Vina [32], the virtual library was screened against multiple kinase active sites. AutoDock Vina provides docking scores in terms of ΔG values and a ΔG value of less than −8.0 kcal/mol was defined as a hit. Computational hit compounds were investigated further for plausible binding modes and novelty of structure in Discovery Studio 3.5. In general, the imidazopyridine library was found to have highly negative docking scores with good ligand efficiency (LE) values for the FLT3 tyrosine kinase (PDB# 1RJB) (Table 1) [33]. Binding analysis was investigated with 3 because of an increase in computational affinity. Unlike 1 or 2, which are mono-substituted, 3 contains diimidazopyridine substitution. Modeling results indicated substitution off the 3 position interacts with Lys614 (cation-Pi interaction) and substitution at the 7 position interacts with Val624 (sigma-Pi interaction) in the FLT3 active site (Fig. 2). Because of the modeling results, the synthesis of a FLT3-directed compound library was completed utilizing the imidazopyridine core. Importantly, generated inhibitors have low molecular weights, high LEs, and are validated hits for further FLT3 inhibitor development.
Fig. 2.
Computational modeling of 3 (17) in FLT3. (A) 3 (17) creates key interactions with Lys614 (cation-pi), Val624 (sigma-pi), and the hinge. (B) Space filling diagram depicting the FLT3 active site in complex with 3 (17). From the modeling study, the inhibitor appears to be directly competitive with ATP for the ATP binding pocket. (C) Alternative angle to (A) to help better illustrate interactions with Lys614, Val624, and the hinge. The hinge is shown in red, the c-helix in brown, and the DFG motif in yellow. PDB# 1RJB [32]. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
2.3. FLT3 inhibitor library synthesis
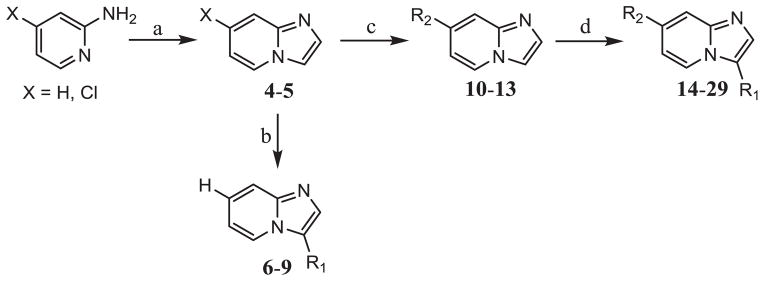
Library generation was accomplished using a rapid 2 or 3 step synthesis that was assisted with microwave irradiation (MWI) (Scheme 2). Although the literature reports aminopyridine cyclization and C–C bond formation in one step [30], the synthetic approach was modified for analoguing purposes and to increase overall yield/purity of the final products. The most innovative aspect to the synthesis is the use of a ligand-free, C–H activating reaction to create substitution at the 5 position of imidazopyridine. Traditionally, imidazopyridine is activated at the 5 position through halogenation [34–41], requiring additional steps to create a C–C bond. We took advantage of an innovate ligand-free, C–H activating reaction to lower the amount of synthetic steps as well as library iteration time [30,31].
Scheme 2.
a) 2-chloroacetaldehyde (1.2 eqv.), 1-butanol, 130 °C, 12 h, b) Br-R1, KOAc (2 eqv.), Pd(OAc)2, DMF, MWI 160 °C, 1 h c) B(OH)2-R2, Pd2(dba)3, P(Cy)3, Na2CO3, DMF:H2O (8:1), MWI 130 °C, 1 h d) Br-R1, KOAc (2 eqv.), Pd(OAc)2, DMF, MWI 160 °C, 1 h.
To construct the imidazopyridine core, 2-aminopyridine or 4-chloro-2-aminopyridine was cyclized with 2-chloroacetaldehyde in 1-butanol under reflux conditions. Imidazopyridine, 4, was subjected to a ligand-free, C–H activating reaction to generate analogs 6–9. To create di-substituted imidazopyridines, 7-chloroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, 5, was reacted with various boronic acids for substitution at the 7 position creating intermediates 10–13. After, the analogs were subjected to a ligand-free, C–H activating reaction for substitution at the 5 position yielding compounds 14–29.
2.4. FLT3 inhibitor biochemical evaluation
After synthesis, compounds were screened against FLT3 at a single point concentration of 20.0 μM (Table 2). Results from single point activity correlate very well with results from computational modeling, as di-substituted imidazopyridines displayed the greatest amount of inhibition. It was found that electron withdrawing functionality at the para position of R1 increased activity. Also, at the R2 position, 5-membered ring systems with a heteroatom were preferred.
Table 2.
FLT3 biochemical inhibition and LE values.
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmpd | R1 | R2 | % Inhibition at 20 μMa | IC50 (μM)b | LEc |
| 4 | -H | -H | 14.6% | / | / |
| 5 | -H | -Cl | 23.8% | / | / |
| 6 | 4-fluoro-3-cyanobenzene | -H | 61.3% | / | / |
| 7 | 4-phenylacetonitrile | -H | 20.0% | / | / |
| 8 | 4-methylbenzene | -H | 77.0% | / | / |
| 9 | 4-fluorobenzene | -H | 94.8% | 0.480 | 0.55 |
| 10 | -H | 2-Thiophene | 79.8% | / | / |
| 11 | -H | 2-Furan | 67.1% | / | / |
| 12 | -H | Phenyl | 0.0% | / | / |
| 13 | -H | 4-Methoxyphenyl | 33.9% | / | / |
| 14 | 4-fluoro-3-cyanobenzene | 2-Thiophene | 29.7% | / | / |
| 15 | 4-phenylacetonitrile | 2-Thiophene | 98.0% | 0.051 | 0.44 |
| 16 | 4-methylbenzene | 2-Thiophene | 89.7% | / | / |
| 17 | 4-fluorobenzene | 2-Thiophene | 99.1% | 0.015 | 0.52 |
| 18 | 4-fluoro-3-cyanobenzene | 2-Furan | 98.7% | 0.470 | 0.38 |
| 19 | 4-phenylacetonitrile | 2-Furan | 97.8% | 0.190 | 0.40 |
| 20 | 4-methylbenzene | 2-Furan | 95.5% | 0.160 | 0.45 |
| 21 | 4-fluorobenzene | 2-Furan | 99.3% | 0.041 | 0.49 |
| 22 | 4-fluoro-3-cyanobenzene | Phenyl | 94.1% | 0.230 | 0.38 |
| 23 | 4-phenylacetonitrile | Phenyl | 96.4% | 0.550 | 0.36 |
| 24 | 4-methylbenzene | Phenyl | 94.1% | 0.300 | 0.41 |
| 25 | 4-fluorobenzene | Phenyl | 98.8% | 0.016 | 0.49 |
| 26 | 4-fluoro-3-cyanobenzene | 4-Methoxyphenyl | 81.4% | / | / |
| 27 | 4-phenylacetonitrile | 4-Methoxyphenyl | 91.0% | 0.430 | 0.34 |
| 28 | 4-methylbenzene | 4-Methoxyphenyl | 91.4% | 0.440 | 0.37 |
| 29 | 4-fluorobenzene | 4-Methoxyphenyl | 98.6% | 0.078 | 0.41 |
| Quizartinib | / | / | / | 0.039 | 0.31 |
Single point values represent the amount of enzyme inhibition at a 20 μM drug concentration. The screening was completed in triplicate at a 190 μM ATP concentration.
IC50 values represent the concentration required to inhibit enzyme activity by 50%. The screening was completed at 190 μM ATP concentration in duplicate.
LE (ligand efficiency) was calculated from the equation LE = 1.4(−log(IC50)/N, where ‘IC50’ is the molar concentration required to inhibit enzyme activity by 50%, and ‘N’ is the amount of non-hydrogen atoms.
Compounds that displayed strong single point inhibition (>90%) were subjected to IC50 calculation (Table 2). At the R1 position, 4-fluorobenzene produced compounds with the best inhibition as seen with 17, 21, 25, and 29, which obtained IC50 values of 0.015, 0.041, 0.016, and 0.078 μM, respectively. This series is predicted to engage Lys614 through a cation-Pi interaction (Fig. 2), and the electron withdrawing properties of fluorine likely increase this interaction. At the R2 position, thiophene as well as phenyl obtained greatest inhibition as seen with 17 and 25, which achieved IC50 values of 0.015 and 0.016 μM, respectively. The R2 position is predicted to contact Val624 through a sigma–pi interaction and thiophene and phenyl appear preferred at this region.
To assess binding energy per atom, ligand efficiency (LE) values were calculated (Table 2). Inhibitors displayed LE values greater than 0.34, which suggests all compounds are extremely energy efficient binders. The FLT3 LE value for crenolanib and quizartinib is 0.38 and 0.31, respectively. Even though both crenolanib and quizartinib achieve strong inhibition of FLT3, LE has not been optimized. For instance, compound 9, which displayed a moderate FLT3 IC50 of 0.480 μM achieved a strikingly high LE value of 0.55. Compound 9 represents an extremely energy efficient binder and crystallography studies are underway to help decipher important binding interactions. The most potent analogs, 17 and 25, displayed LE values of 0.52 and 0.49, respectively. Both compounds 17 and 25 are strategic progressions from compound 9 and illustrate a durable conservation in LE with the imidazopyridine scaffold. Although 17 and 25 achieved low nano-molar inhibition on FLT3, the compounds are still relatively small and can be further improved for enhanced potency.
2.5. FLT3-driven cell-based studies
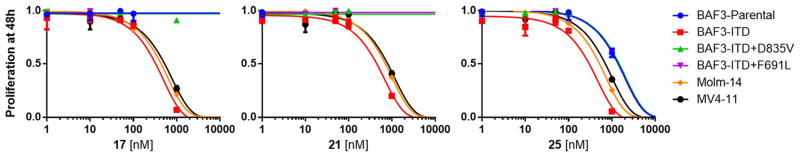
Compounds 17, 21, and 25 were progressed to cell based studies using FLT3-driven cell lines (Fig. 3 and Table 4). In BaF3 cells transformed with FLT3-ITD, all compounds were quite active displaying GI50 values between 0.1 and 1.0 μM (Table 4). In patient-derived Molm-14 and MV4-11 AML cell lines, which harbor a FLT3 ITD mutation, 17, 21, and 25 displayed similar potency (Table 4). However, in BaF3 cells transformed with a FLT3-ITD oncogene containing a secondary quizartinib-resistant activation loop (D835V) or gatekeeper (F691L) point mutation, compounds 17 and 21 were ineffective. While 25 was still able to maintain activity for both activation loop and gatekeeper mutants with an IC50 of ~1.0 μM, similar potency was observed in native BaF3 cells. Therefore, it is unclear if compound 25 is capable of inhibiting these FLT3 mutations or if the compound possesses undesirable cytotoxic properties. Further studies are underway to resolve this ambiguity. Nevertheless, 17, 21, and 25 are cell-membrane permeable and are able to block growth of FLT3-ITD-driven cells in vivo. Because of high LE values and low molecular weights, the compounds represent validated hits that can be further optimized into lead candidates.
Fig. 3.
Cell-based activity of 17, 21, and 25.
Table 4.
Cell-based GI50s of compounds 17, 21, and 25 reported as μM concentrations at 48 h post treatment.
| Cmpd | BaF3 | +ITD | +ITDD835V | +ITDF691L | Molm-14 | MV4-11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | >1.0 | 0.346 | >1.0 | >1.0 | 0.434 | 0.584 |
| 21 | >1.0 | 0.484 | >1.0 | >1.0 | 0.712 | 0.830 |
| 25 | 1.38 | 0.333 | 1.45 | 1.37 | 0.513 | 0.706 |
2.6. Preliminary pre-formulation studies
The imidazopyridine scaffold is known to have low water solubility. Therefore, preliminary salt formation with organic and inorganic acids was investigated to increase water solubility of compound 17 (Table 3). It is hypothesized that the imidazopyridine of 17 has a pKa around 6.0, based on the experimentally determined pKa of Ambien® (zolpidem) (pKa = 6.16) [42]. Inorganic and organic acids with pKas less than 6.0 were stoichiometrically mixed to create the conjugate acid of compound 17 (Table 3). It was found that oxalic acid as well as p-toluenesulfonic acid drastically increased aqueous solubility. Oxalic acid was found to be the best co-salt, increasing aqueous solubility from <0.08 mg/mL to 0.5 mg/mL. Despite the poor solubility of imidazopyridine compounds, formation of highly-soluble salts can increase water solubility and improve adsorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties.
3. Conclusion
New synthetic methodology that generates imidazopyridine analogs was utilized for kinase library synthesis [30,31]. Computational screening identified the imidazopyridine scaffold as an active platform on the FLT3 kinase. Subsequently, a low molecular weight FLT3-directed library was constructed and screened. Resulting FLT3 inhibitors were found to be highly ligand efficient (LE) and possess LE values greater than clinical FLT3 inhibitors. Select compounds were progressed into cell based assays and were found to block FLT3-driven proliferation at sub-micromolar IC50 values, and aqueous solubility was increased by forming highly water soluble salts. The developed analogs represent validated FLT3 hits and can be utilized to identify potent, lead candidates.
4. Experimental section
4.1. General experimental
All solvents were reagent grade or HPLC grade and all starting materials were obtained from commercial sources and used without further purification. Purity of final compounds was assessed using a Shimadzu ultra-high throughput LC/MS system (SIL-20A, LC-20AD, LC-MS 2020, Phenomenex® Onyx Monolithic C-18 Column) at variable wavelengths of 254 nM and 214 nM (Shimadzu PDA Detector, SPD-MN20A) and was >95%, unless otherwise noted. The HPLC mobile phase consisted of a water-acetonitrile gradient buffered with 0.1% formic acid. 1H NMR spectra were recorded at 400 MHz and 13C spectra were recorded at 100 MHz, both completed on a Varian 400 MHz instrument (Model# 4001S41ASP). High-resolution mass spectrometry was completed using a Bruker 9.4 T Apex-Qh hybrid Fourier transfer ion-cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometer. Compound activity was determined with the EZ Reader II plate reader (PerkinElmer®, Walthman, USA). All compounds were purified using silicagel (0.035–0.070 mm, 60 Å) flash chromatography, unless otherwise noted. Microwave assisted reactions were completed in sealed vessels using a Biotage Initiator microwave synthesizer.
4.2. Synthesis and characterization
4.2.1. Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (4)
2-aminopyridine (15 g, 0.159 M) was dissolved in 1-butanol (64 mL) in a 250 mL round bottom flask affixed with a magnetic stir bar. 2-chloroacetaldehyde 50% solution in water (24.3 mL, 0.191 M) was added hitherto and the reaction was heated to 130 °C for 12 h. The reaction solvent was condensed in vacuo and the crude product was adsorbed onto silica. The product was purified via flash chromatography utilizing a DCM/MeOH gradient and isolated as a light, yellow oil (17 g, 90%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.13 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (m, 2H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.19–7.12 (m, 1H), 6.78 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 1H). ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 119.
4.2.2. 7-Chloroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (5)
7-chloroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (5) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined for ‘4.2.1 Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (4)’ and isolated as an off-white solid (79%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.04 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.46 (s, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 8.12 (s, 1H), 7.59 (dd, J = 7.2, 2.0 Hz, 1H). ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 153.
4.2.3. 2-Fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)
Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (4) (100 mg, 0.846 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (4 mL) in a microwave vial affixed with a magnetic stir bar. 5-bromo-2-fluorobenzonitrile (339 mg, 1.693 mmol) was added, followed by potassium acetate (166 mg, 1.693 mmol) and palladium(II) acetate (19 mg, 0.085 mmol) and the vial was sealed. The reaction was heated to 160 °C by microwave irradiation for 1 h. The reaction mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed three times with saturated sodium bicarbonate and three times with deionized water. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The crude product was absorbed onto silica. The product was purified via flash chromatography utilizing a DCM/MeOH gradient and isolated as a brown solid (132 mg, 66%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.77 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (s, 1H), 8.04 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.94–7.90 (m, 1H), 7.79–7.75 (m, 1H), 7.74–7.71 (m,1H), 7.44–7.38 (m, 1H), 7.07 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 163.56 (d, J = 260.1 Hz), 135.99, 134.49 (d, J = 23.2 Hz) 125.87, 123.55, 123.20, 123.06 (d, J = 3.4 Hz), 118.66, 118.25, 117.35, 115.37, 114.36 (d, J = 20.8 Hz), 113.92. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 238.
4.2.4. 2-(4-(Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)acetonitrile (7)
2-(4-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)acetonitrile (7) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined for ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ and isolated as a brown solid (143 mg, 72.4%) 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.31 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.22 (dd, J = 9.1, 7.0 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 146.27, 132.72, 129.80, 129.21, 128.87, 128.56, 124.78, 124.53, 123.19, 118.28, 117.57, 112.83, 23.46. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 234.
4.2.5. 3-(p-Tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (8)
3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (8) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined for ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ and isolated as a brown solid (120 mg, 68%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.29 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.64 (s, 1H), 7.43 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.17–7.13 (m, 1H), 6.78–6.74 (m, 1H), 2.42 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 145.91, 138.08, 132.18, 129.86, 128.94, 127.90, 126.24, 123.98, 123.31, 118.09, 112.35, 21.29. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 209.
4.2.6. 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (9)
3-(4-fluorophenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (9) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined for ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo [1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ and isolated as a brown solid (132 mg, 73%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.25–8.19 (m, 1H), 7.69–7.62 (m, 2H), 7.51–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.22–7.15 (m, 3H), 6.81–6.78 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 162.41 (d, J = 248.4 Hz), 145.94, 132.38, 129.88 (d, J = 8.2 Hz), 125.26 (d, J = 3.4 Hz), 124.58, 123.02, 118.12, 116.25 (d, J = 21.6 Hz), 112.59. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 213.
4.2.7. 7-(Thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10)
7-chloroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (5) (300 mg, 1.97 mmol) was dissolved in 8:1 DMF:H2O (13.1 mL) in a microwave vial affixed with a magnetic stir bar. Thiophen-2-ylboronic acid was added followed by sodium carbonate (834 mg, 7.86 mmol). The reaction mixture was degassed with argon. Pd2(dba)3 (36 mg, 0.039 mmol) and P(Cy)3 (33 mg, 0.118 mmol) was added to the reaction mixture and the vial was sealed. The reaction was heated by microwave irradiation to 130 °C for 1 h. After, the reaction mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed three times with saturated sodium bicarbonate and three times with deionized water. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The crude product was absorbed onto silica. The product was purified via flash chromatography utilizing a DCM/MeOH gradient and isolated as a brown solid (223 mg, 59%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.07 (dd, J = 7.0, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.54 (s, 1H), 7.38 (s, 1H), 7.35–7.30 (m, 1H), 7.14–7.07 (m, 1H), 7.03 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 145.57, 142.02, 134.43, 130.87, 128.29, 125.88, 125.59, 124.20, 112.82, 112.33, 111.40. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 201.
4.2.8. 7-(Furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (11)
7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (11) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.7 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10)’ and was isolated as a brown solid (189 mg, 52%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.12–8.06 (m,1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.64 (s, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 7.08 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (dd, J = 3.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 151.85, 145.55, 142.97, 134.39, 127.02, 125.63, 112.38, 111.97, 110.86, 109.25, 106.85. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 185.
4.2.9. 7-Phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (12)
7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (12) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.7 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a] pyridine (10)’ and was isolated as a brown solid (266 mg, 70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.12–8.07 (m, 2H), 7.96 (s, 1H), 7.72–7.67 (m, 1H), 7.62–7.59 (m, 2H), 7.53–7.49 (m, 1H), 7.48–7.43 (m, 1H), 7.41–7.35 (m, 3H), 7.07–7.03 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 145.06, 133.59, 133.08, 129.09, 128.42, 127.46, 126.79, 125.75, 114.21, 112.75, 112.00. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 195.
4.2.10. 7-(4-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (13)
7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (13) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.7 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10)’ and was isolated as a brown solid (241 mg, 55%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.12 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.54 (s, 1H), 7.04 (dd, J = 7.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.86 (s, 6H), 3.81 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 133.63, 130.90, 127.84, 125.56, 114.46, 113.36, 112.26, 111.83, 55.36. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 225.
4.2.11. 2-Fluoro-5-(7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl) benzonitrile (14)
2-fluoro-5-(7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (14) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10) and was isolated as a brown solid (10.7 mg, 17%) 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.37 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.78 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.54–7.39 (m, 4H), 7.23 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.13 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 152.86, 140.03, 139.38, 136.57, 135.61, 134.42, 132.69, 132.29, 128.54, 126.71, 124.89, 123.13, 122.96, 122.87 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 114.18 (d, J = 20.9 Hz), 113.30, 112.75. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 320.
4.2.12. 2-(4-(7-(Thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl) acetonitrile (15)
2-(4-(7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl) acetonitrile was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10) and was isolated as a brown solid (18 mg, 29%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.28 (dd, J = 7.1, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.72 (d, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.56 (m, 2H), 7.52–7.49 (m, 2H), 7.43 (t, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H), 7.38–7.34 (m, 1H), 7.14–7.11 (m, 2H), 3.85 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 141.76, 133.53, 131.08, 129.87, 128.94, 128.59, 128.47, 128.38, 126.32, 126.12, 124.40, 123.15, 117.49, 113.10, 111.86, 109.99, 23.50. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 316.
4.2.13. 7-(Thiophen-2-yl)-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (16)
7-(thiophen-2-yl)-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (16) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10) and was isolated as a brown solid (33 mg, 56%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (dd, J = 7.3, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (dd, J = 1.8, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.47–7.43 (m, 2H), 7.40 (dd, J = 3.7, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.34–7.31 (m, 3H), 7.11 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.06 (dd, J = 7.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 2.43 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 146.15, 142.07, 138.23, 133.14, 130.48, 129.96, 129.64, 128.31, 127.85, 125.83, 125.61, 124.13, 123.30, 113.11, 111.40, 21.34. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 291.
4.2.14. 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a] pyridine (17)
3-(4-fluorophenyl)-7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (17) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(thiophen-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (10) and was isolated as a brown solid (25 mg, 52%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.23–8.18 (m, 1H), 7.86 (s, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.56–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.43–7.39 (m, 1H), 7.36–7.33 (m, 1H), 7.25–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.13–7.10 (m, 1H), 7.10–7.07 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 162.57 (d, J = 248.8 Hz), 146.21, 141.87, 133.28, 130.81, 129.90 (d, J = 8.2 Hz), 128.35, 127.39, 126.00, 125.13 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 124.29, 123.03, 116.42 (d, J = 21.8 Hz), 113.12, 111.69. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 295. Predicted: 295.06997; Found: 295.06975.
4.2.15. 2-Fluoro-5-(7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl) benzonitrile (18)
2-fluoro-5-(7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (18) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (11) and was isolated as a brown solid (12 mg, 25%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.34 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.96–7.92 (m, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.65–7.60 (m, 1H), 7.58–7.52 (m, 1H), 7.28–7.19 (m, 1H), 7.06–6.98 (m, 1H), 6.96–6.90 (m, 1H), 6.80 (d, J = 3.5 Hz, 1H), 6.55–6.54 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 143.60 (d, J = 17.5 Hz), 136.08, 134.50, 134.03, 123.81, 123.59, 120.76, 119.45, 117.19 (d, J = 4.8 Hz),115.19 (d, J = 15.1 Hz), 112.21, 111.81, 111.18, 110.78, 108.46, 107.78. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 304.
4.2.16. 2-(4-(7-(Furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl) acetonitrile (19)
2-(4-(7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)acetonitrile (19) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (11) and was isolated as a brown solid (22 mg, 46%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.29–8.24 (m, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.70 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.54–7.52 (m, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (dd, J = 7.3, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.77 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (dd, J = 3.4,1.8 Hz,1H), 3.84 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 151.68, 146.46, 143.20, 133.51, 129.83, 128.99 (d, J = 14.4 Hz), 128.48, 127.24, 124.52, 123.19, 117.52, 112.09, 111.18, 109.78, 107.23, 23.50. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 300.
4.2.17. 7-(Furan-2-yl)-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (20)
7-(furan-2-yl)-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (20) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(furan-2-yl) imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (11) and was isolated as a brown solid (26 mg, 70%) 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.28–8.24 (m, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.53–7.50 (m, 1H), 7.44 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.09–7.05 (m, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 6.51 (dd, J = 3.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 2.43 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 151.91, 146.08, 143.02, 138.25, 132.96, 129.94, 129.48, 127.90, 126.80, 126.11, 123.34, 112.02, 111.16, 109.39, 106.90, 21.33. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 275.
4.2.18. 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (21)
3-(4-fluorophenyl)-7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (21) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(furan-2-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (11) and was isolated as a brown solid (29 mg, 69%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.21–8.19 (m, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.56–7.49 (m, 3H), 7.27–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.13–7.07 (m, 1H), 6.75 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (dd, J = 3.4, 1.7 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 162.55 (d, J = 248.8 Hz), 151.76, 146.19, 143.12, 133.24,129.91 (d, J = 8.2 Hz), 127.02, 125.16 (d, J = 3.1 Hz), 123.07, 116.40 (d, J = 21.7 Hz), 115.79, 112.05, 111.18, 109.62, 107.07. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 279.
4.2.19. 2-Fluoro-5-(7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl) benzonitrile (22)
2-fluoro-5-(7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (22) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (12) and was isolated as a brown solid (47 mg, 59%) 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.45 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.81–7.75 (m, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.56–7.43 (m, 5H), 7.29–7.24 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 163.60 (d, J = 260.2 Hz), 139.21, 137.76, 136.20 (d, J = 8.7 Hz), 135.02, 134.45, 134.08, 129.25, 128.85, 128.19 (d, J = 17.4 Hz), 123.20, 122.99 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 119.93, 117.29 (d, J = 8.4 Hz), 115.00, 114.29 (d, J = 20.9 Hz), 113.92. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 314.
4.2.20. 2-(4-(7-Phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl) acetonitrile (23)
2-(4-(7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)acetonitrile (23) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (12) and was isolated as a brown solid (42 mg, 53%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.37 (dd, J = 7.2, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (dd, J = 1.8, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.70–7.66 (m, 2H), 7.64–7.60 (m, 2H), 7.53–7.47 (m, 4H), 7.44–7.41 (m, 1H), 7.15 (dd, J = 7.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 146.84, 138.42, 137.56, 133.52, 129.78, 129.29, 129.24, 129.12, 128.93, 128.49, 128.35, 127.94, 126.73, 123.15, 114.98, 112.76, 23.50. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 310.
4.2.21. 7-Phenyl-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (24)
7-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (24) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (12) and was isolated as a brown solid (27 mg, 46%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.35 (dd, J = 7.2, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.91–7.89 (m, 1H), 7.70 (s, 1H), 7.69–7.65 (m, 2H), 7.50–7.45 (m, 4H), 7.42–7.39 (m, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.09 (dd, J = 7.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 2.44 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 138.60, 138.25, 137.21, 132.70, 129.96, 129.29, 129.08, 128.22, 127.94, 126.73, 126.17, 125.58, 123.34, 114.82, 112.43, 21.35. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 285.
4.2.22. 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (25)
3-(4-fluorophenyl)-7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (25) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (12) and was isolated as a brown solid (28 mg, 48%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.28 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.90–7.87 (m, 1H), 7.69 (s, 1H), 7.68–7.65 (m, 2H), 7.57–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.51–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.42–7.37 (m, 1H), 7.26–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.11 (dd, J = 7.2, 1.9 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 162.54 (d, J = 248.6 Hz), 146.54, 138.50, 137.36, 133.16, 129.93 (d, J = 8.2 Hz), 129.28, 129.10, 128.29, 126.72, 125.29 (d, J = 3.5 Hz), 123.03, 116.40 (d, J = 21.8 Hz), 114.94, 112.62. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 289.
4.2.23. 2-Fluoro-5-(7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (26)
2-fluoro-5-(7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl) benzonitrile (26) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (13) and was isolated as a brown solid (38 mg, 62%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.42 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.80–7.76 (m, 1H), 7.63–7.60 (m, 3H), 7.52 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (d, J = 9.9 Hz, 1H), 7.26–7.23 (m, 1H), 7.03 (dd, J = 8.8, 3.4 Hz, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 163.60 (d, J = 259.9 Hz), 160.35, 147.89, 139.01, 136.20 (d, J = 8.7 Hz), 134.56 (d, J = 26.6 Hz), 133.24, 129.98, 127.96, 123.13, 122.92 (d, J = 3.4 Hz), 114.68, 114.20 (d, J = 20.8 Hz), 113.77, 109.99, 100.07 (d, J = 15.4 Hz), 99.60, 55.44. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 344.
4.2.24. 2-(4-(7-(4-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl) phenyl)acetonitrile (27)
2-(4-(7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)phenyl) acetonitrile (27) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (13) and was isolated as a brown solid (31 mg, 46%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.32 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.82 (s, 1H), 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.63–7.59 (m, 4H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (dd, J = 7.3, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 3.84 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 159.93, 147.03, 137.21, 133.38, 130.79, 129.66, 129.31, 128.90, 128.41, 127.84, 124.44, 123.06, 117.56, 114.54, 113.95, 112.56, 55.41, 23.49. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 340.
4.2.25. 7-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (28)
7-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(p-tolyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (28) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (13) and was isolated as a brown solid (29 mg, 52%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.32 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.63–7.58 (m, 2H), 7.49–7.44 (m, 2H), 7.36–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.07–7.03 (m, 1H), 7.03–6.98 (m, 2H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 2.44 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 159.82, 146.64, 138.08, 136.73, 132.78, 131.04, 129.92, 128.97, 127.86, 127.82, 126.35, 123.22, 114.49, 113.88, 112.17, 55.39, 21.33. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 315.
4.2.26. 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a] pyridine (29)
3-(4-fluorophenyl)-7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (29) was synthesized according to the procedure outlined in ‘4.2.3 2-fluoro-5-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile (6)’ using 7-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (13) and was isolated as a brown solid (28 mg, 50%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.25 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.83–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.56–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.24–7.20 (m, 2H), 7.07 (dd, J = 7.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.86 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 162.49 (d, J = 248.4 Hz), 159.90, 146.71, 137.04, 132.99, 130.88, 129.87 (d, J = 8.2 Hz), 129.51, 127.84, 125.38 (d, J = 3.4 Hz), 122.94, 116.37 (d, J = 21.7 Hz), 114.53, 113.92, 112.45, 55.40. ESIMS m/z [M+H]+ 319.
4.3. FLT3 biochemical inhibition assay [27,28]
Kinase activity was measured in a microfluidics assay that monitors the separation of a phosphorylated product from substrate. The assay was run using a 12-sipper chip on a Caliper EZ Reader II (PerkinElmer®, Walthman, USA) with separation buffer (100 mM HEPES, 10 mM EDTA, 0.015% Brij-35, 0.1% CR-3 [PerkinElmer®, Walthman, USA]). In 96-well polypropylene plates (Greiner, Frickenhausen, Germany) compound stocks (20 mM in DMSO) were diluted into kinase buffer (50 mM HEPES, 0.075% Brij-35, 0.1% Tween 20, 2 mM DTT, 10 mM MgCl2, and 0.02% NaN3) in 12-point ½log dilutions (2 mM–6.32 nM). After, 1 μL was transferred into a 384-well polypropylene assay plate (Greiner, Frickenhausen, Germany). The FLT3 enzyme (Invitrogen™, Grand Island, USA) was diluted in kinase buffer to a concentration of 2 nM and 5 μL of the enzyme mixture was transferred to the assay plate. The inhibitors/ FLT3 enzyme were incubated for 60 min with minor shaking. A substrate mix was prepared containing ATP (Ambresco®, Solon, USA) and 5FAM tagged FLT3 peptide (peptide #22, 5′ FAM-EPLYWSFPA, PerkinElmer®, Walthman, USA) dissolved in kinase buffer, and 5 μL of the substrate mix was added to the assay plate. Running concentrations were as follows: ATP (190 μM), peptide (1.5 μM), compound 12-point ½log dilutions (0.2 mM–0.632 nM). For positive control, no inhibitor was added. For negative control, no enzyme was added. For running control, quizartinib was utilized. The plate was run until 10–20% conversion based on the positive control wells. The following separation conditions were utilized: upstream voltage −500 V; downstream voltage, −1900 V; chip pressure −0.8. Percent inhibition was measured for each well comparing starting peptide to phosphorylated product peaks relative to the baseline. Dose response curves, spanning the IC50 dose, were generated in GraphPad Prisim 6 and fit to an exponential one-phase decay line and IC50 values were obtained from the half-life value of the curve. IC50 values were generated in duplicate and error was calculated from the standard deviation between values.
4.4. Computational modeling [27,28,31]
Computational modeling studies were completed using Auto-Dock Vina [31], AutoDock Tools, and Discovery Studio 3.5. Using AutoDock Tools, kinase crystal structures were prepared as follows: 1) All hydrogens were added as ‘Polar Only’ 2) A grid box for the ATP binding site was created. Compounds to be computationally modeled were assigned appropriate rotatable bonds using Auto-Dock Tools. To computational model the compounds, AutoDock Vina [31] was employed. AutoDock Vina [31] provides docking scores in terms of ΔG values. After the modeling study, kinase targets with high affinity ΔG values were visualized and analyzed with Discovery Studio 3.5.
4.5. Cell cultures
Stable BaF3 populations expressing activated FLT3 were generated by retroviral spinfection with the appropriate mutated plasmid followed by selection and growth factor withdrawal as previously described [26]. The BaF3 cell line was originally obtained from the laboratory of Charles Sawyers and has not been authenticated. MV4; 11 and Molm14 cells were obtained from the laboratory of Scott Kogan and authenticated by Promega STR analysis in June 2013. All cell lines were mycoplasma-free. Cells were incubated with compounds for 48 h and proliferation was assessed using CellTiter-Glo (Promega; Madison, WI) according to the manufacturer’s recommendation on a SpectraMax M3 microplate reader using SpectraMax Software (Molecular Devices; Sunnyvale, CA). All cell viability data shown is reflective of experiments performed a minimum of three times.
4.6. Preliminary pre-formulation studies
Compound 17 was dissolved in a 1:1 DCM/MeOH solution at a concentration of 1.0 mg/mL 1.0 mL of solution was transferred to a 13.0 mL glass tube, followed by a stoichiometric equivalent of an organic or inorganic acid found in Table 3. The organic solvent was evaporated and the newly formed salt complex was dried under high vacuum. In increments of 1.0 mL, 0.2 μM filtered, deionized water was added to the salt of compound 17 and vortexed. The resulting aqueous solution was visually inspected for precipitate using a laser diode at a wavelength of 600 nM (INFINITER® 100 Red Laser Pointer). Water was added until no precipitate was present or until the solubility was determined to be below 0.08 mg/mL.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was graciously supported by two training grants from The National Institutes of Health (3T32GM008804-10S1; T32 GM008804), University of Arizona startup funding, The Caldwell Health Sciences Research Fellowship, the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, and 5R01 CA166616-01 from the National Cancer Institute to N.P.S.
Abbreviations
- FLT3
Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3
- AML
acute myeloid leukemia
- ITD
internal tandem duplication
- JM
juxtamembrane
- RAS
rat sarcoma
- RAF
rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma
- JAK
janus kinase
- STAT
signal transducer and activator of transcription
- PI3K
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- AKT
protein kinase B
- TK
tyrosine kinase
- FDA
food and drug administration
- PK
pharmacokinetic
- LE
ligand efficiency
- CADD
computer aided drug discovery
- MW
molecular weight
- MCR
multi-component reaction
- MWI
microwave irradiation
- IC50
half maximal inhibitory concentration
- GI50
half of maximal inhibition of cell proliferation
- STR
short tandem repeat
- DCM
dichloromethane
- MeOH
methanol
- NMR
nuclear magnetic resonance
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- MHz
megahertz
- LC/MS
liquid chromatography mass spectrometry
- HPLC
high performance liquid chromatography
- FT-ICR
fourier transfer ion-cyclotron resonance
- HEPES
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid
- EDTA
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- DTT
dithiothreitol
- ATP
adenosine triphosphate
- FAM
carboxyfluorescein
- DMF
dimethylformamide
- pTSA
p-toluenesulfonic acid
- ADME
adsorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.02.052.
References
- 1.Swords R, Freeman C, Giles F. Targeting the FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2012;26:2176–2185. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lyman SD, Jacobsen SEW. c-Kit ligand and Flt3 ligand: stem/progenitor cell factors with overlapping yet distinct activities. Blood. 1998;91:1101–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Levis M, Allebach J, Tse KF, Zheng R, Baldwin BR, Smith BD, Jones-Bolin S, Ruggeri B, Dionne C, Small D. A FLT3-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor is cytotoxic to leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2002;99:3885–3891. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.11.3885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meshinchi S, Woods WG, Stirewalt DL, Sweetser DA, Buckley JD, Tjoa TK, Bernstein ID, Radich JP. Prevalence and prognostic significance of Flt3 internal tandem duplication in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2001;97:89–94. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kiyoi H, Towatari M, Yokota S, Hamaguchi M, Ohno R, Saito H, Naoe T. Internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 gene is a novel modality of elongation mutation which causes constitutive activation of the product. Leukemia. 1998;12:1333–1337. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fenski R, Flesch K, Serve S, Mizuki M, Oelmann E, Kratz-Albers K, Kienast J, Leo R, Schwartz S, Berdel WE, Serve H. Constitutive activation of FLT3 in acute myeloid leukaemia and its consequences for growth of 32D cells. Br J Haematol. 2000;108:322–330. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.01831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thiede C, Steudel C, Mohr B, Schaich M, Schäkel U, Platzbecker U, Wermke M, Bornhäuser M, Ritter M, Neubauer A, Ehninger G, Illmer T. Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: association with FAB subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis. Blood. 2002;99:4326–4335. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.12.4326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yakes FM, Chen J, Tan J, Yamaguchi K, Shi Y, Yu P, Qian F, Chu F, Bentzien F, Cancilla B, Orf J, You A, Laird AD, Engst S, Lee L, Lesch J, Chou YC, Joly AH. Cabozantinib (XL184), a novel MET and VEGFR2 inhibitor, simultaneously suppresses metastasis, angiogenesis, and tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:2298–2308. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Auclair D, Miller D, Yatsula V, Pickett W, Carter C, Chang Y, Zhang X, Wilkie D, Burd A, Shi H, Rocks S, Gedrich R, Abriola L, Vasavada H, Lynch M, Dumas J, Trail PA, Wilhelm SM. Antitumor activity of sorafenib in FLT3-driven leukemic cells. Leukemia. 2007;21:439–445. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Metzelder S, Wang Y, Wollmer E, Wanzel M, Teichler S, Chaturvedi A, Eilers M, Enghofer E, Neubauer A, Burchert A. Compassionate use of sorafenib in FLT3-ITD–positive acute myeloid leukemia: sustained regression before and after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2009;113:6567–6571. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-208298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Man CH, Fung TK, Ho C, Han HH, Chow HC, Ma AC, Choi WW, Lok S, Cheung AM, Eaves C, Kwong YL, Leung AY. Sorafenib treatment of FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia: favorable initial outcome and mechanisms of subsequent nonresponsiveness associated with the emergence of a D835 mutation. Blood. 2012;119:5133–5143. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-363960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kancha RK, Grundler R, Peschel C, Duyster J. Sensitivity toward sorafenib and sunitinib varies between different activating and drug-resistant FLT3-ITD mutations. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:1522–1526. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Faivre S, Demetri G, Sargent W, Raymond E. Molecular basis for sunitinib efficacy and future clinical development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:734–745. doi: 10.1038/nrd2380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Andrae N, Kirches E, Hartig R, Haase D, Keilhoff G, Kalinski T, Mawrin C. Sunitinib targets PDGF-receptor and Flt3 and reduces survival and migration of human meningioma cells. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:1831–1841. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shah NP, Talpaz M, Deininger MW, Mauro MJ, Flinn IW, Bixby D, Lustgarten S, Gozgit JM, Clackson T, Turner CD, Haluska FG, Kantarjian H, Cortes JE. Ponatinib in patients with refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: findings from a phase 1 study. Br J Haematol. 2013;162:548–552. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gozgit JM, Wong MJ, Wardwell S, Tyner JW, Loriaux MM, Mohemmad QK, Narasimhan NI, Shakespeare WC, Wang F, Druker BJ, Clackson T, Rivera VM. Potent activity of ponatinib (AP24534) in models of FLT3-driven acute myeloid leukemia and other hematologic malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:1028–1035. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Smith CC, Lasater EA, Zhu X, Lin KC, Stewart WK, Damon LE, Salerno S, Shah NP. Activity of ponatinib against clinically-relevant AC220-resistant kinase domain mutants of FLT3-ITD. Blood. 2013;121:3165–3171. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-442871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zimmerman EI, Turner DC, Buaboonnam J, Hu S, Orwick S, Roberts MS, Janke LJ, Ramachandran A, Stewart CF, Inaba H, Baker SD. Crenolanib is active against models of drug-resistant FLT3-ITD—positive acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2013;122:3607–3615. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-513044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Smith CC, Lasater EA, Lin KC, Wang Q, McCreery MQ, Stewart WK, Damon LE, Perl AE, Jeschke GR, Sugita M, Carroll M, Kuriyan J, Shah NP. Crenolanib is a selective type I pan-FLT3 inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 2014;111:5319–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320661111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ma Galanis H, Rajkhowa T, Ramachandran A, Small D, Cortes J, Levis M. Crenolanib is a potent inhibitor of FLT3 with activity against resistance-conferring point mutants. Blood. 2014;123:94–100. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-529313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grunwald MR, Levis MJ. FLT3 inhibitors for acute myeloid leukemia: a review of their efficacy and mechanisms of resistance. Int J Hematol. 2013;97:683–694. doi: 10.1007/s12185-013-1334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zarrinkar PP, Gunawardane RN, Cramer MD, Gardner MF, Brigham D, Belli B, Karaman MW, Pratz KW, Pallares G, Chao Q, Sprankle KG, Patel HK, Levis M, Armstrong RC, James J, Bhagwat SS. AC220 is a uniquely potent and selective inhibitor of FLT3 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Blood. 2009;114:2984–2992. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-222034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cortes JE, Kantarjian H, Foran JM, Ghirdaladze D, Zodelava M, Borthakur G, Gammon G, Trone D, Armstrong RC, James J, Levis M. Phase I study of quizartinib administered daily to patients with Relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia Irrespective of FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3–Internal tandem duplication Status. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3681–3687. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.48.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. [Accessed 12/16/2014];Phase II Study of crenolanib in Subjects with Relapsed/Refractory AML with FLT3 activating mutations. # NCT01522469. ClinicalTrials.gov.
- 25. [Accessed 12/16/2014];An Open-label Study of Quizartinib Monotherapy vs. Salvage Chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Subjects. # NCT02039726. ClinicalTrials.gov.
- 26.Smith CC, Wang Q, Chin CS, Salerno S, Damon LE, Levis MJ, Perl AE, Travers KJ, Wang S, Hunt JP, Zarrinkar PP, Schadt EE, Kasarskis A, Kuriyan J, Shah NP. Validation of ITD mutations in FLT3 as a therapeutic target in human acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2012;485:260–264. doi: 10.1038/nature11016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Frett B, Moccia M, Carlomagno F, Santoro M, Li HY. Identification of two novel RET kinase inhibitors through MCR-based drug discovery: design, synthesis and evaluation. Eur J Med Chem. 2014;86:714–723. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Frett B, McConnell N, Wang Y, Xu Z, Ambrose A, Li HY. Identification of pyrazine-based TrkA inhibitors: design, synthesis, evaluation, and computational modeling studies. Med Chem Commun. 2014;5:1507–1514. doi: 10.1039/C4MD00251B. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hopkins A, Keserü G, Leeson P, Rees D, Reynolds CH. The role of ligand efficiency metrics in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Disc. doi: 10.1038/nrd4163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, Frett B, Li HY. Efficient access to 2,3-diarylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines via a one-pot, ligand-free, palladium-catalyzed three-component reaction under microwave irradiation. Org Lett. 2014;16:3016–3019. doi: 10.1021/ol501136e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee J, Chung J, Byun SM, Kim BM, Lee C. Direct catalytic C–H arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine with aryl bromides using magnetically recyclable Pd–Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Tetrahedron. 2013;69:5660–5664. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Trott O, Olson AJ. J Comput Chem. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Griffith J, Black J, Faerman C, Swenson L, Wynn M, Lu F, Lippke J, Saxena K. The structural basis for autoinhibition of FLT3 by the juxtamembrane domain. Mol Cell. 2004;13:169–178. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00505-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Burgeson JR, Moore AL, Gharaibeh DN, Larson RA, Cerruti NR, Amberg SM, Hruby DE, Dai D. Lead optimization of an acylhydrazone scaffold possessing antiviral activity against Lassa virus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23:750–756. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.08.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chezal JM, Moreau E, Chavignon O, Lartigue C, Blache Y, Teulade JC. Efficient synthesis of novel dipyridoimidazoles and pyrido[1′,2′;1,2]imidazo[4,5-d]pyridazine derivatives. Tetrahedron. 2003;59:5869–5878. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chezal JM, Moreau E, Desbois N, Blache Y, Chavignon O, Teulade JC. Synthesis of carbamoylpyridine and imidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-1,3-diones via ortho-acetalhydantoin intermediates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004;45:533–556. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Goodacre SC, Street LJ, Hallett DJ, Crawforth JM, Kelly S, Owens AP, Blackaby WP, Lewis RT, Stanley J, Smith AJ, Ferris P, Sohal B, Cook SM, Pike A, Brown N, Wafford KA, Marshall G, Castro JL, Atack JR. Imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines as functionally selective and orally bioavailable GABAAα2/α3 binding site agonists for the treatment of anxiety disorders. J Med Chem. 2006;49:35–38. doi: 10.1021/jm051065l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Enguehard C, Renou JL, Collot V, Hervet M, Rault S, Gueiffier A. Reactivity of 3-Iodoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines using a Suzuki-type cross-coupling reaction. J Org Chem. 2000;65:6572–6575. doi: 10.1021/jo000698z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Akkaoui E, Bassoude I, Koubachi J, Berteina-Raboin S, Mouaddib A, Guillaument G. Pd-catalyzed regiocontrolled Sonogashira and Suzuki cross-coupling reaction of 3,6-dihalogenoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines: one-pot double-coupling approach. Tetrahedron. 2011;67:7128–7138. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kim O, Jeong Y, Lee H, Hong SS, Hong S. Design and synthesis of imidazopyridine analogues as inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling and angiogenesis. J Med Chem. 2011;54:2455–2466. doi: 10.1021/jm101582z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gudmundsson KS, Williams JD, Drach JC, Townsend LB. Synthesis and antiviral activity of novel Erythrofuranosyl imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine c-nucleosides constructed via palladium coupling of iodoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and dihydrofuran. J Med Chem. 2003;46:1449–1455. doi: 10.1021/jm020339r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Durand A, Thénot JP, Bianchetti G, Morselli PL. Comparative pharmacoki- netic profile of two imidazopyridine drugs: zolpidem and alpidem. Drug Metab Rev. 1992;24:239–266. doi: 10.3109/03602539208996294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.