Abstract
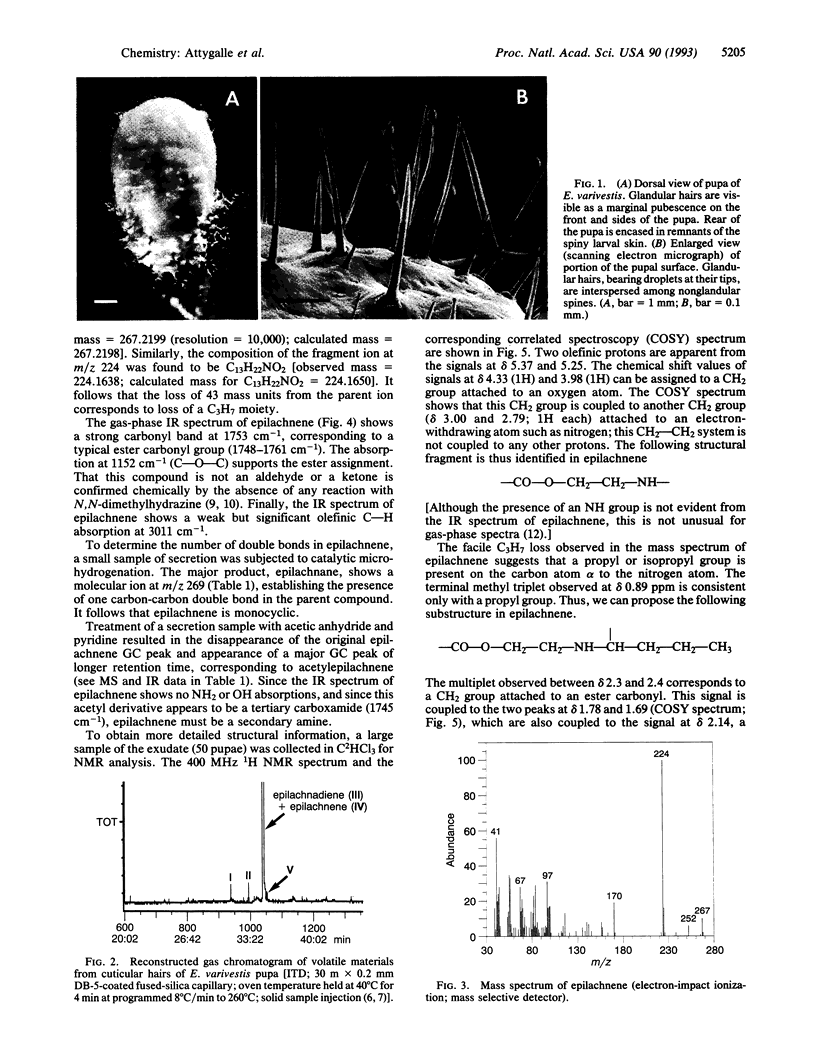
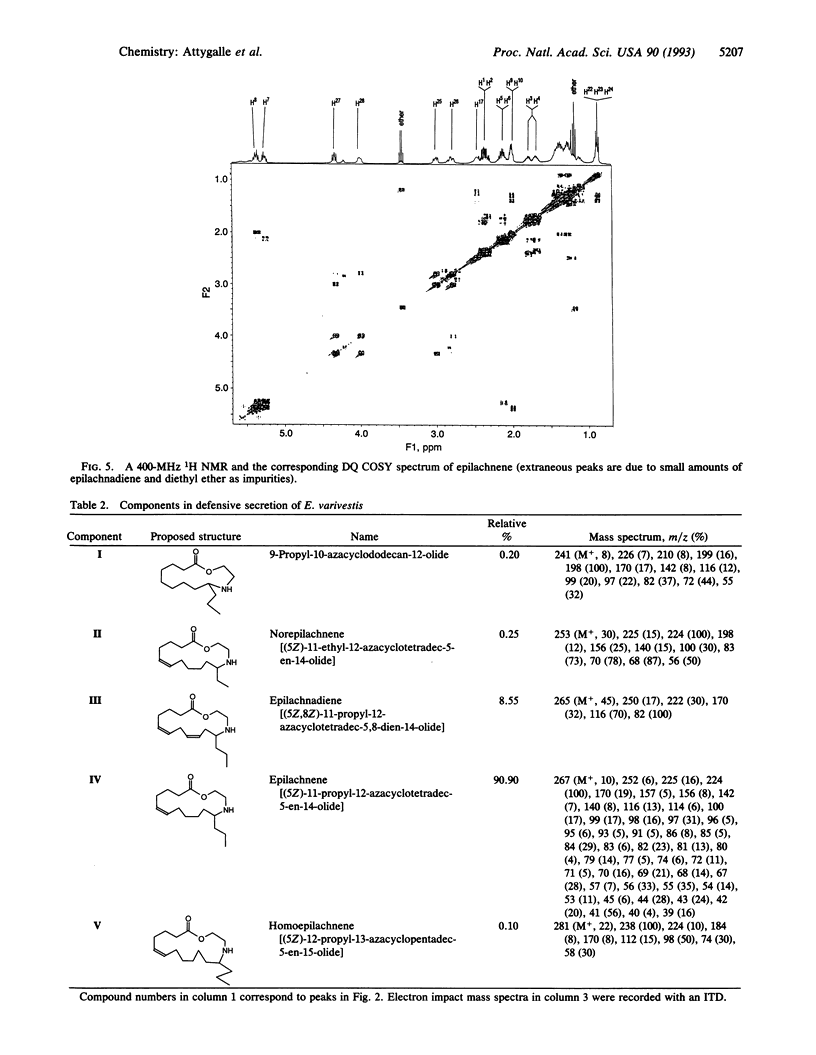
Defensive droplets from glandular hairs of the pupa of the Mexican bean beetle, Epilachna varivestis, contain a group of structurally novel alkaloids, the azamacrolides. The major constituent of this secretion, epilachnene, is shown to be (5Z)-11-propyl-12-azacyclotetradec-5-en-14-olide. The secretion also contains an epilachnadiene and trace amounts of three closely related components.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisner T., Goetz M., Aneshansley D., Ferstandig-Arnold G., Meinwald J. Defensive alkaloid in blood of Mexican bean beetle (Epilachna varivestis). Experientia. 1986 Feb 15;42(2):204–207. doi: 10.1007/BF01952471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Happ G. M., Eisner T. Hemorrhage in a Coccinellid Beetle and Its Repellent Effect on Ants. Science. 1961 Aug 4;134(3475):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3475.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. D., Wadhams L. J. Gas chromatography of volatile compounds in small samples of biological materials. J Chromatogr Sci. 1972 Aug;10(8):528–529. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/10.8.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




