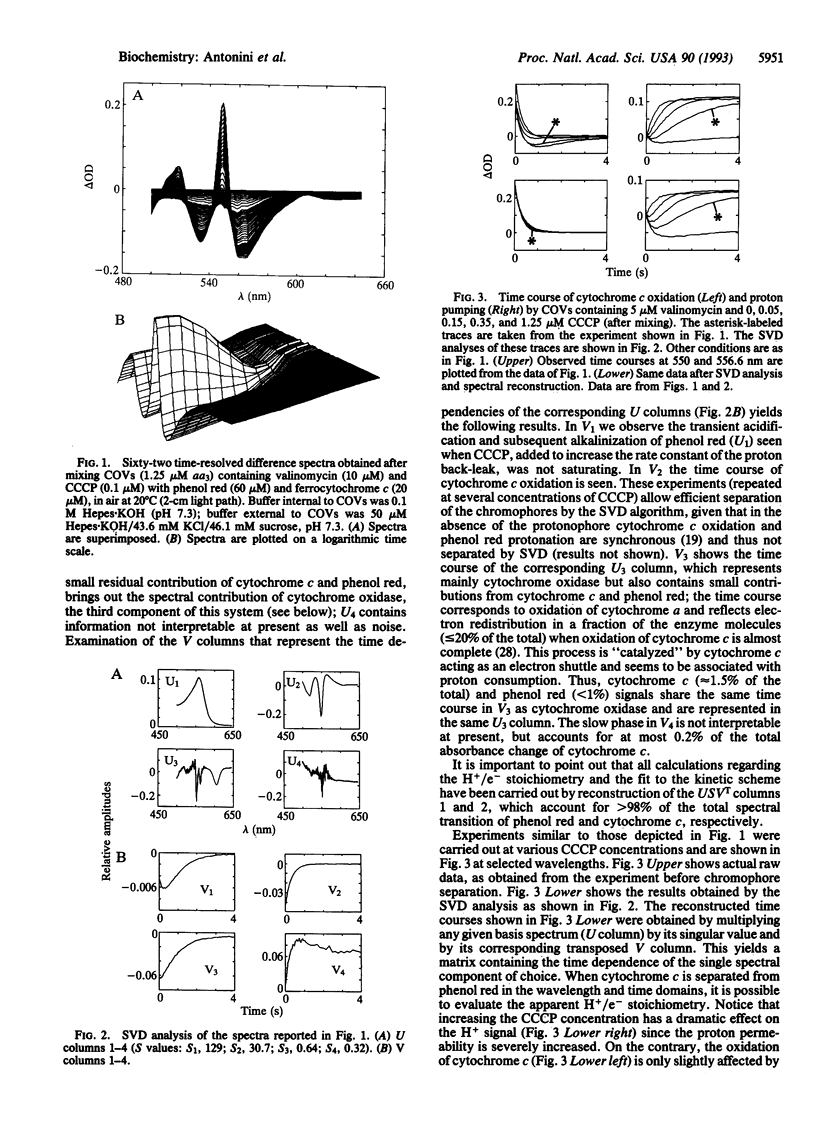
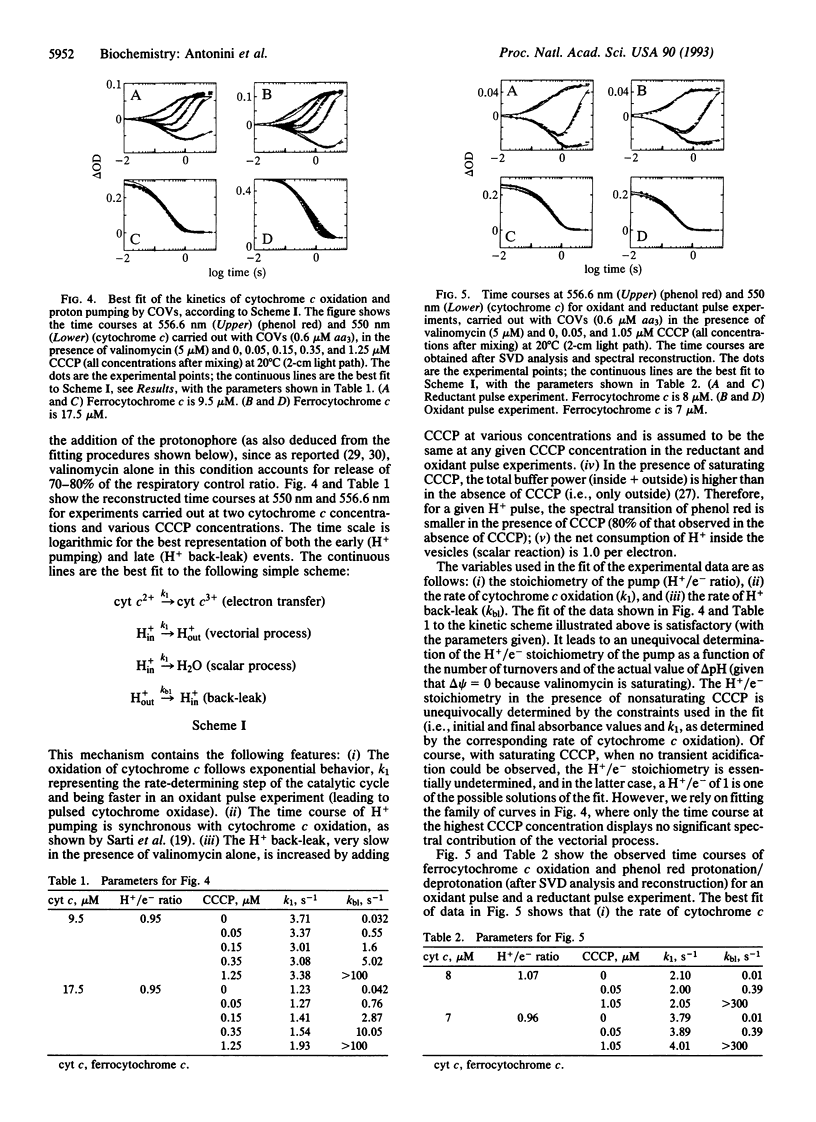
Abstract
The H+/e- stoichiometry for the proton pump of cytochrome c oxidase reportedly varies between 0 and 1, depending on experimental conditions. In this paper, we report the results obtained by a combination of transient optical spectroscopy with a time resolution of 10 ms and a singular value decomposition analysis to follow the kinetics, separate the observed spectral components, and quantitate the stoichiometry of the pump. By using cytochrome oxidase reconstituted into small unilamellar vesicles, we show that the time courses of ferrocytochrome c oxidation and phenol red acidification or alkalinization fit a simple kinetic scheme. The fitting procedure leads to unbiased and objective determination of the H+/e- ratio under various experimental conditions. The proton-pumping stoichiometry was found to be 1.01 +/- 0.10, independent of the number of turnovers, proton back-leak rate, or type of experiment (oxidant or reductant pulse).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Greenwood C., Wilson M. T. Oxygen "pulsed" cytochrome c oxidase: functional properties and catalytic relevance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3128–3132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Greenwood C., Malmström B. G. Catalytic mechanism of cytochrome oxidase. Nature. 1970 Dec 5;228(5275):936–937. doi: 10.1038/228936a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini G., Malatesta F., Sarti P., Brunori M. Control of cytochrome oxidase activity. A transient spectroscopy study. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13193–13202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock G. T., Wikström M. Oxygen activation and the conservation of energy in cell respiration. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):301–309. doi: 10.1038/356301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Antonini G., Malatesta F., Sarti P., Wilson M. T. Cytochrome-c oxidase. Subunit structure and proton pumping. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 16;169(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Colosimo A., Rainoni G., Wilson M. T., Antonini E. Functional intermediates of cytochrome oxidase. Role of "pulsed" oxidase in the pre-steady state and steady state reactions of the beef enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10769–10775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Sarti P., Colosimo A., Antonini G., Malatesta F., Jones M. G., Wilson M. T. Mechanism of control of cytochrome oxidase activity by the electrochemical-potential gradient. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2365–2368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzezinski P., Malmström B. G. Electron-transport-driven proton pumps display nonhyperbolic kinetics: Simulation of the steady-state kinetics of cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capitanio N., Capitanio G., De Nitto E., Villani G., Papa S. H+/e- stoichiometry of mitochondrial cytochrome complexes reconstituted in liposomes. Rate-dependent changes of the stoichiometry in the cytochrome c oxidase vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Chappell J. B., Azzi A. Limited-turnover studies on proton translocation in reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase-containing vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):149–156. doi: 10.1042/bj1820149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Miller S., Brautigan D. L., Margoliash E. Correlation of the kinetics of electron transfer activity of various eukaryotic cytochromes c with binding to mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1104–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Margoliash E. Interaction of cytochrome c with cytochrome c oxidase: an understanding of the high- to low-affinity transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 2;1015(2):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90032-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krab K., Wikström M. Proton-translocating cytochrome c oxidase in artificial phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 11;504(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. P. Slip and leak in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 23;977(2):123–141. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Capitanio N., De Nitto E. Characteristics of the redox-linked proton ejection in beef-heart cytochrome c oxidase reconstituted in liposomes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):507–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttilä T. Properties and reconstitution of a cytochrome oxidase deficient in subunit III. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. Reconstitution of membrane processes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:699–711. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarti P., Colosimo A., Brunori M., Wilson M. T., Antonini E. Kinetic studies on cytochrome c oxidase inserted into liposomal vesicles. Effect of ionophores. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):81–89. doi: 10.1042/bj2090081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarti P., Jones M. G., Antonini G., Malatesta F., Colosimo A., Wilson M. T., Brunori M. Kinetics of redox-linked proton pumping activity of native and subunit III-depleted cytochrome c oxidase: a stopped-flow investigation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapleigh J. P., Hosler J. P., Tecklenburg M. M., Kim Y., Babcock G. T., Gennis R. B., Ferguson-Miller S. Definition of the catalytic site of cytochrome c oxidase: specific ligands of heme a and the heme a3-CuB center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Carafoli E. Quantitative analysis of the proton and charge stoichiometry of cytochrome c oxidase from beef heart reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solioz M., Carafoli E., Ludwig B. The cytochrome c oxidase of Paracoccus denitrificans pumps protons in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1579–1582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G. J., Buse G. Studies on cytochrome c oxidase, IV[1--3]. Primary structure and function of subunit II. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Apr;360(4):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., O'Shea P. S., Petrone G., Azzi A. Proton translocation by a native and subunit III-depleted cytochrome c oxidase reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. Use of fluorescein-phosphatidylethanolamine as an intravesicular pH indicator. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3626–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrom M. K. Proton pump coupled to cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):271–273. doi: 10.1038/266271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigglesworth J. M. Quantization of membrane potential generation by cytochrome c oxidase in small vesicles. J Inorg Biochem. 1985 Mar-Apr;23(3-4):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(85)85040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. III. Improved preparation and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1680–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



