Abstract
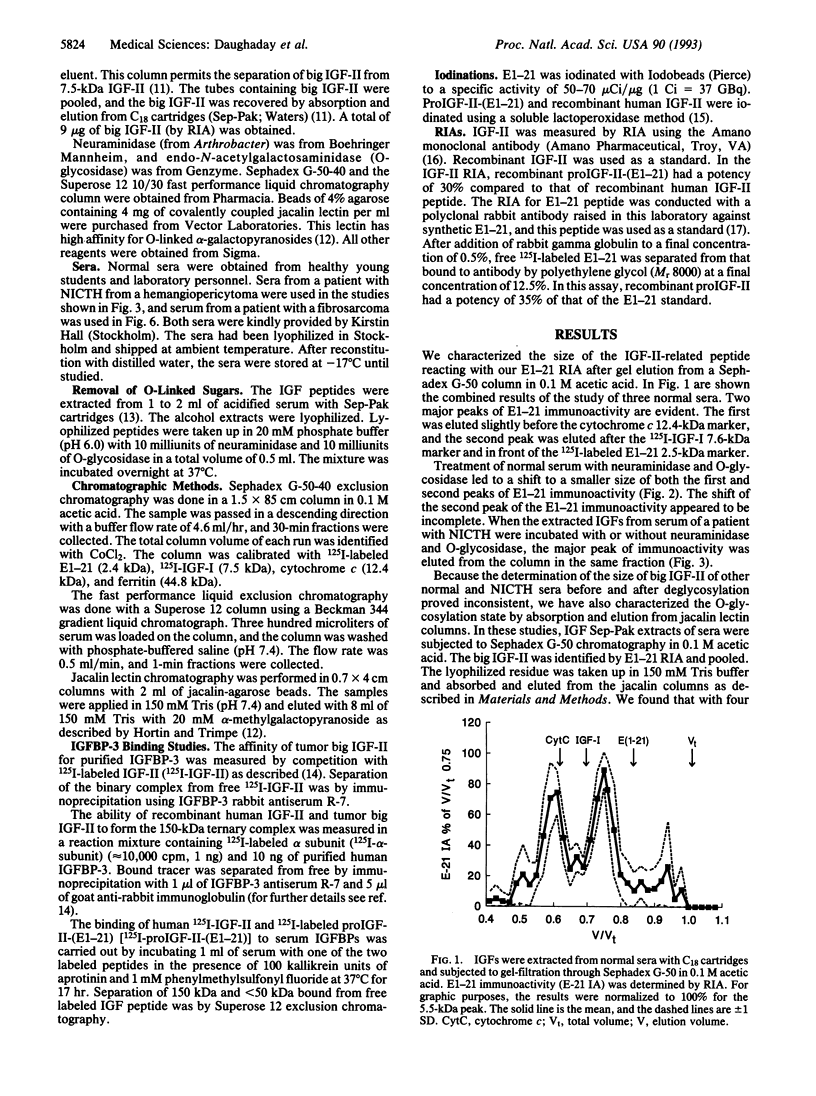
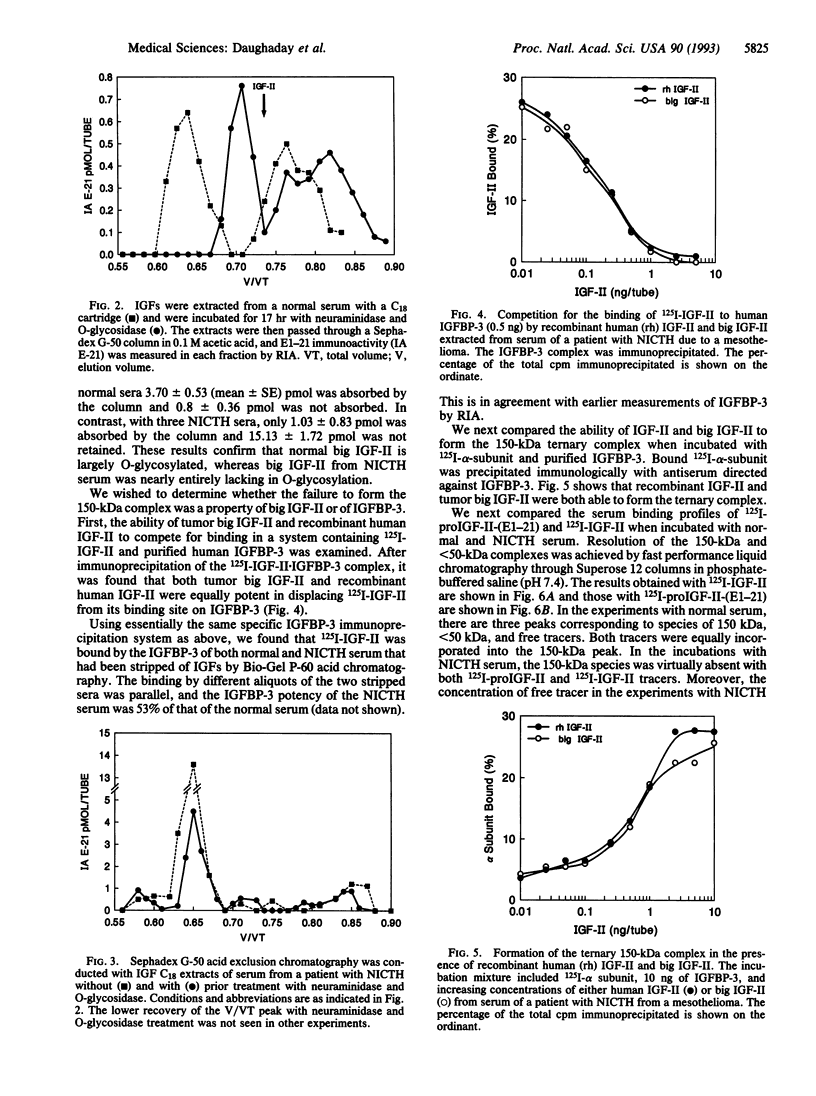
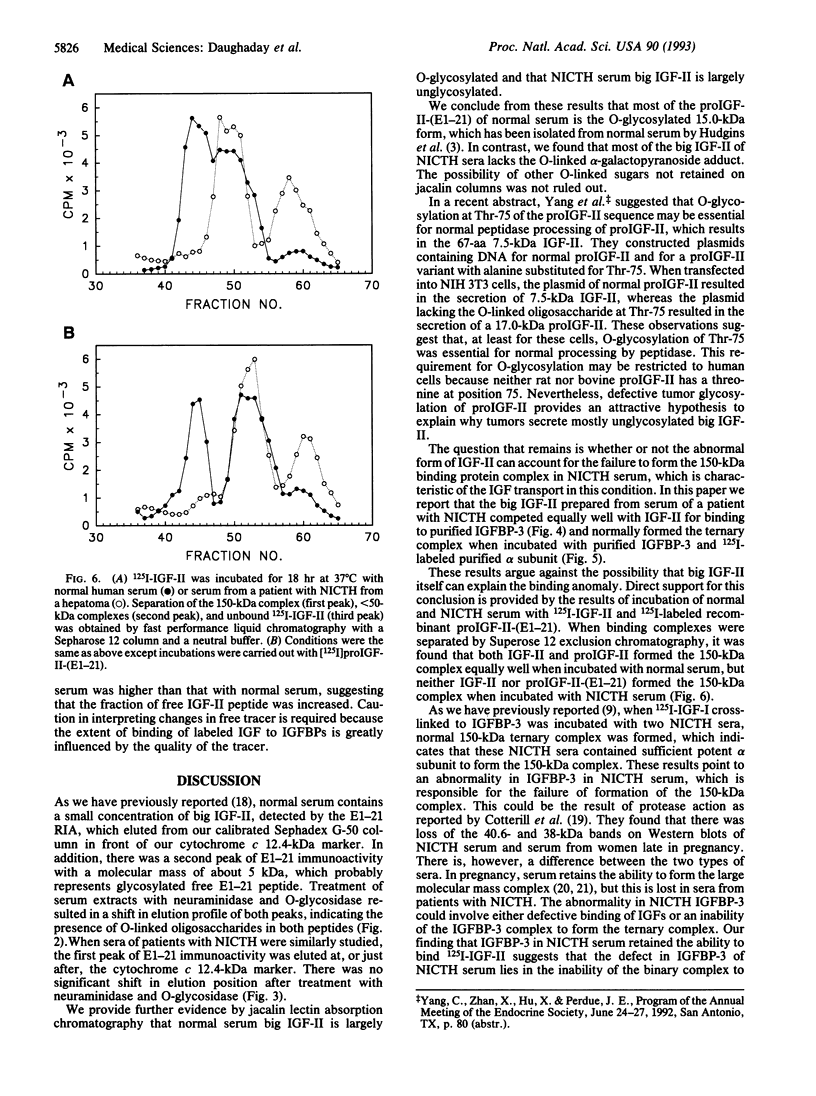
The insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) gene is overexpressed in many mesenchymal tumors and can lead to non-islet-cell tumor hypoglycemia (NICTH). ProIGF-II consists of the 67 aa of IGF-II with a carboxyl 89-aa extension, the E domain. A derivative of proIGF-II containing only the first 21 aa of the E domain [proIGF-II-(E1-21)] has been isolated by others from normal serum and has O-linked glycosylation. We found that the "big IGF-II" of normal serum, as detected by an RIA directed against residues 1-21 of the E domain of proIGF-II, was reduced in size by treatment with neuraminidase and O-glycosidase. The big IGF-II, which is greatly increased in NICTH sera, was unaffected by neuraminidase and O-glycosidase treatment. We have also shown that big IGF-II from normal serum is retained by jacalin lectin columns and that big IGF-II from NICTH serum was not retained, indicating that it lacked O-glycosylation. Normal O-linked glycosylation may be required for proper peptidase processing of proIGF-II. The lack of normal O-linked glycosylation by tumors may explain the predominance of big IGF-II in NICTH sera. In normal serum, most of the IGF-II is present in a 150-kDa ternary complex with IGF-II binding protein (IGFBP) 3 and alpha subunit. In NICTH serum, however, the complexes carrying big IGF-II are < 50 kDa. We investigated whether big IGF-II of NICTH was responsible for this abnormality. Tumor big IGF-II and IGF-II were equally effective in forming the 150-kDa complex with purified IGFBP-3 and 125I-labeled alpha subunit. Both 125I-labeled IGF-II and 125I-labeled proIGF-II-(E1-21), when incubated with normal serum, formed the 150-kDa complex as detected by Superose 12 exclusion chromatography. We conclude that the nonglycosylated big IGF-II of NICTH serum can form normal complexes with serum IGFBPs. The defective binding in NICTH is attributable to defective IGFBP-3 binding.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Bayne M. L., Cascieri M. A. Structural determinants for binary and ternary complex formation between insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):60–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Daughaday W. H. Impaired formation of the ternary insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex in patients with hypoglycemia due to nonislet cell tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Oct;73(4):696–702. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-4-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Structure of the Mr 140,000 growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex: determination by reconstitution and affinity-labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6898–6902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterill A. M., Holly J. M., Davies S. C., Coulson V. J., Price P. A., Wass J. A. The insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in a case of non-islet-cell tumour-associated hypoglycaemia. J Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;131(2):303–311. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Deuel T. F. Tumor secretion of growth factors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1991 Sep;20(3):539–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Emanuele M. A., Brooks M. H., Barbato A. L., Kapadia M., Rotwein P. Synthesis and secretion of insulin-like growth factor II by a leiomyosarcoma with associated hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 1;319(22):1434–1440. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812013192202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Kapadia M. Significance of abnormal serum binding of insulin-like growth factor II in the development of hypoglycemia in patients with non-islet-cell tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6778–6782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H. Radioligand assays for insulin-like growth factor II. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:248–259. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Trivedi B. Heterogeneity of serum peptides with immunoactivity detected by a radioimmunoassay for proinsulin-like growth factor-II E domain: description of a free E domain peptide in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Aug;75(2):641–645. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.2.1379260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Trivedi B. Measurement of derivatives of proinsulin-like growth factor-II in serum by a radioimmunoassay directed against the E-domain in normal subjects and patients with nonislet cell tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):110–115. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1618998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargosky S. E., Owens P. C., Walton P. E., Owens J. A., Robinson J. S., Wallace J. C., Ballard F. J. Most of the circulating insulin-like growth factors-I and -II are present in the 150 kDa complex during human pregnancy. J Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;131(3):491–497. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1310491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarberg B., Tally M., Samuelsson E., Wadensten H., Holmgren E., Hartmanis M., Hall K., Uhlén M., Moks T. Characterization of an extended form of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11058–11062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizuka N., Takano K., Tanaka I., Asakawa K., Miyakawa M., Horikawa R., Shizume K. Demonstration of insulin-like growth factor I in human urine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jun;64(6):1309–1312. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-6-1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortin G. L., Trimpe B. L. Lectin affinity chromatography of proteins bearing O-linked oligosaccharides: application of jacalin-agarose. Anal Biochem. 1990 Aug 1;188(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90605-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgins W. R., Hampton B., Burgess W. H., Perdue J. F. The identification of O-glycosylated precursors of insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8153–8160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Clemmons D., Nissley P., Rechler M. M. NIH conference. Insulin-like growth factors in health and disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 15;116(10):854–862. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-10-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P. Structure, evolution, expression and regulation of insulin-like growth factors I and II. Growth Factors. 1991;5(1):3–18. doi: 10.3109/08977199109000267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suikkari A. M., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 is functionally normal in pregnancy serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jan;74(1):177–183. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.1.1370163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Asami O., Hayano T., Sasaki I., Yoshitake Y., Nishikawa K. Identification of a family of insulin-like growth factor II secreted by cultured rat epithelial-like cell line 18,54-SF: application of a monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):870–877. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer U., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Is extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia associated with elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor II? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):833–839. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Futo E., Peter M., Froesch E. R. Can "big" insulin-like growth factor II in serum of tumor patients account for the development of extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia? J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2574–2584. doi: 10.1172/JCI116152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Guler H. P., Waldvogel M., Hauri C., Futo E., Hossenlopp P., Binoux M., Froesch E. R. Regulation of binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in humans. Increased expression of IGF binding protein 2 during IGF I treatment of healthy adults and in patients with extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):952–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumstein P. P., Lüthi C., Humbel R. E. Amino acid sequence of a variant pro-form of insulin-like growth factor II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3169–3172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


