Abstract
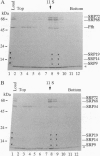
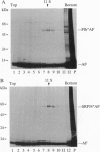
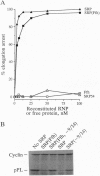
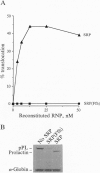
The 54-kDa subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle (SRP54) binds to the signal sequences of nascent secretory and transmembrane proteins and facilitates their cotranslational targeting to the membrane translocation apparatus in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). A 48-kDa Escherichia coli protein that shares extensive sequence similarity with SRP54 was identified in homology searches. Recent genetic experiments by Phillips and Silhavy [Phillips, G. J. & Silhavy, T. J. (1992) Nature (London) 359, 744-746] have shown that depletion of this protein, designated Ffh (fifty-four homolog), leads to a significant secretory defect in vivo. We demonstrate here that Ffh is structurally and functionally related to SRP54 by virtue of its ability to mimic closely its mammalian counterpart in several established biochemical assays, thereby suggesting that it plays a direct role in protein export. Ffh assembled efficiently with mammalian SRP components into a chimeric ribonucleoprotein ["SRP(Ffh)"] and bound at the site normally occupied by SRP54. Like SRP54, the Ffh moiety of the chimeric particle specifically recognized the signal sequence of preprolactin in a photocrosslinking assay. Moreover, Ffh could also act in concert with other SRP components to arrest elongation of preprolactin upon recognition of the signal sequence. In all of these assays, Ffh had approximately the same specific activity as SRP54. In contrast, SRP(Ffh) did not promote the translocation of preprolactin across the membrane of microsomal vesicles, suggesting that Ffh cannot mediate an interaction with a membrane component that is required for the translocation of nascent chains.
Full text
PDF
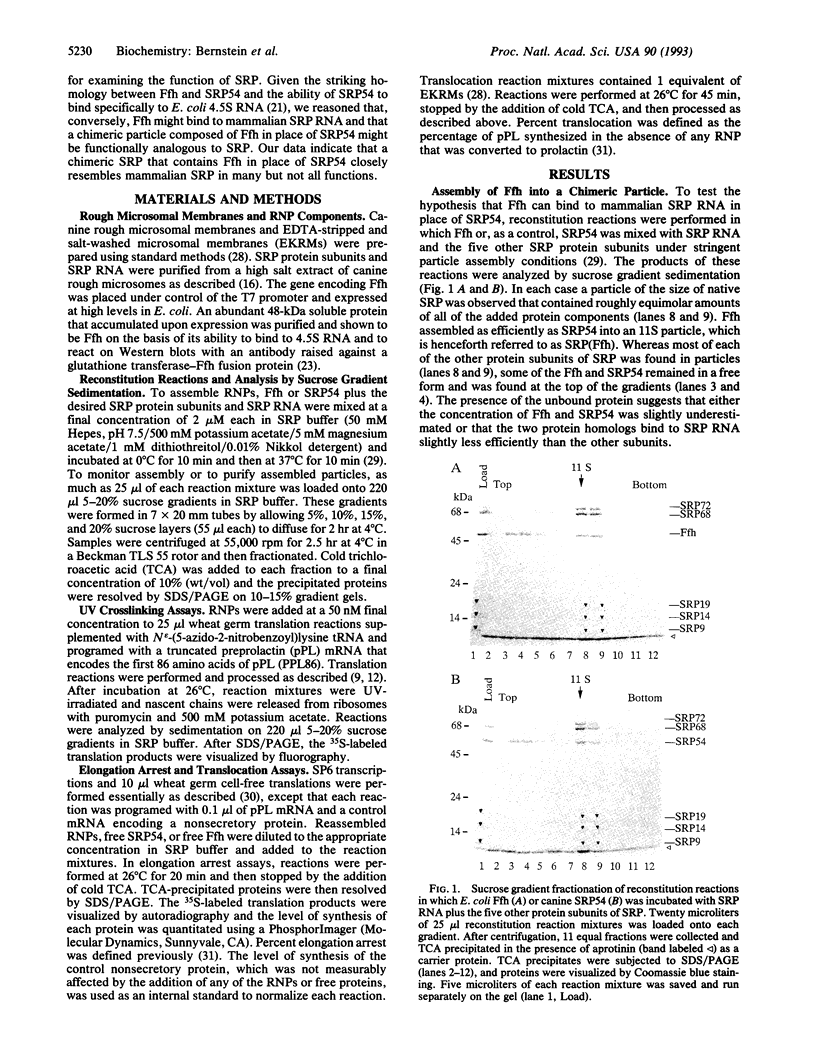
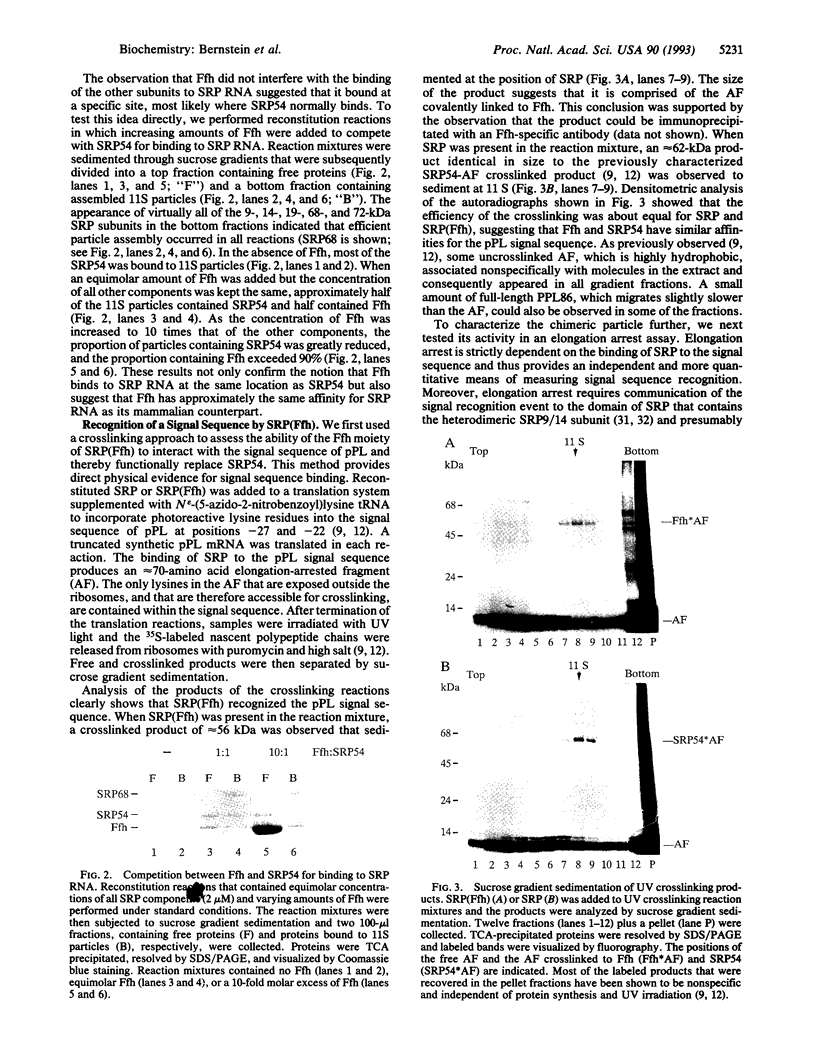
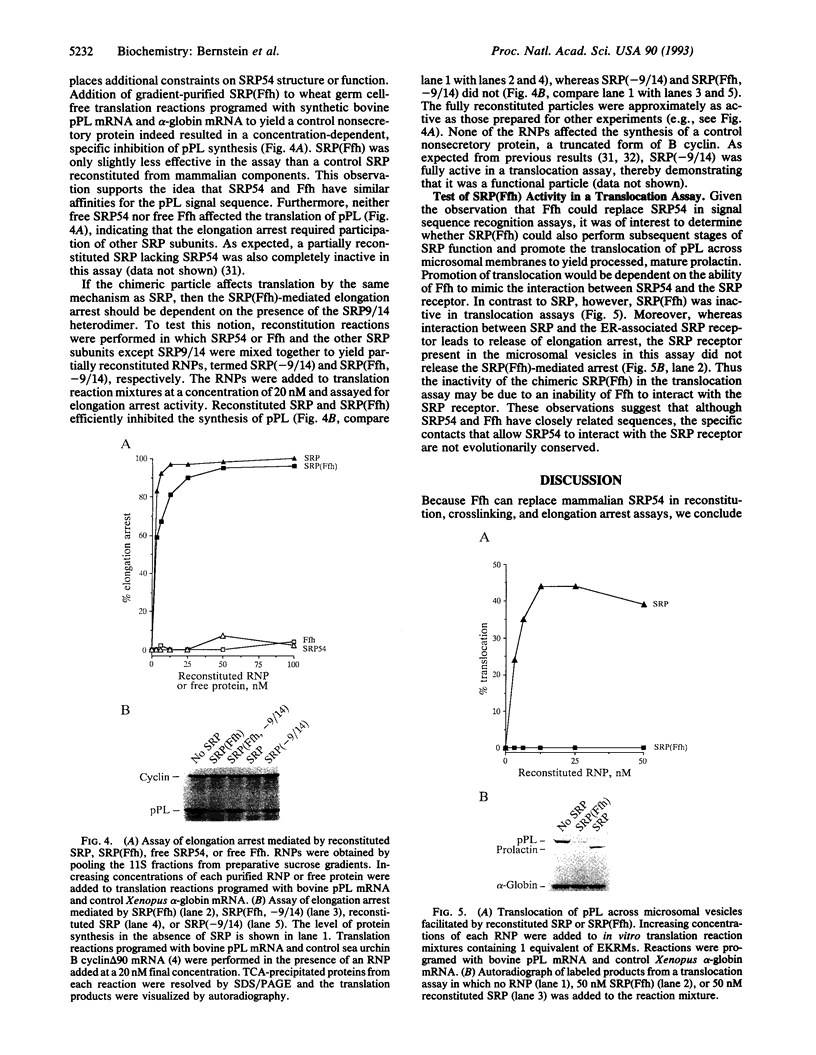

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassford P., Beckwith J., Ito K., Kumamoto C., Mizushima S., Oliver D., Randall L., Silhavy T., Tai P. C., Wickner B. The primary pathway of protein export in E. coli. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):367–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J. "Sequence-gazing?". Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1161–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.2006404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The sec and prl genes of Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):291–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00763169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström A. S., Hjalmarsson K. J., Wikström P. M., Björk G. R. The nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli operon containing genes for the tRNA(m1G)methyltransferase, the ribosomal proteins S16 and L19 and a 21-K polypeptide. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):899–905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hatfull G. F., Salmond G. P. A new cell division operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):134–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02428043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High S., Dobberstein B. The signal sequence interacts with the methionine-rich domain of the 54-kD protein of signal recognition particle. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):229–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Walter P., Johnson A. E. Photocrosslinking of the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin to the 54-kilodalton polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8604–8608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Wiedmann M., Girshovich A. S., Bochkareva E. S., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):634–636. doi: 10.1038/320634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luirink J., High S., Wood H., Giner A., Tollervey D., Dobberstein B. Signal-sequence recognition by an Escherichia coli ribonucleoprotein complex. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):741–743. doi: 10.1038/359741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H., High S., Römisch K., Ashford A. J., Dobberstein B. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kDa subunit of signal recognition particle is sufficient for the interaction with signal sequences. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1543–1551. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Dobberstein B. Identification and characterization of a membrane component essential for the translocation of nascent proteins across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):503–508. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The E. coli ffh gene is necessary for viability and efficient protein export. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):744–746. doi: 10.1038/359744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poritz M. A., Bernstein H. D., Strub K., Zopf D., Wilhelm H., Walter P. An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1111–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1701272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes V., Römisch K., Giner A., Dobberstein B., Tollervey D. E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90454-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römisch K., Webb J., Herz J., Prehn S., Frank R., Vingron M., Dobberstein B. Homology of 54K protein of signal-recognition particle, docking protein and two E. coli proteins with putative GTP-binding domains. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):478–482. doi: 10.1038/340478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Each of the activities of signal recognition particle (SRP) is contained within a distinct domain: analysis of biochemical mutants of SRP. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90529-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel V., Walter P. Removal of the Alu structural domain from signal recognition particle leaves its protein translocation activity intact. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):81–84. doi: 10.1038/320081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Hewitt E. W. The S. cerevisiae SEC65 gene encodes a component of yeast signal recognition particle with homology to human SRP19. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):534–537. doi: 10.1038/356534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Assembly of the Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP): dimerization of the two protein components is required for efficient binding to SRP RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):777–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Toschka H. Y., Specht T., Erdmann V. A. Common structural features between eukaryotic 7SL RNAs, eubacterial 4.5S RNA and scRNA and archaebacterial 7S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7740–7740. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Jackson R. C., Marcus M. M., Lingappa V. R., Blobel G. Tryptic dissection and reconstitution of translocation activity for nascent presecretory proteins across microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Johnson A. E., Walter P. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kd protein subunit of the signal recognition particle contains an RNA binding site and can be crosslinked to a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4511–4517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Walter P. GTPase domain of the 54-kD subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle is required for protein translocation but not for signal sequence binding. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1113–1121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]