Abstract
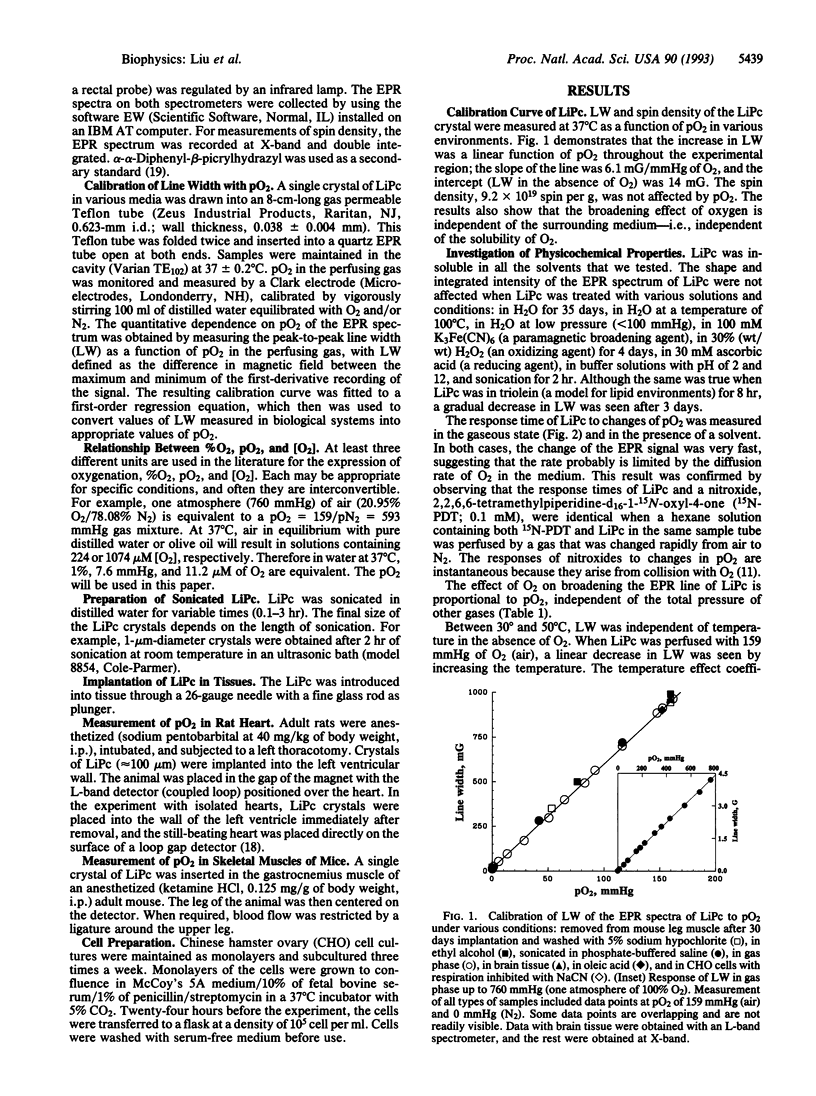
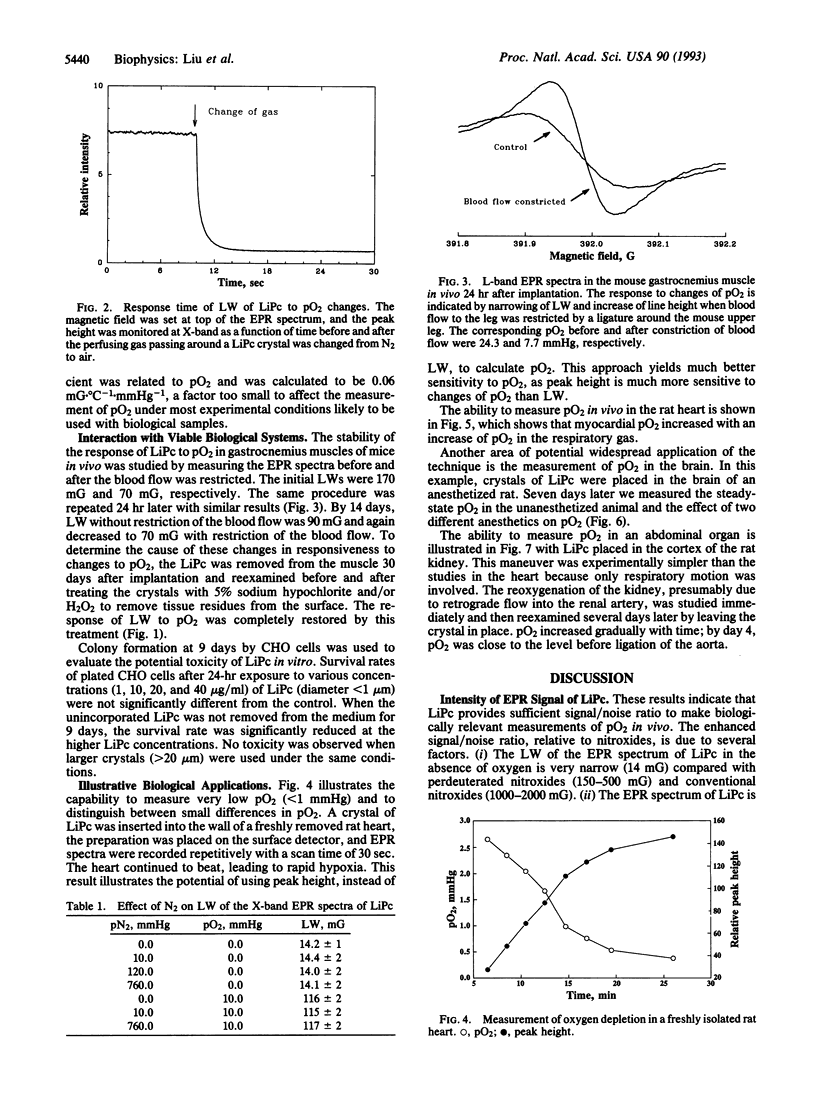
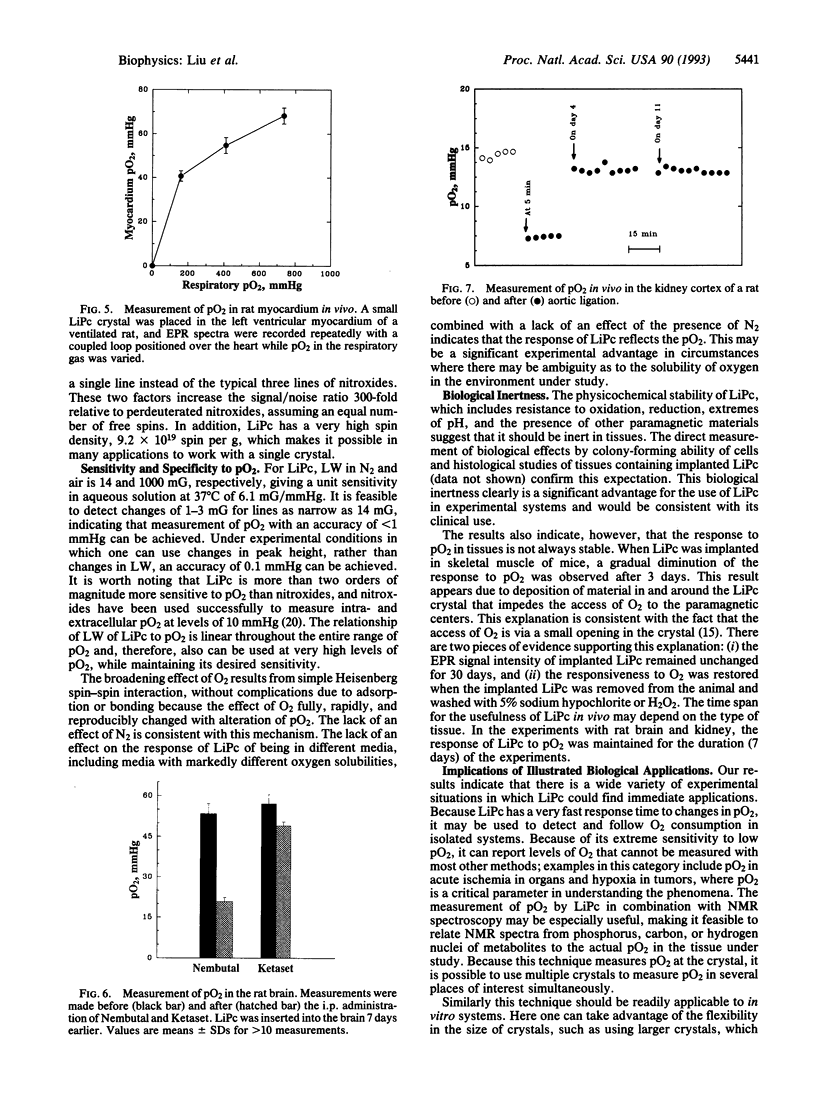
Lithium phthalocyanine (LiPc) is a prototype of another generation of synthetic, metallic-organic, paramagnetic crystallites that appear very useful for in vitro and in vivo electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry. The peak-to-peak line width of the electron paramagnetic resonance spectrum of LiPc is a linear function of the partial pressure of oxygen (pO2); this linear relation is independent of the medium surrounding the LiPc. It has an extremely exchange-narrowed spectrum (peak-to-peak line width = 14 mG in the absence of O2). Physicochemically LiPc is very stable; its response to pO2 does not change with conditions and environments (e.g., pH, temperature, redox conditions) likely to occur in viable biological systems. These characteristics provide the sensitivity, accuracy, and range to measure physiologically and pathologically pertinent O2 tensions (0.1-50 mmHg; 1 mmHg = 133 Pa). The application of LiPc in biological systems is demonstrated in measurements of pO2 in vivo in the heart, brain, and kidney of rats.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONINI E. INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jan;45:123–170. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biaglow J. E., Varnes M. E., Jacobson B., Koch C. J. Factors influencing the oxygen consumption and radiation response of cultured mammalian cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;159:347–358. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7790-0_30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K., Morse P. D., 2nd, Swartz H. M. Kinetics of enzyme-mediated reduction of lipid soluble nitroxide spin labels by living cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 1;943(3):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glockner J. F., Swartz H. M., Pals M. A. Oxygen gradients in CHO cells: measurement and characterization by electron spin resonance. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Sep;140(3):505–511. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz N., Lübbers D. W. Increased resolution power in PO2 analysis at lower PO2 levels via sensitivity enhanced optical PO2 sensors (PO2 optodes) using fluorescence dyes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;180:261–267. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4895-5_25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshino R., Oshino N., Tamura M., Kobilinsky L., Chance B. A sensitifve bacterial luminescence probe for O2 in biochemical systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 26;273(1):5–17. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver I. A. The oxygen micro-electrode. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1973;37A:7–15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3288-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. J., Lucchesi B. R. Free radicals and myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Jul;110(1):13–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz H. M., Boyer S., Gast P., Glockner J. F., Hu H., Liu K. J., Moussavi M., Norby S. W., Vahidi N., Walczak T. Measurements of pertinent concentrations of oxygen in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Aug;20(2):333–339. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910200217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz H. M. Effect of oxygen on freezing damage. 3. Modification by -mercaptoethylamine. Cryobiology. 1971 Dec;8(6):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(71)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Maniara G., Green T. J., Wilson D. F. An optical method for measurement of dioxygen concentration based upon quenching of phosphorescence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5476–5482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F., Rumsey W. L., Green T. J., Vanderkooi J. M. The oxygen dependence of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation measured by a new optical method for measuring oxygen concentration. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2712–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



