Abstract
We describe a novel surgical technique for pterygium removal taking advantage of the properties of amniotic membrane and limbal epithelial stem cells. A total of 10 eyes underwent pterygium excision with amniotic membrane coverage of the bare sclera and placement of pieces of limbal epithelium in a linear fashion in the affected limbal area covered by a second amniotic membrane using fibrin glue. After up to 8 months of follow-up, there were no signs of early recurrence or sight-threatening complications. The minor ipsilateral simple limbal epithelial transplantation technique for the treatment of pterygium requires less tissue than the conventional conjunctival autograft, leaving healthy conjunctiva if needed for another procedure in the future and offers the advantages of epithelial stem cells, which in the long term may reduce the rate of recurrence significantly.
Keywords: Cornea, Conjunctiva, Stem Cells
Introduction
Pterygium is a benign, wing-shaped fibrovascular proliferation extending onto the cornea. As of today, there are many approaches to its treatment once it is decided that surgical intervention is needed. The most common surgical techniques include leaving bare sclera, using a conjunctival or conjunctival limbal autograft, coverage with amniotic membrane (AM) or the use of adjuncts like mitomycin C. Recurrence rates among these techniques vary widely, with reports as high as 88% for the bare sclera technique1–3 and more comparable results among the other mentioned techniques, with a recurrence rate between 0.003% and 40.9%.4–7
Conjunctival-limbal autograft offers a low recurrence rate and fewer complications;6 however, it cannot be performed in cases where a large defect needs to be covered or in patients where the conjunctiva needs to be preserved for future glaucoma surgery to avoid conjunctival scarring at the harvesting site. Some advantages of using an AM are inhibition of angiogenesis and the possibility to cover a large area without the need of harvesting healthy conjunctiva.8 Nevertheless, the cosmetic results, postoperative inflammation and recurrence rates are higher with AM transplantation than they are with conjunctival limbal autografts.3 9 10
Our innovative technique describes the use of an AM graft to cover the bare sclera area combined with a small autologous simple limbal epithelial transplant (mini-SLET) to provide stem cells at the limbal area.
Surgical technique
After placement of topical anaesthesia, a lid speculum is used to expose the surgical field; Westcott scissors are used to excise the pterygium and the underlying Tenon's, leaving bare sclera. The area of bare sclera is measured with the help of a calliper and an AM graft 1 mm larger than the measurement is placed over the bare sclera. Its edges are tucked under the conjunctival margins and fixed with fibrin glue (Tissucol, Baxter). Using a crescent blade, a shallow cut of 3 mm in length is made on the corneal side of the limbus, followed by two radial cuts from the corneal to the conjunctival side of the limbus; these cuts are then joint by a 3 mm peritomy. The crescent blade is then used to create a 2×2 mm strip of limbal tissue by dissecting from the conjunctival side into the cornea. We then cut this limbal tissue into 8–10 pieces with Vannas scissors and distribute them along the conjunctival side of the limbus over the previously fixed AM. These pieces are glued into place and protected with a smaller glued AM overlay. Finally, a bandage contact lens is left in place (figure 1). After surgery, patients are treated with artificial tears, topical moxifloxacin 0.5% drops every 6 h until full epithelial healing and dexamethasone 0.1% drops every 4 h with a 1 month taper. An online supplementary video is available, and the technique is summarised in figure 2. By the time of submission, we had treated 10 eyes of 9 patients with this technique at the Instituto de Oftalmologia ‘Fundación Conde de Valenciana’. Demographic and clinical details are shown in table 1.
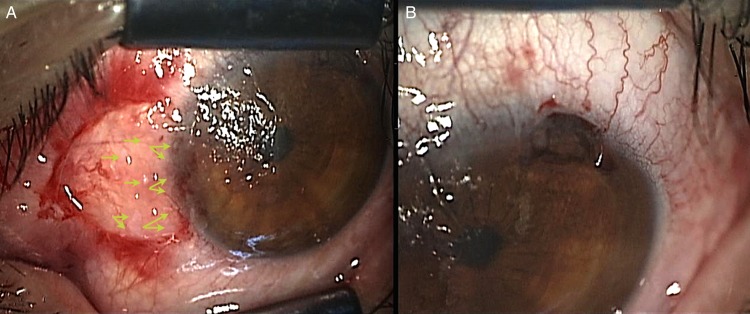
Figure 1.
Intraoperative images of the minor ipsilateral simple limbal epithelial transplantation technique. (A) Notice the pieces of limbal epithelial cells mostly remaining in a linear fashion (arrowheads). (B) Area of the limbal biopsy at the time of the surgery.
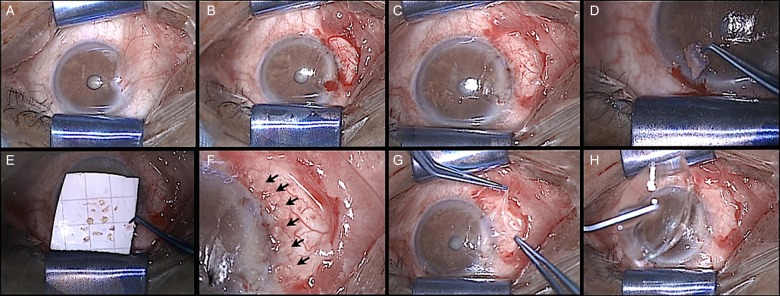
Figure 2.
(A) Nasal, temporal or bilateral pterygium are adequate candidates. (B) Resection of pterygium and excess of Tenon's with conventional techniques leaving bare sclera. (C) Placement of the first amniotic membrane. (D) Resection epithelial limbal stem cells graft of 2×2 mm. (E) Slicing of epithelial limbal strip into 8–10 pieces. (F) Alignment of small limbal pieces (arrowheads) close to the limbal area over the amniotic membrane. (G) Placement of a second amniotic membrane covering the small limbal transplants. (H) Placement of a soft contact lens.
Table 1.
Demographic, preoperative and postoperative outcomes of patients that underwent mini-SLET
| Patient | Gender | Age | Eye | Clinical grading | Site of pterygium | Recurrence | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 34 | OD | T2 | Bilateral | None | None |
| 2 | Male | 82 | OD | T2 | Temporal | None | None |
| 3 | Female | 46 | OS | T1 | Nasal | None | None |
| 4 | Female | 67 | OS | T3 | Nasal | None | None |
| 5 | Male | 57 | OS | T2 | Nasal | None | Pyogenic granuloma |
| 6 | Male | 26 | OD | T3 | Bilateral | None | None |
| 7 | Female | 70 | OD | T2 | Nasal | None | None |
| 8 | Male | 31 | OS | T3 | Nasal | None | None |
| 9 | Male | 49 | OU | T3 | Nasal | None | None |
OD, right eye; OS, left eye; OU, both eyes; SLET, simple limbal epithelial transplantation.
Clinical grading of pterygium was based on the classification by Tan et al,11 in which there are three grades: T1 (episcleral vessels underlying the body of the pterygium unobscured and distinguished), T2 (episcleral vessels are indistinctly seen or partially obscured) and T3 (episcleral vessels are totally obscured by fibrovascular tissue).
The patients had up to 8 months of follow-up, at which point the limbal epithelial pieces were no longer visible, the area of the limbal biopsy showed no focal stem cell deficiency at the last follow-up visit, the cosmetic results were favourable and we had no cases of recurrence (figure 3). The only complication reported was a case of pyogenic granuloma at the junction of AM and conjunctiva that resolved after an increase in topical steroids.
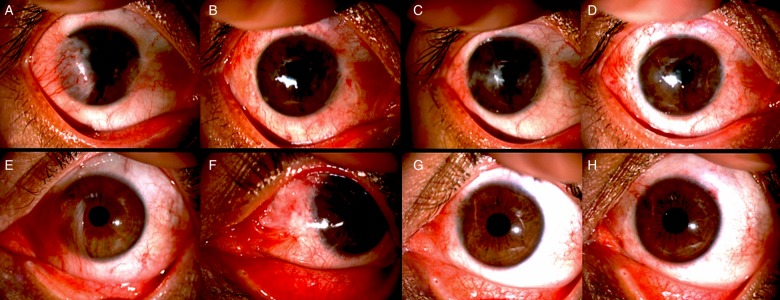
Figure 3.
Preoperative and postoperative clinical photographs of two eyes that underwent minor ipsilateral simple limbal epithelial transplantation. (A) Preoperative photograph of a 26-year-old student (case 6) with bilateral pterygium, the mini-SLET was performed in the temporal lesion. (B) 1 week after surgery. (C) 4 months. (D) 6 months. (E) Preoperative photograph of a 47-year-old male carpenter (case 9). (F) 1 week. (G) 6 months. (H) 8 months.
Discussion
Sangwan et al12 described SLET as a technique for the treatment of stem cell deficiency. Inspired by this technique, we decided to combine the use of an AM graft, which serves as an ideal substrate to support the growth of epithelial progenitor cells 13 14 with a mini-SLET for pterygium in cases that are not good candidates for a conjunctival autograft. Based on the concept that there is a localised limbal stem cell dysfunction or deficiency at the limbal area15 16 and the better outcomes reported with the use of conjunctival autografts compared with AM, we hypothesise that the addition of the stem cells contained in the mini-SLET pieces could reduce recurrence rates and, as a secondary result, improve the cosmetic outcomes.
Despite the fact that additional expenses of AM for patients with primary pterygium might not be justified, in patients with limited amounts of conjunctiva, the need of future surgeries such as glaucoma suspects or patients with previous multiple surgeries, the spending on mini-SLET technique could be acceptable. Surgeon experience influences outcomes and recurrence rate with auto conjunctival grafting.17 A simple technique as described here may help reduce learning curves and surgical skills needed to achieve success.
The clear limitations of our study are the limited number of patients and the somewhat short follow-up, but since this is our initial report we believe that 10 eyes is enough to show the feasibility of the surgical technique and we are now working on a larger randomised trial comparing the mini-SLET technique to AM transplantation.
In conclusion, we describe a new technique in which an AM graft is combined with a mini-SLET for pterygium surgery. We found this technique to be easy to learn and believe it can be an interesting solution for those patients in which we want to preserve as much conjunctiva as possible. Although the initials results are encouraging and promising, results are subject to validation as the number of patients and longer follow-up are available in the future.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
We would like to thank Alexandra Abdala-Figuerola, MD, and Andrew Olivo-Payne, MD, for their invaluable collaboration in the patients’ follow-up and images acquisition. The authors also thank Virender S Sangwan, MD and Sayan Basu, MBSS, MS from LV Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad, India for their support.
Collaborators: Alexandra Abdala-Figuerola and Andrew Olivo-Payne.
Contributors: Design and conduct of study: EH-B and EGH. Analysis and interpretation of data: AL, AN, AR-M and EH-B. Preparation and final approval of the version published: EH-B, AL, GA, AN, EGH and YG.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Ethics approval: Instituto de Oftalmologia Fundacion Conde de Valenciana Ethics Committee.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Contributor Information
Collaborators: Alexandra Abdala-Figuerola and Andrew Olivo-Payne
References
- 1.Cano-Parra J, Diaz-Llopis M, Maldonado MJ, et al. . Prospective trial of intraoperative mitomycin C in the treatment of primary pterygium. Br J Ophthalmol 1995;79:439–41. 10.1136/bjo.79.5.439 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Demirok A, Simsek S, Cinal A, et al. . Intraoperative application of mitomycin C in the surgical treatment of pterygium. Eur J Ophthalmol 1998;8: 153–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ozer A, Yildirim N, Erol N, et al. . Long-term results of bare sclera, limbal-conjunctival autograft and amniotic membrane graft techniques in primary pterygium excisions. Ophthalmologica 2009;223:269–73. 10.1159/000210444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hirst LW. Recurrence and complications after 1,000 surgeries using pterygium extended removal followed by extended conjunctival transplant. Ophthalmology 2012;119:2205–10. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.06.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen PP, Ariyasu RG, Kaza V, et al. . A randomized trial comparing mitomycin C and conjunctival autograft after excision of primary pterygium. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;120:151–60. 10.1016/S0002-9394(14)72602-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tananuvat N, Martin T. The results of amniotic membrane transplantation for primary pterygium compared with conjunctival autograft. Cornea 2004;23:458–63. 10.1097/01.ico.0000116522.57227.97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Malek I, Zghal I, Chebbi A, et al. . [Conjunctival limbal autograft versus simple excision with intra-operative mitomycin C in pterygium surgery: a comparative study]. J Fr Ophtalmol 2013;36:230–5. 10.1016/j.jfo.2012.03.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kenyon KR. Amniotic membrane: mother's own remedy for ocular surface disease. Cornea 2005;24:639–42. 10.1097/01.ico.0000178220.12977.7e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li M, Zhu M, Yu Y, et al. . Comparison of conjunctival autograft transplantation and amniotic membrane transplantation for pterygium: a meta-analysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2012;250:375–81. 10.1007/s00417-011-1820-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kheirkhah A, Nazari R, Nikdel M, et al. . Postoperative conjunctival inflammation after pterygium surgery with amniotic membrane transplantation versus conjunctival autograft. Am J Ophthalmol 2011;152:733–8. 10.1016/j.ajo.2011.04.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tan DT, Chee SP, Dear KB, et al. . Effect of pterygium morphology on pterygium recurrence in a controlled trial comparing conjunctival autografting with bare sclera excision. Arch Ophthalmol 1997;115:1235–40. 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100160405001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sangwan VS, Basu S, MacNeil S, et al. . Simple limbal epithelial transplantation (SLET): a novel surgical technique for the treatment of unilateral limbal stem cell deficiency. Br J Ophthalmol 2012;96:931–4. 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-301164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Meller D, Dabul V, Tseng SC. Expansion of conjunctival epithelial progenitor cells on amniotic membrane. Exp Eye Res 2002;74:537–45. 10.1006/exer.2001.1163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Amescua G, Atallah M, Nikpoor N, et al. . Modified simple limbal epithelial transplantation using cryopreserved amniotic membrane for unilateral limbal stem cell deficiency. Am J Ophthalmol 2014;158:469–75 e2. 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cardenas-Cantu E, Zavala J, Valenzuela J, et al. . Molecular Basis of Pterygium Development. Semin Ophthalmol 2014:1–17. 10.3109/08820538.2014.971822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chui J, Coroneo MT, Tat LT, et al. . Ophthalmic pterygium: a stem cell disorder with premalignant features. Am J Pathol 2011;178:817–27. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.10.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Farrah JJ, Lee GA, Greenrod E, et al. . Outcomes of autoconjunctival grafting for primary pterygia when performed by consultant compared with trainee ophthalmologists. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2006;34:857–60. 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2006.01341.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.