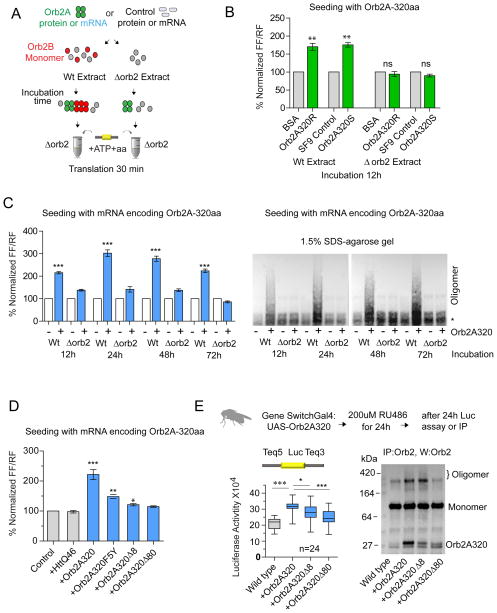
Figure 4. Orb2A N-terminal prion-like domain converts monomeric Orb2B to a translational activator.
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental design. The wild type embryo extract was used as source for monomeric Orb2B. The Δorb2 extract, same amount of purified BSA or similar amount of Sf9 cell extracts serve as a controls. (B) The N-terminal 320aa of Orb2A isolated from bacteria (Orb2A320R) or Sf9 cells (Orb2A320S) enhance translation only in wild type extract. The seeding reaction was carried out for 12 hours at 4°C and translation was measured after 15 min. (C) The mRNA expressing Orb2A320 enhances translation and induces Orb2B oligomerization. The seeding reaction was performed for the indicated time and subsequently translation (left panel) and the oligomeric state of Orb2 (right panel) were assessed in 1.5% SDS-agarose gel. The * indicates a non-specific immunoreactive band visible upon long exposure. (D) Mutation that affects the oligomerization of Orb2A also attenuates its ability to enhance translation. (E) Transient expression of the Orb2A320 using Gene switch Gal4 enhances translation in the adult fly brain (left panel) and Orb2-oligomerization (right panel). Removal of the N-terminal 80 amino acids significantly reduces both activities. Data is expressed as mean ± SEM and * <0.05, ** <0.01, *** <0.001 indicates p value and ns indicates not significant. Please also see supplementary figure 5.