Abstract
Alexandrium ostenfeldii is present in a wide variety of environments in coastal areas worldwide and is the only dinoflagellate known species that produces paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins and two types of cyclic imines, spirolides (SPXs) and gymnodimines (GYMs). The increasing frequency of A. ostenfeldii blooms in the Baltic Sea has been attributed to the warming water in this region. To learn more about the optimal environmental conditions favoring the proliferation of A. ostenfeldii and its complex toxicity, the effects of temperature and salinity on the kinetics of both the growth and the net toxin production of this species were examined using a factorial design and a response-surface analysis (RSA). The results showed that the growth of Baltic A. ostenfeldii occurs over a wide range of temperatures and salinities (12.5–25.5°C and 5–21, respectively), with optimal growth conditions achieved at a temperature of 25.5°C and a salinity of 11.2. Together with the finding that a salinity > 21 was the only growth-limiting factor detected for this strain, this study provides important insights into the autecology and population distribution of this species in the Baltic Sea. The presence of PSP toxins, including gonyautoxin (GTX)-3, GTX-2, and saxitoxin (STX), and GYMs (GYM-A and GYM-B/-C analogues) was detected under all temperature and salinity conditions tested and in the majority of the cases was concomitant with both the exponential growth and stationary phases of the dinoflagellate’s growth cycle. Toxin concentrations were maximal at temperatures and salinities of 20.9°C and 17 for the GYM-A analogue and > 19°C and 15 for PSP toxins, respectively. The ecological implications of the optimal conditions for growth and toxin production of A. ostenfeldii in the Baltic Sea are discussed.
Introduction
In recent decades, dinoflagellate species that are causative agents of harmful algal blooms (HABs) have been studied intensively, due to their global proliferation and their adverse effects on public health, recreation and tourism, fisheries, aquaculture and the ecosystems in which they are found. Although measures to counter HABs are still lacking, it is clear that the control of bloom events requires detailed knowledge of their basic features, including the adaptive strategies of the responsible dinoflagellate species and the environmental factors that regulate them [1]. Among toxin-producing dinoflagellates, members of the genus Alexandrium are the causative agents of the most widespread seafood poisoning syndrome caused by HABs, paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) syndrome. Toxigenic Alexandrium species are mainly distributed within coastal and temperate waters, although toxic populations are also found in sub-tropical, tropical, and perhaps even Arctic waters [2]. Currently, this genus includes 31 morphologically defined species, of which 12 produce PSP toxins [3, 4]. Among these well-known species, Alexandrium ostenfeldii (or synonym Alexandrium peruvianum) is the only member of the genus Alexandrium able to produce toxins of the cyclic imine type, including spirolide (SPX) and gymnodimine (GYM) [5–8]. Cyclic imine toxins are a family of structurally related marine neurotoxins of dinoflagellate origin that contaminate shellfish. Their basic structure consists of an imine moiety as a part of a bicyclic ring system [9]. These toxins display fast-acting toxicity when injected intraperitoneally in laboratory mice, although there have been no reported cases of poisoning in humans [10, 11]. The toxin profiles of A. ostenfeldii are complex. A. ostenfeldii was identified as the source of SPX toxins in Nova Scotia, Canada [5], even though it had been previously reported as a source of PSP-associated neurotoxin, which also causes a toxic syndrome [12]. In recent studies [6–8], GYM was shown to be produced by A. ostenfeldii strains of different geographic origin.
A recent study on phylogenetic, morphological, and toxin profiles of A. ostenfeldii and A. peruvianum strains from diverse geographic origins showed that A. peruvianum should be considered synonymous with A. ostenfeldii, and therefore discontinued as a distinct taxon [13]. Thus, the two species are considered synonymous herein. The first record of A. ostenfeldii was from the northern coast of Iceland [14], but the species has since been reported in most cold water environments, from the high latitudes of the Atlantic Ocean and northern Europe [12, 15–18] to the southern Pacific Ocean off the coast of austral Chile and Argentina [19–22]. However, A. ostenfeldii also occurs in warm waters, including off the coasts of Peru [23, 24], Malaysia [25], Spain [26], Italy [27], and Greece [28]. A. ostenfeldii also tolerates a wide range of salinities, based on its presence in the low-salinity environments of the Baltic Sea [29] and Chilean fiords and channels [22, 30] but also along the Mediterranean coast, where the salinities are higher [27, 31].
The toxin profiles of strains from those diverse environments also vary, with the production of SPX or PSP toxin by some strains depending upon the region of origin [6, 29]. For example, strains of A. ostenfeldii from the Baltic Sea mainly produce PSP toxins but not SPXs; those of the North Sea and Mediterranean Sea produce SPXs [6, 13]; and those of the Kattegat Sea (located between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea) produce both. The production of GYM toxins by Baltic Sea strains was recognized only recently [6, 8] and, thus far, only Narragansett and New River (USA) strains of A. ostenfeldii contain PSP toxins and the two cyclic imines (SPX and GYM) [7, 32, 33].
The relationship between environmental factors and toxin production by dinoflagellates is complex. Experimental studies have shown that the production of either SPXs or PSP toxins by A. ostenfeldii is influenced by salinity, temperature, and nutrients (see [29, 34, 35]). Whether this is also the case for the recently discovered GYM toxins in A. ostenfeldii strains is unclear. Thus, in the present work, we used a kinetic and factorial approach to study the effects of salinity and temperature on growth and toxin production by a strain of A. ostenfeldii isolated from the Baltic Sea.
Material and Methods
Culture conditions
Alexandrium ostenfeldii strain AOTV-B4A was isolated from the Baltic Sea (Åland, Finland) in summer 2004 and is maintained as part of our culture collection of toxic microalgae at the Spanish Institute of Oceanography in Vigo (CCVIEO: http://www.vgohab.es/). The cultures were acclimated gradually to different salinities (max. 3–4 salinity units at a time) and temperatures for at least during three transfers after reaching the stationary phase, according to the experimental conditions selected to develop the factorial design (Table 1). Pyrex glass bottles (1 L) containing 500 mL of L1 medium without silicate [36] were inoculated with exponentially growing cells (2,000–4,000 cells mL-1) to a final concentration of 900 cells mL-1. The medium was prepared using seawater collected from the Galician shelf at a depth of 5 m and adjusted to the salinities listed in Table 1 by the addition of sterile MQ water (Milli-Q; Millipore, USA). A photoperiod of 12 h of light (photon flux approximately 100 μmol m–2 s–1) and 12 h of darkness was used. Growth was monitored as cell yield (cells mL-1) throughout the growth cycle of A. ostenfeldii. Eight or nine samples (6–28 mL) were collected in total from each of the cultures during the experimental period and used in the toxin analyses (PSP toxins and cyclic imines: SPX and GYM) and cell counts. Sampling resulted in the removal of no more than 27% of the total volume of each culture. Samples used to determine cell counts were fixed with Lugol solution. Cell density was determined by light microscopy using a Sedgwick–Rafter chamber.
Table 1. Experimental domain and codification of the independent variables in the factorial rotatable design.
| Coded values | Natural values | |
|---|---|---|
| S | T (°C) | |
| -1.41 | 5.0 | 12.5 |
| -1 | 9.7 | 14.4 |
| 0 | 21.0 | 19.0 |
| +1 | 32.3 | 23.6 |
| +1.41 | 37.0 | 25.5 |
Codification: V c = (V n -V 0)/ΔV n.
Decodification: V n = V 0 + (ΔV n × V c).
Vn = natural value of the variable to be codified.
Vc = codified value of the variable.
V 0 = natural value in the center of the domain.
ΔV n = increment of V n for unit of V c.
Harmful effects due to a high pH and the pH changes resulting from the different cell concentrations in the treatments were controlled through a pH-measurement experiment performed throughout the entire growth cycle of the A. ostenfeldii strain using two replicates at S5/T19 and S9.7/T23.6. The pH kinetics were very similar in the two cultures, which yielded high (S9.7/T23.6 maximum of 22,266 cells mL-1) and low (S5/T19 maximum of 8,485 cells mL-1) rates of growth. The pH varied during growth progression by 1 and 1.5 units, respectively, and never exceeded 9.10. The results showed that CO2 was not a limiting factor for cell growth in the cultures.
Extraction and analysis of toxins
The content and relative proportions of PSP toxin and cyclic imines (SPXs and GYMs) in samples from cultures exposed to different experimental conditions were determined as follows: Two culture subsamples were filtered through GF/F glass-fiber filters (25 mm diameter; Whatman, Maidstone, England) and maintained in a freezer at –20°C. After two freeze/thaw cycles, the samples were sonicated (1 min, 50 Watts) and then centrifuged (14,000 rpm, 10 min, 5°C). One of the filters was extracted twice with 0.05 M acetic acid for PSP toxin analysis and the other twice with 100% methanol for SPX and GYM toxin analyses. The extracts (1.5 mL each) were kept at –20°C until used in the respective analysis, at which time they were left at ambient temperature and then filtered through 0.45-μm syringes filter.
PSP toxins were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with post-column oxidation and fluorescence detection (FD) according to the method of Rourke et al. [37], with slight modifications, and by using a Zorbax Bonus RP (4.6 × 150 mm, 3.5 μm) column. SPX and GYM toxins were identified by liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC–HRMS). The methanolic extracts were analyzed on a Dionex Ultimate 3000 LC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, California) coupled to an Exactive mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany) equipped with an Orbitrap mass analyzer and a heated electrospray source (H–ESI II). Nitrogen (purity > 99.999%) was used as the sheath gas, auxiliary gas, and collision gas. The instrument was calibrated daily in positive and negative ion modes. Mass acquisition was performed in positive ion mode without and with all ion fragmentation (AIF) higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD) of 45 eV. The mass range was m/z 100–1000 in both full-scan and AIF modes. SPXs and GYMs were separated and quantified according to the Standardized Operating Procedure validated by the European Union Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins [38]. In case another SPX or GYM different from the standards was identified in samples, it was quantified as 13-desmethyl SPX-C or as GYM-A equivalents, based on the respective calibrations available and assuming equal responses. The X-Bridge C18 (100 × 2.1 mm, 2.5 μm) column was maintained at 25°C; the injection volume was 20 μL and the flow rate 400 μL min–1 (for details, see [6]).
Mathematical modeling of A. ostenfeldii growth and toxin production
The sigmoid kinetics of A. ostenfeldii growing under different experimental conditions were fitted to the logistic equation [39, 40]:
| (1) |
This equation can be easily reformulated to obtain parameters that describe and characterize the different phases represented in the sigmoid growth curves [41]:
| (2) |
where G is the dinoflagellate growth concentration (cells mL-1); t, the culture time in days (d); G m, the maximum cell concentration (cells mL-1); μ m, the maximum specific growth rate (d−1); τ, the time required to achieve the semi-maximum cell concentration or Gm/2 (d); v m, the maximum growth rate (cells mL−1 d−1); λ, the lag phase (d); and t m, is the time required to achieve the beginning of G m or plateau phase (d).
Net toxin production followed first-order kinetics [39], described by:
| (3) |
where T x is the net production of the PSP (pg cell-1) or the GYM-A analogue (pg GYM-A eq. cell-1) toxins; t, the culture time (d); T 0, the initial toxin content (pg cell-1); and r, the specific net toxin production rate (d−1).
Numerical methods for growth and toxin production curve modeling
Dinoflagellate growth and net toxin production were modeled by minimizing the sum of the quadratic differences between the observed and predicted values, using the non-linear least-squares (quasi-Newton) method provided by the macro “Solver” of the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Confidence intervals from the parametric estimates (Student’s t test) and the consistency of the mathematical models (Fisher’s F test) and residual analysis (Durbin-Watson test) were evaluated by “SolverAid” macro (Levie's Excellaneous website: http://www.bowdoin.edu/~rdelevie/excellaneous).
Experimental design and statistical analysis
The effects of the independent variables salinity (S), in the range 5–37, and temperature (T), in the range 12.5–25.5°C, on the kinetic parameters that characterize the growth (G, in cells mL-1) and net toxin production (T x, in pg cell-1) of A. ostenfeldii were studied using a rotatable second-order design, with five replicates in the center of the experimental domain [42]. Table 1 summarizes the encoding of the independent variables and the experimental conditions employed.
Orthogonal least-squares calculation of the factorial design data were used to obtain [42] empirical equations describing the combined effects of the environmental factors (S and T) on the kinetic parameters obtained from Eqs (1–3). The general form of the polynomial equations is:
| (4) |
where R represents the response (dependent variable) to be modeled (growth and net toxin production parameters); b 0 is the constant coefficient; b i, the coefficient of the linear effect; b ij, the coefficient of the interaction effect; b ii, the coefficients of the squared effect; n, the number of variables; and X i and X j, the independent variables (S and T). The statistical significance of the coefficients was verified using Student t-test (α = 0.05). Goodness-of-fit was established as the adjusted determination coefficient (R 2 adj), and the model’s consistency by Fisher’s F test (α = 0.05) using the following mean squares ratios:
The model is acceptable when
F1 = Model / Total error
F2 = (Model + Lack of fit) / Model
F3 = Total error / Experimental error
F4 = Lack of fit / Experimental error
where are the theoretical values for α = 0.05, with the corresponding degrees of freedom for numerator (num) and denominator (den). The model is acceptable when F1 and F2 are validated. F3 and F4 were additionally calculated to improve the degree of robustness and the consistency of the empirical equations obtained. All fitting procedures, coefficient estimates, and statistical calculations were performed on a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Results
Toxin characterization
The LC analyses showed detectable amounts of PSP toxins in all of the culture extracts of A. ostenfeldii strain AOTV-B4A. The toxin profile was dominated by gonyautoxin (GTX)-3, followed by saxitoxin (STX), and GTX-2 in proportions of 62.7%, 35.5%, and 1.8%, respectively. The proportions were similar in all cultures. In LC–HRMS analyses of the culture methanolic extracts, GYM-A and GYM-B/-C analogues but not SPXs were detected. Since only the standard for GYM-A is available, an equimolar response for the GYM-A analogue detected was assumed and the analogue was quantified as GYM-A equivalents (pg GYM-A eq. cell-1). In addition, although all culture samples were also screened for the presence of 12-methyl GYM, it was not detected under any conditions.
Growth and toxin production kinetics
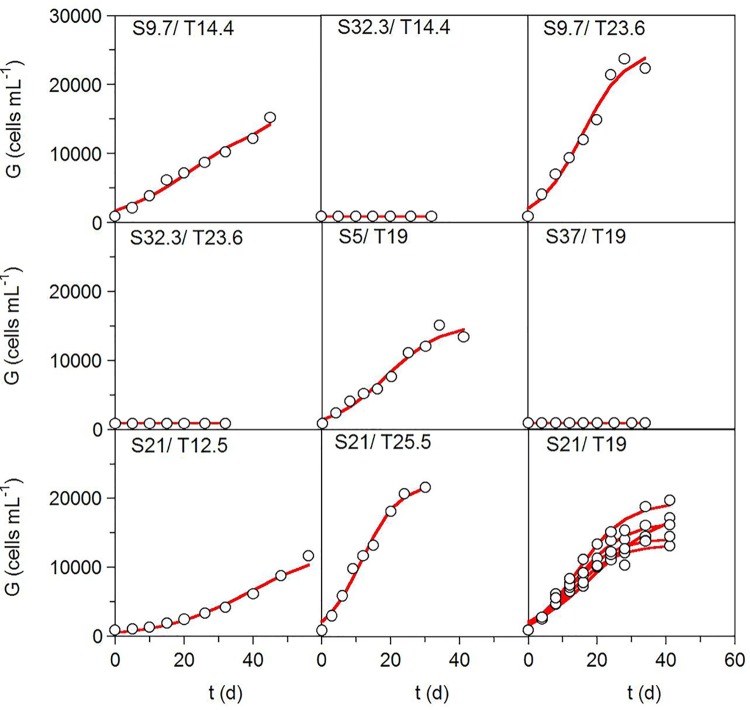
Both the analysis of the growth of A. ostenfeldii under the conditions defined by the factorial design (Table 1) and the kinetic profiles fitted to the experimental data according to Eq (1) are shown in Fig 1. Table 2 lists the values of the kinetic parameters and provides the data used in the statistical analyses of the numerical fittings. The predictive ability of Eq (1) in modeling the experimental data was high, as shown by determination coefficients (R2) ≥ 0.965. All of the parameters for A. ostenfeldii growth, except the numerical values of the lag phases (λ), were statistically significant (α = 0.05). Autocorrelation was not observed in the residuals distribution (data not shown). In three of the experimental conditions (salinities ≥ 32), there was no significant growth of A. ostenfeldii, as determined by the kinetic analysis; the cell yields were not higher than the inoculum (900 cells mL-1) (Fig 1). In those cases, the values of the parameters used as dependent variables (responses) in the subsequent response-surface analysis (RSA) and calculation were set at zero.
Fig 1. Growth kinetic profiles.
Growth kinetics of Alexandrium ostenfeldii strain AOTV-B4A cultivated under the environmental conditions defined by the factorial design summarized in Table 1. Experimental data (symbols) were fitted to Eq (1) (lines).
Table 2. Summary of the parameter values (dependent variables) obtained from fitting the data on A. ostenfeldii growth to Eqs (1) and (2).
X1: salinity and X2: temperature (°C). The natural values of the experimental conditions are shown in brackets.
| Independent variables | Growth parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X 1: S | X 2: T | G m (cells mL-1) | v m (cells mL-1 d-1) | λ (d) | μ m (d-1) | τ (d) | t m (d) | R2 | p-value |
| -1 (9.7) | -1 (14.4) | 17,912 ± 6,775 | 351.2 ± 88.6 | 1.0 (NS) | 0.082 ± 0.043 | 25.5 ± 12.3 | 50.0 ± 24.6 | 0.976 | <0.001 |
| 1 (32.3) | -1 (14.4) | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD |
| -1 (9.7) | 1 (23.6) | 25,239 ± 6,775 | 983.1 ± 314.4 | 2.8 (NS) | 0.156 ± 0.071 | 15.7 ± 4.2 | 28.5 ± 9.2 | 0.973 | <0.001 |
| 1 (32.3) | 1 (23.6) | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD |
| -1.41 (5) | 0 (19) | 15,372 ± 3,132 | 479.3 ± 141.4 | 2.3 (NS) | 0.125 ± 0.054 | 18.3 ± 4.9 | 34.4 ± 11.0 | 0.97 | <0.001 |
| 1.41 (37) | 0 (19) | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD | NGD |
| 0 (21) | -1.41 (12.5) | 13,110 ± 2,389 | 261.1 ± 52.0 | 14.1 ± 5.0 | 0.080 ± 0.024 | 39.2 ± 6.7 | 64.3 ± 13.4 | 0.982 | <0.001 |
| 0 (21) | 1.41 (25.5) | 22,237 ± 2,772 | 1,053.5 ± 257.8 | 1.1 (NS) | 0.190 ± 0.060 | 11.7 ± 2.2 | 22.3 ± 5.0 | 0.987 | <0.001 |
| 0 (21) | 0 (19) | 18,361 ± 3,542 | 476.8 ± 94.9 | 0.4 (NS) | 0.104 ± 0.034 | 19.6 ± 5.0 | 38.9 ± 10.7 | 0.983 | <0.001 |
| 0 (21) | 0 (19) | 16,523 ± 1,506 | 608.5 ± 125.3 | 0.5 (NS) | 0.147 ± 0.038 | 14.0 ± 2.1 | 27.6 ± 5.0 | 0.988 | <0.001 |
| 0 (21) | 0 (19) | 13,222 ± 1,838 | 512.7 ± 184.2 | -0.4 (NS) | 0.155 ± 0.068 | 12.5 ± 3.3 | 25.4 ± 7.8 | 0.965 | <0.001 |
| 0 (21) | 0 (19) | 14,234 ± 1,435 | 538.4 ± 141.5 | -1.2 (NS) | 0.151 ± 0.049 | 12.0 ± 2.4 | 25.2 ± 5.8 | 0.981 | <0.001 |
| 0 (21) | 0 (19) | 19,459 ± 2,062 | 710.2 ± 161.8 | -1.1 (NS) | 0.146 ± 0.042 | 14.8 ± 2.5 | 28.4 ± 5.7 | 0.986 | <0.001 |
Codification: Vc = (Vn–V0)/ ΔVn; Decodification: Vn = V0+(ΔVn×Vc)
Vn = natural value in the center of the variable to be codified; ΔVn = increment of Vn per unit of Vc. Vc = codified value of the variable; V0 = natural value in the center of the domain
NS: not significant; NGD: no growth detected. Error values associated with the parameter determinations are the confidence intervals (CI) for α = 0.05.
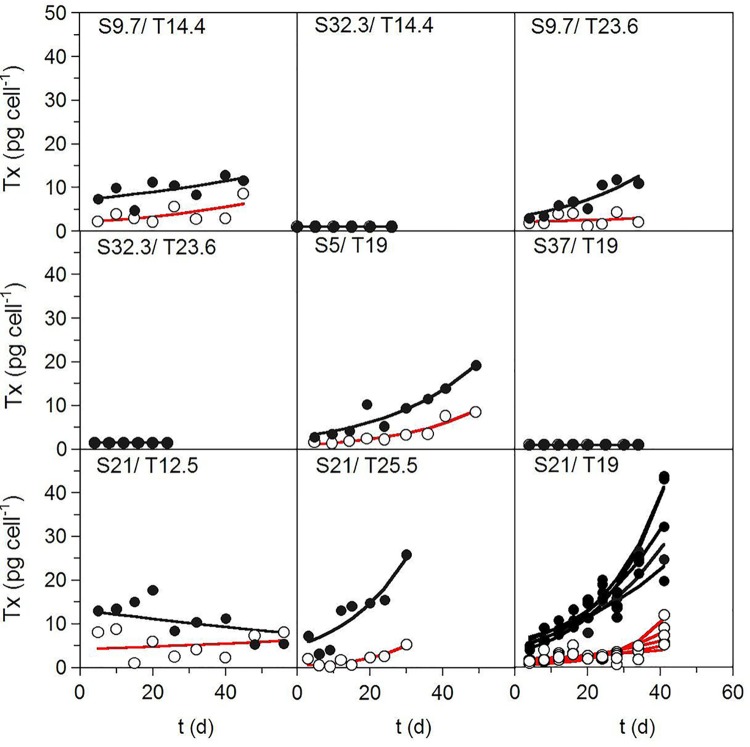
Fig 2 shows the kinetics of the net production of the PSP toxins (sum of GTX-3, GTX-2, and STX) and the GYM-A analogue under the conditions defined by the factorial design (Table 1) and fitted to the first-order kinetic model (3). In general, the experimental kinetics of the net production of those biotoxins over time were acceptably modeled by Eq (3). The coefficients of determination of the fittings were in the range of 0.246–0.957 for PSP toxins and 0.101–0.981 for GYM-A analogue. The kinetics of both groups of toxins were consistent with a mixed-growth-associated model, since content toxin increased during the exponential phase of growth and continued to increase during stationary phase (Figs 1 and 2). No change in toxin content was detected under the experimental conditions in which there was no significant growth (salinities ≥ 32) (Fig 2).
Fig 2. Toxin-production kinetic profiles.
Kinetics of net toxin production by strain AOTV-B4A cultivated under the environmental conditions defined by the factorial design summarized in Table 1. ○: PSP toxins (pg cell-1), ●: GYM-A analogue (pg GYM-A eq cell-1). Experimental data (symbols) were fitted to Eq (3) (lines).
Combined effect of temperature and salinity on growth parameters by RSA
The simultaneous effects of the environmental factors S and T on the kinetic parameters of A. ostenfeldii obtained from the logistic model (Table 2) were studied using a RSA. For the cases in which no growth detected (NGD in Table 2), the experimental response was considered to be zero. The design and numerical responses of the 2-factor rotatable design are summarized in Table 2. Parameter data describing the growth of A. ostenfeldii were converted into second-order polynomial equations as a function of S and T. The polynomial model describing the correlation between the responses and the variables therefore followed the general form described by Eq (4) (Table 3).
Table 3. Second-order equations describing the effects of S and T on the growth parameters of A. ostenfeldii AOTV-B4A (used in coded values according to the criteria defined in Table 1).
The coefficient of adjusted determination (R 2 adj) and the F-values (F 1, F 2, F 3 and F 4) are also shown. S: significant; NS: non-significant.
| Parameters | G m (cells mL-1) | v m (cells mL-1 d-1) | μ m (d-1) | τ (d) | t m (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b 0 (intercept) | 16,365 | 569.6 | 0.141 | 14.60 | 29.14 |
| b 1 (S) | -8,037 | -252.0 | -0.052 | -8.40 | -15.92 |
| b 2 (T) | 2,623 | 219.3 | 0.029 | -6.09 | -10.12 |
| b 12 (SxT) | NS | -158.0 | NS | NS | NS |
| b 11 (S 2 ) | -4,881 | -194.7 | -0.049 | -4.50 | -8.68 |
| b 22 (T 2 ) | NS | NS | NS | 3.69 | NS |
| R 2 adj | 0.829 | 0.844 | 0.773 | 0.689 | 0.703 |
| F1 | 20.33 | 17.17 | 14.63 | 7.65 | 10.46 |
| = 3.86] ⇒ S | = 3.84] ⇒ S | = 3.86] ⇒ S | = 3.84] ⇒ S | = 3.86] ⇒ S | |
| F2 | 0.416 | 0.545 | 0.438 | 0.614 | 0.469 |
| = 8.85] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | = 8.85] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | = 8.85] ⇒ S | |
| F3 | 1.727 | 2.15 | 20.52 | 3.98 | 3.46 |
| = 5.99] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | = 5.99] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | = 5.99] ⇒ S | |
| F4 | 2.308 | 3.29 | 20.52 | 6.96 | 5.44 |
| = 6.26] ⇒ S | = 6.39] ⇒ S | = 6.26] ⇒ S | = 6.39]⇒ NS | = 6.26] ⇒ S |
A high proportion of variability (83% for Gm and 84% for vm) was successfully explained by the second-order equations. The agreement between the experimental and predicted data was always > 69% (Table 3). The robustness of the equations was perfect in all cases except the F4 (Fisher F test) of τ, which was not significant. Thus, the empirical equations shown in Table 3 were very good predictors of the growth of A. ostenfeldii in the S and T ranges evaluated in this study.
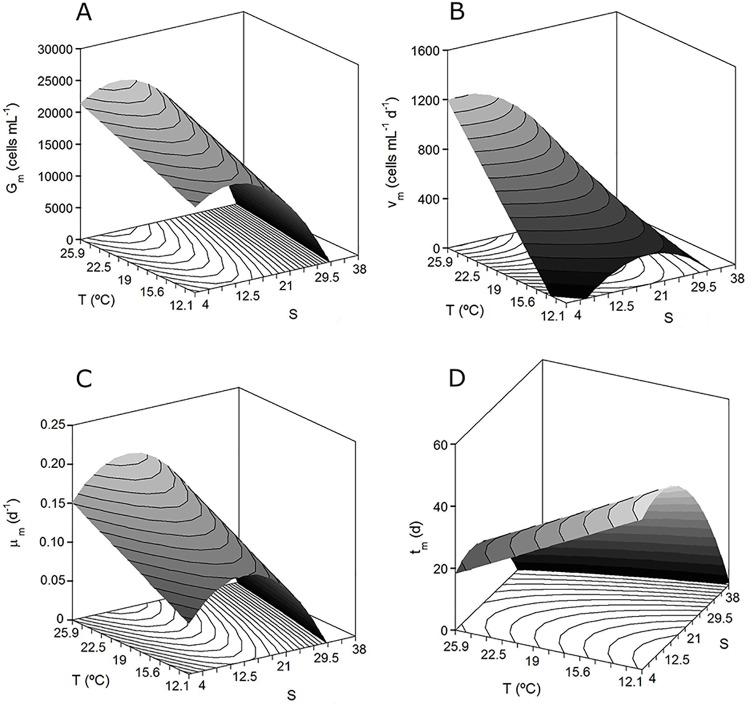
Fig 3 shows the theoretical surfaces for each parameter as the response of a dependent variable. The results of the multivariate analysis showed that, for all growth parameters, the effect of T was only linear whereas S always had significant quadratic negative terms (P < 0.05). The coefficient of interaction between the variables (S × T) was only significant for the vm response. The statistical significance of the coefficient of S 2 and its negative value were graphically translated as a convex dome with a clear maximum point within the experimental domain of the salinity (Fig 3). The salinity concentrations that maximize A. ostenfeldii growth were determined by mathematical optimization using the numerical or manual derivation of the equations in Table 3 [43]. The natural values of those optima and the maximum value of the responses in each case (Ymax) are summarized in Table 4. Thus, the conditions yielding the maximum growth of the dinoflagellate (average of the Gm, vm and μm results) were a salinity of 11.2 and a temperature of at least 25.5°C.
Fig 3. Combined effects of temperature and salinity on growth by RSA.
Theoretical response surfaces describing the combined effects of temperature and salinity on the kinetic parameters described by Eqs (1) and (2): (A) maximum growth (G m), (B) maximum growth rate (v m), (C) specific maximum growth rate (μ m), and (D) time to achieve the plateau phase (t m).
Table 4. Optimal values of salinity and temperature (S opt and T opt) needed to obtain the maximum values (Y max) using the equations shown in Table 3 and for the different dependent variables studied (growth parameters).
| G m (cells mL-1) | v m (cells mL-1 d-1) | μ m (d-1) | τ (d) | t m (d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S opt | 11.68 | 6.79 | 15.04 | 10.44 | 10.63 |
| T opt | >25.5 | >25.5 | >25.5 | <12.5 | <12.5 |
| Y max | 23,607 | 1,206 | 0.198 | 17.69 | 51.62 |
Combined effect of temperature and salinity on toxin production by RSA
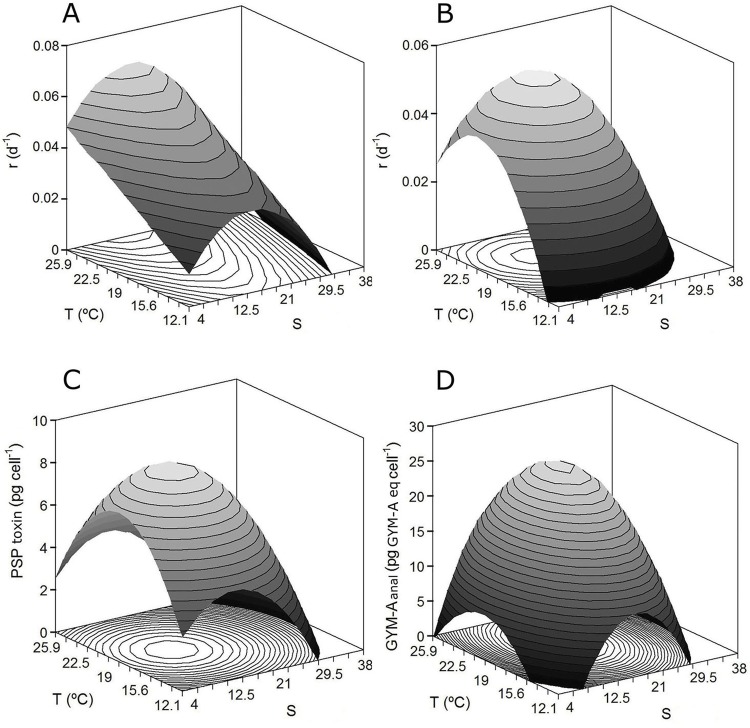
Based on Eq (3), the specific net production rates (r) of the PSP toxins and the GYM-A analogue were selected as the response to be studied with respect to T and S. The effects of temperature and salinity on the toxin concentrations obtained at the end of their production by A. ostenfeldii cells were also evaluated. Fig 4 depicts the surfaces predicted by the second-order equations shown in Table 5. In all cases, the coefficient of the salinity effect (linear and quadratic) was negative, with a parabolic pattern (dome surface), and was in complete concordance with the results obtained for dinoflagellate cell growth. The influence of T was also quadratic except for the r-response of PSP toxin, in which only a linear term was significant as previously described for the growth of A. ostenfeldii (Fig 3).
Fig 4. Combined effects of temperature and salinity on toxin production by RSA.
Theoretical response surfaces describing the combined effects of temperature and salinity on the specific (A) PSP toxin and (B) GYM-A analogue net production rates (r), and on the net production of (C) PSP toxins (pg cell-1) and (D) GYM-A analogue (pg GYM-A eq. cell-1) at the end of the A. ostenfeldii culture period.
Table 5. Second-order equations describing the effects of T and S on net toxin productions (PSP toxin and GYM-A analogue) by A. ostenfeldii.
The coefficient of adjusted determination (R 2 adj) and the F-values (F 1, F 2, F 3, and F 4) are also shown. S: significant; NS: non-significant.
| PSP toxin | GYM-A analogue | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | r (d-1) | PSP toxin (pg cell-1) | r (d-1) | GYM-A analogue (pg GYM-A eq. cell-1) |
| b 0 (intercept) | 0.047 | 7.82 | 0.047 | 24.57 |
| b 1 (S) | -0.014 | -2.85 | -0.015 | -4.47 |
| b 2 (T) | 0.012 | NS | 0.013 | 3.98 |
| b 12 (SxT) | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| b 11 (S 2 ) | -0.017 | -2.24 | -0.015 | -10.91 |
| b 22 (T 2 ) | NS | -2.00 | -0.013 | -5.95 |
| (R 2 adj ) | 0.504 | 0.664 | 0.715 | 0.819 |
| F1 | 4.05 | 8.91 | 8.54 | 14.53 |
| = 3.86] ⇒ S | = 3.86] ⇒ S | = 3.84] ⇒ S | = 3.84] ⇒ S | |
| F2 | 0.713 | 0.465 | 0.571 | 0.56 |
| = 8.85] ⇒ S | = 8.85] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | |
| F3 | 5.370 | 1.537 | 1.265 | 5.94 |
| = 5.99] ⇒ S | = 5.99] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | = 6.04] ⇒ S | |
| F4 | 8.867 | 1.967 | 1.530 | 10.88 |
| = 6.26] ⇒ NS | = 6.26] ⇒ S | = 6.39] ⇒ S | = 6.39] ⇒ NS | |
The optimal S and T values needed to maximize toxin concentrations and the theoretical maximum values of the variables (Ymax) calculated from these optima are summarized in Table 6. These levels were different depending on the toxin; thus, the Sopt values for PSP toxin and GYM-A analogue were 15 and 17, respectively (calculated in each case as the average of the two responses selected). The Topt for the GYM-A analogue was 20.9°C whereas that for PSP toxin was 19°C.
Table 6. Optimal values of salinity and temperature (S opt and T opt) needed to obtain the maximum values (Y max) using the equations shown in Table 5 and for the different dependent variables studied (toxin productions).
| PSP toxin | GYM-A analogue | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r (d-1) | PSP toxin (pg cell-1) | r (d-1) | GYM-A analogue (pg GYM-A eq. cell-1) | |
| S opt | 16.1 | 13.8 | 15.3 | 18.7 |
| T opt | >25 | 19.0 | 21.2 | 20.5 |
| Y max | 0.067 | 8.73 | 0.054 | 25.7 |
Discussion
Growth and toxin production kinetics and the combined effects of temperature and salinity
The results of the present work clearly demonstrated the effects of temperature and salinity on the growth of one strain of A. ostenfeldii from the Baltic Sea. The values of the six kinetic parameters used (Gm, vm, λ, μm, τ, and tm) during each experimental condition were accurately predicted by the logistic function of Eq (1). The resulting sigmoid patterns and the validity of the model (1) that described them have been frequently reported for microorganisms cultivated under batch conditions [44–49] and for higher organisms subjected to extensive or intensive feeding [50–52]. The growth of marine organisms, including bacteria, rotifers, molluscs, dinoflagellates, and microalgae, is also well-fitted by a logistic function, reflecting the involvement of autocatalytic pathways [53–57]. Our results are in agreement with the growth rates reported for strains of A. ostenfeldii isolated from the Baltic Sea, Skagerrak, North Sea, and Nova Scotia [29, 34, 58] and for the yessotoxin-producing dinoflagellate P. reticulatum [39]. However, the values of the parameters Gm or K, vm and μm were generally lower for A. ostenfeldii than for P. reticulatum. Also, the growth of A. ostenfeldii was slower than that of Alexandrium species (A. tamarense, A. minutum, and A. tamutum) in Scottish waters [59] and Alexandrium isolates from other latitudes [60–62].
RSA based on a factorial design is used to optimize the effect of environmental factors for a small number of experiments (13, with 5 replicates in the center of the experimental domain for a second-order rotatable design) [42]. The empirical equation obtained from this analysis provides the information needed to predict the values of the dependent variables in the experimental range studied. Although this type of approach is not commonly used to study the growth of marine organisms in response to different effectors, previous results have demonstrated its validity and its potential as a process predictor. For example, the influence of three factors (temperature, salinity, and irradiance) on the growth kinetics of P. reticulatum was studied by means of a first-order factorial design [39]. Similar statistical tools were used to assess the positive and negative effects of salinity, inoculum size, and temperature on cyst and planozygote formation by A. minutum [63]. Analysis of the enhancement of rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis) growth in the presence of a combination of lactic acid bacteria was optimized by RSA [55]. The approach used in this work can be applied to define the environmental windows allowing species growth, especially those species with an extended geographic distribution, as is the case for A. ostenfeldii. Although generalizations based on culture studies should consider within-species variation [64, 65], it adds to the limited data available on the autecology of this species and allows conclusions to be drawn regarding the biogeography of the different populations of this dinoflagellate, based on comparisons between culture data and data on the environmental conditions of its habitats.
In our study, the temperature- and salinity-dependent growth window for Baltic A. ostenfeldii AOTV-B4A reflected the broad tolerance of this strain to a wide range of temperatures and to low salinities. In fact, the only condition completely limiting growth was a salinity ≥ 32. Although we could not determine the maximum threshold value for salinity, in a previous study it was 25 [6]. In the present study, cell growth occurred at a salinity range of 5–21 and at temperatures of 12.5–25.5°C, with optima at a salinity of 11.2 and a minimum temperature of 25.5°C. These results, and particularly the optimal salinity, are consistent with the values reported by Kremp et al. [16] for A. ostenfeldii strains AOTV-A1 and AOTV-A4, isolated, as our strain, from the Åland islands (Finnish Baltic Sea). Similar temperature ranges for growth were determined by Østergaard and Moestrup [17] for cultures of a Danish strain isolated from Limfjord (Kattegat Sea), whereas salinities allowing growth were between 10 and 40, with optimum growth achieved at 15–20. We have no information on the salinities of the waters where the Danish strain was isolated; however, its adaptation to a higher salinity suggests that it is from an area of the Kattegat Sea located closer to the North Sea than to the most northern part of the Baltic Sea [29], which is where our strain was obtained. The positive effects of temperature on Gm, vm, and μm (increasing response at increasing temperature) are compatible with the Arrhenius theory but with a linear rather than the typical exponential relationship. This may be due to the narrow experimental range selected in this study and/or to the type of factorial design, in which only linear and quadratic coefficients, and not exponential expressions, could be evaluated. The robustness of our results was confirmed by the negative value of the temperature linear coefficient in the equations describing τ ant tm (Table 3), which were inversely proportional to those obtained for the other parameters. This was expected because when growth is higher and faster (high Gm and high vm and μm), the values of τ and tm are smaller.
Our results also demonstrated the influence of temperature and salinity on the kinetics of net toxin production of A. ostenfeldii. The bioproduction of lipophilic (GYM-A analogue) and PSP toxins in most cases occurred concomitantly during the exponential growth and stationary phases, following characteristics of mixed metabolites as described by the Luedeking-Piret definition (Figs 1 and 2). A similar behavior was reported for yessotoxin production by P. reticulatum, nodularin synthesis by Nodularia spumigena [54], and net PSP production by A. ostenfeldii from the Baltic Sea [29] and by several other Alexandrium species from diverse geographic origins [61, 66, 67]. Nevertheless, in our study there were also culture conditions in which toxin production differed from that described above. Specifically, when the cultures were exposed to low temperature, net toxin production was not consistent with growth (see plots for 12.5°C in Figs 1 and 2), suggesting the involvement of other factors. In fact, in our experiment, in the absence of a clear stationary phases (temperatures of 12.5°C and 14.4°C), the error associated with the Gm-parameter was higher than in cultures in which a well-defined asymptotic phase occurred. The changes in cell size may explain this difference. Both Granéli and Flynn [68] and Anderson et al. [69] noted that, during the growth cycle, the observed changes in the culture and in cell toxin content may simply reflect changes in cell size and the variability of growth or life-cycle stages as a function of changes in nutrient status, temperature, or salinity. This is consistent with the variations in the size of A. ostenfeldii cells in strains exposed to different experimental conditions [6, 16, 17, 59], which demonstrated that cell size variations are common in the life cycle of the species and are related to the culture growth phase and to the sexual vs. asexual origin of the cells. A larger mean cell volume during stationary phase as well as abundant large and small temporary cysts, most likely of asexual and sexual origin [70], were reported from Danish strain cultures by Østergaard and Moestrup [17]. Microscopic analysis of cells from our 12.5°C culture showed an abundance of large, dark, elongated cells suggestive of planozygotes. This culture condition also resulted in the largest numbers of double-walled (resting) cysts (unpublished data). Previous studies of the same strain showed that a temperature of 15°C results in significantly (P < 0.05; n = 90) larger cells than obtained at higher temperatures [6]. These observations suggest that sexual reproduction is induced in the cultures at low temperatures, which might also explain the fluctuations in toxin production observed at 12.5°C in this study as well as the higher error associated with the Gm-parameter at low temperatures.
Little is known about the diversity, distribution, and production of GYMs by A. ostenfeldii. The only other producer of GYMs (GYM-A, GYM-B and GYM-C) identified to date is the phylogenetically distant dinoflagellate Karenia selliformis [11, 71–74], such that most studies of GYM toxin production have focused on this species. Thus far, the only study to quantify GYM production was conducted by Tatters et al. [75], using an isolate of A. peruvianum (syn. of A. ostenfeldii) from the New River Estuary, North Carolina (USA). Under nutrient-replete culture conditions, 12-methyl GYM concentrations peaked (up to 73.3 pg cell-1) during stationary phase (day 36), as was the case in most of our cultures. Harju et al. [8] provided a qualitative description of two separate GYM analogues produced by isolates from the Baltic Sea and Saanich (Canada) and of GYM-like compounds produced by some cultures established from the Baltic Sea. It is demonstrated that, as with SPX and PSP toxin, GYM production by A. ostenfeldii is geographically highly variable, including within a particular region [6, 13, 18, 29, 59, 76]. Thus far, lipophilic toxin production by A. ostenfeldii has been mainly linked to SPXs [34, 77, 78]. However, further studies quantifying GYM production in this species will provide greater insight into the dynamics of the biosynthesis of this toxin and its variability.
Ecological implications
The accurate prediction and assessment of toxic episodes by dinoflagellates are hindered by the poor understanding of the factors affecting toxin production by dinoflagellates. Chemical, physical, and biotic factors are known to influence toxin production, including nutrients, temperature, salinity, irradiance, and grazing [68, 79]. For example, the complex ecological mechanisms underlying toxin production responses are evidenced by grazing, which can act to restrain dinoflagellate populations or enhance toxin content [80]. Our data are robust enough to allow the use of RSA as a predictor of a changing environment, although some limitations must be considered. First, the system giving rise to toxin production cannot be considered in its entirety. Second, because the results were derived from a single strain, any broader ecological interpretation must be made with caution [64]. According to our observations on the growth of the Baltic A. ostenfeldii strain AOTV-B4A, salinities in the range of 5–21 and temperature of 12.5–25.5°C are compatible with growth, although the respective values resulting in maximum growth were 11.2 and 25.5°C. Consequently, the strain appears to be a eurytherm adapted to brackish-water conditions. Although this strain may not be representative of all Baltic Sea populations of the species or of the species in general, for which we would need to work with many isolates, our data and those reported in the literature raise several interesting issues. For example, the intraspecific and intrapopulation variability of A. ostenfeldii with respect to temperature and salinity is not well known yet, although variations in the responses of different strains from different geographic locations characterized by a very wide range of environmental conditions have been extensively described [6, 17, 29, 34, 35, 58, 81]. Reaction norms of multiple isolates for temperature and salinity have not been published so far, but previous studies on Baltic isolates suggest that the environmental window described herein for A. ostenfeldii AOTV-B4A represents the range of Baltic Sea population(s) [16, 58]. An optimum of ca. 25°C is consistent with the findings of Kremp et al. [58] who reported general growth stimulation in response to an increased temperature, despite variability in the responses of eight strains of A. ostenfeldii isolated from the same site as our strain.
While further investigations into the variability of strain responses to salinity are needed, our results can be compared with those in the literature. Thus, the optimal salinities allowing growth as determined in the present work are in agreement with those reported by Kremp et al. [16] and Suikkanen et al. [29] for other isolates from the same region (Åland islands, between Finland and Sweden). However, in the strain from Limfjord, Denmark (Kattegat Sea) studied by Østergaard and Moestrup [17] as in the strain from Skagerrak studied by Suikkanen et al. [29], the values were higher and salinities of up to 35–40 were tolerated. This variation suggests that both Limfjord and Skagerrak strains belong to a different, high-salinity-adapted population, a conclusion supported by the genetic study carried out by Kremp et al. [13], who showed that strains from the Baltic Sea and Limfjord were grouped within distinct phylogenetic clades. The low optimum salinity (11.2) recorded for our A. ostenfeldii strain is consistent with its adaptation to the low salinities of the shallow coastal embayments of the northern Baltic Sea, where salinities are typically between 6 and 7 [16, 29]. Furthermore, our results along with those of previous studies [6, 29] show that a salinity > 25 is a limiting factor for growth. Extrapolated to the natural environment, this would limit the geographic distribution of the population to areas influenced by freshwater inputs, such as the most northern and eastern areas of the Baltic Sea [29]. The adaptation of A. ostenfeldii to specific environments of the Baltic Sea is indicative of an early post-glacial colonization and the continued isolation of the respective subpopulations due their limited dispersal [82].
Our results on the temperature preferences of one strain of A. ostenfeldii support the concerns expressed by other authors regarding the potential increase in blooms of this species as a possible response to climate change [58]. Summer conditions in the Baltic Sea, when the water is warm, stratified, and nutrient-poor are optimal for dinoflagellate growth [58] and for increased toxin production (19°C for PSP toxin and 20.9°C for GYM-A analogue). This is especially the case in shallow and sheltered embayments, where the temperature may be well above 20°C [16]. In fact, large summer blooms of A. ostenfeldii in the brackish estuaries and shallow coastal inlets of diverse areas during warm-water periods have become increasingly common in recent years [15, 33, 83].
Conclusions
Both cell growth and net toxin (GYM and PSP toxin) production were directly responsive to temperature and salinity changes. While increasing temperatures stimulated growth as well as net toxin production, salinities higher than 21 were growth-limiting. The present study also provides the first quantitative determination of a GYM-A analogue in A. ostenfeldii and the first report of changes in its production in response to variations in temperature and salinity. The changes in PSP toxin and GYM-A analogue production suggest a mixed-growth-associated model, since net toxin production typically occurred in exponentially growing and in stationary-phase cells. The optimal temperature and salinity that resulted in maximum toxin concentrations were: 20.9°C and 17 for the GYM-A analogue and > 19°C and 15 for PSP toxins, respectively. The RSA presented herein is a valuable approach for evaluating the combined effect of temperature and salinity on A. ostenfeldii growth and net toxin production. While further studies estimating the magnitude of within-species variation are needed, our data suggest that warming of the water would stimulate both the growth of A. ostenfeldii and its toxin production.
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Fernández-Villamarín for technical assistance in processing the toxin samples, and I. Ramilo and P. Rial for technical assistance with the cultures. This article is going to be part of the thesis of P. Salgado that is attached to the framework of the doctoral program “Marine Science, Technology and Management” (DO*MAR) of the University of Vigo.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper.
Funding Statement
This work is a contribution of the Unidad Asociada "Microalgas Nocivas" (CSIC-IEO) and was financially supported by the CCVIEO project and CICAN-2013-40671-R (Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness). P. Salgado is a researcher at IFOP, which has provided financial support for his doctoral stay.
References
- 1. Smayda T. Adaptive ecology, growth strategies and the global bloom expansion of dinoflagellates. J Oceanogr. 2002; 58:281–94. [Google Scholar]
- 2. Cembella AD. Ecophysiology and metabolism of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine microalgae In: Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM, editors. Physiological ecology of harmful algal blooms. Springer,Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 381–403 NATO ASI Series 41; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Murray S, Hoppenrath M, Orr R, Bolch C, John U, Diwan R, et al. Alexandrium diversaporum sp. nov., a new non-saxitoxin producing species: Phylogeny, morphology and sxtA genes. Harmful Algae. 2014; 31:54–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Anderson DM, Alpermann T, Cembella A, Collos Y, Masseret E, Montresor M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae. 2012; 14:10–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Cembella A, Lewis N, Quilliam M. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia. 2000; 39(1):67–74. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Salgado P, Riobó P, Rodríguez F, Franco JM, Bravo I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon. 2015; 103:85–98. 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.06.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Van Wagoner R, Misner I, Tomas C, Wright J. Occurrence of 12-methylgymnodimine in a spirolide-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum and the biogenetic implications. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011; 52:4243–46. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Harju K, Kremp A, Suikkanen S, Kankaanpää H, Vanninen P. Mass spectrometric screening of novel gymnodimine-like compounds in isolates of Alexandrium ostenfeldii. 16th Internation Conference on Harmful Algae; 27–31 October; Wellington, New Zealand2014.
- 9. Molgó J, Aráoz R, Benoit E, Iorga B. Cyclic imine toxins: chemistry, origin, metabolism, pharmacology, toxicology, and detection In: Botana LM, editor. Seafood and Freshwater Toxins 3rd edition CRC Press, Boca Raton: 2014. p. 951–89. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Richard D, Arsenault E, Cembella A, Quilliam M. Investigations into the toxicology and pharmacology of spirolides, a novel group of shellfish toxins In: Hallegraeff GM, Blackburn SI, Bolch CJ, Lewis RJ, editors. Harmful Algal Blooms 2000: Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO; 2001. p. 383–86. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Marrouchi R, Benoit E, Kharrat R, Molgo J. Gymnodimines: a family of phycotoxins contaminating shellfish. In: Berbier J, Benoit, E., Marchot, P., Mattei, C., Servent, D., editor. Advances and new technologies in Toxinology: SFET Editions: Meetings on Toxinology, E-book RT18.; 2010. p. 79–83.
- 12. Hansen P, Cembella A, Moestrup Ø. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: Paralytic shellfish toxin concentration, composition, and toxicity to a tintinnid ciliate. J Phycol. 1992; 28:597–603. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kremp A, Tahvanainen P, Litaker W, Krock B, Suikkanen S, Leaw CP, et al. Phylogenetic relationships, morphological variation, and toxin patterns in the Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) complex: implications for species boundaries and identities. J Phycol. 2014; 50:81–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Paulsen O. Plankton-investigations in the waters round Iceland in 1903. Medd Kommn Havunders Kobenh Ser Plankt. 1904; 1:1–40. [Google Scholar]
- 15. Burson A, Matthijs H, de Bruijne W, Talens R, Hoogenboom R, Gerssen A, et al. Termination of a toxic Alexandrium bloom with hydrogen peroxide. Harmful Algae. 2014; 31:125–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kremp A, Lindholm T, Dreßler N, Erler K, Gerdts G, Eirtovaara S, et al. Bloom forming Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) in shallow waters of the Åland Archipelago, Northern Baltic Sea. Harmful Algae. 2009; (8):318–28. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Østergaard M, Moestrup Ø. Autecology of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: life history and growth at different temperatures and salinities. Eur J Phycol. 1997; 32:9–18. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Tillmann U, Kremp A, Tahvanainen P, Krock B. Characterization of spirolide producing Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the western Arctic. Harmful Algae. 2014; 39:259–70. [Google Scholar]
- 19. Almandoz G, Montoya N, Hernando M, Benavides H, Carignan M, Ferrario M. Toxic strains of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex in southern South America (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Harmful Algae. 2014; 37:100–09. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guzmán L, Vidal G, Pizarro G, Salgado P, Vivanco X, Iriarte L, et al. Programa de manejo y monitoreo de las mareas rojas en las regiones de Los Lagos, Aisén y Magallanes, etapa VII 2013–14. Convenio Asesoría integral para la pesca y la acuicultura (ASIPA). Subsecretaría de Economía y empresas de menor tamaño–Instituto de Fomento Pesquero2013. p. 45 + Figures + Tables + annexes.
- 21. Haro D, Aguayo A, Acevedo J. Características oceanográficas y biológicas de las comunidades del plancton y necton del área marina costera protegida Francisco Coloane: una revisión. An Inst Patagon. 2013; 41(1):77–90. [Google Scholar]
- 22. Avaria S, Cáceres C, Castillo P, Muñoz P. Distribución del microfitoplancton marino en la zona Estrecho de Magallanes-Cabo de Hornos, Chile, en la primavera de 1998 (Crucero Cimar 3 Fiordos). Ciencia y Tecnología del March 2003; 26(2):79–96. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Balech E, de Mendiola BR. Un nuevo Gonyaulax productor de hemotalasia en Perú. Neotropica. 1977; 23:49–54. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sanchez S, Villanueva P, Carbajo L. Distribution and concentration of Alexandrium peruvianum (Balech and de Mendiola) in the Peruvian coast (03°24′–18°20′ LS) between 1982–2004. XI International Conference on Harmful Algal Blooms; November 15–19; Cape Town, South Africa2004. p. 227.
- 25. Lim PT, Usup G, Leaw CP, Ogata T. First report of Alexandrium taylori and Alexandrium peruvianum (Dinophyceae) in Malaysia waters. Harmful Algae. 2005; 4:391–400. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Bravo I, Garcés E, Diogène J, Fraga S, Sampedro N, Figueroa R. Resting cysts of the toxigenic dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium in recent sediments from the Western Mediterranean coast, including the first description of cysts of A. kutnerae and A. peruvianum . Eur J Phycol. 2006; 41(3):293–302. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ciminiello P, Dell’Aversano C, Fattorusso E, Magno S, Tartaglione L, Cangini M, et al. Toxin profile of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the Northern Adriatic Sea revealed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Toxicon. 2006; 47:597–604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Katikou P, Aligizaki K, Zacharaki T, Iossifidis D, Nikolaidis G, editors. First report of spirolides in Greek shellfish associated with causative Alexandrium species. 14th International Conference on Harmful Algae; 2010; Crete, Greek, 1–5 November.
- 29. Suikkanen S, Kremp A, Hautala H, Krock B. Paralytic shellfish toxins or spirolides? The role of environmental and genetic factors in toxin production of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex. Harmful Algae. 2013; 26:52–59. [Google Scholar]
- 30. Lembeye G. Florecimientos algales nocivos en aguas australes In: Silva N, Palma S, editors. Avances en el conocimiento oceanográfico de las aguas interiores chilenas. Valparaiso, Chile: Comité Oceanográfico Nacional—Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso; 2006. p. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Franco JM, Paz B, Riobó P, Pizarro G, Figueroa R, Fraga S, et al. First report of the production of spirolids by Alexandrium peruvianum (Dinophyceae) from the Mediterranean Sea. 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae; Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September2006.
- 32. Borkman D, Smayda T, Tomas C, York R, Strangman S, Wright J. Toxic Alexandrium peruvianum (Balech and de Mendiola) Balech and Tangen in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island (USA). Harmful Algae. 2012; 19:92–100. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Tomas C, Van Wagoner R, Tatters R, White K, Hall S, Wright J. Alexandrium peruvianum (Balech and Mendiola) Balech and Tangen a new toxic species for coastal North Carolina. Harmful Algae. 2012; 17:54–63. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Maclean C, Cembella A, Quilliam M. Effects of Light, Salinity and Inorganic Nitrogen on Cell Growth and Spirolide Production in the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Paulsen) Balech et Tangen. Bot Mar. 2003; 46:466–76. [Google Scholar]
- 35. Otero A, Alfonso A, Vieytes MR, Cabado AG, Vieites JM, Botana LM. Effects of environmental regimens on the toxin profile of Alexandrium ostenfeldii . Environ Toxicol Chem. 2010; 29(2):301–10. 10.1002/etc.41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Guillard RRL, Hargraves PE. Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not achrysophyte. Phycologia. 1993; 32:234–36. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Rourke WA, Murphy CJ, Pitcher G, Van de Riet JM, Garth Burns B, Thomas KM, et al. Rapid postcolumn methodology for determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish tissue. J AOAC Int. 2008; 91(3):589–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.EURLMB. EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC–MS/MS. European Union Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins. http://aesan.msps.es/en/CRLMB/web/home.shtml. 2011.
- 39. Paz B, Vázquez JA, Riobó P, Franco JM. Study of the effect of temperature, irradiance and salinity on growth and yessotoxin production by the dinoflagellate Protoceratium reticulatum in culture by using a kinetic and factorial approach. Mar Environ Res. 2006; 64(2):286–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Vázquez JA, Murado MA. Mathematical tools for objective comparison of microbial cultures. Application to evaluation of 15 peptones for lactic acid bacteria productions. Biochem Eng J. 2008; 39:276–87. [Google Scholar]
- 41. Vázquez JA, Lorenzo JM, Fuciños P, Franco D. Evaluation of non-linear equations to model different animal growths with mono and bi-sigmoid profiles. J Theor Biol. 2012; 39:276–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Box GE, Hunter JS, Hunter WG. Statistics for experimenters: Design, innovation, and discovery 2nd ed: New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Wardhani DH, Vázquez JA, Pandiella SS. Optimization of antioxidants extraction from fermented soybeans by Aspergillus oryzae . Food Chem. 2010; 118(3):731–39. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Dantigny P, Marín S, Beyer M, Magand N. Mould germination: Data treatment and modelling. Int J Food Microbiol. 2007; 114:17–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Jayakar SS, Singhal RS. Kinetic modeling and scale up of lipoic acid (LA) production from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a stirred tank bioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2013; 36:1063–70. 10.1007/s00449-012-0859-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Liu JZ, Weng LP, Zhang QL, Xu H, Ji LN. A mathematical model for gluconic acid fermentation by Aspergillus niger . Biochem Eng J. 2003; 14:137–41. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Spor A, Dillmann C, Wanga S, de Vienne D, Sicard D, Sicard D. Hierarchical Bayesian modelling for Saccharomyces cerevisiae population dynamics. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010; 142:25–35. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.05.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Vázquez JA, Docasal SF, Prieto MA, González MP, Murado MA. Growth and metabolic features of lactic acid bacteria in media with hydrolysed fish viscera. An approach to bio-silage of fishing by-products. Bioresource Technol. 2008; 99:6246–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Wardhani DH, Vázquez JA, Pandiella SS. Mathematical modeling of the development of antioxidant activity in soybeans fermented with Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus awamori in the solid state. J Agric Food Chem. 2009; 57:540–44. 10.1021/jf802492s [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Franco D, Crecente S, Vázquez JA, Gómez M, Lorenzo JM. Effect of cross breeding and amount of finishing diet on growth parameters, carcass and meat composition of foals slaughtered at 15 months. Meat Sci. 2013; 93:547–56 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.11.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Franco D, Rois D, Vázquez JA, Purriños L, González R, Lorenzo JM. Breed effect between Mos rooster (Galician indigenous breed) and Sasso T-44 line and finishing feed effect of commercial fodder or corn. Poult Sci. 2012; 91:487–98. 10.3382/ps.2011-01546 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Kebreab E, Schulin-Zeuthen M, Lopez S, Soler J, Dias RS, de Lange CFM, et al. Comparative evaluation of mathematical functions to describe growth and efficiency of phosphorus utilization in growing pigs. J Anim Sci 2007; 85:2498–507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Hui W, Shiwei F, Zhigang L. Optimal prediction of adductor percentage for Argopecten irradians concentricus (Say) cultured in Beibu bay in China. Aquaculture. 2008; 284:68–73. [Google Scholar]
- 54. Paz B, Vázquez JA, Riobó P, Franco JM. Mathematical description of yessotoxin production by Protoceratium reticulatum in culture. Harmful Algae. 2009; 8:730–35. [Google Scholar]
- 55. Planas M, Vázquez JA, Marques J, Pérez R, González MP, Murado M, A. Enhancement of rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis) growth by using terrestrial acid lactic bacteria. Aquaculture. 2004; 240:313–29 [Google Scholar]
- 56. Rial D, Murado M, A., Menduíña A, Fuciños P, González MP, Mirón J, et al. Effects of spill-treating agents on growth kinetics of marine microalgae. J Hazard Mater. 2013; 263:374–81. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Vázquez JA, González MP, Murado MA. A new marine medium. Use of the different fish peptones and comparative study of the growth of selected species of marine bacteria. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2004; 35:385–92 [Google Scholar]
- 58. Kremp A, Godhe A, Egardt J, Dupont S, Suikkanen S, Casabianca S, et al. Intraspecific variability in the response of bloom-forming marine microalgae to changed climate conditions. Ecol Evol. 2012; 2(6):1195–207. 10.1002/ece3.245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Brown L, Bresnan E, Graham J, Lacaze JP, Turrell E, Collins C. Distribution, diversity and toxin composition of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) in Scottish waters. Eur J Phycol. 2010; 45(4):375–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Etheridge SM, Roesler CS. Effects of temperature, irradiance, and salinity on photosynthesis, growth rates, total toxicity, and toxin composition for Alexandrium fundyense isolates from the Gulf of Maine and Bay of Fundy. Deep-Sea Res Pt II. 2005; 52:2491–500. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Grzebyk D, Béchemin C, Ward CJ, Vérité C, Codd GA, Maestrini SY. Effects of salinity and two coastal waters on the growth and toxin content of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum . J Plankton Res. 2003; 25(10):1185–99. [Google Scholar]
- 62. Laabir M, Jauzein C, Genovesi B, Masseret E, Grzebyk D, Cecchi P, et al. Influence of temperature, salinity and irradiance on the growth and cell yield of the harmful red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella colonizing Mediterranean waters. J Plankton Res. 2011; 0(0):1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 63. Figueroa R, Vázquez JA, Massanet A, Murado MA, Bravo I. Interactive effects of salinity and temperature on planozigote and cyst formation of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) in culture. J Phycol. 2011; 47:13–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Lakeman MB, Dassow PV, Cattolico RA. The strain concept in phytoplankton ecology. Harmful Algae. 2009; 8:746–58. [Google Scholar]
- 65. Wood AM, Leatham T. The species concept in phytoplankton ecology. J Phycol. 1992; 28:723–29. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Hwang D, Lu Y. Infuence of environmental and nutritional factors on growth, toxicity, and toxin profile of dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum . Toxicon. 2000; 38:1491–503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Wang D, Hsieh D. Growth and toxin production in batch cultures of a marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense HK9301 isolated from the South China Sea. Harmful Algae. 2005; 4:401–10. [Google Scholar]
- 68. Granéli E, Flynn K. Chemical and physical factors influencing toxin content In: Granéli E, Turner J, editors. Ecology of Harmful Algae. ed. Springer-Verlag; Berlin Heidelberg: Ecological Studies Series 189; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 69. Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Sullivan JJ, Hall S. Toxin composition variations in one isolate of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense . Toxicon. 1990; 28(8):885–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Figueroa RI, Bravo I, Garcés E. The significance of sexual versus asexual cyst formation in the life cycle of the noxious dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum . Harmful Algae. 2008; 7:653–63. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Miles C, Wilkins A, Stirling D, MacKenzie L. New Analogue of Gymnodimine from a Gymnodinium Species. J Agric Food Chem. 2000; 48:1373–76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Miles C, Wilkins A, Stirling D, MacKenzie L. Gymnodimine C, an Isomer of Gymnodimine B, from Karenia selliformis . J Agric Food Chem. 2003; 51:4838–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Haywood A, Steidinger K, Truby E, Bergquist P, Bergquist P, Adamson J, et al. Comparative morphology and molecular phylogenetic analysis of three new species of the genus Karenia (Dinophyceae) from New Zealand. J Phycol. 2004; 40:165–79. [Google Scholar]
- 74. Medhioub W, Sechet V, Truquet P, Bardouil M, Amzil Z, Lassus P, et al. Alexandrium ostenfeldii growth and spirolide production in batch culture and photobioreactor. Harmful Algae. 2011; 10:794–803. [Google Scholar]
- 75. Tatters R, Van Wagoner R, Wright J, Tomas C. Regulation of spiroimine neurotoxins and hemolytic activity in laboratory cultures of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum (Balech & Mendiola) Balech & Tangen. Harmful Algae. 2012; 19:160–68. [Google Scholar]
- 76. Gribble K, Keafer B, Quilliam M, Cembella A, Kulis D, Manahan A, et al. Distribution and toxicity of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) in the Gulf of Maine, USA. Deep-Sea Res Pt II. 2005; 52:2745–63. [Google Scholar]
- 77. MacKinnon S, Walter J, Quilliam M, Cembella A, LeBlanc P, Burton I, et al. Spirolides Isolated from Danish Strains of the Toxigenic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii . J Nat Prod. 2006; 69(7):983–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Aasen J, MacKinnon S, LeBlanc P, Walter J, Hovgaard P, Aune T, et al. Detection and Identification of Spirolides in Norwegian Shellfish and Plankton. Chem Res Toxicol. 2005; 18:509–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Senft-Batoh CD, Dam HG, Shumway SE, Wikfors GH, Schlichting CD. Influence of predator–prey evolutionary history, chemical alarm-cues, and feeding selection on induction of toxin production in a marine dinoflagellate. Limnol Oceanogr. 2015; 00:1–21. [Google Scholar]
- 80. Senft-Batoh CD, Dam HG, Shumway SE, Wikfors GH. A multi-phylum study of grazer-induced paralytic shellfish toxin production in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense: A new perspective on control of algal toxicity. Harmful Algae. 2015; 44:20–31. [Google Scholar]
- 81. Gu H. Morphology, phylogenetic position, and ecophysiology of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the Bohai Sea, China. J Syst Evol. 2011; 49(6):606–16. [Google Scholar]
- 82. Tahvanainen P, Alpermann T, Figueroa R, John U, Hakanen P, Nagai S, et al. Patterns of post-glacial genetic differentiation in marginal populations of a marine microalga. PLoS ONE. 2012; 7(12):e53602 10.1371/journal.pone.0053602 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Hakanen P, Suikkanen S, Franzén J, Franze H, Kankaanpää H, Kremp A. Bloom and toxin dynamics of Alexandrium ostenfeldii in a shallow embayment at the SW coast of Finland, northern Baltic Sea. Harmful Algae. 2012; 15:91–99. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper.