Abstract
Myeloid sarcoma (MS) is defined as a tumor mass consisting of myeloid blast with or without maturation occurring at an anatomical site other than bone marrow with normal architectural effacement. It can also precede the onset of leukemia which is called non-leukemic MS. Non-leukemic MS is a kind of rare disease and easy to be misdiagnosed as other common malignancies due to the rarity and nonspecific manifestation. We herein report an unusual case of non-leukemic MS involving the vulva, vagina, and cervix in a female patient. The bone marrow aspiration and biopsy of the patient revealed no hematological abnormality. Immunohistochemical staining of the biopsies was strongly positive for myeloperoxidase, CD68, leukocyte common antigen (LCA), CD117, CD34, CD38, CD79a, and negative for cytokeratin (CK), epithelial memberane antigen (EMA), CD2, CD3, CD20, CD5, CD138. Then a diagnosis of non-leukemic MS was made. Unfortunately, our patient received only one cycle of chemotherapy consisting of cytosine arabinoside and daunorubicin, then refused any further treatment and died 4 months after diagnosis. Although systemic chemotherapy is widely accepted to be a promising strategy, its benefit still needs to be further assessed. Certain questions still need to be answered for this disease: 1) Why can approximately 20% of the patients with non-leukemic MS remain disease-free after local therapy alone? 2) How many cycles of chemotherapy are needed for these patients after achievement of complete remission? 3) What are the prognostic or risk factors in these patients who have no abnormality of karyotype, fusion genes, or gene mutation to predict responsiveness to chemotherapy and outcome? 4) What is the risk factor for relapse? The rarity of non-leukemic MS makes it almost impossible to conduct large-scale randomized trials, but judicious study for each patient with MS is helpful for a further understanding of the nature of the disease.
Keywords: myeloid sarcoma, genital tract, leukemia, chemotherapy
Introduction
Myeloid sarcoma (MS) is defined as a tumor mass consisting of myeloid blast with or without maturation occurring at an anatomical site other than bone marrow (BM) with normal architectural effacement.1 It was first described by Burns2 in 1811 and then referred as chloroma by King3 in 1853 because of its greenish color on exposure to the air. Most MS cases have close relationships with acute or chronic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome or myeloproliferative neoplasm.4–11
The MS can also precede acute myeloid leukemia (AML) at which time the BM aspiration and biopsy reveal no hematological disease. This type of MS is called isolated, primary, or non-leukemic MS. It is a rare disease with an incidence of 2/1,000,000 in adults. It has been identified to be solitary or multiple.4,12 The non-leukemic MS is always difficult to be diagnosed. There are only case reports and some small series recorded in the literature, most of which are retrospective studies. We herein report an unusual case of the non-leukemic MS that involved the vulva, vagina, and cervix, and review the literatures.
Case report
A 40-year-old woman with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 1 was hospitalized because of small amount of vaginal bleeding for 2 months and a painless mass in vulva as the first presentation. There was no history of fever, fatigue, or bleedings from other sites of the body. Physical examination revealed several swelling lymph nodes in the left inguinal region. Other superficial lymph nodes, liver, and spleen were impalpable. There was no sternal tenderness.
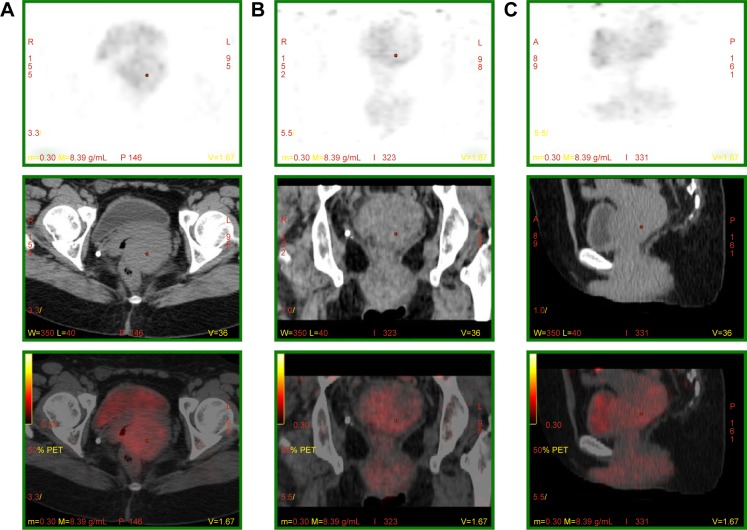
Gynecological and colposcopic examination revealed normal skin color of the vulva, swelling of both bilateral greater and lesser lips of the pudendum. Tough masses were palpable and extended to the bottom of the pelvic cavity. The top of the vagina and zone of the fornix swelled up like strip, and almost surrounded the cervix. The cervix was also swelling and bleeding when palpated. There was a small ulcer on the lower lip. The uterine corpus was antepositioned and normal in size. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scan was performed and found a soft tissue mass lesion of 5.5×5.7×9.0 cm across the vulva, vagina, and cervix with an irregular shape, ill-defined boundary, and with a maximum standardized uptake value (SUV[max]) of 2.4 (Figure 1). Several lymph nodes were detected in the left inguinal region.
Figure 1.
PET-CT, showing a soft tissue mass approximately 5.5×5.7×9.0 cm in the vulva, vagina, and cervix, with irregular shape, unclear border, and with a maximum standardized uptake value (SUV[max]) of 2.4.
Notes: (A) Atrial volume, (B) coronal volume, and (C) sagittal volume.
Abbreviation: PET-CT, positron emission tomography–computed tomography.
The patient underwent a biopsy of the tumor mass. Two pieces of tissue approximately 1.5×1 cm and 2×1 cm were surgically resected from the involved cervix and left greater lips of pudendum, and electric coagulation was used to stop bleeding. The cut surface of the biopsies was gray color. Pathohistologic study revealed infiltration of medium-sized to large blasts with finely dispersed chromatin, prominent nucleoli, and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Immunohistochemical staining was strongly positive for myeloperoxidase, CD68, leukocyte common antigen (LCA), CD117, CD34, CD38, CD79a, and negative for cytokeratin (CK), epithelial memberane antigen (EMA), CD2, CD3, CD20, CD5, CD138. Ki67 was expressed in 70% of the tumor cells (Figures 2 and 3). Complete blood count (CBC) was normal: WBC 7.5×109/L, hemoglobin 12.1 g/dL, platelet 344×109/L, and 54% neutrophils, 36% lymphocytes, 6% eosinophils, and 4% monocytes in peripheral blood smear. Tumor markers (CA199, CA125, CEA) and complete biochemical panel including lactose dehydrogenase and uric acid were all in the normal range. The BM aspiration on left iliac bone demonstrated normal marrow cellularity with trilineage differentiation, and there were no increased percentage of myeloid blasts. The BM biopsy was normal.
Figure 2.
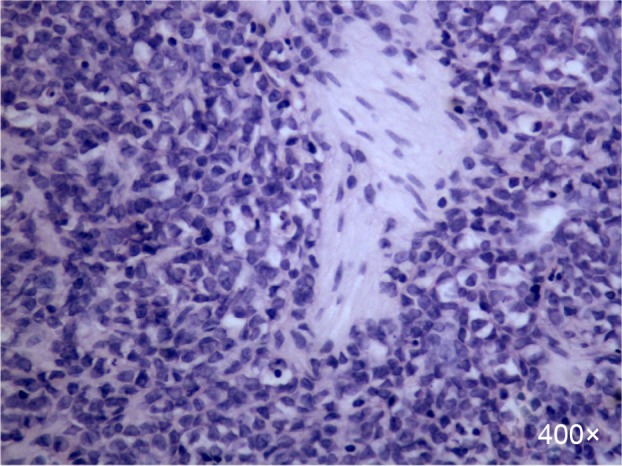
H&E stain of the biopsy sample.
Notes: There were medium-sized to large cells with finely dispersed chromatin, prominent nucleoli, and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (×400).
Abbreviation: H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.
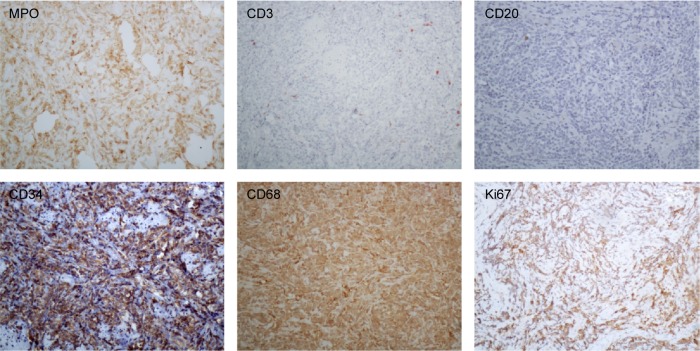
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemical stain of the biopsy sample.
Notes: The tumor cells were positive for myeloperoxidase (MPO), CD34, CD68, and negative for CD3, CD20. Ki67 evaluation was of 70% of the tumor cells (×200).
Recurrent fusion genes in AML such as AML1/ETO, Bcr/Abl, PML/RARα, and CBFB/MYH11 were all negative. Nucleophosmin (NPM1), FMS-like tyrosine kinase (FLT3), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA), and c-KIT mutation were not detected. Chromosomal analysis of the BM showed a normal 46, XX karyotype, and flowcytometric analysis revealed no abnormality. The diagnosis of the non-leukemic MS was finally made. She was then treated with conventional chemotherapy for acute myelobalstic leukemia, consisting of cytosine arabinoside 100 mg/m2/d for 7 days and daunorubicin 45 mg/m2/d for 3 days. She received only one cycle of chemotherapy and refused any further treatment or any kind of physical or laboratory examination except for CBC because of personal reason. Three months later, the patient experienced fatigue, low-grade fever, and recurrent irregular vaginal bleeding, and she gradually developed leukocytosis, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The last CBC showed: WBC 57.4×109/L, hemoglobin 6.5 g/dL, platelet 17×109/L. Four months after telephone follow-up, she was said to have a sudden headache, vomiting, and unconsciousness. Then she was reported to die suddenly at home 4 hours after the onset of the aforementioned symptoms, presumably due to intracranial hemorrhage.
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s family.
Discussion
The MS is a solid tumor composed of myeloblasts with heterogenetic extramedullary involvements. The disease can occur solely, or can be the antecedent manifestation of hematological diseases, AML in particular over months or years before an overt leukemia occurs, or can be the first sign of leukemia relapse. Commonly affected areas include the skin, bone, soft tissue, gastrointestinal tract, and lymph nodes, and rarely affected areas are the heart, spinal cord, liver, etc.1,13–16
Non-leukemic MS can be presented with miscellaneous clinical manifestations depending on the initially involved sites or organs and the size of the lesions. In the past decades, misdiagnosis of the MS was common. Approximately 75% of the patients with non-leukemic MS were misdiagnosed with other malignancies such as lymphoma (50%) or non-hematopoietic neoplasms (25%),17–19 due partially to the rarity and nonspecific manifestation of the disease. However, in recent days, the misdiagnosis rate has been reported to be declined.20,21 The diagnosis of MS depends majorly on biopsy of the tumor mass and its histopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis. Hematologic malignancies such as lymphoma, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, and non-hematopoietic tumors should be differentiated. An immunohistochemical panel, including CD34, CD43, lysozyme, myeloperoxidase, CD68 (or CD163), CD117, CD3, and CD20 can successfully identify the majority of MS in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. With extensive morphological and immunohistochemical analyses, the MS were classified into five types: a) immature granulocytic sarcoma; b) differentiated granulocytic sarcoma; c) monoblastic sarcoma; d) monocytic sarcoma; and e) myelomonocytic sarcoma.22,23
At the same time, the morphological, immunophenotypical, and genetic characteristics of the MS features are all contributive to its further classification into the AML subgroups.24
Nearly half of the patients with non-leukemic MS will develop acute leukemia in a short interval. The mean interval between initial diagnosis and the onset of overt acute leukemia has been reported to be approximately 5–11 months.19,21,25 Since only approximately 20% of the non-leukemic MS cases will remain disease-free after local therapy only (either surgical excision or radiotherapy or both), it is considered not an optimal choice for these patients but can be used in emergent situations. Rapid symptomatic relief, initial debulking, inadequate response to chemotherapy, and recurrence after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation are some of the indications for these ancillary therapeutic modalities.26
Although it is widely accepted that systemic treatment with agents used in the patients with AML should be given to the patients with primary MS immediately, the most optimal therapy is still unclear by now.21,27,28 Yamauchi and Yasuda21 analyzed 74 patients with non-leukemic MS using a literature search on Medline (including two patients in their institute), and found that the non-leukemic period after the diagnosis of granulocytic sarcoma was significantly longer in the patients who received systemic chemotherapy than those who received surgical resection or irradiation (12 months versus 3 months versus 6 months), this study also revealed that in the patients treated with chemotherapeutic agents containing cytosine arabinoside and anthracycline, the period of progression to acute leukemia was significantly longer than in those who were treated with regimens used in lymphomas.
In the latest National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline, the initial treatment should still be based on systemic induction chemotherapy. However, all these modalities, if needed at all, should be optimally deferred until after blood cell count recovery to avoid excess toxicity. The risk-strategy is necessary to decide how and when and yes or no to start the systemic treatment. In the study of Pileri et al, the clinical behavior and response to therapy of the MS did not seem to be influenced by any of the following factors: age; sex; anatomic site; de novo presentation or clinical history related to AML, myelodysplastic syndrome, or myeloproliferative neoplasm; histotype; phenotype; or cytogenetic findings. Notably, the patients treated with allogeneic or autologous BM transplantation seem to have a higher probability of prolonged survival or cure.7 Each patient should be individually assessed base upon multiple prognostic factors to work out an optimal treatment plan. The patients with central nervous system MS can be treated with intrathecal injections of chemotherapeutic agents and radiotherapy, particularly those with myeloblasts in the cerebrospinal fluid.29
Clinically, the non-leukemic MS involving the female genital tract is very unusual. The most commonly involved organ is the ovary estimated at 36.4% followed by the cervix and uterus.30,31 The patients usually have various presentations such as bleeding, mass, pain, abnormal leukorrhea or discharge, and abnormal cells on routine Papanicolaou test. Thirty-one patients with non-leukemic MS involving the female genital tract were reported (30 in the literature, including one additional case in this report). The age of them ranged from 12 to 77 years with a mean age of 39 years, and they were treated with different regimens (Table 1).31–50 Two patients’ follow-ups were not available. Ten patients were alive with no evidence of leukemia and three patients were alive with leukemia at last follow-up. A total of 16 patients died of the disease (6 days to 11 years after diagnosis). The common regimens used for them are similar to those for AML mentioned earlier, which include systemic chemotherapy and/or locoregional therapy, BM transplantation/hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Recently, hypomethylating agents like decitabine and 5-azacitdine have been an alternative treatment option for the elderly patients who are not candidates for standard induction chemotherapy. It is generally well tolerated and may take longer than four cycles to obtain a complete or partial remission.35
Table 1.
Literature review of non-leukemic MS involving the female genital tract
| Organ involved/references | Published date | Age (y) | Treatment | Outcome after diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uterine cervix | ||||
| Berard et al36 | 1936 | 39 | Radiation | Died, 5 mo |
| Seo et al37 | 1977 | 65 | Radiation | Recurrence, 26 mo; died, 34 mo |
| Abeler et al38 | 1983 | 59 | Radiation | AML, 3 mo; died, 4 mo |
| Harris and Scully39 | 1984 | 71 | CT | AML, 12 mo |
| Kao et al40 | 1984 | 34 | CT | Died, 17 mo |
| Banik et al41 | 1989 | 32 | Radiation and CT | ANEL, 11 mo |
| Reynaud et al42 | 1995 | 48 | CT | Died, 24 mo |
| Hernandez et al43 | 2002 | 48 | CT and BMT | AML-M2, 8 mo; died, 10 mo |
| Garcia et al32 | 2006 | 37 | CT | ANEL, 2 mo |
| 2006 | 34 | CT | ANEL, 12.5 y | |
| Uterine corpus | ||||
| Spahr et al44 | 1982 | 39 | No | Died, 6 d |
| Ovary | ||||
| Schafer et al45 | 1974 | 28 | Not stated | AML, 3 mo |
| Pressler et al46 | 1992 | 49 | Not stated | ANEL, 12 mo |
| Aguiar et al47 | 1993 | 31 | CT | AML-M2, 12 mo; died, 14 mo |
| Oliva et al30 | 1997 | 30 | Not stated | Died, 24 mo |
| 1997 | 31 | CT | Not stated | |
| 1997 | 31 | Not stated | Not stated | |
| 1997 | 43 | CT | ANEL, 18 mo | |
| Jung et al48 | 1999 | 12 | Not stated | ANEL, 7 mo |
| Sreejith et al49 | 2000 | 26 | CT | ANEL, 12 mo |
| Garcia et al32 | 2006 | 25 | CT | Recurrence, 24 mo; ANEL, 30 mo |
| Vagina | ||||
| Oliva et al30 | 1997 | 73 | Radiation | Recurrence, 30 mo; died, 31 mo |
| Hernandez et al43 | 2002 | 48 | CT and BMT | AML-M5a, 4 mo; died, 10 mo |
| Modi et al35 | 2015 | 68 | CT | ANEL, 4 mo |
| Skeete et al33 | 2010 | 77 | Radiation | Died, 5 mo |
| Policarpo-Nicolas et al31 | 2012 | 16 | CT | ANEL, 11 mo |
| ≥2 gynecologic sites | ||||
| Harris and Scully39 | 1984 | 48 | Radiation and CT | AML, 2 mo |
| Garcia et al32 | 2006 | 59 | CT | Died, 2 mo |
| 2006 | 17 | Radiation | AML, 2 mo; died, 5 mo | |
| Chiang and Chen34 | 2010 | 52 | CT and operation | Died, 11 y |
| Our case | – | 40 | CT | Died, 4 mo |
Abbreviations: AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ANEL, alive with no evidence of leukemia; BMT, bone marrow transplantation; CT, chemotherapy; MS, myeloid sarcoma; d, day; mo, month; y, year.
Conclusion
The non-leukemic MS is a rare disease, and involvement of the female genital tract is even rarer. There are only scant cases reported in the literatures by now. Biopsy and histopathologic workup are crucial to the definitive diagnosis and management strategy. Unfortunately, our patient received only one cycle of chemotherapy consisting of cytosine arabinoside and daunorubicin, and then refused any further treatment and died 4 months after diagnosis. Leukocytosis, anemia, and thrombocytopenia indicated that the disease has developed to acute leukemia due to the inadequate chemotherapy.
Although systemic chemotherapy is widely accepted to be a promising strategy, its benefit still needs to be further assessed. Certain questions still need to be answered for this disease: 1) Why can approximately 20% of the patients with non-leukemic MS remain disease-free after local therapy alone? 2) How many cycles of chemotherapy are needed for the patients with non-leukemic MS after achievement of complete remission? 3) What are the prognostic or risk factors in the patients with non-leukemic MS patients who have no abnormality of karyotype, fusion genes, or gene mutation to predict responsiveness to chemotherapy and outcome? 4) What is the risk factor for relapse? The rarity of the non-leukemic MS makes it almost impossible to conduct large-scale randomized trials, but judicious study for each patient with MS is helpful for further a understanding of the nature of the disease.
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81300384).
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Pileri SA, Orazi A, Falini B. Myeloid sarcoma. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al., editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors, WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008. pp. 140–141. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Burns A. Observation of Surgical Anatomy, Head and Neck. Edinburgh, Scotland: Thomas Royce and Co; 1811. [Google Scholar]
- 3.King A. A case of chloroma. Monthly J Med. 1853;7:97. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Neiman RS, Barcos M, Berard C, et al. Granulocytic sarcoma: a clinicopathologic study of 61 biopsied cases. Cancer. 1981;48:1426–1437. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810915)48:6<1426::aid-cncr2820480626>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Balleari E, Panarello S, Capello E, et al. Granulocytic sarcoma: an unusual cause of spinal cord compression. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007;12:234–237. doi: 10.1007/s10147-006-0645-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tsimberidou AM, Kantarjian HM, Estey E, et al. Outcome in patients with nonleukemic granulocyctic sarcoma treated with chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy. Leukemia. 2003;17:1100–1103. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pileri SA, Ascani S, Cox MC, et al. Myeloid sarcoma: clinicopathologic, phenotypic and cytogenetic analysis of 92 adult patients. Leukemia. 2007;21:340–350. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kasahara S, Tsurumi H, Hara T, Goto H, Moriwaki H. Idiopathic myelofibrosis developing isolated granulocytic sarcoma with der (1;7)(q10; p10) after splenectomy and finally transforming to acute myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;39:427–433. doi: 10.3109/10428190009065844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Szomor A, Baranyai F, Tornóczky T, Losonczy H. Penile chloroma in a patient with secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Eur J Haematol. 2002;68:322. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0609.2002.02713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maeng H, Cheong JW, Lee ST, et al. Isolated extramedullary relapse of acute myelogenous leukemia as a uterine granulocytic sarcoma in an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipient. Yonsei Med J. 2004;45:330–333. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2004.45.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Campidelli C, Agostinelli C, Stitson R, Pileri SA. Myeloid sarcoma: extramedullary manifestation of myeloid disorders. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;132:426–437. doi: 10.1309/AJCP1ZA7HYZKAZHS. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yilmaz AF, Saydam G, Sahin F, Baran Y. Granulocytic sarcoma: a systematic review. Am J Blood Res. 2013;3:265–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Paydas S, Zorludemir S, Ergin M. Granulocytic sarcoma: 32 cases and review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47:2527–2541. doi: 10.1080/10428190600967196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Choi EK, Ha HK, Park SH, et al. Granulocytic sarcoma of bowel: CT findings. Radiology. 2007;243:752–759. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2433060747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kitagawa Y, Sameshima Y, Shiozaki H, et al. Isolated granulocytic Sarcoma of the small intestine successfully treated with chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2008;87:410–413. doi: 10.1007/s12185-008-0067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Antic D, Vuckovic M, Elezovic I. Right atrial myeloid sarcoma causing superior vena cava syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2008;141:134. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Byrd JC, Edenfield WJ, Shields DJ, Dawson NA. Extramedullary myeloid cell tumors in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia: a clinical review. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:1800–1816. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.7.1800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Williams MP, Olliff JF, Rowley MR. CT and MR findings in parameningeal leukemic masses. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990;14:736–742. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199009000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meis JM, Butler JJ, Osborne BM, Manning JT. Granulocytic sarcoma in nonleukemic patients. Cancer. 1986;58:2697–2709. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861215)58:12<2697::aid-cncr2820581225>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Antic D, Elezovic I, Milic N, et al. Is there a “gold” standard treatment for patients with isolated myeloid sarcoma? Biomed Pharmacother. 2013;67:72–77. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2012.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yamauchi K, Yasuda M. Comparison in treatments of nonleukemic granulocytic sarcoma: report of two cases and a review of 72 cases in the literature. Cancer. 2002;94:1739–1746. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chang CC, Eshoa C, Kampalath B, et al. Immunophenotypic profile of myeloid cells in granulocytic sarcoma by immunohistochemistry. Correlation with blast differentiation in bone marrow. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;114:807–811. doi: 10.1309/WWW7-DG6X-HC16-D7J2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alexiev BA, Wang W, Ning Y, et al. Myeloid sarcomas: a histologic, immunohistochemical, and cytogenetic study. Diagn Pathol. 2007;2:42. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-2-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bakst RL, Tallman MS, Douer D, Yahalom J. How I treat extramedullary acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2011;118:3785–3793. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-347229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chevallier P, Mohty M, Lioure B, et al. Allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myeloid sarcoma: a retrospective study from the SFGM-TC. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4940–4943. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.6315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bakst R, Wolden S, Yahalom J. Radiation therapy for chloroma (granulocytic sarcoma) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:1816–1822. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, et al. European LeukemiaNet. European LeukemiaNet Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2010;115:453–474. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tsimberidou AM, Kantarjian HM, Wen S, et al. Myeloid sarcoma is associated with superior event-free survival and overall survival compared with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 2008;113:1370–1378. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Xiao RZ, Long ZJ, Xiong MJ, Wang WW, Lin DJ. Diagnosis and treatment of a patient with isolated spinal granulocytic sarcoma: a case report. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:1229–1232. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Oliva E, Ferry JA, Young RH, et al. Granulocytic sarcoma of the female genital tract: a clinicopathologic study of 11 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:1156–1165. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199710000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Policarpo-Nicolas ML, Valente PT, Aune GJ, Higgins RA. Isolated vaginal myeloid sarcoma in a 16-year-old girl. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2012;16:374–379. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2011.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garcia MG, Deavers MT, Knoblock RJ, et al. Myeloid sarcoma involving the gynecologic tract: a report of 11 cases and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;125:783–790. doi: 10.1309/H9MM-21FP-T7YB-L3PW. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Skeete DH, Cesar-Rittenberg P, Jong R, Murray SK, Colgan TJ. Myeloid sarcoma of the vagina: a report of 2 cases. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2010;14:136–141. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0b013e3181be2999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chiang YC, Chen CH. Cervical granulocytic sarcoma: report of one case and review of the literature. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2010;31:697–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Modi G, Madabhavi I, Panchal H, et al. Primary vaginal myeloid sarcoma: a rare case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2015;2015:957490. doi: 10.1155/2015/957490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Berard L, Martin JF, Ponthus P. Etude d’un myélo-sarcome (hemocyto-blastosarcome myéloïde) du col utérin et de ses généralisations squelettiques. [A report of myloid sarcoma of the uterine cervix with bone involvement] Bull Assoc Fr Etude Cancer. 1936;25:611–620. French. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Seo IS, Hull MT, Pak HY. Granulocytic sarcoma of the cervix as a primary manifestation: case without overt leukemic features for 26 months. Cancer. 1977;40:3030–3037. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197712)40:6<3030::aid-cncr2820400640>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Abeler V, Kjorstad KE, Langholm R, Marton PF. Granulocytic sarcoma (chloroma) of the uterine cervix: report of two cases. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1983;2:88–92. doi: 10.1097/00004347-198301000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Harris NL, Scully RE. Malignant lymphoma and granulocytic sarcoma of the uterus and vagina: a clinicopathologic analysis of 27 cases. Cancer. 1984;53:2530–2545. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840601)53:11<2530::aid-cncr2820531127>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kao KL, Yang YS, Lee CJ, Shieh HT, Lee EF, Chen YC. Granulocytic sarcoma of the cervix uteri: a case report. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1984;83:618–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Banik S, Grech AB, Eyden BP. Granulocytic sarcoma of the cervix: an immunohistochemical, histochemical, and ultrastructural study. J Clin Pathol. 1989;42:483–488. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reynaud P, Le Bouedec G, Dechelotte P, Dauplat J, Chassagne J, Fonck Y. Rare tumors of the cervix: three case reports: rhabdomyosarcoma, granulocytic sarcoma and lymphoma [in French] J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1995;24:30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hernandez JA, Navarro JT, Rozman M, et al. Primary myeloid sarcoma of the gynecologic tract: a report of two cases progressing to acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:2151–2153. doi: 10.1080/1042819021000016096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Spahr J, Behm FG, Schneider V. Preleukemic granulocytic sarcoma of cervix and vagina: initial manifestation by cytology. Acta Cytol. 1982;26:55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schafer RJ, Hill K, Reitz H. Myelosarcoma (leucotik sarcoma) of the ovary preceeding leukemia (author’s transl) [in German] Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1974;118:467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pressler H, Horny HP, Wolf A, Kaiserling E. Isolated granulocytic sarcoma of the ovary: histologic, electron microscopic, and immunohistochemical findings. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1992;11:68–74. doi: 10.1097/00004347-199201000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Aguiar RC, Pozzi DH, Chamone DA. Granulocytic sarcoma of the ovary in a nonleukemic patient. Haematologica. 1993;78:53–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jung SE, Chun KA, Park SH, Lee EJ. MR findings in ovarian granulocytic sarcoma. Br J Radiol. 1999;72:301–303. doi: 10.1259/bjr.72.855.10396223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sreejith G, Gangadharan VP, Elizabath KA, Preetha S, Chithrathara K. Primary granulocytic sarcoma of the ovary. Am J Clin Oncol. 2000;23:239–240. doi: 10.1097/00000421-200006000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]