Abstract
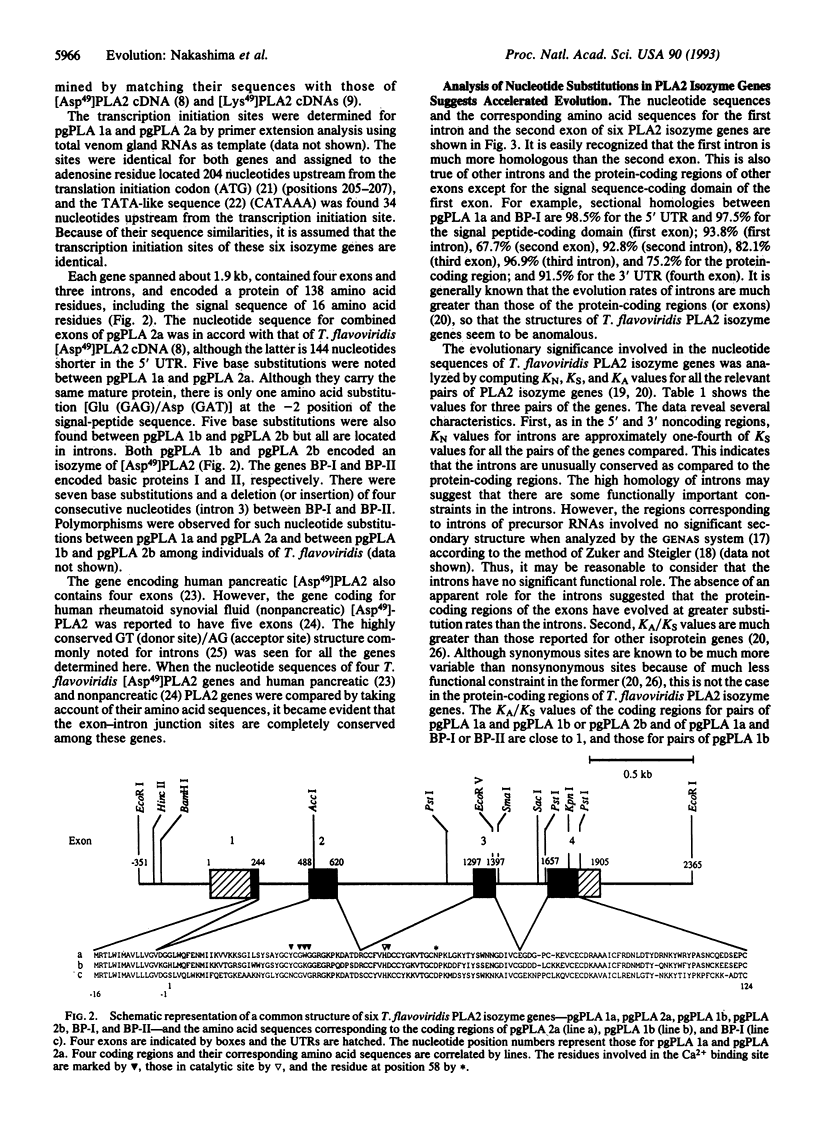
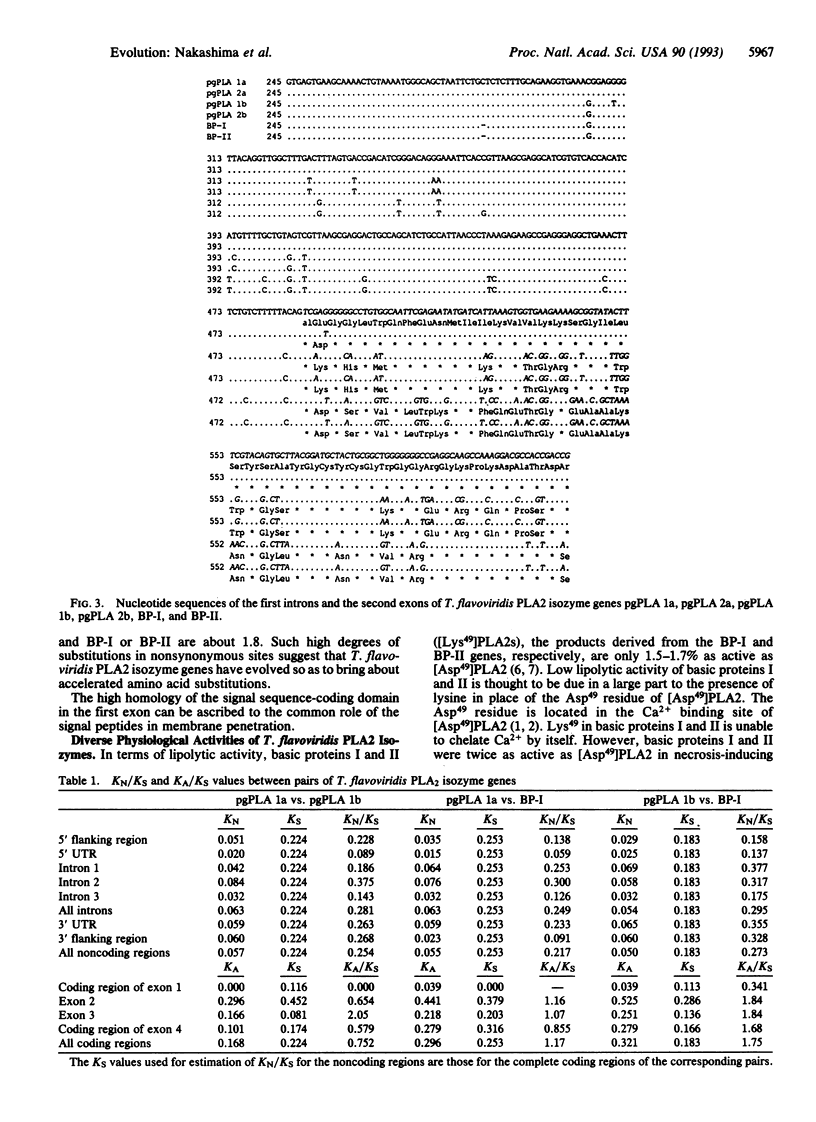
Six Trimeresurus flavoviridis (Habu snake) venom gland phospholipase A2 (PLA2) isozyme genes were found to consist of four exons and three introns and to encode proteins of 138 amino acid residues, including the signal sequence of 16 amino acid residues. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences showed that the introns are much more homologous than the protein-coding regions of exons except for the signal peptide-coding region of the first exon. The numbers of nucleotide substitutions per site (KN) for introns are approximately one-fourth of the numbers of nucleotide substitutions per synonymous site (KS) for the protein-coding regions, indicating that the introns are unusually conserved. The absence of an apparent functional role for the introns suggests that the protein-coding regions, except for the signal peptide-coding domains, have evolved at greater substitution rates than introns. The fact that the numbers of nucleotide substitutions per nonsynonymous site (KA) are close to or larger than KS values for relevant pairs of genes revealed that Darwinian-type accelerated substitutions have occurred in the protein-coding regions or exons. This is compatible with the presence of PLA2 species with diverse physiological activities in the venom.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra B. W., Kalk K. H., Hol W. G., Drenth J. Structure of bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at 1.7A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):97–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fucharoen S., Fucharoen G., Fucharoen P., Fukumaki Y. A novel ochre mutation in the beta-thalassemia gene of a Thai. Identification by direct cloning of the entire beta-globin gene amplified using polymerase chain reactions. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7780–7783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa T., Matsumoto H., Shimohigashi Y., Ogawa T., Oda N., Chang C. C., Ohno M. Sequence determination and characterization of a phospholipase A2 isozyme from Trimeresurus gramineus (green habu snake) venom. Toxicon. 1992 Nov;30(11):1331–1341. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90510-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Hastie N. D. Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):96–99. doi: 10.1038/326096a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru K., Kihara H., Ohno M. Purification and properties of phospholipase A from venom of Trimeresurus flavoviridis (Habu snake). J Biochem. 1980 Aug;88(2):443–451. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara H., Uchikawa R., Hattori S., Ohno M. Myotoxicity and physiological effects of three Trimeresurus flavoviridis phospholipases A2. Biochem Int. 1992 Dec;28(5):895–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhara S., Matsuo F., Futamura S., Fujita A., Shinohara T., Takagi T., Sakaki Y. GENAS: a database system for nucleic acid sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):89–99. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. Y., Yoshizumi K., Oda N., Ohno M., Tokunaga F., Iwanaga S., Kihara H. Purification and amino acid sequence of basic protein II, a lysine-49-phospholipase A2 with low activity, from Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):400–408. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraganore J. M., Merutka G., Cho W., Welches W., Kézdy F. J., Heinrikson R. L. A new class of phospholipases A2 with lysine in place of aspartate 49. Functional consequences for calcium and substrate binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13839–13843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T. Molecular evolution of mRNA: a method for estimating evolutionary rates of synonymous and amino acid substitutions from homologous nucleotide sequences and its application. J Mol Evol. 1980 Sep;16(1):23–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01732067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda N., Ogawa T., Ohno M., Sasaki H., Sakaki Y., Kihara H. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for Trimeresurus flavoviridis phospholipase A2, and consequent revision of the amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1990 Nov;108(5):816–821. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Oda N., Nakashima K., Sasaki H., Hattori M., Sakaki Y., Kihara H., Ohno M. Unusually high conservation of untranslated sequences in cDNAs for Trimeresurus flavoviridis phospholipase A2 isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renetseder R., Brunie S., Dijkstra B. W., Drenth J., Sigler P. B. A comparison of the crystal structures of phospholipase A2 from bovine pancreas and Crotalus atrox venom. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11627–11634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Randall T. L., Yamanaka M., Johnson L. K. Pancreatic phospholipase A2: isolation of the human gene and cDNAs from porcine pancreas and human lung. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):519–527. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Mohri N., Kihara H., Ohno M. Amino acid sequence of Trimeresurus flavoviridis phospholipase A2. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):281–289. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizumi K., Liu S. Y., Miyata T., Saita S., Ohno M., Iwanaga S., Kihara H. Purification and amino acid sequence of basic protein I, a lysine-49-phospholipase A2 with low activity, from the venom of Trimeresurus flavoviridis (Habu snake). Toxicon. 1990;28(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90005-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



