Abstract
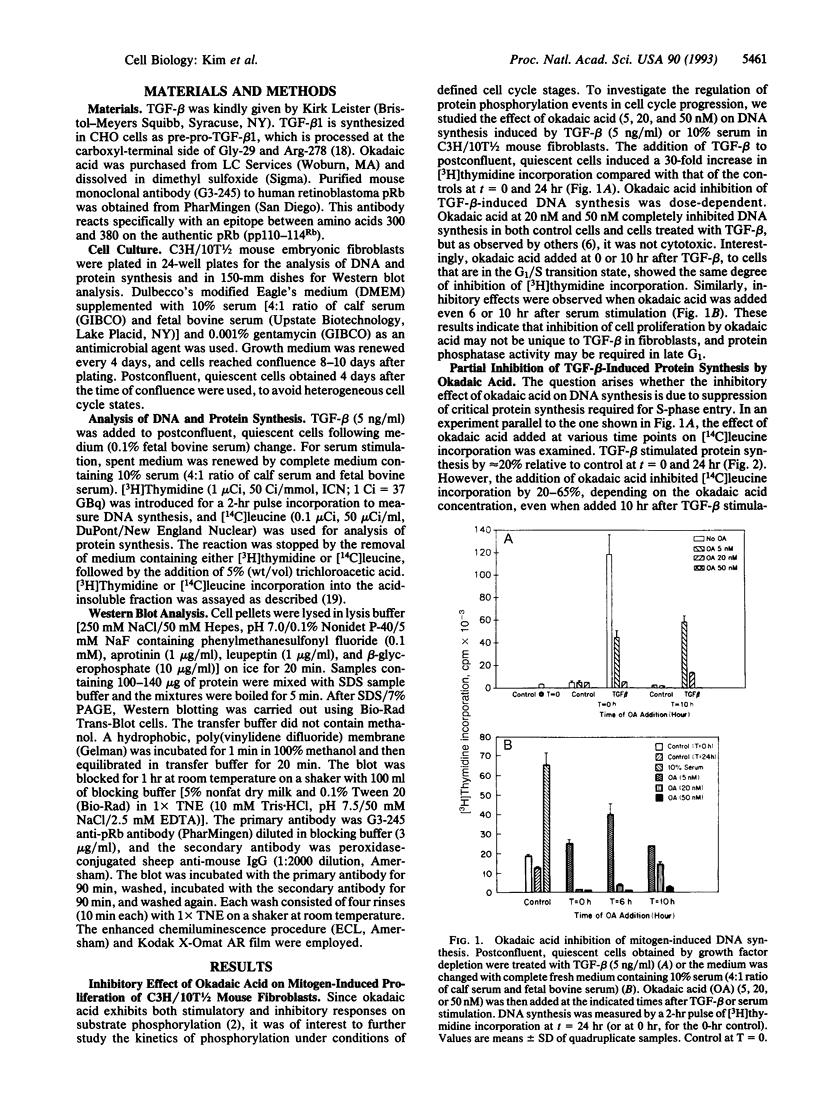
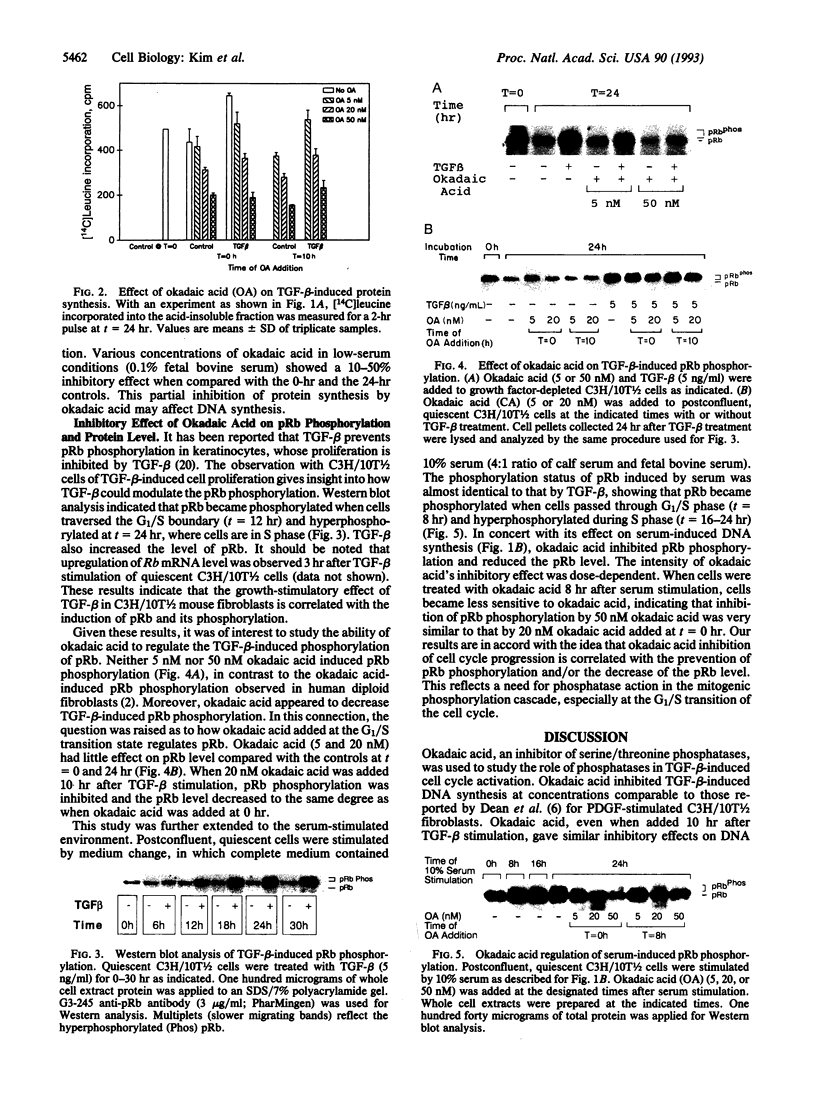
Okadaic acid, a specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A, was used to study the mechanism of action of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) on cell cycle progression in C3H/10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblasts, where TGF-beta exerts a growth-stimulatory effect. Concentrations of okadaic acid as low as 5 nM inhibited TGF-beta (5 ng/ml)- or 10% serum-induced [3H]thymidine incorporation into postconfluent, quiescent cells. Further, these inhibitory effects were observed when okadaic acid was added as late as 10 hr after TGF-beta or serum stimulation. Since C3H/10T1/2 fibroblasts undergo the G1/S transition at 10-14 hr after TGF-beta and 8-12 hr after serum stimulation, these observations indicate that a phosphatase activity may be required for S-phase entry. In a parallel experiment, okadaic acid partially inhibited TGF-beta-induced [14C]leucine incorporation by 20-65%, depending upon the okadaic acid concentration. In conjunction with the effect of okadaic acid on DNA and protein synthesis, Western blot analysis indicated that okadaic acid inhibited phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product and decreased its protein level, even when added 10 hr after TGF-beta or 8 hr after serum stimulation. These findings strongly suggest that protein phosphatases play a pivotal role for S-phase entry in mouse fibroblasts. Moreover, protein phosphatases may be required in the intermediate steps of TGF-beta or serum growth factor signal-transduction pathways for the stimulation of phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein, especially in late G1.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adunyah S. E., Unlap T. M., Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S. Induction of differentiation and c-jun expression in human leukemic cells by okadaic acid, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases. J Cell Physiol. 1992 May;151(2):415–426. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Ohuchi T., Sumida S., Matsumoto K., Toyoshima K. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein by cdk2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7900–7904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Sunwoo J., Labbé J. C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cell cycle oscillation of phosphatase inhibitor-2 in rat fibroblasts coincident with p34cdc2 restriction. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):74–78. doi: 10.1038/344074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutry A. F., Kinniburgh A. J., Twardzik D. R., Wenner C. E. Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF alpha) induction of C-FOS and C-MYC expression in C3H 10T1/2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):216–222. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80702-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Furukawa Y., Ajchenbaum F., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. The retinoblastoma-susceptibility gene product becomes phosphorylated in multiple stages during cell cycle entry and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1795–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean N. M., Mordan L. J., Tse K., Mooberry S. L., Boynton A. L. Okadaic acid inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and decreases PDGF receptor number in C3H/10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Apr;12(4):665–670. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Sarabia M. J., Sutton A., Zhong T., Arndt K. T. SIT4 protein phosphatase is required for the normal accumulation of SWI4, CLN1, CLN2, and HCS26 RNAs during late G1. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2417–2428. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Lioubin M. N., Purchio A. F., Marquardt H. Molecular events in the processing of recombinant type 1 pre-pro-transforming growth factor beta to the mature polypeptide. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4162–4168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Cao X., Chua S. P., Tan Y. H. Okadaic acid mimics multiple changes in early protein phosphorylation and gene expression induced by tumor necrosis factor or interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1846–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holladay K., Fujiki H., Bowden G. T. Okadaic acid induces the expression of both early and secondary response genes in mouse keratinocytes. Mol Carcinog. 1992;5(1):16–24. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940050106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Buchkovich K. J., Marshak D. R., Anderson C. W., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated on multiple sites by human cdc2. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4279–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Pietenpol J. A., Pittelkow M. R., Holt J. T., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor beta 1 regulation of c-myc expression, pRB phosphorylation, and cell cycle progression in keratinocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuki M., Massagué J. Evidence for the involvement of protein kinase activity in transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):261–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Association of cdk2 kinase with the transcription factor E2F during S phase. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1312258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redpath N. T., Proud C. G. The tumour promoter okadaic acid inhibits reticulocyte-lysate protein synthesis by increasing the net phosphorylation of elongation factor 2. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):69–75. doi: 10.1042/bj2620069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A. Okadaic acid--a valuable new tool for the study of signal transduction and cell cycle regulation? New Biol. 1992 Jan;4(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Tsukitani Y., Feramisco J. R. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of c-fos expression by the tumor promoter okadaic acid. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):423–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soma Y., Grotendorst G. R. TGF-beta stimulates primary human skin fibroblast DNA synthesis via an autocrine production of PDGF-related peptides. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):246–253. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma gene and cell growth control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Yasuda H., Pines J., Yasumoto K., Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Hunter T., Sugimura T., Nishimoto T. Okadaic acid, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases, activates cdc2/H1 kinase and transiently induces a premature mitosis-like state in BHK21 cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4331–4338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






