Abstract
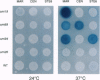
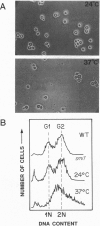
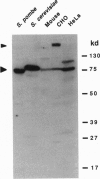
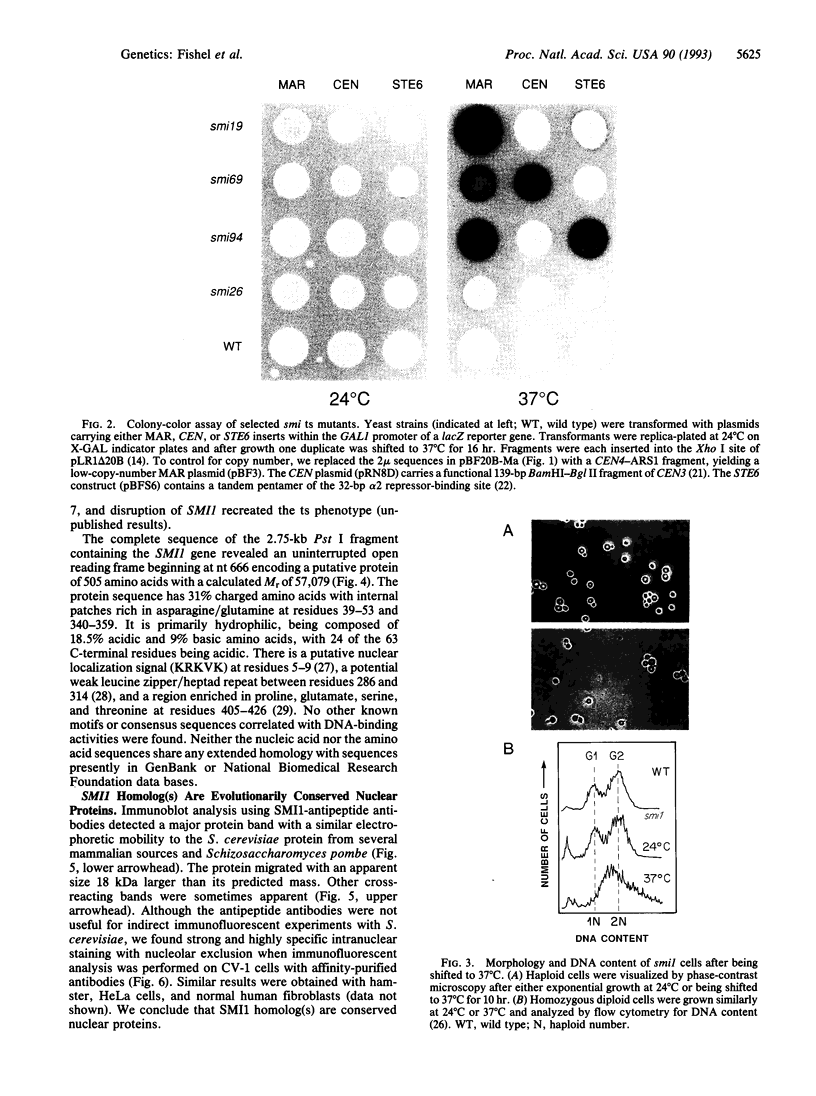
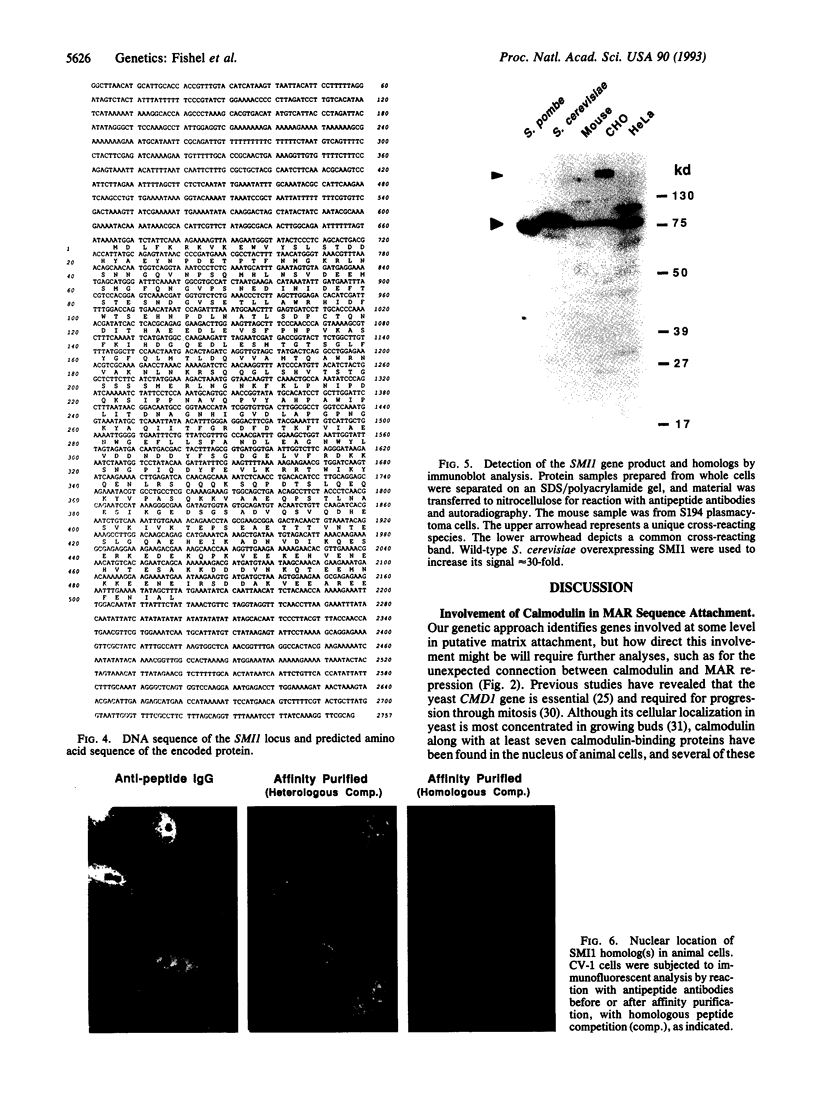
Chromatin becomes reorganized during mitosis each cell cycle. To identify genes potentially involved in these supramolecular events, we have used a colony-color assay to screen temperature-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. When a sequence that mediates attachment to the nuclear matrix in vitro was inserted into the GAL1 promoter of a lacZ fusion gene, beta-galactosidase synthesis was inhibited. This observation permitted screening for temperature-sensitive-inducible mutants on 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl beta-D-galactoside plates. Only 1 of 20 complementation groups of newly isolated mutants exhibited temperature-sensitive inducibility for the matrix association region but not for control CEN3 or STE6 inserts--a cmd1 mutant in which the last 7 amino acids of calmodulin were truncated by an ochre termination codon. Another mutant (smi1) exhibited a rare phenotype at the nonpermissive condition, which included S phase and budding arrest. We cloned and sequenced the SMI1 gene, which encodes a 57-kDa polypeptide with evolutionarily conserved epitope(s) found in mammalian cell nuclei. Thus, we provide evidence for involvement of calmodulin and another conserved protein in the in vivo binding of a matrix association region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Gasser S. M. Drosophila scaffold-attached regions bind nuclear scaffolds and can function as ARS elements in both budding and fission yeasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5442–5454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachs O., Lanini L., Serratosa J., Coll M. J., Bastos R., Aligué R., Rius E., Carafoli E. Calmodulin-binding proteins in the nuclei of quiescent and proliferatively activated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18595–18600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockerhoff S. E., Davis T. N. Calmodulin concentrates at regions of cell growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):619–629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. N. A temperature-sensitive calmodulin mutant loses viability during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):607–617. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. N., Urdea M. S., Masiarz F. R., Thorner J. Isolation of the yeast calmodulin gene: calmodulin is an essential protein. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman L. A., Garrard W. T. DNA supercoiling in chromatin structure and gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):165–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M., Yanagida M. The TPR snap helix: a novel protein repeat motif from mitosis to transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90070-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Chang M., Kim U. J., Grunstein M. Histone H2B repression causes cell-cycle-specific arrest in yeast: effects on chromosomal segregation, replication, and transcription. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Laroche T., Brand A. H., Gasser S. M. RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90788-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Herskowitz I. A repressor (MAT alpha 2 Product) and its operator control expression of a set of cell type specific genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Redd M. J., Schultz J., Carlson M., Johnson A. D. Ssn6-Tup1 is a general repressor of transcription in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ktistakis N. T., Roth M. G., Bloom G. S. PtK1 cells contain a nondiffusible, dominant factor that makes the Golgi apparatus resistant to brefeldin A. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1009–1023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périer F., Carbon J. A colony color assay for Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants defective in kinetochore structure and function. Genetics. 1992 Sep;132(1):39–51. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Regulation of enzyme levels by proteolysis: the role of pest regions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1988;27:135–151. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(88)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The selection of S. cerevisiae mutants defective in the start event of cell division. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):561–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Broach J. R. Cloning genes by complementation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:195–230. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry A. O., Fishel B. R., Garrard W. T. Mutations that affect nuclear organization in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;35:525–541. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60586-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]