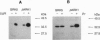Abstract
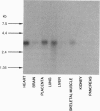
Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G-protein)-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) specifically phosphorylate the agonist-occupied form of G-protein-coupled receptors such as the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin. The best characterized members of this family include the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase (beta ARK) and rhodopsin kinase. To identify additional members of the GRK family, the polymerase chain reaction was used to amplify human heart cDNA using degenerate oligonucleotide primers from highly conserved regions unique to the GRK family. Here we report the isolation of a cDNA that encodes a 590-amino acid protein kinase, termed GRK5, which has 34.8% and 47.2% amino acid identities with beta ARK and rhodopsin kinase, respectively. Interestingly, GRK5 has an even higher homology with Drosophila GPRK-2 (71.0% identity) and the recently identified human IT11 (69.1% identity). Northern blot analysis of GRK5 with selected human tissues reveals a message of approximately 3 kilobases with highest levels in heart, placenta, lung > skeletal muscle > brain, liver, pancreas > kidney. GRK5, overexpressed in Sf9 insect cells using the baculovirus system, was able to phosphorylate rhodopsin in a light-dependent manner. In addition, GRK5 neither contains a consensus sequence for isoprenylation like rhodopsin kinase nor is activated by G-protein beta gamma subunits like beta ARK1. Thus, GRK5 represents a member of the GRK family that likely has a unique physiological role.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrose C., James M., Barnes G., Lin C., Bates G., Altherr M., Duyao M., Groot N., Church D., Wasmuth J. J. A novel G protein-coupled receptor kinase gene cloned from 4p16.3. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):697–703. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., DeBlasi A., Stone W. C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: primary structure delineates a multigene family. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):235–240. doi: 10.1126/science.2552582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Onorato J. J., Arriza J. L., Stone W. C., Lohse M., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2. A new member of the receptor kinase family. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14939–14946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Regan J. W., Matsui H., Mayor F., Jr, Cotecchia S., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17251–17253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownds D., Dawes J., Miller J., Stahlman M. Phosphorylation of frog photoreceptor membranes induced by light. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):125–127. doi: 10.1038/newbio237125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassill J. A., Whitney M., Joazeiro C. A., Becker A., Zuker C. S. Isolation of Drosophila genes encoding G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11067–11070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Glickman J. F., Lorenz W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Isoprenylation of a protein kinase. Requirement of farnesylation/alpha-carboxyl methylation for full enzymatic activity of rhodopsin kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1422–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Koch W. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Isoprenylation in regulation of signal transduction by G-protein-coupled receptor kinases. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):147–150. doi: 10.1038/359147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra M. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Hosey M. M. Phosphorylation of chick heart muscarinic cholinergic receptors by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4543–4547. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra M. M., Hosey M. M. Phosphorylation of the cardiac muscarinic receptor in intact chick heart and its regulation by a muscarinic agonist. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12429–12432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Dreyer W. J. Light dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin by ATP. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Ostrowski J., Chesnut L. C., Kurose H., Raymond J. R., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Sites in the third intracellular loop of the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor confer short term agonist-promoted desensitization. Evidence for a receptor kinase-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4740–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple pathways of rapid beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Delineation with specific inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3202–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz W., Inglese J., Palczewski K., Onorato J. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The receptor kinase family: primary structure of rhodopsin kinase reveals similarities to the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8715–8719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier K., Klein C. An unusual protein kinase phosphorylates the chemotactic receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2181–2185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Structure of the adrenergic and related receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:67–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Benovic J. L. G-protein-coupled receptor kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90157-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher J. A., Inglese J., Higgins J. B., Arriza J. L., Casey P. J., Kim C., Benovic J. L., Kwatra M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Role of beta gamma subunits of G proteins in targeting the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase to membrane-bound receptors. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1264–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.1325672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reneke J. E., Blumer K. J., Courchesne W. E., Thorner J. The carboxy-terminal segment of the yeast alpha-factor receptor is a regulatory domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichi H., Somers R. L. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin. Purification and properties of rhodopsin kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):7040–7046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan R. A., Devreotes P. N. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of the cAMP receptor from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14538–14543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Kühn H. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin: number of phosphorylation sites. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):3014–3022. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]