Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies that target the programmed death-1 (PD-1)/programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) axis have antitumor activity against multiple cancers. The presence of sarcomatoid differentiation in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is associated with resistance to targeted therapy and poor responses to interleukin-2 immunotherapy. Given the aggressive nature of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation and the exclusion of sarcomatoid histology from metastatic RCC clinical trials, less is understood regarding selection of therapies. Here, we characterized the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. We directly compared two PD-L1 antibodies and found concordance of PD-L1 positivity in 89% of tested RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation. Coexpression of PD-L1 on neoplastic cells and the presence of PD-1–positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was identified in 50% (13/26) of RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation. In contrast, only 1 of 29 clear cell RCCs (3%) had concurrent expression of PD-L1 and PD-1 (P=.002). Our study suggests that RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation may express PD-1/PD-L1 at a higher percentage than RCC without sarcomatoid differentiation and patients with these tumors may be good candidates for treatment with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies.
Keywords: programmed death-1, programmed death ligand-1, renal cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid
Introduction
Monoclonal antibodies that target the programmed death-1 (PD-1)/programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) axis have antitumor activity against multiple tumor types, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC) (1). RCC and other tumors evade immune surveillance by upregulation of PD-L1, which binds PD-1 on the surface of activated T and B cells and negatively regulates the immune system. Therapeutic blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction is associated with durable responses in approximately 26% of patients with RCC, and studies suggest that tumor expression of PD-L1 is associated with a greater response to treatment (1–3).
Sarcomatoid differentiation with malignant spindle-shaped cell histologic features occurs in 5% of RCCs and shares some common pathologic features with sarcomas. It is also associated with significantly worse prognosis, with median overall survivals ranging from 4 to 9 months, compared with 29 months for clear cell RCC (ccRCC) (4–6). The presence of sarcomatoid differentiation in more than 20% of cells in metastatic RCCs (mRCCs) is associated with intrinsic resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-directed therapy, and poor responses to interleukin-2 (IL-2) immunotherapy (7,8).
Given the aggressive nature of mRCC with sarcomatoid differentiation, the rarity of the entity, and the exclusion of sarcomatoid differentiation from many clinical trials in mRCC, the selection of systemic therapy for this entity is often empiric. Increased expression of PD-L1 on RCC tumor cells is associated with higher nuclear grade and tumor necrosis (9). We aimed to analyze the PD-1/PD-L1 axis by characterizing the expression of these proteins in RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. We examined the numbers of PD-1–positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (PD-1+TILs) and PD-L1 expression on tumor cells and also report a response to anti–PD-1 immunotherapy in a patient with mRCC with sarcomatoid differentiation.
Methods
Case Selection and Histologic Review
After approval from the Mayo Clinic Institutional Review Board, we used the Multidisciplinary Genitourinary Diseases Biospecimen Bank at Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Arizona, to identify patients treated for RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation from 2007 through 2013 (10). As part of the biospecimen effort, an experienced urologic pathologist (M.L.S.) centrally reviewed hematoxylin-eosin–stained slides for all patient tumors to confirm histologic classification and to systematically record standard pathologic features. In an independent cohort, cases of kidney cancer referred to Caris Life Sciences between 2003 and 2014 for commercial molecular profiling were retrieved and evaluated for sarcomatoid components with central pathology review (D.B.). Both pathologists were blinded to treatment outcomes.
Immunohistochemistry for PD-L1 and PD-1 Expression
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were cut in 5-μm slices and were deparaffinized and rehydrated. All slides were sectioned within 2 months of staining. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis was performed on tumor samples using commercially available detection kits, automated staining techniques (Benchmark XT, Ventana; AutostainerLink 48, Dako), and antibodies against PD-1 (BD Pharmingen 561273) and PD-L1 (R+D systems clone 130021; Spring Bioscience Clone SP142). For the purposes of IHC scoring in RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation, only the sarcomatoid component was evaluated.
Samples were dichotomized as having positive or negative staining for each protein (11). For the detection of PD-1+TILs, the entire tumor was reviewed at ×4 magnification, and the area of highest density of PD-1+TILs adjacent to malignant cells was counted at ×400 (No. of PD-1+TILs/high-power field). For PD-1, a count of 0+ PD-1+TILs per high-power field was considered negative, and a count of 1+ or greater was considered positive. For PD-L1, the expression was evaluated on a semiquantitative scale (0–3+): 0 for absent, 1+ for weak, 2+ for moderate, and 3+ for strong membranous and cytoplasmic staining. The percentage of PD-L1–positive cells at the highest intensity was recorded. For PD-L1, less than 5% staining or a score of 0 or 1+ was considered negative, and 5% or more staining or a score of 2+ or 3+ was considered positive. All testing was performed at Caris Life Sciences (Phoenix, Arizona), a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act–certified and College of American Pathologists–accredited molecular profiling laboratory.
Statistical Methods
Prism v6.02 software (GraphPad) was used for statistical analysis. Comparisons between ccRCC and RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation were evaluated with the Fisher exact test, and a 2-tailed P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Comparison of Patient Characteristics and Clinicopathologic Features
From the Mayo Clinic Biospecimen Bank, we retrieved samples from 19 patients with RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation; the independent (Caris) cohort included 112 cases of renal cancer, 91 of which were ccRCC without sarcomatoid differentiation and 21 were RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. The Table compares the demographic, pathologic, and clinical features of the 2 groups: RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation (n=40) and ccRCC (n=91). In both groups, tumors were collected from more men than women. In RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation, 83% of the tumors were metastatic at the time of molecular profiling.
Table.
Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
| Characteristic | Groupa
|
P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCC-Sarc (n=40) | ccRCC (n=91) | ||
| Age, y | 51 (33–88) | 65 (40–86) | |
| Men | 34 (85) | 68 (75) | .25 |
| Documented metastasis at time of tumor profiling | <.001 | ||
| Metastatic | 33 (83) | 29 (32) | |
| Missing | 7 (17) | 62 (68) | |
| Sarcomatoid component, % | 72 (10–100) | 0 | <.001 |
| Fuhrman grade | <.001 | ||
| 4 | 40 (100) | 6 (7) | |
| 3 | 0 | 31 (34) | |
| 2 | 0 | 40 (44) | |
| 1 | 0 | 13 (14) | |
| Missing | 0 | 1 (1) | |
Abbreviations: ccRCC, clear cell renal cell carcinoma; RCC-Sarc, renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation.
Values are median (range) or No. of patients (%).
To determine the concordance between the commercially available anti–PD-L1 antibody clones, serial sections from the 19 biobank samples of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation were stained with either the SP142 or 130021 antibody (Fig. 1). When PD-L1 IHC scoring was dichotomized, 17 of the 19 samples (89%) had concordant positive or negative scores in serial sections (Supplementary Table).
Figure 1.
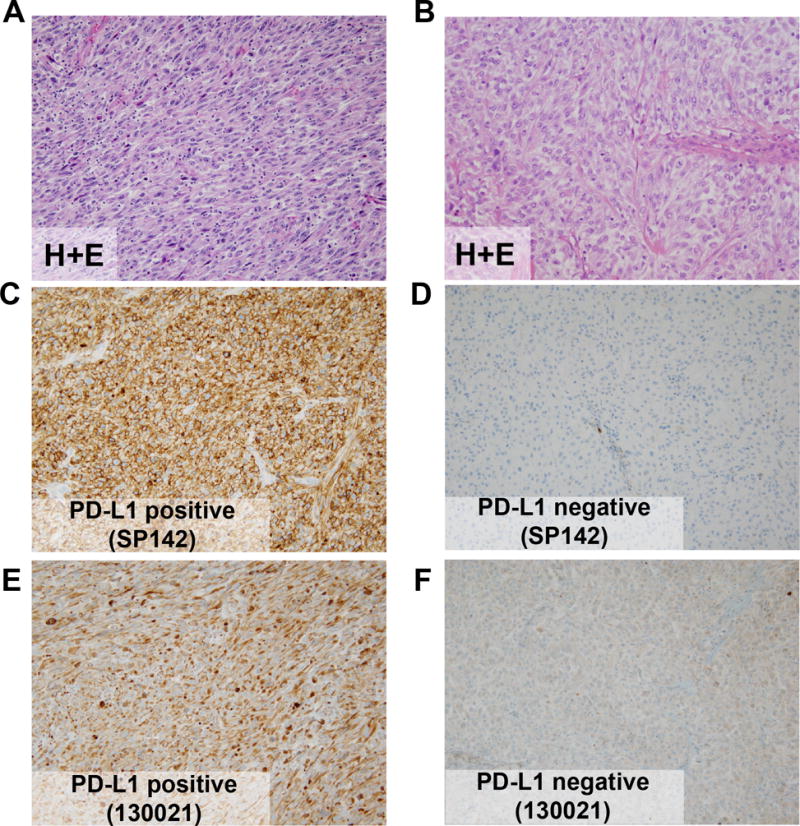
Representative PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Staining in Two Samples of RCC With Sarcomatoid Differentiation. A and B, Hematoxylin-eosin staining (H+E). C and D, Staining with SP142 anti–PD-L1 antibody showing positive (C) and negative staining (D). E and F, Staining with 130021 anti–PD-L1 antibody showing positive (E) and negative staining (F). Panels A, C, and E are from a PD-L1 positive RCC. Panels B, D, and F are from a PD-L1 negative RCC. All panels, original magnification ×20.
Coexpression of PD-1 and PD-L1
Of the 112 Caris cases, IHC results for both PD-1 and PD-L1 were available for 29 cases of ccRCC and seven cases of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. In the 26 total cases of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation, the presence of PD-1+ TILs was identified in 25 cases (96%) (Fig. 2). In contrast, PD-1+ TILs were identified in 18 of 29 cases of ccRCC (62%) (P=.003). PD-L1 expression was identified in 14 cases (54%) of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation and five cases (17%) of ccRCC (P=.006). Coexpression of PD-1/PD-L1 was identified in 13 cases (50%) of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. In contrast, only one ccRCC case (3%) had concurrent PD-1/PD-L1 expression (P=.002).
Figure 2.
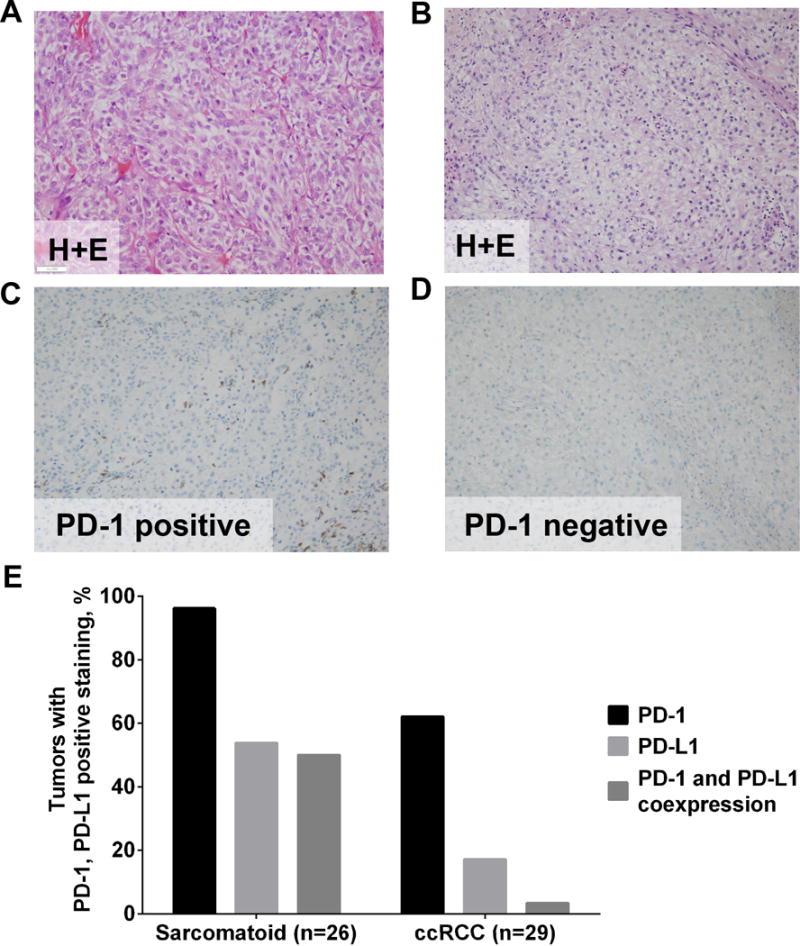
Representative Immunohistochemical Staining of PD-1 Expression in RCC With Sarcomatoid Features and Clear Cell RCC. Staining of sarcomatoid (A and C) and ccRCC (B and D) samples. A and B, Hematoxylin-eosin staining (H+E). C and D, Staining with anti–PD-1 antibody showing positive staining of sarcomatoid RCC (C) and negative staining of ccRCC (D). All panels, original magnification ×20. E, Percentage of tumors with PD-L1 expression (clone 130021), PD-1+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, or coexpression of PD-L1 and PD-1 in sarcomatoid RCC or ccRCC.
Tumor Response to Anti–PD-1 Immunotherapy
In April 2014, a 47-year-old man sought care for headaches and left-sided ptosis. Imaging revealed a right renal mass (5.9-cm lesion) with multifocal brain and lung metastases. A biopsy of a lung nodule confirmed sarcomatoid differentiation. He was started on palliative radiation to his brain metastases in April 2014, followed by sequential systemic therapies consisting of gemcitabine/doxorubicin (3 cycles), gemcitabine/capecitabine/bevacizumab (4 cycles), pazopanib (2 cycles), and axitinib (2 cycles) until March 2015. While he was taking axitinib, a new subcutaneous nodule developed and he underwent a core biopsy of the nodule to evaluate the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. The biopsy revealed 75% sarcomatoid differentiation with the remainder clear cell elements. The sarcomatoid component was PD-L1 positive (IHC 2+, 5%) and PD-1 negative (0 PD-1+TILs/high-power field) (Figure 3). On the basis of the PD-L1 expression, he was then treated with off-label pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg) beginning in March 2015. Imaging demonstrated disappearance of the biopsied PD-L1–positive subcutaneous nodule. To date, the patient has completed 4 cycles of pembrolizumab, and his most recent imaging in July 2015 showed mixed response, with progression in subcarinal lymph nodes and no recurrence of the previously biopsied nodule.
Figure 3.
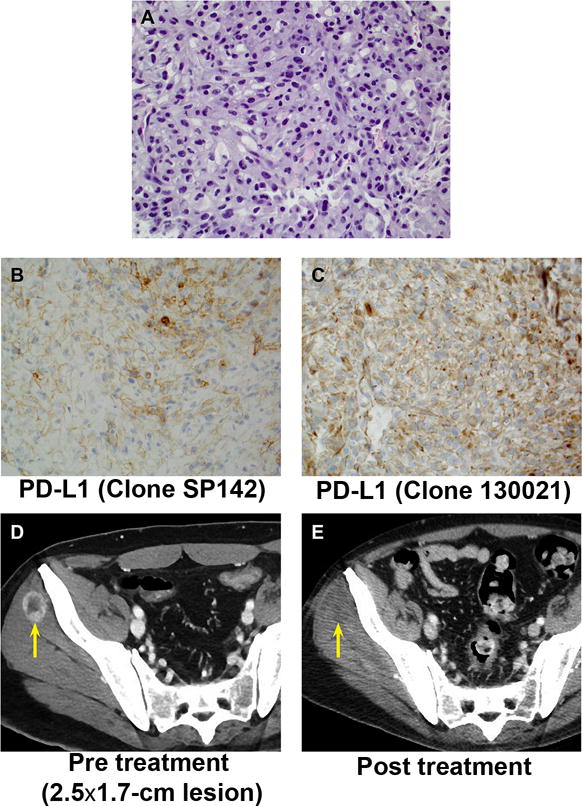
PD-L1 Expression and Tumor Response to Anti–PD-1 Immunotherapy in a Patient With Metastatic RCC With Sarcomatoid Differentiation. A–C, Staining of biopsied tumor nodule with hematoxylin-eosin (A), with antibody SP142 to PD-L1 (B) or with antibody 130021 to PD-L1 (C). All panels, original magnification ×40. D and E, Serial computed tomographic imaging of biopsied tumor nodule (arrow) before (D) and after (E) initiation of pembrolizumab.
Discussion
The presence of sarcomatoid histologic features in RCC is associated with a significantly worse prognosis. In addition, patients with RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation are thought not to be ideal candidates for high-dose IL-2 immunotherapy and only receive modest benefit from targeted therapies, when compared with ccRCC (7,8). Although PD-L1 expression has been studied in ccRCC and non-ccRCC, few data exist regarding the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation (12,13). To our knowledge, our study is the first report of increased expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells concurrent with PD-1+ TILs in RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. We also report the regression of a VEGF-refractory mRCC nodule with sarcomatoid differentiation after anti–PD-1 treatment, similar to a case presented by McDermott et al (14) with the anti-PD-L1 agent MPDL3280A. These cases continue to support the therapeutic potential of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade for sarcomatoid RCC.
Aberrant expression of PD-L1, as assessed by antibody clone 5H1, occurs in 24% of ccRCCs and is associated with more aggressive pathologic features including higher T stage and higher-grade tumors (15). PD-L1 expression, as assessed by clones SP142 and 130021, was identified in 17% of ccRCCs without sarcomatoid differentiation and 54% of RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation in our study. Concurrent PD-1/PD-L1 expression with sarcomatoid differentiation was observed in 50% of tested tumors, compared with 0% to 79% of various solid tumors in a prior study (11). Anti–PD-1 therapies are approved in the second-line setting by the US Food and Drug Administration for lung cancer and melanoma, which have concurrent PD-1/PD-L1 expression of 43% and 58%, respectively.
Reports have also demonstrated an inverse relationship between PD-L1 expression and VEGF activation. In the first report, Joseph et al (16) identified in ccRCC an inverse association between PD-L1 and genes in the VEGF pathway, including VEGFA, VEGFR1, and VEGFR2. In the second report, Choueiri et al (13) demonstrated that patients with PD-L1–positive tumors were less likely to respond to anti-VEGF tyrosine kinase inhibitors. These findings suggest that patients with PD-L1–positive RCC may benefit more from monoclonal antibodies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis than from traditional anti-VEGF agents. The presence of PD-1+ TILs suggests an increase in antitumor response, but despite the increased inflammatory infiltrates, the presence of sarcomatoid differentiation is associated with a poor response to targeted therapies and shorter overall survivals. The concurrent expression of PD-L1 may attenuate the antitumor response and negatively regulate the immune system.
Our study has several limitations. First, our study is retrospective and we could not define an amount of PD-L1 or PD-1 expression that was associated with response to therapeutic blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction. We dichotomized PD-L1 as positive or negative, based on a threshold determined in a phase I clinical trial of anti–PD-L1 immunotherapy, in which the SP142 clone was used to screen for PD-L1+ tumors (1). PD-L1 positivity was defined as 5% or more of tumor cells with a 20% PD-L1 prevalence by IHC in RCC tumors, and similar thresholds were used in multiple studies for both PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors (1,11). In our study, PD-L1 expression was identified in 54% and 17% of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation and ccRCC, respectively. Further study is warranted to identify expression thresholds linked to improved treatment responses.
Second, tumor heterogeneity can make the molecular characterization of sarcomatoid differentiation challenging to study because it can arise from various RCC histologies and is often intermixed with adjacent epithelial components. Discordant PD-L1 expression between primary kidney tumors and metastases was observed in 21% of samples in one study (17). For scoring PD-L1 and PD-1, only the sarcomatoid component was evaluated by our pathologists, and we did not segregate tumor-associated macrophages expressing PD-L1 (13). Serial slides from whole blocks were evaluated rather than tissue microarrays since tissue microarrays may not accurately represent PD-L1 and PD-1 heterogeneity (18). We directly compared two commercial PD-L1 antibodies on serial formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections and found concordance of PD-L1 positivity in 89% of tested RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation. We also assessed both PD-L1 expression and treatment response in a subcutaneous nodule after one cycle of pembrolizumab.
Third, our molecular profiling results were from tests ordered by clinicians as part of clinical care. There may be selection bias, and our cohort most likely represents more advanced cancer cases. Indeed, if our results are confirmed in future studies, these tumor subsets should not be excluded from clinical trials of monoclonal antibodies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis.
Compared with ccRCC, challenges exist in defining a standard of care for mRCC with sarcomatoid features. In an analysis of RCC treated with VEGF-directed therapy, no response was noted in RCC with sarcomatoid histologies making up more than 20% of the tumor (7). In a retrospective study, most patients had progressive disease as their best response to mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) therapy. Similarly, the presence of sarcomatoid histology is associated with poor responses to IL-2 immunotherapy (8). Cytotoxic chemotherapy is often initiated; in a phase II study of gemcitabine/ifosfamide, the median progression-free survival was 2.2 months (6,19). In a phase II trial using the combination of doxorubicin 50 mg/m2 and gemcitabine 1,500 mg/m2 every 2 weeks in 39 patients with RCC with sarcomatoid features, partial responses (16%) and stable disease (26%) were observed (20).
Our data indicate that RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation express both PD-L1 and PD-1, which supports the potential for therapeutic blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway for this entity that traditionally has poor responses to IL-2 immunotherapy.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank all patients and their families for their contributions to this study. We acknowledge the support provided by the Gloria A. and Thomas J. Dutson, Jr, Kidney Research Endowment (Mayo Clinic). This project was supported in part by funding from the Center for Individualized Medicine (CIM).
Grant Support: T. H. Ho is supported by funding from the ASCO Young Investigator Award from the Kidney Cancer Association, the Action to Cure Kidney Cancer, a Kathryn H. and Roger Penske Career Development Award to Support Medical Research, Gerstner Family Foundation Career Development Award and a US National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant (K12CA90628). R. W. Joseph is supported by a grant from the American Association of Cancer Research and the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine established through a gift from the Gerstner Family. This publication was made possible by CTSA Grant Number UL1 TR000135 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NIH.
Abbreviations
- ccRCC
clear cell RCC
- IHC
immunohistochemistry
- IL
interleukin
- mRCC
metastatic RCC
- PD-1
programmed death-1
- PD-1+TILs
PD-1–positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
- PD-L1
programmed death ligand-1
- RCC
renal cell carcinoma
- VEGF
vascular endothelial growth factor
Footnotes
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
D. Bryant, Z. Gatalica, and S. Reddy are employees of Caris Life Sciences. S. Z. Millis is a former employee of Caris Life Sciences. N. J. Vogelzang is consultant to Roche/Genentech and to Caris Life Sciences. T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, E. M. Carballido, A. H. Bryce, M. L. Stanton, and E. P. Castle have no disclosures.
Authors’ Contributions
Conception and design: T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, S. Z. Millis, E. M. Carballido, A. H. Bryce, E. P. Castle, and M. L. Stanton
Development of methodology: T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, A. H. Bryce, D. Bryant, Z. Gatalica, S. Z. Millis, and M. L. Stanton
Acquisition of data: T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, D. Bryant, S. Z. Millis, and M. L. Stanton
Analysis and interpretation of data: T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, E. P. Castle, S. Z. Millis, A. H. Bryce, N. J. Vogelzang, and M. L. Stanton
Writing and review of manuscript: T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, E. M. Carballido, S. Z. Millis, Z. Gatalica, N. J. Vogelzang, and M. L. Stanton
Study supervision: T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, E. P. Castle, N. J. Vogelzang, and M. L. Stanton
References
- 1.Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS, et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 2014 Nov 27;515(7528):563–7. doi: 10.1038/nature14011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ, Topalian SL, Hwu P, et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012 Jun 28;366(26):2455–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200694. Epub 2012 Jun 2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012 Jun 28;366(26):2443–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. Epub 2012 Jun 2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Negrier S, et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013 May;14(6):552–62. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70093-7. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Erratum in: Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jun;14(7):e254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shuch B, Said J, La Rochelle JC, Zhou Y, Li G, Klatte T, et al. Cytoreductive nephrectomy for kidney cancer with sarcomatoid histology: is up-front resection indicated and, if not, is it avoidable? J Urol. 2009 Nov;182(5):2164–71. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.07.049. Epub 2009 Sep 16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Escudier B, Droz JP, Rolland F, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Gravis G, Beuzeboc P, et al. Genitourinary Group of the French Federation of Cancer Centers Doxorubicin and ifosfamide in patients with metastatic sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: a phase II study of the Genitourinary Group of the French Federation of Cancer Centers. J Urol. 2002 Sep;168(3):959–61. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64551-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Golshayan AR, George S, Heng DY, Elson P, Wood LS, Mekhail TM, et al. Metastatic sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jan 10;27(2):235–41. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0000. Epub 2008 Dec 8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Leibovich BC, Han KR, Bui MH, Pantuck AJ, Dorey FJ, Figlin RA, et al. Scoring algorithm to predict survival after nephrectomy and immunotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a stratification tool for prospective clinical trials. Cancer. 2003 Dec 15;98(12):2566–75. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thompson RH, Dong H, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, et al. PD-1 is expressed by tumor-infiltrating immune cells and is associated with poor outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 15;13(6):1757–61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ho TH, Nateras RN, Yan H, Park JG, Jensen S, Borges C, et al. A multidisciplinary biospecimen bank of renal cell carcinomas compatible with discovery platforms at Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Arizona. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 16;10(7):e0132831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gatalica Z, Snyder C, Maney T, Ghazalpour A, Holterman DA, Xiao N, et al. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in common cancers and their correlation with molecular cancer type. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Dec;23(12):2965–70. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0654. Epub 2014 Nov 12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Choueiri TK, Fay AP, Gray KP, Callea M, Ho TH, Albiges L, et al. PD-L1 expression in nonclear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2014 Nov;25(11):2178–84. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu445. Epub 2014 Sep 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Choueiri TK, Figueroa DJ, Fay AP, Signoretti S, Liu Y, Gagnon R, et al. Correlation of PD-L1 tumor expression and treatment outcomes in patients with renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib or pazopanib: results from COMPARZ, a randomized controlled trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Mar 1;21(5):1071–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1993. Epub 2014 Dec 23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McDermott DF, Sznol M, Sosman JA, Soria JC, Gordon MS, Hamid O, et al. Immune correlates and long term follow up of a phase IA study of MPDL3280A, an engineered PD-L1 antibody, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (MRCC) [abstract] Ann Oncol. 2014;25(suppl 4):iv280. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu337.2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Dong H, Lohse CM, Webster WS, et al. Tumor B7-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 1;66(7):3381–5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Joseph RW, Parasramka M, Eckel-Passow JE, Serie D, Wu K, Jiang L, et al. Inverse association between programmed death ligand 1 and genes in the VEGF pathway in primary clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;1(6):378–85. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0042. Epub 2013 Aug 29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Callea M, Albiges L, Gupta M, Cheng SC, Genega EM, Fay AP, et al. Differential expression of PD-L1 between primary and metastatic sites in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 May 26; doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0043. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Eckel-Passow JE, Lohse CM, Sheinin Y, Crispen PL, Krco CJ, Kwon ED. Tissue microarrays: one size does not fit all. Diagn Pathol. 2010 Jul 7;5:48. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-5-48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bangalore N, Bhargava P, Hawkins MJ, Bhargava P. Sustained response of sarcomatoid renal-cell carcinoma to MAID chemotherapy: case report and review of the literature. Ann Oncol. 2001 Feb;12(2):271–4. doi: 10.1023/a:1008352024762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Haas NB, Lin X, Manola J, Pins M, Liu G, McDermott D, et al. A phase II trial of doxorubicin and gemcitabine in renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid features: ECOG 8802. Med Oncol. 2012 Jun;29(2):761–7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-9829-8. Epub 2011 Feb 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


