Abstract
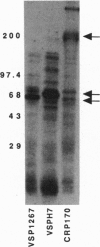
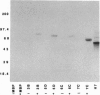
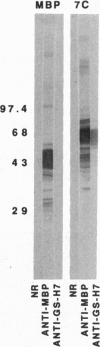
Giardia lamblia undergoes surface antigenic variation. The variant-specific surface proteins (VSPs) are a distinct family of cysteine-rich proteins. Characteristically, cysteine residues occur mostly as CXXC tetrapeptides. Four of the reported five VSPs contain a putative metal-binding domain that resembles other metal-binding motifs; the fifth is closely related but lacks an essential histidine. Three different native VSPs bound Zn2+. Co2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ inhibited Zn2+ binding. Analysis of recombinant VSP fusion proteins showed that the putative binding motif bound Zn2+. Surprisingly, peptide fragments from other regions of the VSP contain numerous CXXCXnCXXC motifs that also bound Zn2+. Analysis of deduced amino acid sequences showed well-conserved CXXC spacing in three out of five VSPs, suggesting conservation of structure despite amino acid sequence divergence. The function of VSPs is unknown, but by binding Zn2+ or other metals in the intestine, VSPs may contribute to Zn2+ malnutrition or inhibition of metal-dependent intestinal enzymes, which would lead to malabsorption, a well-known consequence of giardiasis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D., Aggarwal A., Lal A. A., de La Cruz V. F., McCutchan T., Nash T. E. Antigenic variation of a cysteine-rich protein in Giardia lamblia. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):109–118. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam R. D., Yang Y. M., Nash T. E. The cysteine-rich protein gene family of Giardia lamblia: loss of the CRP170 gene in an antigenic variant. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1194–1201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal A., Merritt J. W., Jr, Nash T. E. Cysteine-rich variant surface proteins of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 1;32(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Nichols C. R., Fukushima T. An outbreak of giardiasis in a group of campers. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 May;25(3):384–389. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinert H. Recent developments in the field of iron-sulfur proteins. FASEB J. 1990 May;4(8):2483–2491. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.8.2185975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. Elements for interactions between macromolecules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6513–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Dykes A. C., Sinclair S. P., Wells J. G. Giardiasis in day-care centers: evidence of person-to-person transmission. Pediatrics. 1977 Oct;60(4):486–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Foroni L., Kennedy M., Rabbitts T. H. The rhombotin gene belongs to a class of transcriptional regulators with a potential novel protein dimerisation motif. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1103–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky R. E., Spencer H. C., Jr, Schultz M. G. Giardiasis in American travelers to the Soviet Union. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):319–323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foroni L., Boehm T., White L., Forster A., Sherrington P., Liao X. B., Brannan C. I., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Rabbitts T. H. The rhombotin gene family encode related LIM-domain proteins whose differing expression suggests multiple roles in mouse development. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):747–761. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90630-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyd G., Kim S. K., Horvitz H. R. Novel cysteine-rich motif and homeodomain in the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell lineage gene lin-11. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):876–879. doi: 10.1038/344876a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Hagblom P., Harwood J., Aley S. B., Reiner D. S., McCaffery M., So M., Guiney D. G. Isolation and expression of the gene for a major surface protein of Giardia lamblia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4463–4467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard A. D., Borrow J., Freemont P. S., Solomon E. Characterization of a zinc finger gene disrupted by the t(15;17) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1720570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. E6 protein of human papillomavirus type 18 binds zinc. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1089–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Alexander W. S., Barri G., Klinken S. P., Adams J. M. Novel zinc finger gene implicated as myc collaborator by retrovirally accelerated lymphomagenesis in E mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90383-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempe J. M., Cousins R. J. Cysteine-rich intestinal protein binds zinc during transmucosal zinc transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9671–9674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. E., Henderson S. T., Petes T. D., Prakash S., Bankmann M., Prakash L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD5-encoded DNA repair protein contains DNA helicase and zinc-binding sequence motifs and affects the stability of simple repetitive sequences in the genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3807–3818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Thor S., Norberg T., Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Insulin gene enhancer binding protein Isl-1 is a member of a novel class of proteins containing both a homeo- and a Cys-His domain. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):879–882. doi: 10.1038/344879a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. F., McRee D. E., Fisher C. L., O'Handley S. F., Cunningham R. P., Tainer J. A. Atomic structure of the DNA repair [4Fe-4S] enzyme endonuclease III. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):434–440. doi: 10.1126/science.1411536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Serup P., Gonzalez G., Edlund T., Montminy M. The LIM family transcription factor Isl-1 requires cAMP response element binding protein to promote somatostatin expression in pancreatic islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6247–6251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P. M., Reichert J., Freyd G., Horvitz H. R., Walsh C. T. The LIM region of a presumptive Caenorhabditis elegans transcription factor is an iron-sulfur- and zinc-containing metallodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9210–9213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Aggarwal A., Nash T. E. Carboxy-terminal sequence conservation among variant-specific surface proteins of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90065-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Aggarwal A., Adam R. D., Conrad J. T., Merritt J. W., Jr Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Aggarwal A. Cytotoxicity of monoclonal antibodies to a subset of Giardia isolates. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2628–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Banks S. M., Alling D. W., Merritt J. W., Jr, Conrad J. T. Frequency of variant antigens in Giardia lamblia. Exp Parasitol. 1990 Nov;71(4):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90067-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Conrad J. T., Merritt J. W., Jr Variant specific epitopes of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Aug;42(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90120-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Gillin F. D., Smith P. D. Excretory-secretory products of Giardia lamblia. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2004–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Herrington D. A., Levine M. M., Conrad J. T., Merritt J. W., Jr Antigenic variation of Giardia lamblia in experimental human infections. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4362–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Keister D. B. Differences in excretory-secretory products and surface antigens among 19 isolates of Giardia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1166–1171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., McCutchan T., Keister D., Dame J. B., Conrad J. D., Gillin F. D. Restriction-endonuclease analysis of DNA from 15 Giardia isolates obtained from humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):64–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Merritt J. W., Jr, Conrad J. T. Isolate and epitope variability in susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to intestinal proteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1334–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1334-1340.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Mowatt M. R. Characterization of a Giardia lamblia variant-specific surface protein (VSP) gene from isolate GS/M and estimation of the VSP gene repertoire size. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Apr;51(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90072-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Mowatt M. R. Identification and characterization of a Giardia lamblia group-specific gene. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Dec;75(4):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90250-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. Surface antigen variability and variation in Giardia lamblia. Parasitol Today. 1992 Jul;8(7):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90119-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Inostroza J., Maxon M. E., Flores O., Admon A., Reinberg D., Tjian R. Structure and functional properties of human general transcription factor IIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):369–373. doi: 10.1038/354369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimenta P. F., da Silva P. P., Nash T. Variant surface antigens of Giardia lamblia are associated with the presence of a thick cell coat: thin section and label fracture immunocytochemistry survey. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3989–3996. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3989-3996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. A., Etkin L. D., Freemont P. S. A novel zinc finger coiled-coil domain in a family of nuclear proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Sep;17(9):344–345. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90308-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Characterization of a zinc blotting technique: evidence that a retroviral gag protein binds zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmerin M. J., Jones T. C., Klein H. Giardiasis: association with homosexuality. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jun;88(6):801–803. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-6-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster T. A., Nagy A. K., Conly D. C., Farber D. B. Direct zinc binding to purified rhodopsin and disc membranes. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):123–128. doi: 10.1042/bj2820123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udomkesmalee E., Dhanamitta S., Sirisinha S., Charoenkiatkul S., Tuntipopipat S., Banjong O., Rojroongwasinkul N., Kramer T. R., Smith J. C., Jr Effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on the nutriture of children in Northeast Thailand. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Jul;56(1):50–57. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/56.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Lee G., Liebhaber S. A., Cooke N. E. Human cysteine-rich protein. A member of the LIM/double-finger family displaying coordinate serum induction with c-myc. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9176–9184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. Y., Aley S. B., Stanley S. L., Jr, Gillin F. D. Cysteine-dependent zinc binding by membrane proteins of Giardia lamblia. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):520–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.520-524.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]