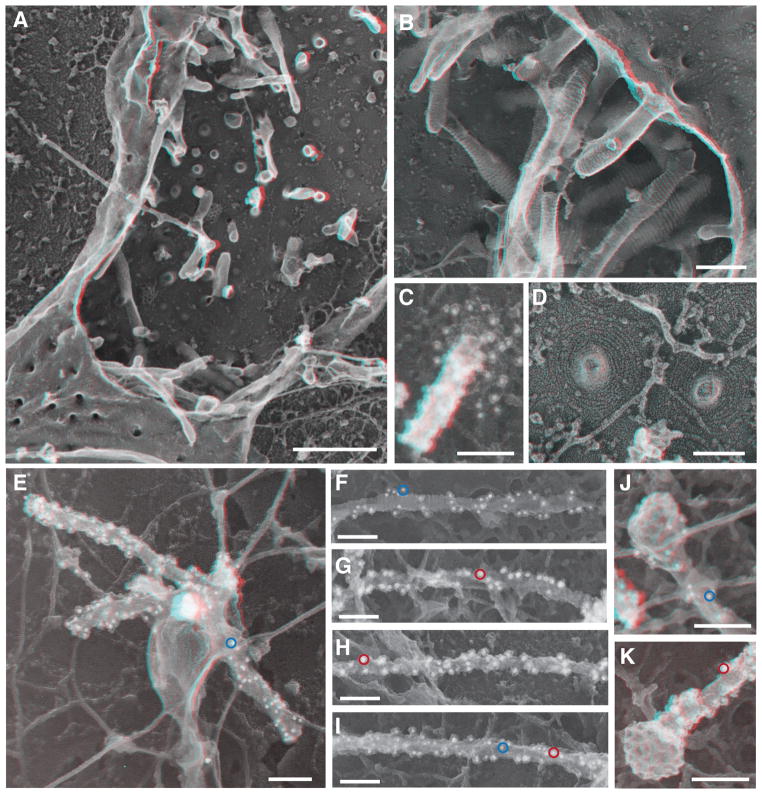
Fig. 3. CHMP1B and IST1 tubulated cellular membranes.
(A) Survey view of the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane in an unroofed COS-7 cell expressing FLAG-CHMP1B. Tubular invaginations extending into the cell interior are apparent along the exposed plasma membrane and as stabilized openings at the edges of the cell. Use view glasses for 3D viewing of anaglyphs (left eye = red). (B) Higher magnification view of tubular invaginations induced and coated by FLAG-CHMP1B filaments. (C) Immunodecoration confirmed the presence of CHMP1B around and along a tubule in a cell expressing untagged CHMP1B. Antibody detected with 12 nm gold is white in these contrast reversed EM images. (D) Higher magnification view of FLAG-CHMP1B filament spirals on exposed plasma membrane. (E) CHMP1B-immunoreactive organelle in an unroofed COS-7 cell expressing untagged CHMP1B. Antibody detected with 12 nm gold is white in these contrast reversed EM images; a representative gold particle is circled in blue. (F to I) Representative internal tubules from cells co-expressing untagged CHMP1B (12 nm gold, example circled in blue) and IST1-myc (18 nm gold); examples circled in red. (J and K) Clathrin coated bud capping the end of CHMP1B (J) and IST1-myc (K) immuno-labeled tubules from co-transfected cells. Importantly, measurements of filament diameter (and interstrand spacing) showed that when apparently unitary filaments were resolvable, their diameter varied from 5–10 nm including platinum. These measurements are generally consistent with the dimensions of IST1-CHMP1B and CHMP1B filaments formed in vitro. Scale bars 500nm (A), 100nm (B) to (K).