Abstract
The inability of the autologous host to reject resident tumor cells is frequently the result of inadequate generation of tumor-specific T cells. Specific activation of T cells occurs after delivery of two signals by the antigen-presenting cell. The first signal is antigen-specific and is the engagement of the T-cell antigen receptor by a specific major histocompatibility complex antigen-peptide complex. For some T cells, the second or costimulatory signal is the interaction of the T-cell CD28 receptor with the B7 activation molecule of the antigen-presenting cell. In the present study, we demonstrate that mouse sarcoma cells genetically engineered to provide both T-cell activation signals stimulate potent tumor-specific CD4+ T cells that cause rejection of both engineered and wild-type neoplastic cells. Two other recent studies have also demonstrated that costimulation via B7 can improve tumor immunity. However, our study differs from these reports by two important observations. (i) One of these studies utilized mouse tumor cells expressing xenogenic viral antigens, and hence, the results are not applicable to wild-type resident tumors. Our study, however, demonstrates that coexpression of B7 by major histocompatibility complex class II+ tumor cells induces immunity in the autologous host that is specific for naturally occurring tumor antigens of poorly immunogenic tumors. (ii) In both earlier studies, only CD8+ T cells were activated after coexpression of B7, whereas in the present report, tumor-specific CD4+ T cells are generated. This report therefore illustrates the role of B7 activation molecule in stimulating potent tumor-specific CD4+ T cells that mediate rejection of wild-type tumors and provides a theoretical basis for immunotherapy of established tumors.
Full text
PDF
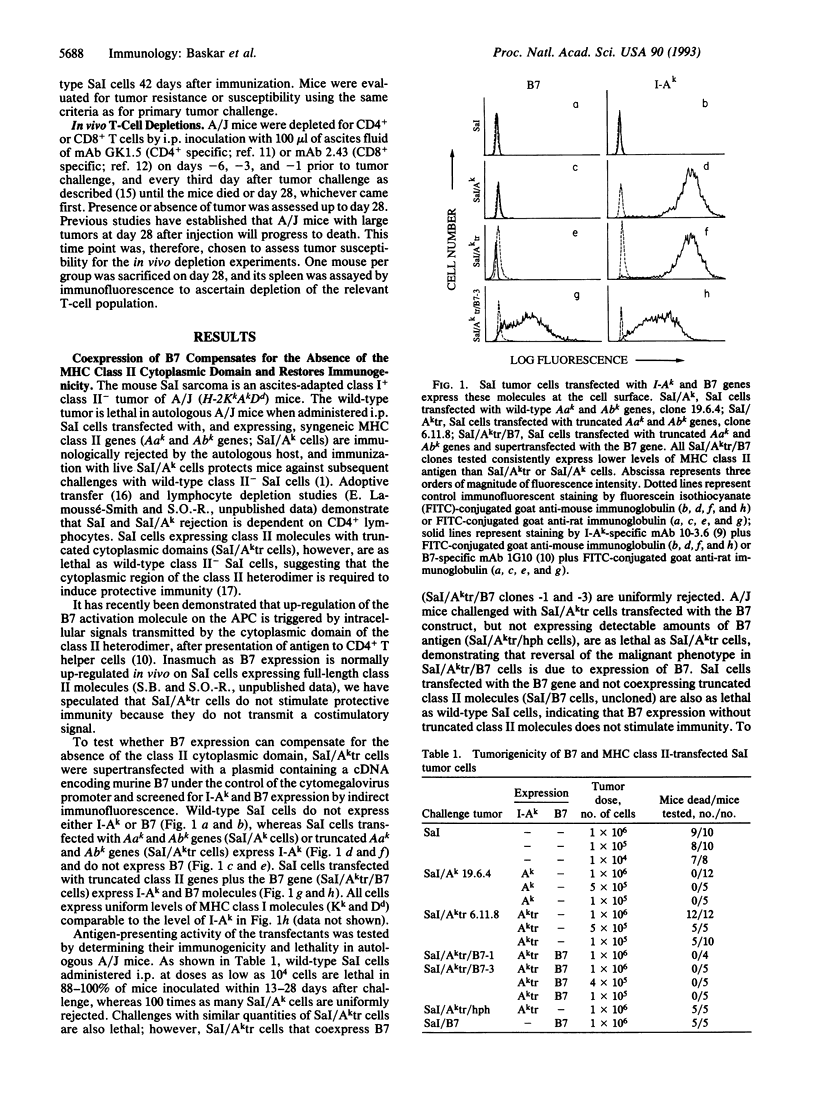

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakke O., Dobberstein B. MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Ashe S., Brady W. A., Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Ledbetter J. A., McGowan P., Linsley P. S. Costimulation of antitumor immunity by the B7 counterreceptor for the T lymphocyte molecules CD28 and CTLA-4. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1093–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements V. K., Baskar S., Armstrong T. D., Ostrand-Rosenberg S. Invariant chain alters the malignant phenotype of MHC class II+ tumor cells. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2391–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. A., Ostrand-Rosenberg S. Rejection of allogeneic tumor is not determined by host responses to MHC class I molecules and is mediated by CD4-CD8+ T lymphocytes that are not lytic for the tumor. Cell Immunol. 1991 May;134(2):480–490. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott W. L., Stille C. J., Thomas L. J., Humphreys R. E. An hypothesis on the binding of an amphipathic, alpha helical sequence in Ii to the desetope of class II antigens. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2949–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Pardoll D. M., Itaya T., Golumbek P., Levitsky H. I., Simons J. W., Karasuyama H., Vogelstein B., Frost P. Interleukin-2 production by tumor cells bypasses T helper function in the generation of an antitumor response. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90591-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Gray G. S., Gimmi C. D., Lombard D. B., Zhou L. J., White M., Fingeroth J. D., Gribben J. G., Nadler L. M. Structure, expression, and T cell costimulatory activity of the murine homologue of the human B lymphocyte activation antigen B7. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):625–631. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghobrial R. R., Boublik M., Winn H. J., Auchincloss H., Jr In vivo use of monoclonal antibodies against murine T cell antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Sep;52(3):486–506. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Sugita K., Freedman A. S., Morimoto C., Nadler L. M. B-cell surface antigen B7 provides a costimulatory signal that induces T cells to proliferate and secrete interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6575–6579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi L. E., Koppelman B., Blum J. S., Marks M. S., Cresswell P., Brodsky F. M. Co-localization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):133–139. doi: 10.1038/343133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulova L., Clark E. A., Shu G., Dupont B. The CD28 ligand B7/BB1 provides costimulatory signal for alloactivation of CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):759–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Grosmaire L., Aruffo A., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. Binding of the B cell activation antigen B7 to CD28 costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 mRNA accumulation. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):721–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotteau V., Teyton L., Peleraux A., Nilsson T., Karlsson L., Schmid S. L., Quaranta V., Peterson P. A. Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):600–605. doi: 10.1038/348600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Freeman G. J., Gault A., Godfrey D., Nadler L. M., Glimcher L. H. Signalling through the MHC class II cytoplasmic domain is required for antigen presentation and induces B7 expression. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):266–268. doi: 10.1038/360266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Ghogawala Z., Myer A., Griffith I. J., Wade W. F., Chen Z. Z., McKean D. J., Glimcher L. H. Antigen presentation abrogated in cells expressing truncated Ia molecules. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1444–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrand-Rosenberg S., Roby C. A., Clements V. K. Abrogation of tumorigenicity by MHC class II antigen expression requires the cytoplasmic domain of the class II molecule. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2419–2422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrand-Rosenberg S., Thakur A., Clements V. Rejection of mouse sarcoma cells after transfection of MHC class II genes. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):4068–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. J., Neefjes J. J., Oorschot V., Ploegh H. L., Geuze H. J. Segregation of MHC class II molecules from MHC class I molecules in the Golgi complex for transport to lysosomal compartments. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):669–676. doi: 10.1038/349669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razi-Wolf Z., Freeman G. J., Galvin F., Benacerraf B., Nadler L., Reiser H. Expression and function of the murine B7 antigen, the major costimulatory molecule expressed by peritoneal exudate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Cresswell P. Invariant chain association with HLA-DR molecules inhibits immunogenic peptide binding. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):615–618. doi: 10.1038/345615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz K. R., Klarnet J. P., Gieni R. S., HayGlass K. T., Greenberg P. D. The role of B cells for in vivo T cell responses to a Friend virus-induced leukemia. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.2118273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockinger B., Pessara U., Lin R. H., Habicht J., Grez M., Koch N. A role of Ia-associated invariant chains in antigen processing and presentation. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90590-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyton L., O'Sullivan D., Dickson P. W., Lotteau V., Sette A., Fink P., Peterson P. A. Invariant chain distinguishes between the exogenous and endogenous antigen presentation pathways. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):39–44. doi: 10.1038/348039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend S. E., Allison J. P. Tumor rejection after direct costimulation of CD8+ T cells by B7-transfected melanoma cells. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):368–370. doi: 10.1126/science.7678351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Kappler J., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating L3T4 in class II MHC antigen reactivity; monoclonal antibody GK1.5 (anti-L3T4a) blocks class II MHC antigen-specific proliferation, release of lymphokines, and binding by cloned murine helper T lymphocyte lines. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2178–2183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



