Abstract
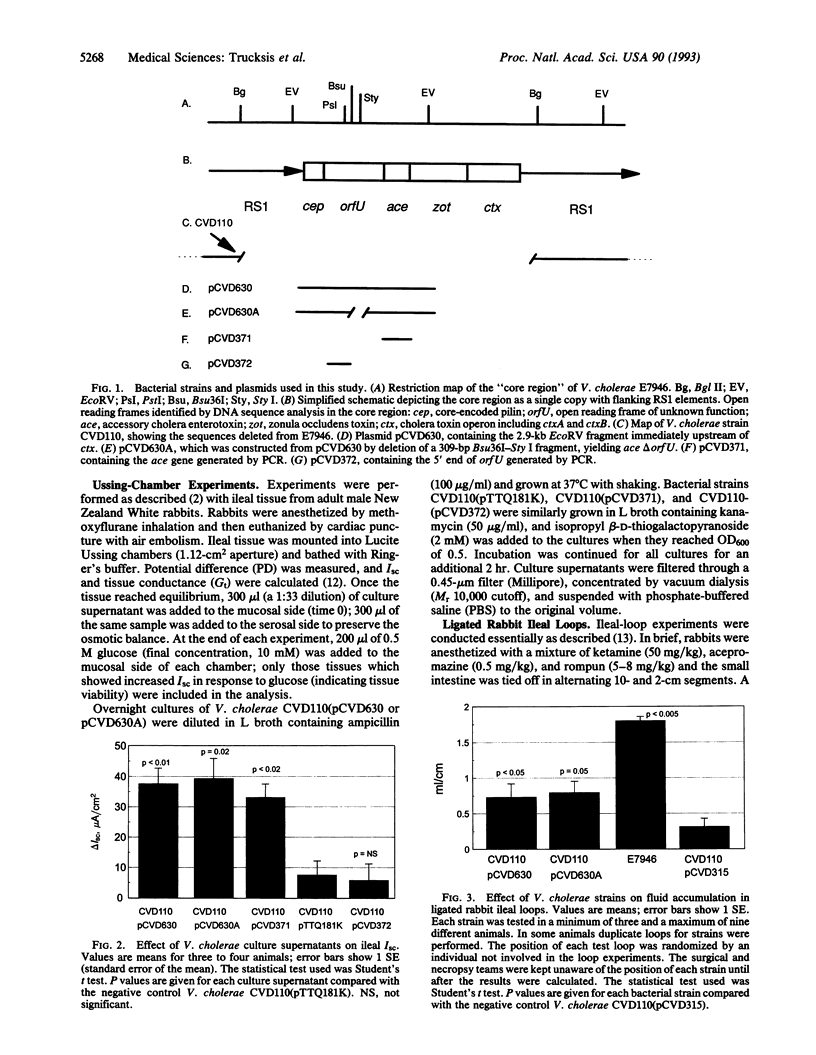
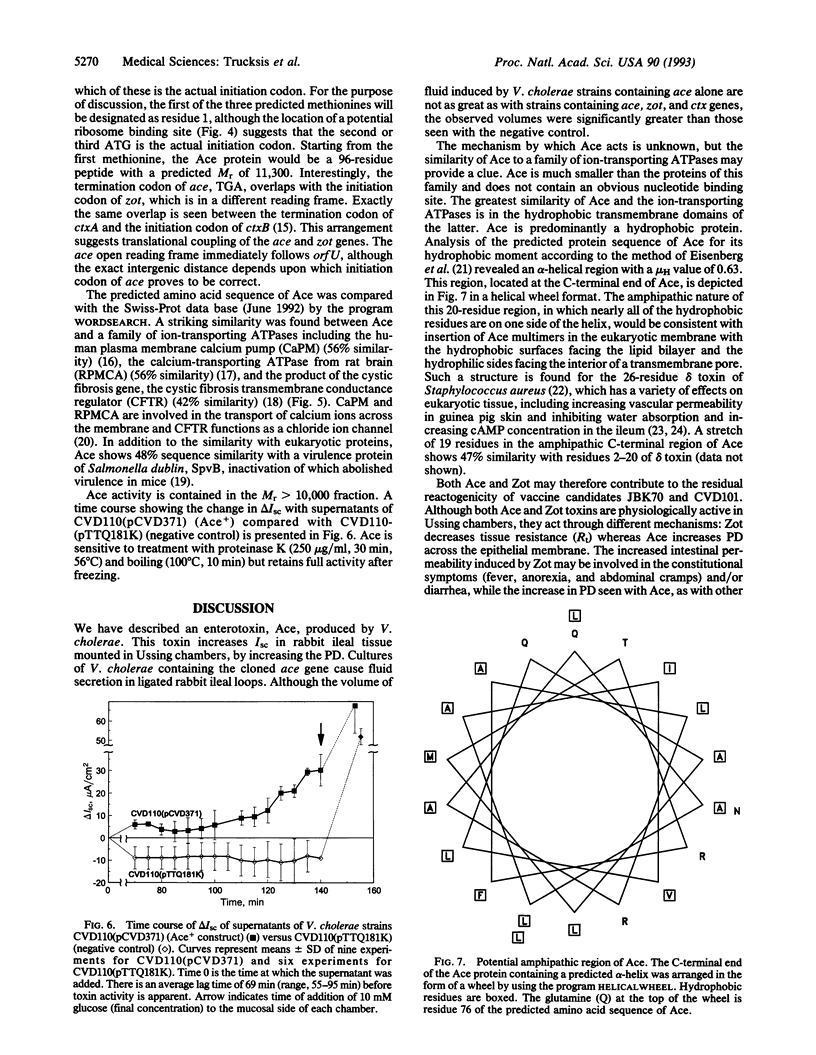
Vibrio cholerae causes the potentially lethal disease cholera through the elaboration of the intestinal secretogen cholera toxin. A second toxin of V. cholerae, Zot, decreases intestinal tissue resistance by modifying intercellular tight junctions. In this report, a third toxin of V. cholerae, Ace (accessory cholera enterotoxin), is described. Ace increases short-circuit current in Ussing chambers and causes fluid secretion in ligated rabbit ileal loops. The predicted protein sequence of Ace shows striking similarity to eukaryotic ion-transporting ATPases, including the product of the cystic fibrosis gene. The gene encoding Ace is located immediately upstream of the genes encoding Zot and cholera toxin. The ctx, zot, and ace genes, which are located on a dynamic sector of the chromosome, comprise a V. cholerae "virulence cassette."
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudry B., Fasano A., Ketley J., Kaper J. B. Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.428-434.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear C. E., Li C. H., Kartner N., Bridges R. J., Jensen T. J., Ramjeesingh M., Riordan J. R. Purification and functional reconstitution of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano A., Baudry B., Pumplin D. W., Wasserman S. S., Tall B. D., Ketley J. M., Kaper J. B. Vibrio cholerae produces a second enterotoxin, which affects intestinal tight junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5242–5246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Birkbeck T. H. Possible conformation of delta-lysin, a membrane-damaging peptide of Staphylococcus aureus. J Theor Biol. 1982 Feb 7;94(3):535–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Mekalanos J. J. Effect of a recA mutation on cholera toxin gene amplification and deletion events. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):723–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.723-731.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., O'Brien A. D., Ruff P. D., Drugan W. J., Jr Inhibition of water absorption in the intestine by Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):140–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.140-145.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary M. H., Richardson S. H. Fluid accumulation in infant mice caused by Vibrio hollisae and its extracellular enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):626–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.626-630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Roudier C., Fierer J., Harwood J., Guiney D. Molecular analysis of the virulence locus of the Salmonella dublin plasmid pSDL2. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):307–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Cisneros L., Saah A., Nalin D. R., Gill D. M., Craig J. P., Young C. R., Ristaino P. The pathogenicity of nonenterotoxigenic Vibrio cholerae serogroup O1 biotype El Tor isolated from sewage water in Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1982 Mar;145(3):296–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Ketley J., Losonsky G., Tacket C. O., Tall B., Cryz S. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of recombinant live oral cholera vaccines, CVD 103 and CVD 103-HgR. Lancet. 1988 Aug 27;2(8609):467–470. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman H., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the A2 and B subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13722–13726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus H., Ketley J. M., Kaper J. B., Holmes R. K. Effects of DNase production, plasmid size, and restriction barriers on transformation of Vibrio cholerae by electroporation and osmotic shock. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Kapral F. A. Increased cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate content in guinea pig ileum after exposure to Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):152–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.152-162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., DiRita V. J., Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. New attenuated derivatives of Vibrio cholerae. Res Microbiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;141(7-8):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90127-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Woods A., Chiang S. L., Mekalanos J. J. CTX genetic element encodes a site-specific recombination system and an intestinal colonization factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3750–3754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Adler B., Tobe T., Okada N., Nagai S., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of virulence Region-2 on the large virulence plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Makino S., Yamada M., Okada N., Yoshikawa M. Virulence-associated genetic regions comprising 31 kilobases of the 230-kilobase plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2480–2484. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2480-2484.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suharyono, Simanjuntak C., Witham N., Punjabi N., Heppner D. G., Losonsky G., Totosudirjo H., Rifai A. R., Clemens J., Lim Y. L. Safety and immunogenicity of single-dose live oral cholera vaccine CVD 103-HgR in 5-9-year-old Indonesian children. Lancet. 1992 Sep 19;340(8821):689–694. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Filoteo A. G., Stanford D. R., Wieben E. D., Penniston J. T., Strehler E. E., Fischer R., Heim R., Vogel G., Mathews S. Complete primary structure of a human plasma membrane Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14152–14159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



