Summary
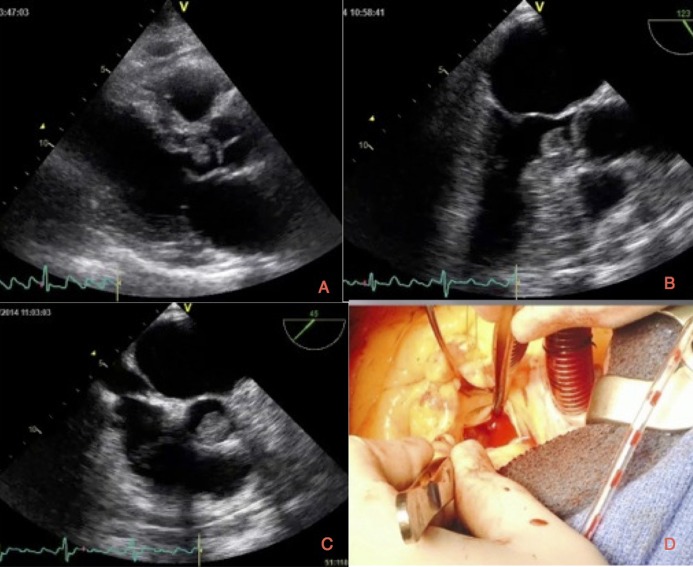
A 69-year-old gentleman presented with sudden-onset dizziness and diplopia. Clinical examination findings were suggestive of posterior circulation stroke. He was found to be in atrial flutter on admission, reverting spontaneously to sinus rhythm. Three weeks before admission, he was admitted to a different hospital with anterior circulation stroke, which left him with minor residual weakness. He was found to be in sinus rhythm during that admission and was discharged home on dual-anti platelet therapy. Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) performed to exclude a cardiac source of emboli showed a highly mobile echogenic structure in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) attached to the interventricular septum (Fig. 1A and Video 1). Subsequent transoesophageal echocardiogram (TOE) confirmed a highly mobile mass in the LVOT, which appears to be prolapsing through the aortic valve (Fig. 1B, C and Videos 2, 3). The left atrium and appendage are free of spontaneous contrast or thrombus and there are no atherosclerotic plaques noted in the aorta. Given the history of recurrent stroke, the highly mobile nature of the mass and its position in the LVOT, the patient was referred for urgent surgery. The patient underwent complete surgical excision of the mass (Fig. 1D), which was then confirmed to be benign papillary fibroelastoma (PFE) on histopathology. PFE is the second most common cardiac tumour which usually originate from the valvular endothelium. PFE arising from this non-valvular location is exceptionally rare. When present in such a location, they are often mistaken for myxoma from TTE and usually warrants further imaging such as TOE or cardiac MRI to confirm diagnosis. Surgery is curative in most cases and prompt referral should be considered (1).
Figure 1.
(A) Transthoracic echocardiogram (PLAX view) showing the mass in the LVOT attached to the inter-ventricular septum. (B) Transoesophageal echocardiogram confirming the mass measuring 1.1×1.1 cm in the LVOT attached to the inter-ventricular septum. (C) Transoesophageal echocardiogram showing the mass prolapsing through the aortic valve. (D) Intraoperative picture showing the jelly-like mass attached to the inter-ventricular septum.
Transthoracic echocardiogram (PLAX view) showing a highly mobile mass in the LVOT attached to the inter-ventricular septum. Download Video 1 via http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERP-14-0080-v1.
Download Video 1 (840.4KB, avi)
Transoesophageal echocardiogram showing a highly mobile mass in the LVOT which appears to prolapsing through the aortic valve. Download Video 2 via http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERP-14-0080-v2.
Download Video 2 (1.1MB, avi)
Transoesophageal echocardiogram showing a highly mobile mass in the LVOT which appears to prolapsing through the aortic valve. Download Video 3 via http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERP-14-0080-v3.
Download Video 3 (1.3MB, avi)
Patient consent
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient.
Author contribution statement
B Sekar was responsible for managing the patient along with cardiologist in-charge and helped in manuscript preparation. H Vohra performed the surgery and helped in manuscript preparation. S Nishtar performed the TOE and helped in manuscript preparation. J Ehtisham is the cardiologist in-charge of the patient and critically revised the paper.
Reference
- 1. Bossert T Gummert JF Battellini R Richter M Barten M Walther T Falk V Mohr FW Surgical experience with 77 primary cardiac tumors Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 4 2005. 311–315. 10.1510/icvts.2004.103044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Transthoracic echocardiogram (PLAX view) showing a highly mobile mass in the LVOT attached to the inter-ventricular septum. Download Video 1 via http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERP-14-0080-v1.
Download Video 1 (840.4KB, avi)
Transoesophageal echocardiogram showing a highly mobile mass in the LVOT which appears to prolapsing through the aortic valve. Download Video 2 via http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERP-14-0080-v2.
Download Video 2 (1.1MB, avi)
Transoesophageal echocardiogram showing a highly mobile mass in the LVOT which appears to prolapsing through the aortic valve. Download Video 3 via http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERP-14-0080-v3.
Download Video 3 (1.3MB, avi)



 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a