The authors would like to correct panel H in Fig 3 to show the correct MFI values of PD-L1 expression on human CD4+ T cells. The error occurred during preparation of the figure for manuscript revision. The percentages of infected CD4 cells expressing PD-L1 were accidentally duplicated from panel I in Fig 3. Please see the corrected version of Fig 3 here.
Fig 3. PD-L1 expression on cells infected in vitro with FV or HIV.
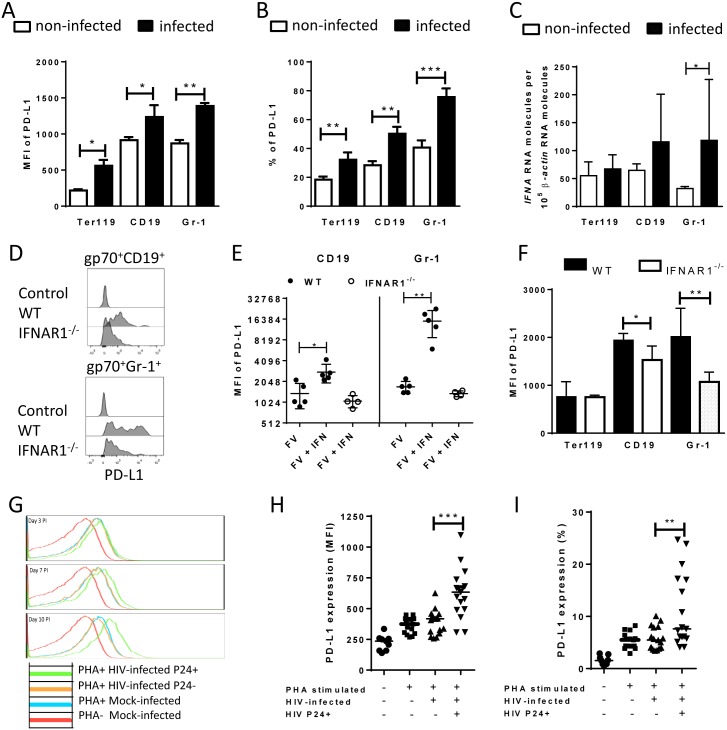
Spleen cells were isolated from naive B6 mice and cultivated with F-MuLV infected Mus Dunni cells to infect mouse cells in vitro. Multi-parameter flow cytometry was used to determine PD-L1 expression (MFI) (A) and the percentage of PD-L1high cells (B) in different target cell populations of FV. C. Ter119+, CD19+, and Gr-1+ cells were isolated from naïve wild type mice and were infected with F-MuLV in vitro. mRNA from infected and non-infected cells was isolated for real time PCR quantification of the IFNα mRNA expression. The numbers of IFNα mRNA copies in relation to 105 copies of mRNA for β-actin is shown. Data was pooled from at least two independent experiments with similar results. Spleen cells were isolated from naїve wild type mice or from naïve IFNAR1-/- mice and cultivated with F-MuLV infected Mus Dunni cells to infect mouse cells in vitro. Multi-parameter flow cytometry was used to determine PD-L1 expression (MFI) on infected CD19+ and Gr-1+ cells (D) and in the presence of IFNα (E) Data was pooled from at least two independent experiments with similar results. F. Multi-parameter flow cytometry was used to determine the expression of PD-L1 on the sur-face of gp70+Ter119+, gp70+CD19+, and gp70+Gr-1+ cells isolated from spleens of 6 day FV infected WT and IFNAR1-/- mice. Data was pooled from two independent experiments with similar results. Multi-parameter flow cytometry was used to determine the expression of PD-L1 on the surface of human CD4+ T cells after HIV-1 infection. Representative histograms of PD-L1 expression on human CD4+ T cells non-stimulated and non-infected, stimulated in vitro with PHA and infected with HIV-1 or cells only stimulated with PHA are shown. The data is shown for day three, seven and ten after infection (G). Expression of PD-L1 on human CD4+ T cells (H) and the percentage of PD-L1high CD4+ T cells (I) in populations of non-stimulated and non-infected, stimulated in vitro with PHA and infected with HIV-1 or cells only stimulated with PHA are shown at day ten after infection. Mean numbers plus SD from three independent experiments with similar results was shown. Differences between FV infected (gp70+) and FV non-infected (gp70-) mice cells were analyzed by an unpaired t-test. Differences between HIV infected (p24+) and HIV non-infected (p24-) CD4+ cells were analyzed by Mann-Whitney t test. Statistically significant differences between the groups are indicated in the figure (*p˂0.05, **p˂0.005).
Reference
- 1. Akhmetzyanova I, Drabczyk M, Neff CP, Gibbert K, Dietze KK, Werner T, et al. (2015) PD-L1 Expression on Retrovirus-Infected Cells Mediates Immune Escape from CD8+ T Cell Killing. PLoS Pathog 11(10): e1005224 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005224 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]