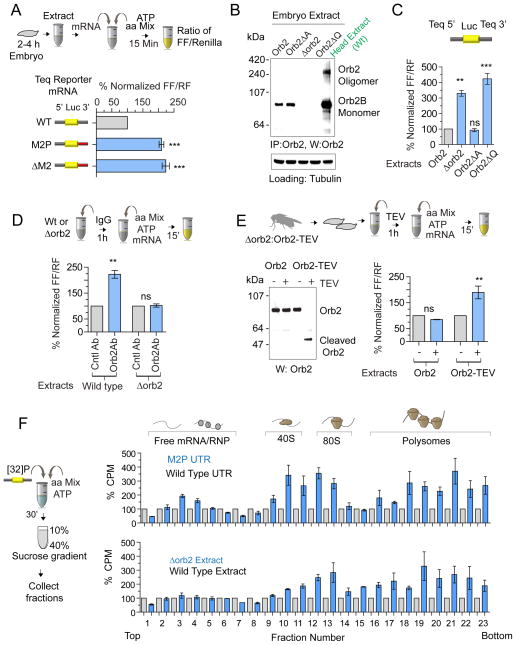
Figure 2. Orb2 acts as a translational repressor.
(A) Loss of Orb2 recruitment increases protein expression in vitro. Top panel: Schematic of the in vitro translation assay using Drosophila embryo extract. Lower panel: normalized ratio of firefly and Renilla enzyme activity of 3 independent experiments. Each experiment was comprised of three technical repeats. (B) Embryonic translation extract contains only monomeric Orb2B unlike adult head extract, which contains both Orb2 monomer and oligomer. The Δorb2 flies lack the entire Orb2 locus, the Orb2ΔQ lacks the Q-rich 80 amino acids common to Orb2A/B and Orb2ΔA lacks only the Orb2A-specific exon. Tubulin serves as loading control. (C) The absence of Orb2 enhances wild type Tequila reporter expression. (D) Treatment of embryo extract with anti-Orb2 antibody enhances reporter expression. Addition of Orb2 antibody in extract lacking Orb2 (Δorb2) has no effect. (E) Acute inactivation of Orb2 enhances translation. Top panel: A genomic rescue fragment in orb2 null background that contains a TEV-protease site within the Orb2 gene. Left panel: Western blot analysis of TEV enzyme treated wild type and Orb2-TEV embryo extract. Right panel: addition of TEV in Orb2-TEV, but not wild type (Orb2) embryo extract enhances reporter expression. (F) Polysome profile analysis of in vitro translation reaction shows the relative abundance of translating mRNA. Left panel: schematic of polysome assay using [P32]-label mRNA. Right upper panel: mutant reporter (M2P) mRNA is more abundant in polysome fractions compared to wild type. Right lower panel: wild type reporter is more abundant in polysome when translated in Δorb2 embryo extract. Data is expressed as mean ± SEM and * <0.01, ** <0.001 and *** <0.0001 indicates p value. Please also see supplementary figure 2.