Abstract
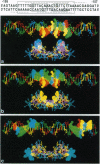
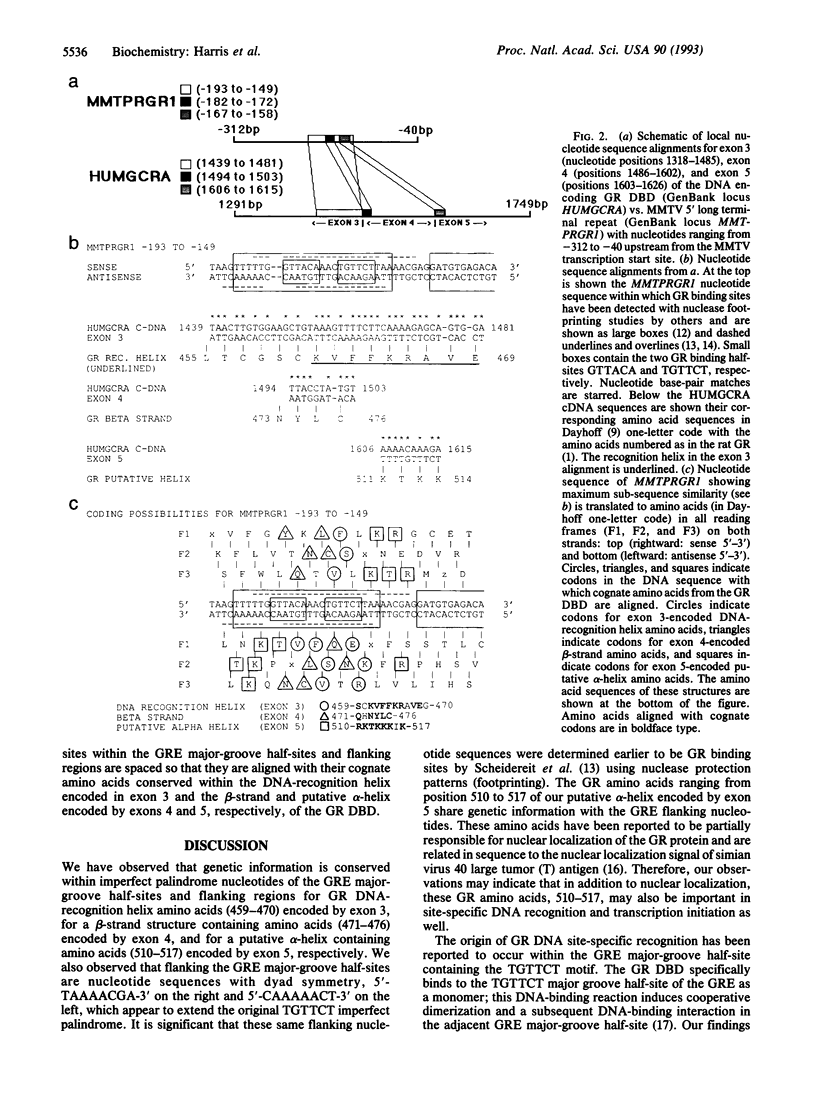
We present findings of genetic information conservation between the glucocorticoid response element (GRE) DNA and the cDNA encoding the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) DNA-binding domain (DBD). The regions of nucleotide sub-sequence similarity to the GRE in the GR DBD occur specifically at nucleotide sequences on the ends of exons 3,4, and 5 at their splice junction sites. These sequences encode the DNA recognition helix on exon 3, a beta-strand on exon 4, and a putative alpha-helix on exon 5, respectively. The nucleotide sequence of exon 5 that encodes the putative alpha-helix located on the carboxyl terminus of the GR DBD shares sequence similarity with the flanking nucleotide regions of the GRE. We generated a computer model of the GR DBD using atomic coordinates derived from nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to which we attached the exon 5-encoded putative alpha-helix. We docked this GR DBD structure at the 39-base-pair nucleotide sequence containing the GRE binding site and flanking nucleotides, which contained conserved genetic information. We observed that amino acids of the DNA recognition helix, the beta-strand, and the putative alpha-helix are spatially aligned with trinucleotides identical to their cognate codons within the GRE and its flanking nucleotides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al'tshtein A. D., Efimov A. V. Fiziko-khimicheskaia osnova proiskhozhdeniia geneticheskogo koda: stereokhimicheskii analiz vzaimodeistviia aminokislot i nukleotidov na osnove gipotezy progenov. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1988 Sep-Oct;22(5):1411–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B. Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstein K. L., Jewell C. M., Cidlowski J. A. Human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA contains sequences sufficient for receptor down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7284–7291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjarlais J. R., Berg J. M. Redesigning the DNA-binding specificity of a zinc finger protein: a data base-guided approach. Proteins. 1992 Feb;12(2):101–104. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Encío I. J., Detera-Wadleigh S. D. The genomic structure of the human glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7182–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry L. B., Bransome E. D., Jr, Hutson M. S., Campbell L. K. A newly discovered stereochemical logic in the structure of DNA suggests that the genetic code is inevitable. Perspect Biol Med. 1984 Summer;27(4):623–651. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1984.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungck J. R. The genetic code as a periodic table. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):211–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01734482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothekar V. Transcription regulation by steroid hormones: a computer simulation study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1992 Aug;10(1):49–62. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1992.10508629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey J. C., Jr, Mullins D. W., Jr Experimental studies related to the origin of the genetic code and the process of protein synthesis--a review. Orig Life. 1983 Mar;13(1):3–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00928761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey J. C., Jr, Mullins D. W., Jr, Khaled M. A. The case for the anticode. Orig Life. 1984;14(1-4):505–511. doi: 10.1007/BF00933698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L. Amino acid catalyzed condensation of purines and pyrimidines with 2-deoxyribose. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2843–2846. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L. Amino acid-directed nucleic acid synthesis. A possible mechanism in the origin of life. J Mol Evol. 1978 Jun 20;11(2):109–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01733887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieber M., Tohá J. Code dependent conservation of the physico-chemical properties in amino acid substitutions. Orig Life. 1983 Dec;13(2):139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00928891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxinger C., Ponnamperuma C. Interactions between amino acids and nucleotides in the prebiotic milieu. Orig Life. 1974 Jan-Apr;5(1):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Beato M. Contacts between hormone receptor and DNA double helix within a glucocorticoid regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3029–3033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):458–461. doi: 10.1038/348458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström M., Wold S. A multivariate study of the relationship between the genetic code and the physical-chemical properties of amino acids. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):272–277. doi: 10.1007/BF02099756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. Models for the evolution of codon assignments. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. An RNA-amino acid complex and the origin of the genetic code. New Biol. 1991 Feb;3(2):183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Christian E. L. Genetic code origins. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):349–350. doi: 10.1038/342349b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]