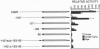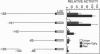Abstract
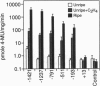
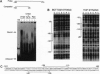
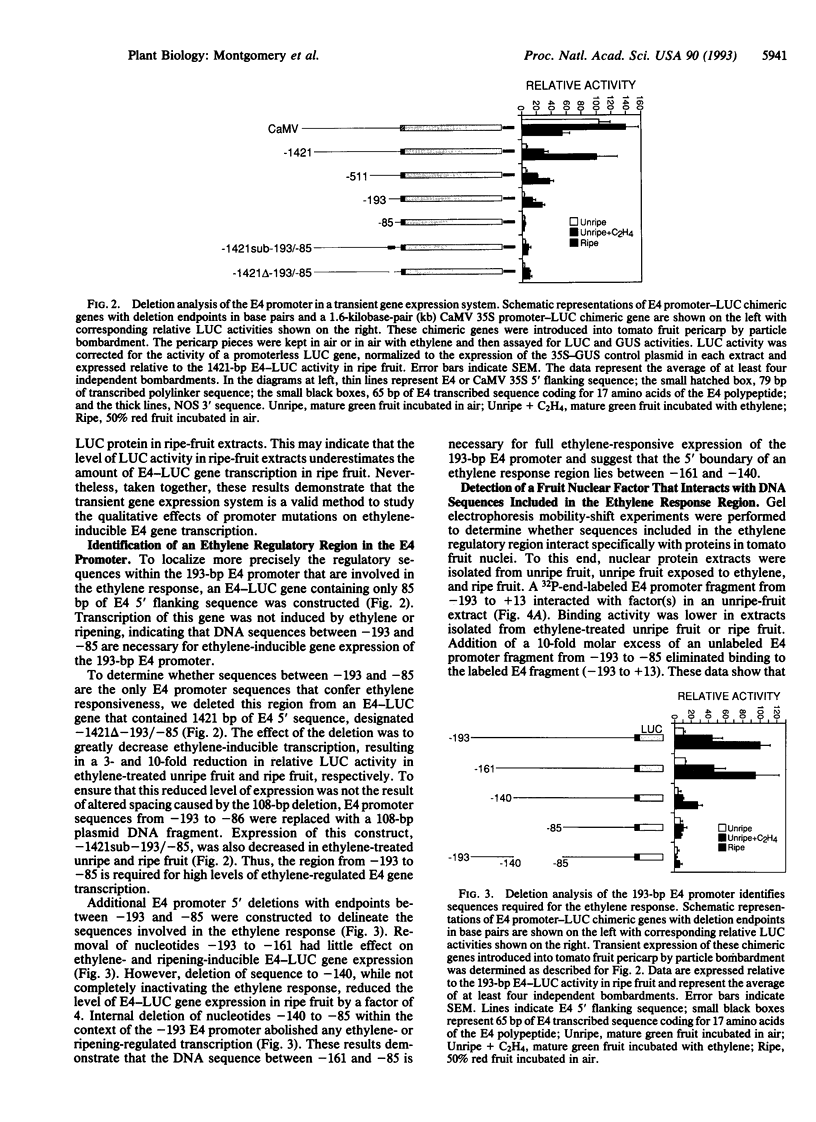
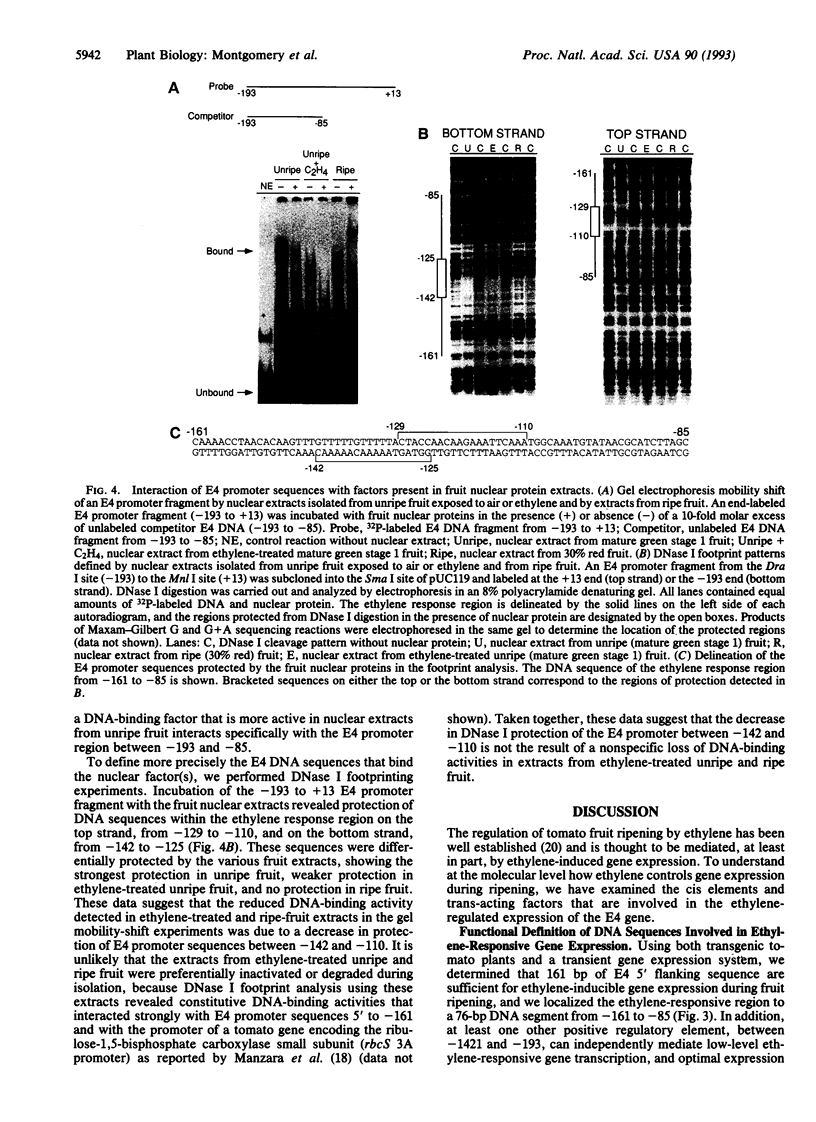
Transcription of the E4 gene is controlled by an increase in ethylene concentration during tomato fruit ripening. To investigate the molecular basis for ethylene regulation, we have examined the E4 promoter to identify cis elements and trans-acting factors that are involved in E4 gene expression. In transgenic tomato plants a chimeric gene construct containing a 1.4-kilobase E4 promoter fused to a beta-glucuronidase reporter gene is rapidly induced by ethylene in ripening fruit. Deletion of E4 promoter sequences to 193 base pairs reduces the level of GUS activity but does not affect ethylene induction. Transient expression of E4 promoter-luciferase chimeric gene constructs containing various deletions, introduced into tomato fruit pericarp by particle bombardment, indicates that a positive ethylene-responsive region is localized between nucleotides -161 and -85 relative to the transcription start site. DNase I footprint analysis shows that a nuclear factor in unripe fruit interacts specifically with sequences in this element, from -142 to -110, which are required for the ethylene response. The DNase I footprint of this factor is reduced in ethylene-treated unripe fruit and undetectable in ripe fruit. Based on the correlation of a nuclear factor binding site with promoter sequences required for ethylene induction, we propose that this in vitro DNA-binding activity may represent a factor that is involved in ethylene-regulated E4 gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broglie K. E., Biddle P., Cressman R., Broglie R. Functional analysis of DNA sequences responsible for ethylene regulation of a bean chitinase gene in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell. 1989 Jun;1(6):599–607. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass L. G., Kirven K. A., Christoffersen R. E. Isolation and characterization of a cellulase gene family member expressed during avocado fruit ripening. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):76–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00315799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes S., Deikman J., Margossian L. J., Fischer R. L. Interaction of a developmentally regulated DNA-binding factor with sites flanking two different fruit-ripening genes from tomato. Plant Cell. 1989 Oct;1(10):1025–1034. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.10.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deikman J., Fischer R. L. Interaction of a DNA binding factor with the 5'-flanking region of an ethylene-responsive fruit ripening gene from tomato. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3315–3320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deikman J., Kline R., Fischer R. L. Organization of Ripening and Ethylene Regulatory Regions in a Fruit-Specific Promoter from Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Plant Physiol. 1992 Dec;100(4):2013–2017. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.4.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon-Kamm W. J., Spencer T. M., Mangano M. L., Adams T. R., Daines R. J., Start W. G., O'Brien J. V., Chambers S. A., Adams W. R., Jr, Willetts N. G. Transformation of Maize Cells and Regeneration of Fertile Transgenic Plants. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):603–618. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J., Picton S., Shabbeer J., Schuch W., Grierson D. Molecular biology of fruit ripening and its manipulation with antisense genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):69–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00015607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney A. L., Park E. A., Giralt M., Liu J., Hanson R. W. Opposing actions of Fos and Jun on transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene. Dominant negative regulation by Fos. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18133–18139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln J. E., Cordes S., Read E., Fischer R. L. Regulation of gene expression by ethylene during Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) fruit development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln J. E., Fischer R. L. Diverse mechanisms for the regulation of ethylene-inducible gene expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Apr;212(1):71–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00322446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln J. E., Fischer R. L. Regulation of Gene Expression by Ethylene in Wild-Type and rin Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) Fruit. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):370–374. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Carrasco P., Gruissem W. Developmental and organ-specific changes in promoter DNA-protein interactions in the tomato rbcS gene family. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1305–1316. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeller P. W., Lu M. W., Taylor L. P., Pike D. A., Theologis A. Reversible inhibition of tomato fruit senescence by antisense RNA. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):437–439. doi: 10.1126/science.1925603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., DE Wet J. R., Helinski D. R., Howell S. H., Wood K. V., Deluca M. Transient and stable expression of the firefly luciferase gene in plant cells and transgenic plants. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):856–859. doi: 10.1126/science.234.4778.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghothama K. G., Lawton K. A., Goldsbrough P. B., Woodson W. R. Characterization of an ethylene-regulated flower senescence-related gene from carnation. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;17(1):61–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00036806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M. A., Nelson H., Weissbach H., Brot N. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the Escherichia coli peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15549–15551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roby D., Broglie K., Gaynor J., Broglie R. Regulation of a chitinase gene promoter by ethylene and elicitors in bean protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1991 Sep;97(1):433–439. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. The complexities of eukaryotic transcription initiation: regulation of preinitiation complex assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90164-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]