Abstract
Here we assessed how intake reductions induced by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) occur within and across access periods by examining drinking microstructure. After training, RYGB (n = 8–10) or sham-operated (SHAM, n = 12) rats were given 60-min access first to 0.3 M sucrose, then to 5% Intralipid, and finally to milk-chocolate Ensure Plus across 5 days each. Initially, total licks taken during the first meal of sucrose and Intralipid by RYGB and SHAM rats did not differ, but, across subsequent test periods, RYGB rats licked less than SHAM rats. First Ensure meal size also did not differ between RYGB and SHAM rats, but SHAM rats increased licking across test periods while the behavior of RYGB rats remained stable. The intake differences between the surgical groups, when they occurred, were most often due to smaller burst sizes in RYGB rats. Importantly, the surgical-group difference in sucrose and Intralipid intakes could not be explained by altered palatability of these solutions because, throughout testing, both groups had similar early meal licking behavior thought to represent the motivational potency of stimulus orosensory features. Although, overall, RYGB rats displayed lower early meal licking of Ensure relative to the SHAM rats, this appeared to be driven primarily by increases in the latter group across test periods; the RYGB group stayed relatively stable. Collectively, these results suggest that some level of postoral experience with these stimuli and/or their components is necessary before intake differences emerge between surgical groups, and, even when differences occur, often immediate taste-motivated ingestive behavior remains unaltered.
Keywords: sugar, fat, licking patterns, conditioned avoidance, bariatric surgery
patients after roux-en-y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) lose body mass (e.g., Ref. 19), in part by minimizing their intakes of calorically dense foods (e.g., Ref. 9). Many high-calorie foods contain large amounts of sugar and/or fat and are considered palatable. That these types of foods are reported as selected proportionally less often following bariatric intervention has promoted the hypothesis that RYGB alters basic taste sensibility and/or reward. Indeed, after RYGB, patients can more easily detect the presence of sugar (2, 3), although this does not seem to affect hedonic ratings of “ideal sweetness” (2). Studies using a rat model of RYGB show that sugar- and fat-containing foods and fluids are still consumed and often preferred after the surgery but at a level lower than that of sham-operated animals (e.g., Refs. 2, 4, 10, 17, 27). There is also evidence that, in some situations, greater experience with nutritive fluids and, thus more exposure to their postingestive consequences, can further alter behavior (2, 10).
While humans and rats after RYGB eat less and may at times display altered food choices, it is unclear how these intake outcomes are achieved. Although many factors can exert control over the amount of food consumed, all do so by influencing either one or both of two basic classes of neural mechanisms: those that activate ingestive behavior and those that terminate ingestive behavior (c.f., Refs. 7, 20). After RYGB, rats took smaller but more frequent meals of Ensure across 24-h periods, suggesting that RYGB influenced both of these classes of neural mechanisms to balance a slightly lower overall intake (27). Additionally, at least early after surgery, RYGB rats consumed Ensure at a slower rate than sham-operated animals (27). While smaller meals and a slower rate of ingestion may be indicative of decreased fluid palatability, it is also suggestive of heightened satiation and/or decreased appetition (14, 21, 22). Thus it remains unclear whether these changes in meal parameters were influenced by changes in orosensation, postingestive events, or both. Furthermore, these animals had been maintained on a choice diet that included both a high-fat diet and Ensure, and it is unknown if presurgical and/or chronic exposure to these consumables influenced ingestive postsurgical behavior.
It is also not yet understood how much time or experience with a nutritive stimulus RYGB rats require for intake decreases to emerge. In contrast to long-term tests (24-h intake or 2-bottle preference tests), few differences have been observed between RYGB and sham-operated rats in tests that minimize fluid access such as the brief-access taste test (stimulus concentration arrays presented in 10-s trials; Ref. 12, although see Refs. 9, 20, 26) and progressive ratio tests (75 μl of the stimulus serving as reinforcers after increasingly difficult operant workloads; Ref. 10), suggesting that some modicum of postingestive feedback is necessary to promote sustained differences in preference. However, it is difficult to equate intakes volumetrically and calorically between surgical groups since the gut capacities and nutritional needs of rats given RYGB are so different from those of sham-operated rats. Indeed, gastric emptying is completely altered as the pylorus now exists in a part of the digestive tract that no longer encounters food.
To address the microstructural manner in which rats consume liquid nutrients after RYGB and how consumption may change after repeated exposure, we sought to examine the microstructural organization of licking patterns by rats consuming meals of sweet and/or fatty nutritive stimuli following RYGB or sham surgery. The analysis of the patterns by which a rat ingests a nutritive solution across time serves as a powerful tool to assess how manipulations lead to intake outcomes as it revolves around the most fundamental level of drinking, the lick. Rats lick in runs called bursts (sometimes referred to as “clusters”). The number of licks in a burst (i.e., burst size) can be influenced by stimulus palatability and meal progress (e.g., Refs. 6, 7, 21). Through the analysis of early meal measures, such as the rate of licking at the beginning of the session and the size of the first burst, the role of stimulus palatability can be dissociated from events related to the postoral accumulation of the stimulus because the latter processes are minimal shortly after intake has just started. Accordingly, in this series of studies, we examined how RYGB affects the microstructure of licking for nutritive stimuli as a function of experience in an effort to further understand the underlying basis of the intake-reducing effects of RYGB.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
Thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River) ∼3 mo of age, weighing 464–553 g at the beginning of the study were used across the phases of the experiment. All of the rats were individually housed in conventional polycarbonate tub cages in a vivarium with automatically controlled temperature (set at 72 °F), humidity (held between 30–70%), and lighting (lights on 0700–1900). All procedures were conducted while the lights were on. The rats were given ad libitum access to deionized water and maintenance chow (PMI 5001 LabDiet) except when noted for surgical or experimental reasons. All procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Florida State University.
Taste Stimuli
During training, deionized water and Polycose (Abbott Nutrition) were used as test stimuli, and, during testing, 0.3 M sucrose (0.41 kcal/ml; BDH Chemicals), 5% Intralipid (0.55 kcal/ml; Fresenius Kabi), and milk-chocolate flavored Ensure Plus (1.5 kcal/ml; Abbott Nutrition) were used. All solutions were presented at room temperature.
Apparatus
The apparatus used throughout the experiment was similar to that described previously (e.g., Ref. 21) except that modified polycarbonate tub cages replaced the stainless steel hanging cages. Stainless steel plates were attached to the inside of the front wall of each of the six cages to provide a foot pad, and an opening was constructed to provide a spout-access slot. A drinking spout holding unit containing a preamplifying buffer circuit was attached to the outside of the cage wall, which, in turn, was connected to an electronic interface that processed the signal before being transmitted to a computer. A 100-ml bottle with a curved drinking spout was positioned behind the access slot. When a rat stood on the foot pad and licked the spout, a circuit passing no more than 50 nA through the rat was completed. The onset time of each lick made in each chamber was saved to an individual file at the end of the session by a computer for later analysis.
Training Procedures
Water bottles were removed from the rats ∼23 h before their first training period in which they were allowed to lick water from a spout in the apparatus for 60 min. A second water training period followed on the next consecutive day, ∼1 h after which water bottles were returned to the rats. These training periods were intended to familiarize the rats with the testing situation and allow them to learn to lick the spout while in a highly motivated state (e.g., water-deprived). After a 72-h duration with ad libitum access to food and water, chow was removed from the rats ∼23 h before further training in which they were allowed to lick 10% Polycose for 60 min. Polycose, a highly preferred mixture of short-chain glucose polymers, was chosen so as to not provide presurgical experience with the test stimuli of interest (e.g., Refs. 12, 16; c.f., Ref. 15). Food was returned to the rats ∼1 h after the completion of training. A final training period in which the rats were allowed to lick 10% Polycose for 60 min while nondeprived occurred 48 h after refeeding. These periods were intended to train the rats that an appetitive stimulus would be available from the spout and motivate them to lick even while nondeprived.
Surgical Procedures
The rats were assigned to either RYGB or sham-operated (SHAM) surgery groups such that body weight, Polycose intake while nondeprived, and interlick interval (ILI) during the second day of water-deprived water training were not significantly different. The rats weighed 469–587 g at the time of surgery.
Preoperative conditions and surgical procedures were conducted as previously described (e.g., Ref. 10). Briefly, on the day before surgery, the rats were moved to an empty tub cage equipped with a raised stainless steel mesh floor, and all food less a 10 g ration was removed. On the day of surgery, anesthesia was induced with isoflurane and oxygen (2–5% in 1 l/min) and each rat was injected subcutaneously with an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent [carprofen (Rimadyl); 5 mg/kg] and an antibiotic [enrofloxycin (Baytril); 2.3 mg/kg]. All procedures were conducted under aseptic conditions by one surgeon (C. M. Mathes). For the RYGB, the small intestine was transected 6–8 cm distal to the ligament of Trietz and each end was tied off, forming two stumps. A 5- to 7-mm slit was cut in the proximal stump, and a side-to-side anastomosis was formed with a similarly sized incision of the small bowel ∼25 cm oral from the cecum, creating the bileopancreatic limb. A 5- to 7-mm cut was made in the distal stump, and an end-to-side anastomosis was performed with a 4- to 5-mm portion of the stomach, which had been transected just aboral to and remained continuous with the esophagus, thus creating the small gastric pouch and the alimentary limb. The remaining stomach was closed but remained attached to the bileopancreatic limb. For the SHAM surgery, no gastrointestinal reorganizations were made, but, instead, three to four running sutures were placed where the small intestine would have been transected, where the common channel would have started in the RYGB surgery, and along the front wall of the stomach. In both operation types, the abdominal wall and skin were each closed in a single layer.
Immediately following surgery, each rat was injected subcutaneously with 7 ml of saline and placed in an empty polycarbonate cage until full recovery from anesthesia. The rat was then returned to its home cage and, no less than 1 h after surgery, provided with 10 g of a mixture of powdered chow and distilled water (∼1:4; wet mash), which was placed in a petri dish and set on the mesh floor in the home cage. For the first 3 days after surgery, the rats were injected with carprofen and enrofloxycin (as above) and given ad libitum access to the very thin wet mash, which was provided fresh twice daily. The rats also remained on the mesh floors during this time. On the 4th day after surgery, the rats were presented with a small piece (∼3 g) of pelleted chow, which most rats consumed readily. All of the rats were given at least 20 days to fully recover from surgery during which time they were weighed and monitored daily.
In total, RYGB surgery was performed on 18 rats and SHAM surgery on 12 rats across 9 days. Of the 18 RYGB rats, 2 died during surgery and 4 were euthanized within 5 days following surgery. Minor complications in the RYGB group included excessive salivation, dehydration, and loose stool, which was successfully treated with subcutaneous injections of saline and the provision of wet mash. No complications were seen in the SHAM group.
Testing Procedures
Sucrose.
During each test, the rats were allowed to lick 0.3 M sucrose for 60 min. Food was removed from some of the animals in each surgical group ∼23 before the first test; thus subgroup A (RYGB = 5, SHAM = 6) was tested while food deprived and subgroup B was tested while nondeprived (RYGB = 7, SHAM = 6). When applicable, food was returned ∼60 min after completion of each test. A total of three tests were conducted under these conditions, with the second test conducted 2–3 days after the first and the third 5 days after the second. These “recovery periods” were necessary because many of the RYGB rats that were food deprived for the first test (i.e., RYGB subgroup A) were slow in returning to their ad libitum body weight. Four days after the third test, the deprivation states of the subgroup squads were switched such that the animals that had been previously tested food deprived (e.g., subgroup A) were tested while nondeprived, and those that had been previously been tested nondeprived (e.g., subgroup B) were tested while food deprived. A total of two tests separated by 48 h were run in these conditions. Because RYGB rats had problems recovering body weight after food deprivation, we chose to simplify the experimental design used with Intralipid and Ensure and test all rats while they were in a nondeprived state.
Intralipid.
Testing with 5% Intralipid began 11 days after the completion of sucrose testing by which time all of the RYGB rats had returned to stable postsurgical ad libitum body weights. One 60-min test a day was conducted over 5 consecutive days during which all animals had access to food and water ad libitum.
Ensure.
We chose milk chocolate Ensure Plus as a complex taste stimulus representing both “sweet” and “fat.” Testing with Ensure began 48 h after the completion of Intralipid testing and consisted of 5 consecutive days of one 60-min test per day while the rats were ad libitum fed and watered.
Data Analysis
For all taste stimuli during each test, we analyzed overall intake, which was measured by subtracting the volume of fluid remaining after the test from the volume at the start (to nearest 0.5 ml). We used this measure divided by the number of licks taken across the entire 60-min period to calculate the amount of fluid taken per lick. A meal was defined as the total number of licks produced before a 5-min pause (as per 21). We chose to restrict microstructural analysis to the first meal since this would provide a way to behaviorally standardize satiation between the RYGB and SHAM rats who have very different gut capacities and geometries as well as hormone levels. Furthermore, we analyzed the rate at which licks were taken during the first minute of testing starting with the second lick, which, while an arbitrary duration, is considered short enough to precede satiation since it increases monotonically across concentration (e.g., 6, 7, 21).
The total number of licks taken during the first meal by each rat in each test was organized into bursts using a pause criterion of 1 s, as recommended by a prior parametric analysis of the influence of pause criteria on these measures (21). The number of bursts and the number of licks per burst (e.g., burst size) were analyzed. To preclude electrical artifacts registering as a lick at the very start of the session and to guarantee that the animal was engaged in stimulus sampling, the first burst had to consist of at least three licks. The ILI was defined as the duration between consecutive lick onsets filtered to include those between 50 and 250 ms (c.f., Refs. 5, 7, 25). The mean ILI served as a measure of licking competence and was analyzed for the first burst as well as for the meal.
Two-way ANOVAs with surgery (RYGB vs. SHAM) and test period as factors were used to analyze the 60-min intakes during each test for each stimulus, except for sucrose. Sucrose intake data were analyzed via four-way ANOVA with surgery, test period, deprivation condition (food-deprived vs. nondeprived), and counterbalanced run order (subgroup A or B) as factors. Significant interactions involving run order prevented combining the groups (see results for F and P values). However, as there were no main or interactive effects of deprivation group on intake for either surgical group in the first three tests, the deprivation subgroups were combined and the data analyzed via two-way ANOVA as per the other stimuli for those three tests.
The microstructural data for each test stimulus were also analyzed with two-way ANOVAs. However, on day 2 of sucrose testing, a malfunction of the computer controlling the microstructure apparatus resulted in the loss of burst, rate, and ILI data of some rats. Because of this loss, an average of the burst, rate, and ILI data, as well as intakes, from days 2 and 3 for each rat, when available, was used in analysis. Because of experimenter error, microstructural data during IL testing were lost for one squad of rats on day 2, and so an average of the burst, rate, and ILI data, as well as 60-min intakes, from days 2 and 3 for each rat, when available, was used in analysis. When surgery × test period interactions were revealed during two-way ANOVAs of intake or microstructural data, one-way ANOVAs within surgical groups across test periods and t-tests evaluating differences between the surgical groups during each test period were performed and Bonferroni corrected. Effects in which P ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Only animals that completed all of the analyzed tests for a given stimulus were included in the analysis of that stimulus. During sucrose testing, two of the RYGB rats from subgroup A continued to progressively lose body weight despite refeeding after their first test while food deprived and so were removed from the study. During IL testing, one RYGB rat failed to take any licks on the fifth testing period and so was excluded but was included once again during Ensure testing since it took licks during all tests.
RESULTS
Body Weight
By the start of postsurgical experimental procedures, RYGB rats had lost significantly more weight than SHAM rats [t(20) = −8.68, P < 0.001; Fig. 1].
Fig. 1.
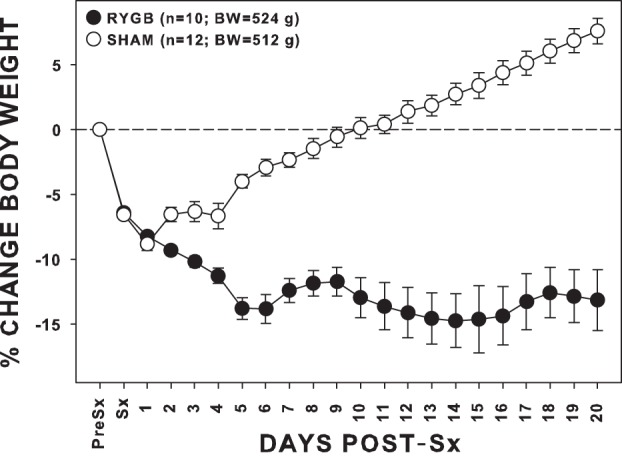
Mean (±SE) cumulative changes in body weight (BW) from the day before surgery (Pre-Sx) through the end of the standardized recovery period of rats given either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or sham (SHAM) surgery (Sx). The average absolute Pre-Sx BW of each group is provided in the legend. By the end of the recovery period, SHAM rats weighed significantly more than RYGB rats.
Sucrose
There was a significant interaction among food-deprivation condition, test period, and run order on sucrose intake in those animals able to complete all five tests after surgery [F(1,15) = 5.157, P = 0.038; data not shown]; thus we were unable to combine the counterbalanced groups for statistical analysis. Furthermore, some of the RYGB rats did not readily recover their body weight from food deprivation and were unable to complete the full 5-day test period. Consequently, we only analyzed the data derived from the tests conducted before the deprivation state crossover. When sucrose intakes from this more complete data set were analyzed via a three-way ANOVA, there was surprisingly no significant main effect of deprivation [F(1,18) = 0.862, P = 0.365] nor significant test period × deprivation interaction [F(1,18) = 3.281, P = 0.087] or test period × deprivation × surgery interaction [F(1,18) = 0.232, P = 0.636]. Thus we combined the data of the animals in each surgical subgroup for subsequent analysis with two-way ANOVA. Paired comparisons with the combined subgroups indicated that RYGB rats had lower intakes compared with that of SHAM rats only on days 2 and 3 (P ≤ 0.001; Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
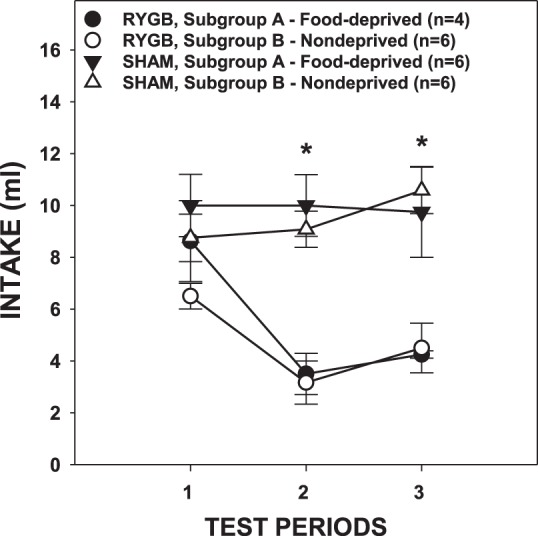
Mean (±SE) intakes of 0.3 M sucrose solution across 3 test periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery and tested while ∼23-h food deprived (subgroup A) or while nondeprived (subgroups B). *P ≤ 0.05, Bonferroni adjusted between the surgical groups (combined subgroups) on the testing periods indicated.
As expected, RYGB rats consumed less sucrose than SHAM rats [Fig. 3A; Table 1; this was also the case when the deprivation groups were separated: F(1,18) = 17.595, P = 0.001]. Interestingly, the influence of surgery on intake changed across testing periods. The volume of sucrose consumed did not differ between RYGB and SHAM rats during the first test period [t(20) = −1.858, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.156]. However, RYGB rats drank significantly less than SHAM rats during the second test period [i.e., the average of days 2 and 3; t(20) = −6.535, Bonferroni-adjusted P < 0.001]. Furthermore, RYGB rats decreased their intakes across the testing periods [t(9) = 4.278, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.004] while the intakes of SHAM rats remained stable [t(11) = −0.947, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.728].
Fig. 3.
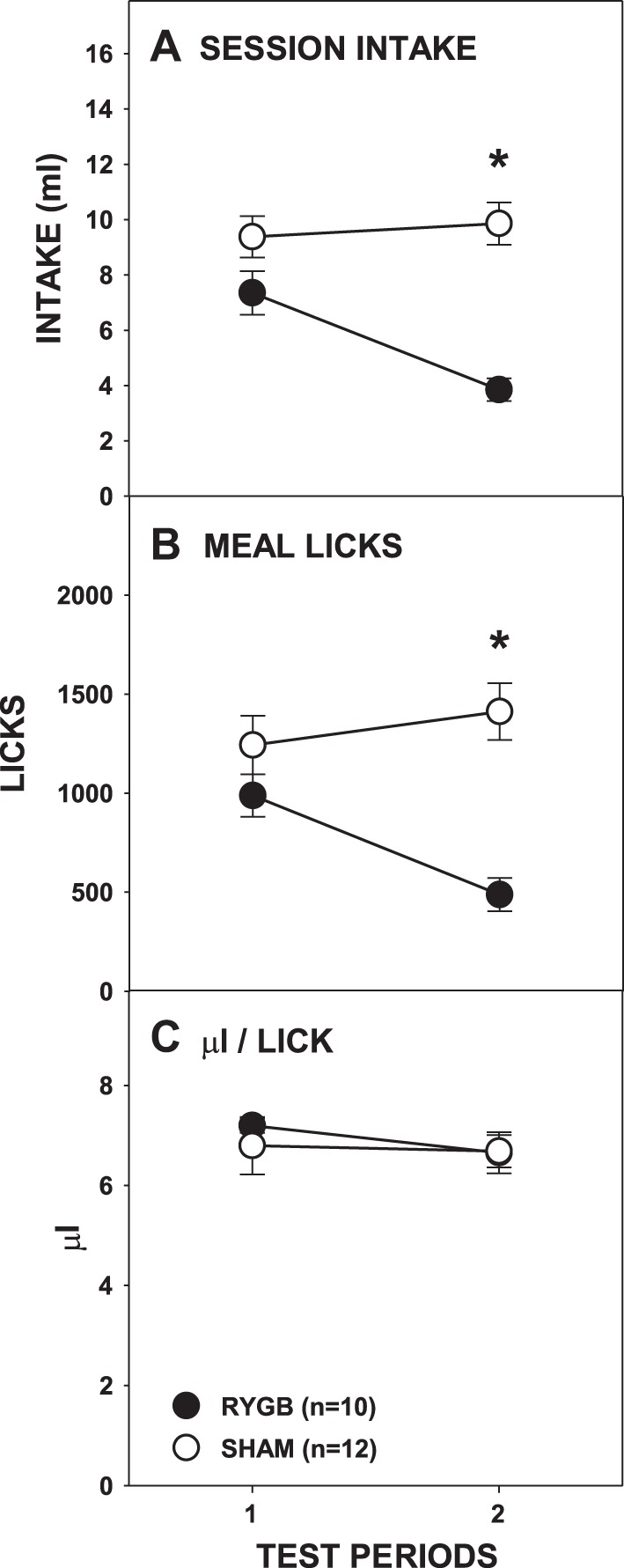
Mean (±SE) full-session intakes (A), meal licks (B), and calculated average volume per lick (C) of 0.3 M sucrose across 2 testing periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, Bonferroni adjusted between the surgical groups on the testing periods indicated. Error bars in A and C are not clear due to very low SE.
Table 1.
Two-way ANOVA results for measures during testing with 0.3 M sucrose
| Surgery | Testing Period | Surgery × Period | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full session intake | F(1,20) = 2 0.14, P < 0.001 | F(1,20) = 10.58, P = 0.004 | F(1,20) = 18.37, P < 0.001 |
| Meal licks | F(1,20) = 12.34, P = 0.002 | F(1,20) = 5.370, P = 0.031 | F(1,20) = 21.818, P < 0.01 |
| Meal bursts | F(1,20) = 3.038, P = 0.097 | F(1,20) = 1.531, P = 0.23 | F(1,20) = 0.065, P = 0.802 |
| Meal burst size | F(1,20) = 4.742, P = 0.042 | F(1,20) = 0.226, P = 0.64 | F(1,20) = 4.006, P = 0.059 |
| Meal ILI | F(1,20) = 8.466, P = 0.009 | F(1,20) = 10.103, P = 0.005 | F(1,20) = 0.066, P = 0.8 |
| First burst size | F(1,20) = 0.136, P = 0.716 | F(1,20) = 8.449, P = 0.009 | F(1,20) = 0.014, P = 0.75 |
| First minute lick rate | F(1,20) = 1.472, P = 0.239 | F(1,20) = 15.455, P = 0.001 | F(1,20) = 0.304, P = 0.587 |
| First burst ILI | F(1,20) = 2.843, P = 0.107 | F(1,20) = 0.195, P = 0.664 | F(1,20) = 0.355, P = 0.558 |
| Microliters per lick | F(1,20) = 0.144, P = 0.709 | F(1,20) = 1.032, P = 0.322 | F(1,20) = 0.453, P = 0.509 |
ILI, interlick interval.
The effects of RYGB on overall intake across the hour were also seen in the analysis of the number of licks taken during the meal (Fig. 3B; Table 1), a measure that balances stimulus contact between surgical groups based on a criterion-based satiation (i.e., pause ≥5 min) rather than an arbitrary experimenter-imposed time. During the meal, the number of licks taken by RYGB and SHAM rats did not differ during the first testing period [t(20) = −1.346, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.386], but RYGB rats took significantly fewer licks than SHAM rats during the second test period [t(20) = −5.273, Bonferroni-adjusted P < 0.001]. Similarly, RYGB rats decreased the number of licks in their meal across the test periods [t(9) = 5.854, P < 0.001], but SHAM rats did not [t(11) = −1.541, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.304]. These results show that upon first access RYGB rats drank 0.3 M sucrose in amounts comparable to SHAM rats but, on subsequent exposures, drank less during an entire 60-min period and during their first meal of the test.
To determine the microstructural manner in which the differences in intake outcomes between RYGB and SHAM rats were achieved, especially during the second test period, we compared the number and size of bursts taken during the meal across access periods. Compared with SHAM rats, RYGB rats took smaller bursts overall (Fig. 4A; Table 1), but further analysis showed that this was the case only during the second access period [t(20) = −2.709, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.026; first test period: t(20) = −0.256, Bonferroni-adjusted P > 0.8]. The number of bursts taken never differed between surgical groups nor changed across test periods (Fig. 4B; Table 1). This suggests that some of the difference between the licks taken by RYGB and SHAM rats during the second access period was due to the RYGB rats taking smaller, but not fewer, bursts. However, the very first burst taken by RYGB and SHAM rats was of a similar size, and the first-minute lick rates of surgical groups also did not differ (Fig. 5, A and B; Table 1). These comparable early meal lick responses to sucrose by RYGB and SHAM rats suggest that behavior guided primarily by orosensory-based motivation is not impacted by the surgery, even on testing periods during which intakes differed and effects on overall burst size were observed.
Fig. 4.
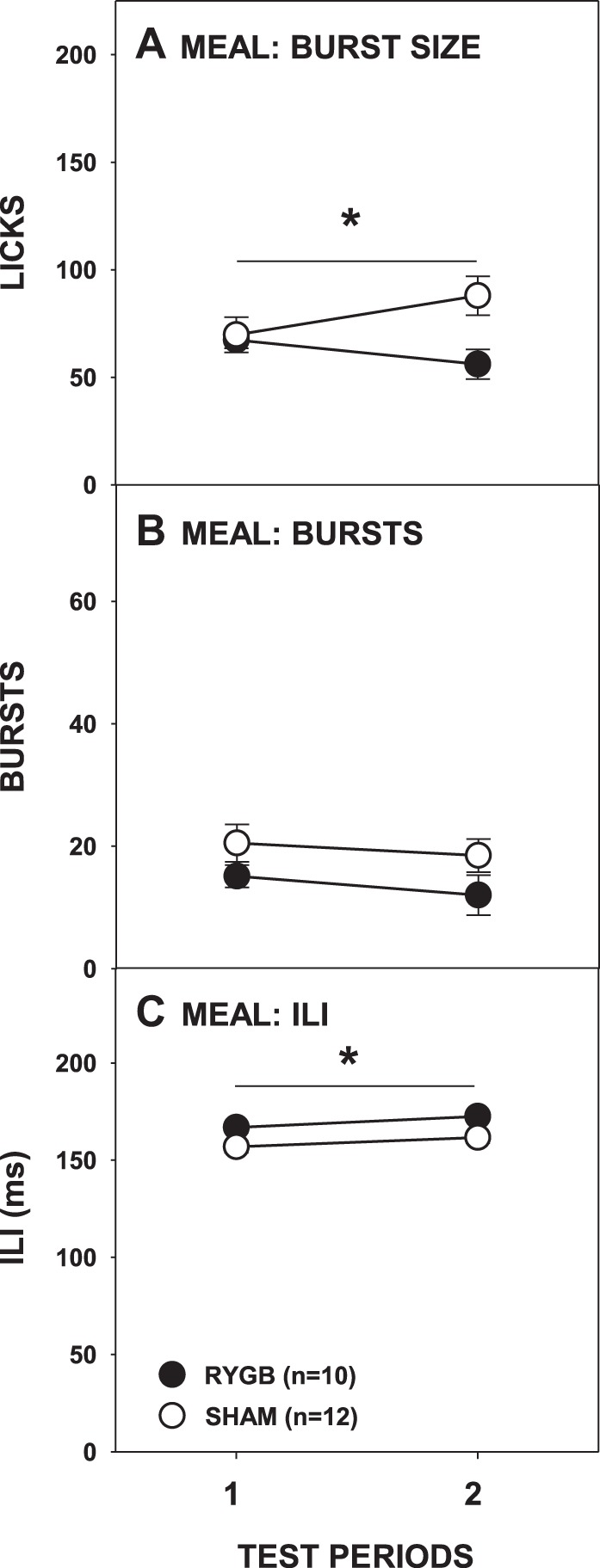
Mean (±SE) burst size (A), burst number (B), and interlick interval (ILI; C) during the meal of 0.3 M sucrose across 2 testing periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, main ANOVA effect of between the surgical groups across the testing period span indicated by the line. Error bars in C are not visible due to very low SE.
Fig. 5.

Mean (±SE) size of the very 1st burst (A), lick rate during the 1st minute (B), and 1st-burst ILI (C) during access to 0.3 M sucrose across 2 testing periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM. Errors bars in C are not visible due to very low SE.
While there were no differences in early meal licking burst size or rate, we observed that RYGB lengthened the ILIs of rats licking sucrose in the first meal (Fig. 4C; Table 1), although not in the very first burst (Fig. 5C; Table 1). Despite this evidence that RYGB possibly slows the putative central pattern generator governing local lick rate (c.f., Refs. 5, 25, 26), the amount of fluid taken per lick across the entire 60-min test period did not differ significantly between the surgical groups (Fig. 3C; Table 1). Although the local rate of licking for sucrose within bursts was lower in RYGB rats, the global rate is largely determined by the durations of bursts and the pauses between them and thus the lengthened ILI does not likely account for the RYGB-induced decrease in intake.
Intralipid
As with sucrose intake, overall the RYGB rats consumed less Intralipid than the SHAM rats, and this difference progressed across testing periods (Fig. 6A; Table 2). The intakes of the SHAM rats did not change across testing periods [F(3,33) = 2.148, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.226]; those of the RYGB rats tended to decrease but did not survive the Bonferroni correction [F(3,21) = 3.336, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.078]. No intake differences between the RYGB and SHAM groups were seen on the first testing period [t(18) = 0.416, Bonferroni-adjusted P > 0.68] or the second testing period [t(18) = −1.521, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.584], but RYGB rats drank significantly less Intralipid than SHAM rats on the third testing period [t(18) = −2.913, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.036] and the fourth testing period [t(18) = −3.125, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.024]. Compared with SHAM rats, RYGB rats also took fewer licks during their meal (Fig. 6B; Table 2) on the third testing period [t(18) = −4.67, Bonferroni-adjusted P < 0.001] although not on the fourth testing period [t(18) = −1.568, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.536]. Similar to overall intake, licks taken during the meal by RYGB rats decreased across test periods [F(3,21) = 4.413, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.03], whereas those of SHAM rats remained stable [F(3,33) = 1.855, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.314]. Thus, in a pattern similar to that seen with sucrose, RYGB rats initially consumed amounts of Intralipid similar to that of SHAM rats, but RYGB rats drank less than SHAM rats upon subsequent presentations.
Fig. 6.
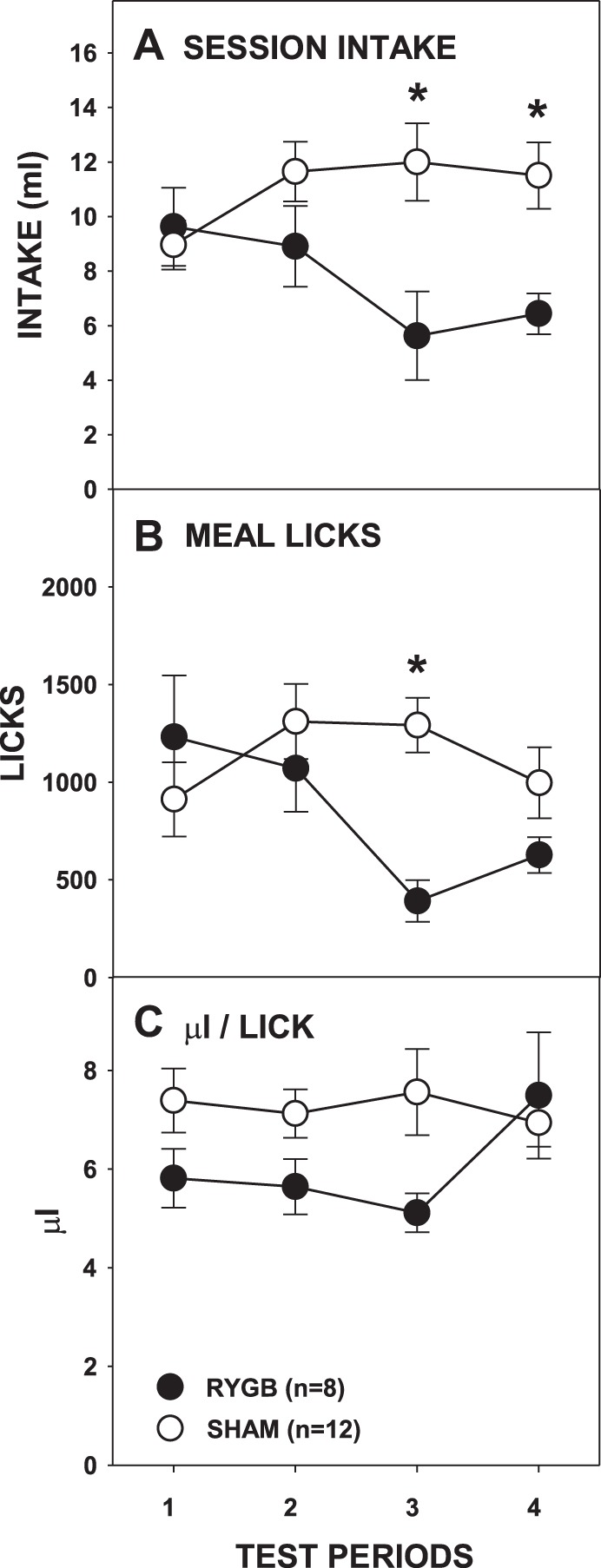
Mean (±SE) full-session intakes (A), meal licks (B), and calculated average volume per lick (C) of 5% Intralipid across 4 testing periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, Bonferroni adjusted differences between the surgical groups on the testing periods indicated.
Table 2.
Two-way ANOVA results for measures during testing with 5% Intralipid
| Surgery | Testing Period | Surgery × Period | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full session intake | F(1,18) = 6.59, P = 0.019 | F(3,54) = 0.823, P = 0.487 | F(3,54) = 4.541, P = 0.011 |
| Meal licks | F(1,18) = 2.685, P = 0.119 | F(3,54) = 2.38, P = 0.08 | F(3,54) = 4.462, P = 0.007 |
| Meal bursts | F(1,18) = 0.147, P = 0.706 | F(3,54) = 10.42, P < 0.001 | F(3,54) = 3.91, P = 0.013 |
| Meal burst size | F(1,18) = 4.398, P = 0.05 | F(3,54) = 6.282, P = 0.001 | F(3,54) = 1.82, P = 0.155 |
| Meal ILI | F(1,18) = 18.39, P < 0.001 | F(3,54) = 5.452, P = 0.002 | F(3,54) = 0.915, P = 0.44 |
| First burst size | F(1,18) = 0.175, P = 0.681 | F(3,54) = 5.248, P = 0.003 | F(3,54) = 0.5, P = 0.684 |
| First minute lick rate | F(1,18) = 0.082, P = 0.778 | F(3,54) = 9.488, P < 0.001 | F(3,54) = 0.496, P = 0.687 |
| First burst ILI | F(1,18) = 7.818, P = 0.012 | F(3,54) = 0.065, P = 0.978 | F(3,54) = 0.834, P = 0.481 |
| Microliters per lick | F(1,18) = 2.535, P = 0.129 | F(3,54) = 1.145, P = 0.339 | F(3,54) = 2.833, P = 0.047 |
The effect of RYGB surgery on burst number was more complex than that observed with sucrose. There was no main effect of surgery, but there was a main effect of period and a significant interaction (Fig. 7B; Table 2). Paired comparisons failed to show any differences between the surgical groups on individual test periods. Similar to sucrose testing, RYGB rats overall took smaller bursts than SHAM rats (Fig. 7A; Table 2); although the interaction of surgical group and test period did not reach significance, further t-tests showed that RYGB rats had smaller bursts than SHAM rats only during the second testing period [t(18) = −2.959, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.032; all other Bonferroni-adjusted P ≥ 0.32]. Although there were some changes in the average burst number and burst size across the entire meal as a function of RYGB, neither the size of the first burst nor the first-minute lick rate differed between the surgical groups (Fig. 8, A and B; Table 2). This demonstrates that, similar to sucrose testing, RYGB rats displayed normal early meal responses to Intralipid before the onset of satiation and that this licking pattern did not change even when there were overall differences between surgical groups in terms of licks during the meal and session intake.
Fig. 7.
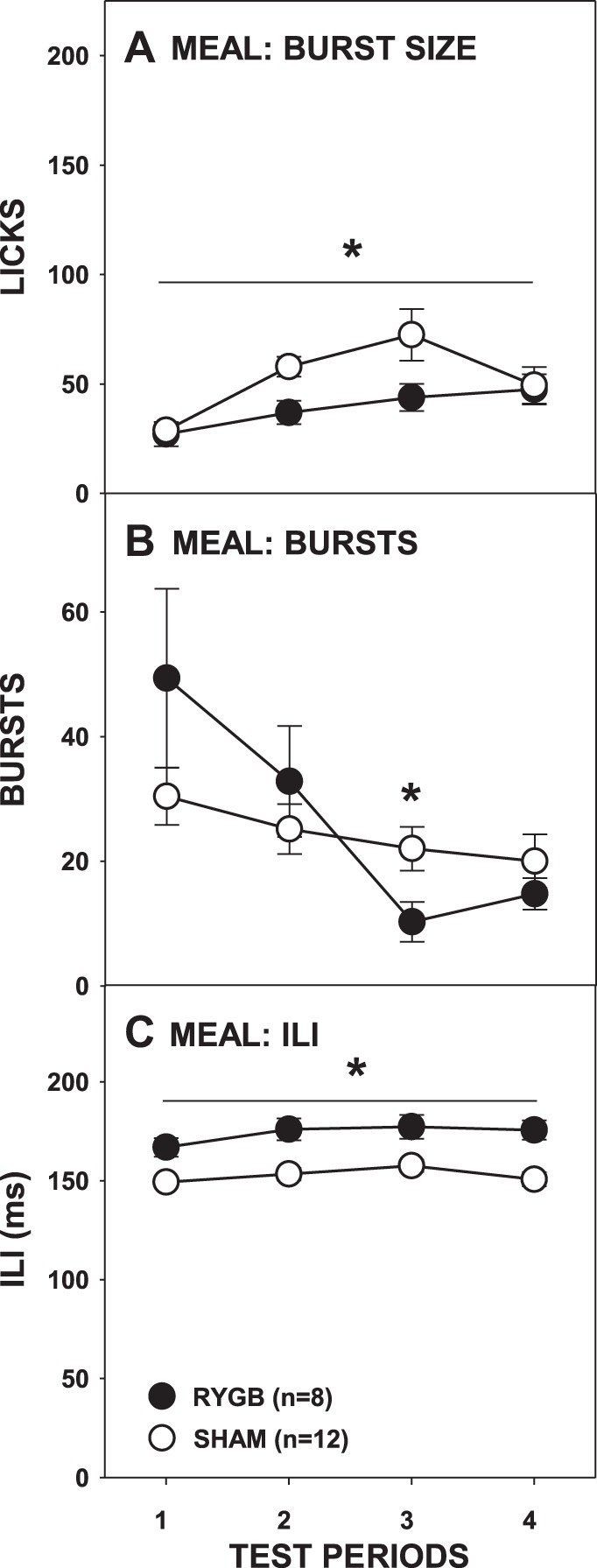
Mean (±SE) burst size (A), burst number (B), and ILI (C) during the meal of 5% Intralipid across 4 testing periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, main ANOVA effect between the surgical groups across the testing period span indicated by the line. Errors bars in A and C are not always visible due to very low SE.
Fig. 8.
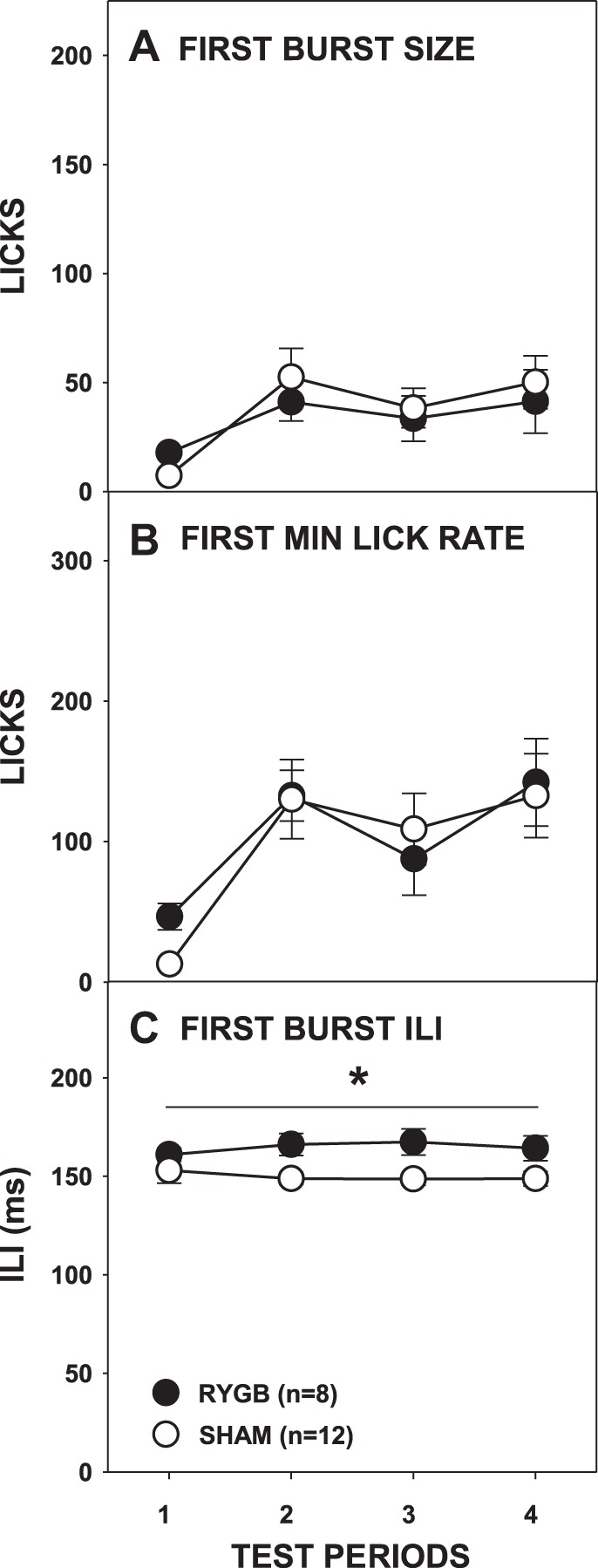
Mean (±SE) size of the 1st burst (A), lick rate in the 1st minute (B), and ILI (C) during access to 5% Intralipid across 4 testing periods by rats given RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, a main ANOVA effect between the surgical groups across the testing period span indicated by the line. Errors bars in A–C are not always visible due to very low SE.
We once again observed that RYGB lengthened ILIs, and during Intralipid access it occurred both throughout the meal (Fig. 7C) and during the first burst (Fig. 8C; Table 2). Unlike what was seen with sucrose, there was a significant surgery × test period interaction in the amount of fluid taken per lick (Fig. 6C; Table 2), but t-tests revealed no differences between the groups on any testing period (all Bonferroni-adjusted P values > 0.1).
Ensure
As expected, RYGB rats consumed less Ensure than SHAM rats (Fig. 9A; Table 3), but, unlike what was observed with sucrose and Intralipid, this occurred on all of the testing periods (all Bonferroni-adjusted P ≤ 0.05). However, this was not necessarily due to changes in the RYGB group; after RYGB, rats drank similar amounts of Ensure across test periods [F(4,32) = 1.470, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.468] whereas SHAM rats drank increasingly greater amounts [F(4,44) = 33.115, P < 0.001]. Interestingly, RYGB and SHAM rats took a similar number of licks during the meal of the first test period [F(1,19) = 1.466, Bonferroni-adjusted P > 0.99], but RYGB rats took fewer licks during their meals than SHAM rats on the other test periods (all P ≤ 0.001). These results suggest that although differences in Ensure intake between the surgical groups were evident on the very first test, they only appeared after completion of the first meal.
Fig. 9.
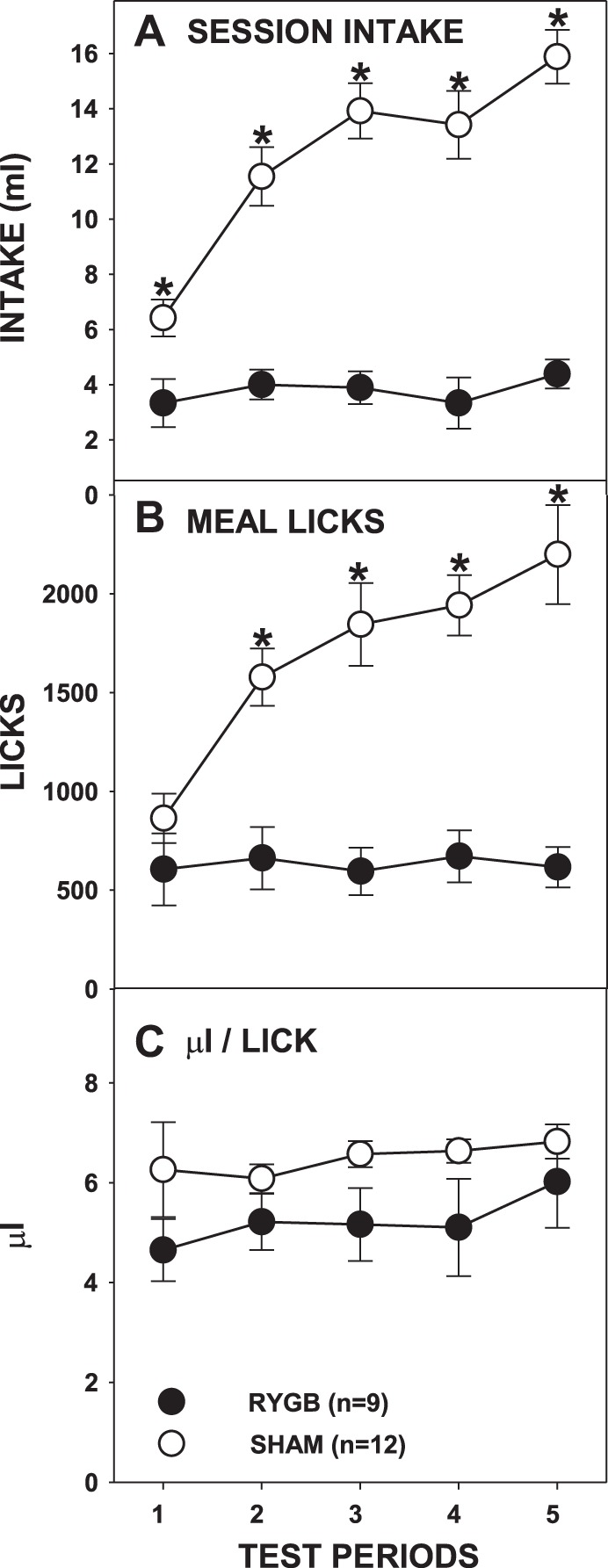
Mean (±SE) full-session intakes (A), meal licks (B), and calculated average volume per lick (C) of milk-chocolate flavored Ensure Plus across 5 test periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, Bonferroni adjusted between the surgical groups on the testing periods indicated.
Table 3.
Two-way ANOVA results for measures during testing with milk-chocolate flavored Ensure
| Surgery | Testing Period | Surgery × Period | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full session intake | F(1,19) = 57.86, P < 0.001 | F(4,76) = 24.23, P < 0.001 | F(4,76) = 17.4, P < 0.001 |
| Meal licks | F(1,19) = 27.03, P < 0.001 | F(4,76) = 11.57, P < 0.001 | F(4,76) = 10.93, P < 0.001 |
| Meal bursts | F(1,19) = 1.999, P = 0.174 | F(4,76) = 1.326, P = 0.268 | F(4,76) = 0.985, P = 0.421 |
| Meal burst size | F(1,19) = 8.725, P = 0.008 | F(4,76) = 3.009, P = 0.020 | F(4,76) = 1.253, P = 0.296 |
| Meal ILI | F(1,19) = 11.1, P = 0.004 | F(4,76) = 6.580, P < 0.001 | F(4,76) = 0.493, P = 0.741 |
| First burst size | F(1,19) = 5.643, P = 0.028 | F(4,76) = 2.515, P = 0.048 | F(4,76) = 0.636, P = 0.638 |
| First minute lick rate | F(1,19) = 4.365, P = 0.050 | F(4,76) = 2.723, P = 0.036 | F(4,76) = 2.938, P = 0.026 |
| First burst ILI | F(1,19) = 3.883, P = 0.064 | F(4,76) = 4.769, P = 0.002 | F(4,76) = 0.584, P = 0.675 |
| Microliters per lick | F(1,19) = 3.304, P = 0.085 | F(4,76) = 1.357, P = 0.257 | F(4,76) = 0.377, P = 0.824 |
The differences in meal licks between RYGB and SHAM rats were not the result of differences in the number of bursts initiated (Fig. 10B) but rather due to smaller-sized bursts taken by RYGB rats compared with SHAM rats (Fig. 10A; Table 3). However, similar to overall test intake, the average burst size of RYGB rats did not change across test periods [F(4,32) = 1.006, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.839] but rather those of SHAM rats increased in an apparently monotonic fashion [F(4,44) = 3.154, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.046]. It should also be noted that the burst size of RYGB rats did not differ from that of SHAM rats during the very first meal of Ensure (Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.27).
Fig. 10.
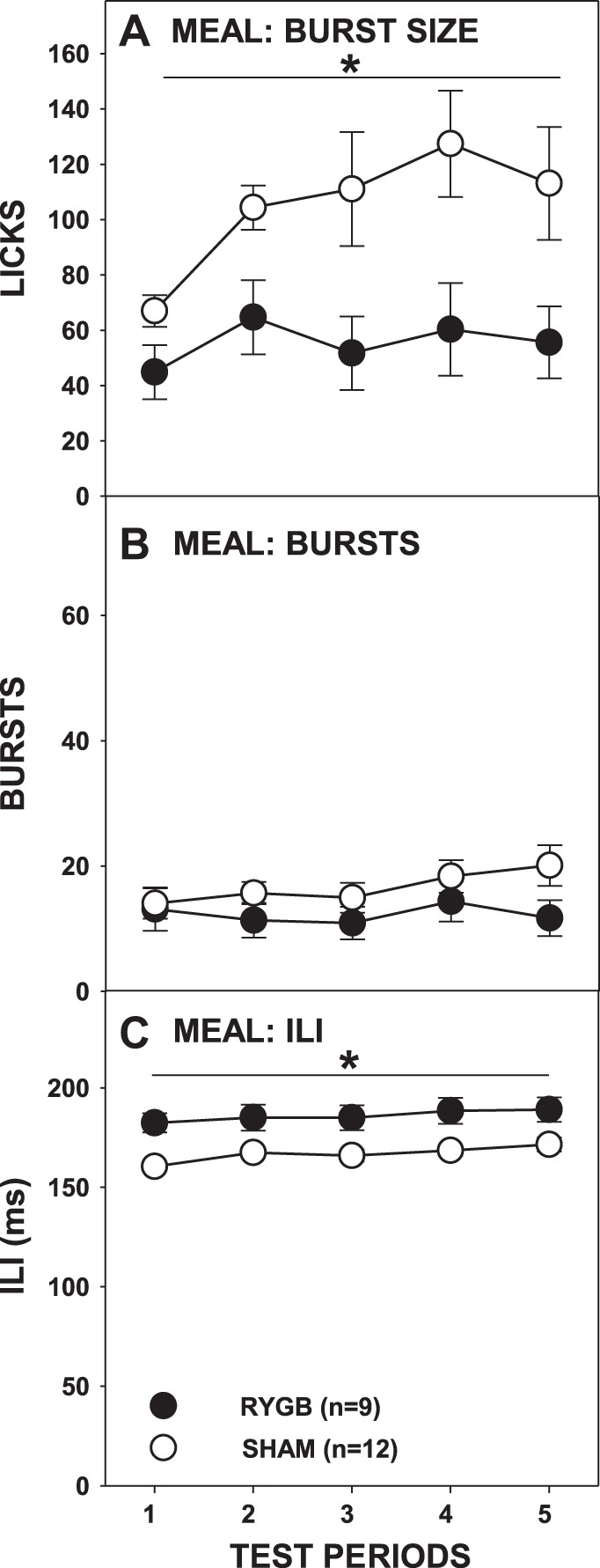
Mean (±SE) burst size (A), burst number (B), and ILI (C) during the meal of milk-chocolate flavored Ensure Plus across 5 test periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, main ANOVA effect between the surgical groups across the testing period span indicated by the line. Errors bars is C are not always visible due to very low SE.
When Ensure served as the test stimulus, RYGB rats overall took smaller first bursts (Fig. 11A) and had overall slower first-minute lick rates (Fig. 11B; Table 3). While there was also a significant interaction of testing period and surgical group on first-minute lick rates, further analysis revealed statistical significance only on the third and fifth testing periods, both of which disappeared with Bonferroni correction (P < 0.1). This suggests that, unlike in the sessions in which sucrose or IL served as stimuli, the orosensory-guided responses of RYGB rats to Ensure were somewhat blunted compared with those of SHAM rats. Interestingly, some of this may have stemmed from the fact that the first-minute lick rates of SHAM rats appeared to generally increase across test periods [F(4,44) = 5.045, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.004] whereas that of the RYGB rats remained stable [F(4,32) = 0.876, Bonferroni-adjusted P = 0.978].
Fig. 11.
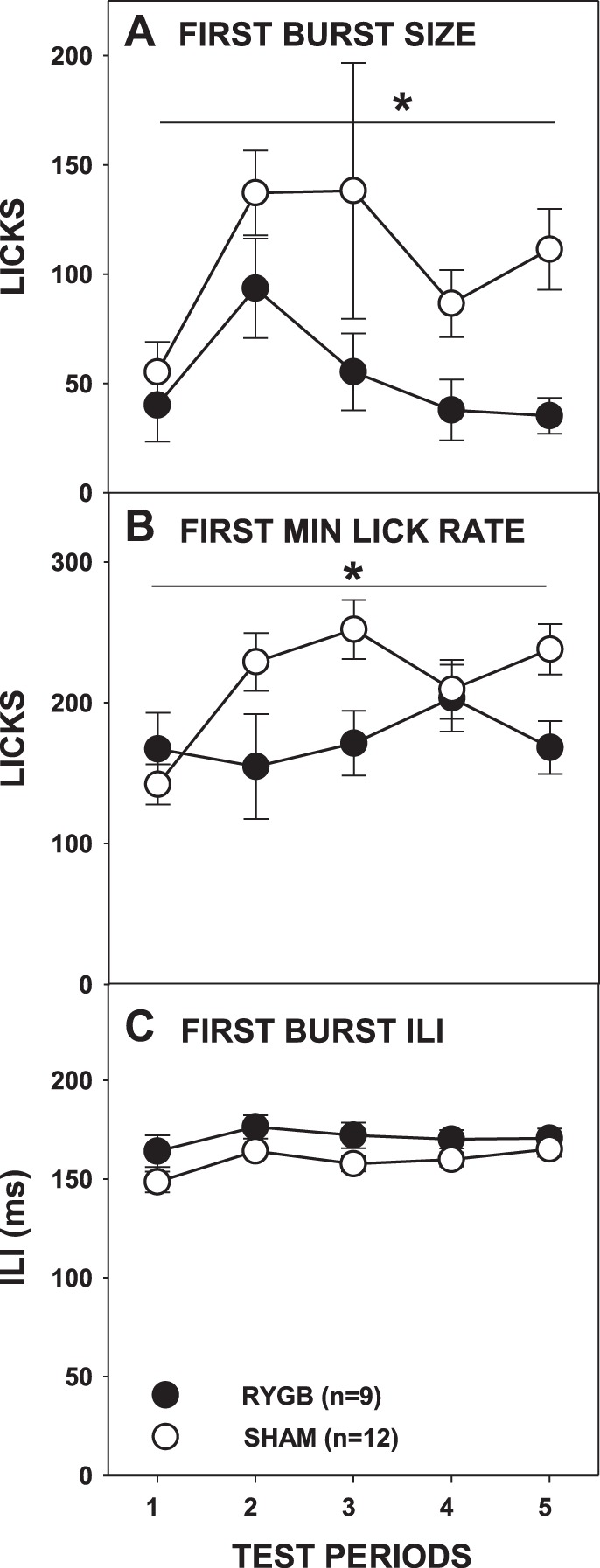
Mean (±SE) size of the 1st burst (A), lick rate in the 1st minute (B), and ILI (C) during access to milk-chocolate flavored Ensure Plus across 5 test periods by rats given either RYGB or SHAM surgery. *P ≤ 0.05, main ANOVA effect between the surgical groups across the testing period span indicated by the line or on the testing periods indicated. Errors bars in C are not always visible due to very low SE.
Rats given RYGB once again displayed slower ILIs during the first meal when tested with Ensure (Fig. 10C; Table 3), although the analysis of ILIs in the first burst narrowly missed significance (Fig. 11C). Lick volume did not significantly differ between RYGB and SHAM rats across test periods(Fig. 9C; Table 3).
DISCUSSION
As expected, RYGB rats consumed less of each of the nutritive stimuli tested than did SHAM rats. What was more interesting, though, was how intakes changed between the surgical groups across testing periods. Indeed, during sucrose and Intralipid testing, consumption by the RYGB rats did not differ from that of the SHAM rats until the second or third test period. Our group and others have previously shown that RYGB rats display less intake of and preference for sucrose and Intralipid compared with SHAM rats within a 24- to 48-h preference test (2, 4, 10, 27), but it was unclear if these intake differences would be apparent in shorter term intake tests. Here we demonstrated that, while RYGB rats did eventually drink less sucrose and Intralipid than SHAM rats, this intake difference took at least a full 60-min test period to emerge. This behavioral pattern is suggestive of a learned process based on postingestive consequences as opposed to an immediate reaction to changes in the perceived orosensory properties of the stimuli.
The behavior associated with Ensure was notably different from that associated with sucrose or Intralipid: RYGB rats consumed less of the sweet and fatty nutritional supplement compared with SHAM rats from the first access period. Importantly, however, RYGB and SHAM rats licked similar amounts of Ensure during the first meal on the first test period, suggesting that more than a meal's worth of experience was necessary for the subsequent difference in licking to emerge. While RYGB rats drank less Ensure than SHAM rats, the intakes of the RYGB rats remained stable across test periods where as those of SHAM rats increased. More efficient learning with Ensure may have occurred since the stimulus includes some of the components that the rats had previously experienced (e.g., fat, sucrose, and/or maltodextrin), although it could also (or additionally) be because Ensure contains protein and/or micronutrients and has a higher caloric density. Overall these data show that intake differences do not occur between rats receiving gastric bypass and sham operation when the first testing period is equated on the basis of satiation (i.e., analyzed by a criterion-defined meal), and, collectively, they demonstrate that experience with the caloric liquids is necessary before intake differences emerge between RYGB and SHAM rats, at least under these testing conditions.
The current study also revealed the behavioral mechanism underlying the differences in intake between RYGB and SHAM rats. Generally, unless lick volume changes significantly, intake outcomes can differ based on two factors: either the animal approaches the stimulus less often and thus initiates fewer bursts and/or the animal takes fewer licks during the bursts that it initiates. In these experiments, the number of bursts initiated did not typically differ between the surgical groups, suggesting that the appetitive drive to approach sweet and/or fatty nutritive stimuli was rarely diminished by RYGB. These results are congruent with our previous report that RYGB did not blunt the amount of work performed during a progressive ratio test in which Ensure, 5% Intralipid, or 1.0 M sucrose served as the reinforcer (10). Both of these findings differ, however, from a prior study in which RYGB rats initiated more trials for a concentration series of sucrose solutions in a brief-access taste test (11). That lower sucrose concentrations were present in the brief-access but not the progressive ratio or microstructural tests may have produced this disparity. On the surface, these findings appear to differ from those seen by Zheng et al. (27) who reported an increase in Ensure meal frequency. However, Zheng et al. (27) examined the size and number of meals distributed over 24 h and did not focus on the microstructure of ingestion within individual meals. It is possible that the increased meal initiation could represent a compensatory response to the decreased meal size that was also reported.
Although burst number did not typically differ between the surgical groups, the average burst size tended to be lower in RYGB compared with SHAM rats. This suggests that RYGB decreases the tendency to sustain a run of consecutive licks without pauses. Burst size is a parameter that is thought to reflect consummatory behavior in response to the stimulus. This is not in line with our previous results in which, during a brief-access taste test, the number of licks of sucrose that RYGB rats took per trial was not lower than that of SHAM rats (Ref. 11; although see Refs. 8, 18, 24). However, although burst size is a measure that decreases as concentration decreases, and thus suggestive of orosensory acceptability, burst size also decreases as postingestive caloric/colligative load accumulates across a meal (21). Indeed, when testing with sucrose and Intralipid, we saw no differences in the early meal measures (first-burst size and first-minute lick rates) between RYGB and SHAM rats. The latter outcomes indicate that the immediate orosensory-based responses before the postoral accumulation and postingestive consequences of these stimuli were not altered by RYGB. It appears, then, that the overall decrease in burst size was influenced more by postingestive consequences than by “taste.” Again, the results with Ensure were different: RYGB rats took overall fewer licks in their first burst and displayed overall slower lick rates in the first minute compared with SHAM rats. This is somewhat similar to the results of Zheng et al. (27) in which, early after surgery, ingestion rate was slower in RYGB compared with sham-operated rats. As discussed, interestingly, the behavior of the SHAM rather than RYGB rats changed over time, and this could be due to experience and/or nutrient content and density and requires further assessment.
Consistently across stimuli in this study, RYGB lengthened ILI, a phenomenon we have previously observed (11) and that suggests that a physiological and/or neural consequence of RYGB slows the ability of rats to lick. We suspect that this is mediated via hormonal changes resulting from the surgery since the motor disturbance is recapitulated after administration of the glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonist Exendin-4 (11) and other forms of neuropeptide modulation (c.f., Ref. 1). These data suggest that that RYGB potentially disrupts the output of the putative central pattern generator for licking (c.f., Refs. 5, 23, 25, 26). Despite this impairment, RYGB rats displayed no consistent or robust differences from SHAM rats in terms of the fluid volume acquired with each lick. This observation differs from that discussed by Zheng et al. (27), who reported anecdotally that RYGB rats took less fluid with each lick compared with SHAM rats. Regardless, based on their extent and inconsistent nature, it does not seem in the current report that any motor effects were at the root of the intake differences between the surgical groups.
Overall, these findings support the hypothesis that RYGB does not explicitly alter the immediate orosensory-based behavior towards normally preferred nutritive stimuli. Rather, ingestive experience appears to be a prerequisite antecedent to the emergence of the reduced caloric intake that characteristically follows this form of bariatric surgery, at least in rats. We have shown that, after RYGB, rats need not drink the nutritive fluids tested here across an entire 24-h period (or more) to learn about the consequence; behavioral differences appear after only an hour-long session or so. When the intakes of RYGB rats do drop, it is often due to a decrease in the number of licks taken per burst. While burst size decreasing may in some instances suggest a change in the “palatability” of a stimulus, this measure is also sensitive to meal progress during which there is postoral accumulation of the stimulus (21). The latter seems to be at play in RYGB rats, as their responses within the first burst or minute, which can be considered as occurring before the accumulation of any significant amount of fluid in the gut, typically do not differ from those of SHAM rats.
Perspectives and Significance
This study further supports the hypothesis that RYGB does not change preference for foods high in sugar and/or fat by altering their “taste,” per se, but instead suggests that reduced selection and decreased consumption of these foods is a learned phenomenon. While, for example, chocolate cake may still possess a reinforcing taste, eating too much after RYGB could produce gastrointestinal consequences. These consequences may come in various forms, but if they lead to discomfort, an individual could learn how much cake could be tolerated without unpleasant consequences and reduce their intake accordingly. In this study, early meal measures suggest that the nutritive stimuli tested here maintain their palatability and only intake decreases, akin to the phenomenon of conditioned avoidance as opposed to conditioned taste aversion. In other words, after RYGB rats still find the sweet and fatty stimuli palatable and initially avidly consume them upon presentation, but with experience they learn to adjust their intake to potentially avoid negative postingestive consequences (see 13). Future studies will need to more explicitly interrogate the learning mechanisms that potentially underlie these experience-related modifications in ingestive behavior. The one thing that remains clear is that the decrease in intake and preference for sugar- and fat-containing fluids after RYGB progress over time, indicating that experience plays role.
GRANTS
This work was supported by National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders Grant R21-DC-012751 (to A. C. Spector). C. W. le Roux is supported by Science Foundation Ireland Grant 12/YI/B2480.
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Author contributions: C.M.M., C.W.l.R., and A.C.S. conception and design of research; C.M.M. and R.A.B. performed experiments; C.M.M. analyzed data; C.M.M., C.W.l.R., and A.C.S. interpreted results of experiments; C.M.M. prepared figures; C.M.M. drafted manuscript; C.M.M., R.A.B., C.W.l.R., and A.C.S. edited and revised manuscript; C.M.M., R.A.B., C.W.l.R., and A.C.S. approved final version of manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Ginger Blonde for technical assistance and for insightful comments on a previous version of the manuscript. We also thank Chanel Letourneau and Taylor Murphy for animal care assistance during portions of the studies. These data were presented at the April 2014 meeting of the Association for Chemoreception Sciences.
Present address of C. M. Mathes: Dept. of Psychology and Neuroscience Program, Baldwin Wallace University, Berea, OH.
REFERENCES
- 1.Aja S, Ewing C, Lin J, Hyunn J, Moran TH. Blockade of central GLP-1 receptors prevents CART-induced hypophagia and brain c-fos expression. Peptides 27: 157–164, 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bueter M, Miras AD, Chichger H, Fenske W, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Unwin RJ, Lutz TA, Spector AC, le Roux CW. Alterations of sucrose preference after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Physiol Behav 104: 709–721, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Burge JC, Schaumburg JZ, Choban PS, DiSilvestro RA, Flancbaum L. Changes in patients' taste acuity after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for clinically severe obesity. J Am Diet Assoc 95: 666–670, 1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chelikani PK, Shah IH, Taqi E, Sigalet DL, Koopmans HH. Comparison of the effects of Rpoux-en-Y gastric bypass and ileal transposition surgeries on food intake, body weight, and circulating peptide YY concentrations in rats. Obes Surg 20: 1281–1288, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Corbit JD, Luschei ES. Invariance of the rat's rate of drinking. J Comp Physiol Psychol 60: 119–125, 1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Davis JD, Perez MC. Food deprivation- and palatability-induced microstructural changes in ingestive behavior. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 264: R97–R103, 1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Davis JD, Smith GP. Analysis of the microstructure of the rhythmic tongue movements of rats ingesting maltose and sucrose. Behav Neurosci 106: 217–228, 1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hajnal A, Kovacs P, Ahmed T, Meirelles K, Lynch CJ, Cooney RN. Gastric bypass surgery alters behavioral and neural taste functions for sweet taste in obese rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299: G967–G979, 2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Laurenius A, Larsson I, Melanson KJ, Lindroos AK, Lonrth H, Bosaeus I, Olbers T. Decreased energy density and changes in food selection following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Eur J Clin Nutr 67: 168–173, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mathes CM, Bohnenkamp RA, Cortevillie C, Bueter M, Lutz TA, le Roux CW, Spector AC. Gastric bypass in rats does not decrease appetitive behavior towards fatty fluids despite at times blunting preferential intake of fat. Physiol Behav 142: 179–188, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mathes CM, Bueter M, Smith KR, Lutz TA, le Roux CW, Spector AC. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in rats increases sucrose taste-related motivated behavior independent of pharmacological GLP-1 receptor modulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302: R751–R767, 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nissenbaum JW, Sclafani A. Qualitative differences in polysaccharide and sugar tastes in the rat: a two-carbohydrate taste model. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 11: 187–196, 1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Parker LA. Taste avoidance and taste aversion: evidence for two different processes. Learn Behav 31: 165–172, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sclafani A. But-brain nutrient signaling, appetition vs. satiation. Appetite 71: 454–458, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sclafani A. The sixth taste? Appetite 43: 1–3, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sclafani A, Mann S. Carbohydrate taste preferences in rats: glucose, sucrose, maltose, fructose and polycose compared. Physiol Behav 40: 563–568, 1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Seyfried F, Miras AD, Bueter M, Prechtl CG, Spector AC, le Roux CW. Effects of preoperative exposure to a high-fat versus a low-fat diet on ingestive behavior after gastric bypass surgery in rats. Surg Endos 27: 4192–4201, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shin AC, Zheng H, Pistell PJ, Berthoud HR. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery changes food reward in rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 35: 642–651, 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sjöström L, Narbro K, Sjöström CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, Lystig T, Sullivan M, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Bengtsson C, Dahlgren S, Gummesson A, Jacobson P, Karlsson J, Lindroos AK, Lönroth H, Näslund I, Olbers T, Stenlöf K, Torgerson J, Agren G, Carlsson LM; Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 357: 741–752, 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Smith GP. The direct and indirect controls of meal size. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 20: 41–46, 1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Spector AC, Klumpp PA, Kaplan JM. Analytical issues in the evaluation of food deprivation and sucrose concentration effects on the microstructure of licking behavior in the rat. Behav Neurosci 112: 678–694, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Spector AC, Smith JC. A detailed analysis of sucrose drinking in the rat. Physiol Behav 33: 127–136, 1984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stellar E, Hill JH. The rat's rate of drinking as a function of water deprivation. J Comp Physiol Psychol 45: 96–102, 1952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tichansky DS, Glatt AR, Madan AK, Harper J, Tokita K, Boughter JD. Decrease in sweet taste in rats after gastric bypass surgery. Surg Endosc 25: 1176–1181, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Travers JB, DiNardo LA, Karimnamazi H. Motor and premotor mechanisms of licking. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21: 631–647, 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wiesenfeld Z, Halpern BP, Tapper DN. Licking behavior: evidence of a hypoglossal oscillator. Science 196: 1122–1124, 1977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zheng H, Shin AC, Lenard NR, Townsend RL, Patterson LM, Sigalet DL, Berthoud HR. Meal patterns, satiety, and food choice in a rat model of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297: R1273–R1282, 2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


