Abstract
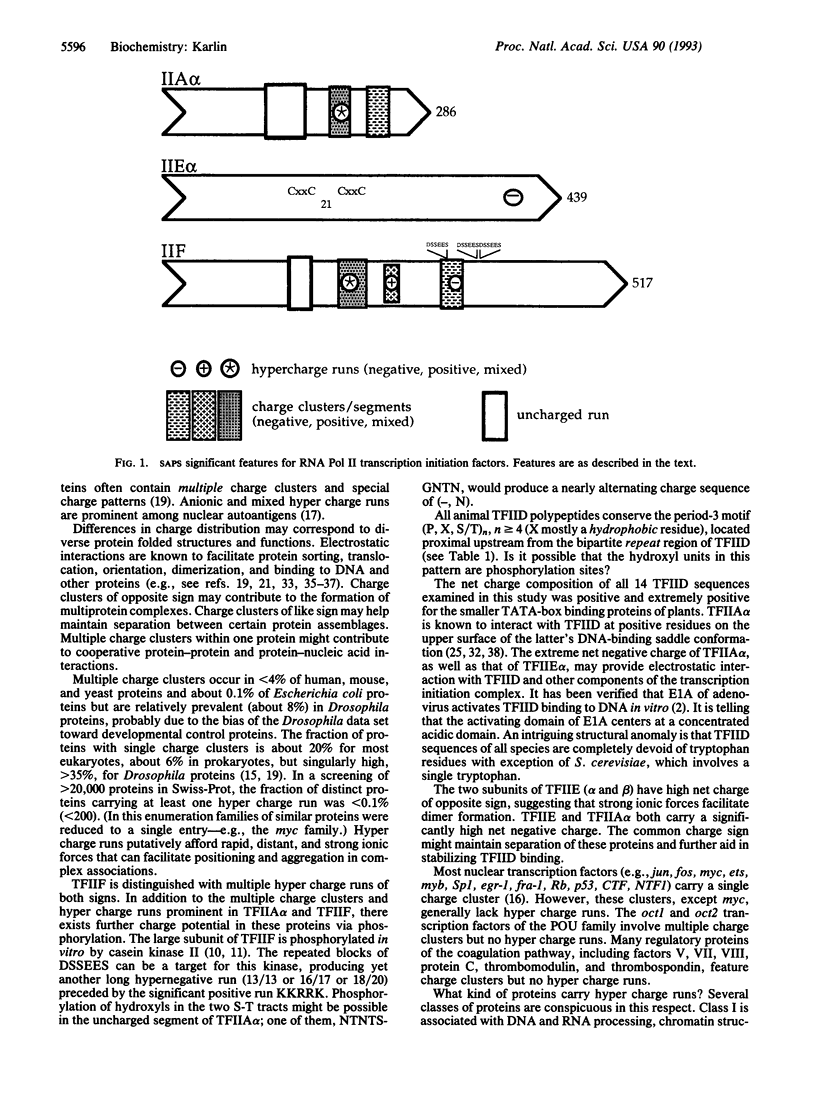
A systematic analysis of the primary sequences of the polymerase II initiation complex has revealed unusual charge features in the TFII family proteins. In particular, the proteins TFIIA alpha, TFIIE alpha, and TFIIF carry multiple charge clusters and hyper charge runs, sequence features occurring in < 4% of all (available) eukaryotic proteins. Possible implications for these charge structures are discussed in relation to the assembly and function of the polymerase II transcriptional complex.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aso T., Vasavada H. A., Kawaguchi T., Germino F. J., Ganguly S., Kitajima S., Weissman S. M., Yasukochi Y. Characterization of cDNA for the large subunit of the transcription initiation factor TFIIF. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):461–464. doi: 10.1038/355461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Bucher P., Nourbakhsh I. R., Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Methods and algorithms for statistical analysis of protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Dohlman J., Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Very long charge runs in systemic lupus erythematosus-associated autoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1536–1540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Karlin S. Association of charge clusters with functional domains of cellular transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bungert J., Waldschmidt R., Kober I., Seifart K. H. Transcription factor IIA is inactivated during terminal differentiation of avian erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11678–11682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. Transcription factor IID mutants defective for interaction with transcription factor IIA. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1130–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1546314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C. Anionic regions in nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1479–1482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Kostrub C. F., Li J., Chavez D. P., Wang B. Q., Fang S. M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F. A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):464–467. doi: 10.1038/355464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gileadi O., Feaver W. J., Kornberg R. D. Cloning of a subunit of yeast RNA polymerase II transcription factor b and CTD kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1389–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.1445600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. RNA polymerase-associated transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90165-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Transcription. Riding high on the TATA box. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):16–17. doi: 10.1038/360016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Fujita H., Hasegawa S., Roeder R. G., Horikoshi M. Conserved structural motifs within the N-terminal domain of TFIID tau from Xenopus, mouse and human. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3788–3788. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A., Sinn E., Yamamoto T., Wang J., Roy A., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Highly conserved core domain and unique N terminus with presumptive regulatory motifs in a human TATA factor (TFIID). Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):387–390. doi: 10.1038/346387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Blaisdell B. E., Brendel V. Identification of significant sequence patterns in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:388–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Blaisdell B. E., Bucher P. Quantile distributions of amino acid usage in protein classes. Protein Eng. 1992 Dec;5(8):729–738. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.8.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Brendel V., Bucher P. Significant similarity and dissimilarity in homologous proteins. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Jan;9(1):152–167. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Brendel V. Charge configurations in oncogene products and transforming proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Bucher P., Brendel V., Altschul S. F. Statistical methods and insights for protein and DNA sequences. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:175–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Chasman D. I., Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K., Kornberg R. D. Yeast and human TFIIDs are interchangeable for the response to acidic transcriptional activators in vitro. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):296–303. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Granston A. E. Similarity between the DNA-binding domains of IHF protein and TFIID protein. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1037–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90280-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov D. B., Hu S. H., Lin J., Gasch A., Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Chua N. H., Roeder R. G., Burley S. K. Crystal structure of TFIID TATA-box binding protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):40–46. doi: 10.1038/360040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Hashimoto S., Roeder R. G., Horikoshi M. Structural conservation of putative functional motifs between Xenopus and human TFIIE-beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4363–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Diverse transcriptional functions of the multisubunit eukaryotic TFIID complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranish J. A., Lane W. S., Hahn S. Isolation of two genes that encode subunits of the yeast transcription factor IIA. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.1546313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. The complexities of eukaryotic transcription initiation: regulation of preinitiation complex assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90164-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. TATA-binding protein is a classless factor. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):819–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Sumita K., Fujino I., Aoyama A., Horikoshi M., Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G., Muramatsu M., Mikoshiba K. Striking homology of the 'variable' N-terminal as well as the 'conserved core' domains of the mouse and human TATA-factors (TFIID). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3861–3865. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J. Investigating protein-protein interaction surfaces using a reduced stereochemical and electrostatic model. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 20;206(2):381–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90487-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R. The basic RNA polymerase II transcriptional machinery. Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):81–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Horikoshi M., Wang J., Hasegawa S., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. A bipartite DNA binding domain composed of direct repeats in the TATA box binding factor TFIID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita S., Wada K., Horikoshi M., Gong D. W., Kokubo T., Hisatake K., Yokotani N., Malik S., Roeder R. G., Nakatani Y. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding Drosophila transcription factor TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Net N-C charge imbalance may be important for signal sequence function in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



