Abstract
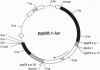
The goal of this work is to develop a method for the functional analysis of malaria genes using the method of DNA transfection. We have developed a transient transfection vector by constructing a chimeric gene in which the firefly luciferase gene was inserted in frame into the coding region of the pgs28 gene of Plasmodium gallinaceum. This plasmid DNA was introduced into P. gallinaceum gametes and fertilized zygotes by electroporation, and luciferase expression was assayed after 24 hr. This report of successful introduction and expression of a foreign gene in a malaria parasite demonstrates the feasibility of this approach to developing methods for the functional analysis of parasite genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter R., Gwadz R. W., Green I. Plasmodium gallinaceum: Transmission-blocking immunity in chickens. II. The effect of antigamete antibodies in vitro and in vivo and their elaboration during infection. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Apr;47(2):194–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R., Gwadz R. W., McAuliffe F. M. Plasmodium gallinaceum: transmission-blocking immunity in chickens. I. Comparative immunogenicity of gametocyte- and gamete-containing preparations. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Apr;47(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy P. E., Pimenta P., Kaslow D. C. Pgs28 belongs to a family of epidermal growth factor-like antigens that are targets of malaria transmission-blocking antibodies. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):505–510. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst C. A., Kumar N., Carter R., Kaushal D. C. A surface protein expressed during the transformation of zygotes of Plasmodium gallinaceum is a target of transmission-blocking antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):775–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.775-777.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal D. C., Carter R., Rener J., Grotendorst C. A., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Monoclonal antibodies against surface determinants on gametes of Plasmodium gallinaceum block transmission of malaria parasites to mosquitoes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2557–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijhout M. M., Carter R. Gamete development in malaria parasites: bicarbonate-dependent stimulation by pH in vitro. Parasitology. 1978 Feb;76(1):39–53. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000047375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R., Koontz L. C., Carter R. Infection of Aedes aegypti with zygotes of Plasmodium gallinaceum fertilized in vitro. J Parasitol. 1982 Aug;68(4):653–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieber K. P., Huber M., Kaslow D., Banks S. M., Torii M., Aikawa M., Miller L. H. The peritrophic membrane as a barrier: its penetration by Plasmodium gallinaceum and the effect of a monoclonal antibody to ookinetes. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Feb;72(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90132-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoff M. J., Moorman A. F., Lamers W. H. Electroporation in 'intracellular' buffer increases cell survival. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2902–2902. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]