Abstract
Background
Published criteria defining the accelerated phase in chronic myeloid leukemia are heterogeneous and little is known about predictors of poor outcome.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of 139 subjects in the accelerated phase of chronic myeloid leukemia treated with imatinib at a single center in Brazil. The objective was to identify risk factors for survival, major cytogenetic response and progression to blast phase in this population. The factors analyzed were: blasts 10–29%, basophils ≥ 20%, platelets > 1 × 106/μL or <1 × 105/μL and white blood cells > 1 × 105/μL in the peripheral blood, as well as clonal evolution, splenomegaly, hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, time between diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia and imatinib treatment, and hematologic toxicity.
Results
Risk factors for poor survival in multivariate analysis were Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity (p-value = 0.001), blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.023), and hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.04). Risk factors for not achieving major cytogenetic response were blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.007), hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.001), and previous use of interferon (p-value = 0.032). Risk factors for progression to the blast phase were hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.005), basophils ≥ 20% (p-value = 0.023), and time from diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia to imatinib treatment > 12 months (p-value = 0.030).
Conclusion
These data indicate that patients with the above risk factors have a worse prognosis. This information can guide the therapy to be used.
Keywords: Chronic myeloid leukemia, Accelerated phase, Imatinib, Prognostic factor, Mortality
Introduction
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cells characterized by the reciprocal translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11) which determines the Philadelphia chromosome and constitutive activation of the breakpoint cluster region-Abelson (BCR-ABL) tyrosine kinase.1, 2 At the time of diagnosis, 90% of patients are in the chronic phase (CP). However, CML can progress from the CP to a more aggressive clinical picture – the accelerated phase (AP), when disease control is more difficult. AP is a signal of progression and transformation to the usually fatal blast phase (BP).
Over the past decade, the introduction of imatinib mesylate has been considered the first-line therapy for all phases of CML.3, 4, 5, 6, 7 Clinical trials have established the efficacy of imatinib in targeting the pathophysiology of CML, resulting in increased survival and fewer side effects than with the use of interferon.8, 9, 10 In Brazil, the delayed approval of imatinib mesylate for first line therapy led many patients to receive this therapy only at advanced phases of the disease. In the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, it is important to define prognostic factors not only prior to therapy but also during the course of treatment. The biological characteristics of the disease can strongly influence the degree and duration of response to imatinib and the overall survival (OS).
The criteria of the AP vary in the literature (Table 1). While some criteria are included in most classifications, such as percentage of basophils and blasts in the peripheral blood (PB), others are subjective and are included in only some classifications, e.g. persistent splenomegaly. The International Blood and Marrow Transplant (IBMTR) criteria have been used in studies that involved bone marrow transplantation.11 In 2001 the World Health Organization (WHO) proposed a new classification system in order to refine the criteria for the AP and BP.12 In 2006, the MD Anderson Cancer Center reclassified patients and compared their outcomes with imatinib as well, based on standard definitions and on the new WHO classification system.6 The European Leukemia net (ELN) criteria were revised in 2013.13
Table 1.
List of the criteria defining accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia as recommended by MDACC,6 IBMTR,11 WHO12 and ELN.13
| Criteria | MDACC | IBMTR | WHO | ELN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blasts | PB or BM 10–29% | PB or BM ≥ 10% | PB or BM 10–19% | PB or BM 15–29% |
| Blasts and promyelocytes | ≥30% | PB or BM ≥ 20% | NA | ≥30% with blasts < 30% |
| Basophils | PB or BM ≥ 20% | PB ≥ 20% | PB ≥ 20% | PB ≥ 20% |
| Platelets | >1000 × 109/L, or <100 × 109/L, unresponsive to therapy | Persistent thrombocytosis | >1000 × 109/L, or <100 × 109/L, unresponsive to therapy | Persistent thrombocytopenia (<100 × 109/L) unrelated to therapy |
| WBC | >10 × 109/L | Difficult control | Increasing WBC count unresponsive to therapy | NA |
| Anemia | NA | Unresponsive to therapy | NA | NA |
| Splenomegaly | Persistent splenomegaly unresponsive to sustained therapy | Increasing spleen size | Increasing spleen size | NA |
| Cytogenetic | NA | CE | CE not present at the time of diagnosis | Clonal chromosome abnormalities in Ph+ cells (CCA/Ph1), major route, on treatment |
| Others | Myelofibrosis, chloromas | Large foci or clusters of blasts in bone marrow biopsy |
MDACC: M. D. Anderson Cancer Center; IBMTR: International Blood and Marrow Transplant Registry; WHO: World Health Organization; ELN: European LeukemiaNet; NA: not applicable; CE: clonal evolution; WBC: white blood cell; PB: peripheral blood; BM: bone marrow.
Objective
The main purpose of this study was to identify which risk factors were associated with poor survival, with the lack of major cytogenetic response (MCR), and with progression to BP in a Brazilian AP-CML population from a single referral center.
Methods
This retrospective study, performed from January 2000 to November 2011, comprised 139 patients with AP-CML who were treated with imatinib at the hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) center of Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Paraná, Brazil. The WHO criteria are routinely used to evaluate patients with AP-CML at this center. However, as the objective of this study was to do an exploratory analysis of published risk factors, subjects were categorized with AP-CML if they had at least one of the aforementioned published criteria.6, 11, 12, 13 All patients received imatinib at an initial dose of 600 mg as first therapy for AP-CML. Doses were incremented (maximum of 800 mg) in cases of inadequate response or reduced (minimum of 300 mg) in cases of hematological or non-hematological toxicity, as necessary. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital de Clínicas, Universidade Federal do Paraná, which waived the requirement of informed consent, as this was a retrospective study with collection of data from medical records.
The following risk factors, some of which were selected according to previously published criteria (Table 1), were evaluated: basophils ≥ 20% in PB, platelets > 1000 × 109/L unresponsive to therapy or <100 × 109/L in PB, white blood cells (WBC) >100 × 109/L in PB, blast 10–29% in PB, presence of clonal evolution (CE), hemoglobin <10 g/dL, and splenomegaly. Splenomegaly was considered when the spleen was palpable ≥10 cm from the left costal margin despite the use of hydroxyurea. Other clinical factors relevant to the disease were also analyzed, including the Sokal score > 0.8 (calculated at the time of diagnosis), time between diagnosis of CML and treatment with imatinib > 12 months, previous use of interferon, age > 60 years, and Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity.
As the PB blasts cut-off point varies in the existing criteria, this study analyzed PB blasts as a continuum with death as the endpoint. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve with death as the endpoint was designed to identify a cut-off value for the PB blast count.
Cytogenetic analysis was performed by the G-banding technique. Bone marrow specimens were examined on direct short-term (24-h) cultures with at least 20 metaphases being analyzed. BCR-ABL transcripts were detected by analyzing peripheral blood with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) according to the International Scale.
Statistic analyses were performed using the STATA program version 8.0. Bivariate and multivariate analyses were performed using the Cox proportional hazards regression model. Variables with p-values < 0.20 in the bivariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis model. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Disease free survival (DFS) was defined as the time from the beginning of treatment to loss of MCR.
The primary endpoint of this study was the identification of risk factors for survival. Risk factors for lack of MCR and transformation to BP were evaluated as secondary endpoints. The BP considered PB or marrow blasts ≥30%.
Results
One hundred and sixty-three patients in AP-CML were identified. Twenty-four patients treated with dasatinib or nilotinib were excluded. Thus, 139 AP-CML patients were treated with imatinib. Of these 139 patients, 60 (43.2%) patients who presented at this center with AP had only received hydroxyurea previously. The remaining 79 (56.8%) patients progressed from CP CML treated mainly with hydroxyurea or interferon alpha in isolation or with Ara-C. Of the 139 patients included, 62 (44.6%) were female and 77 (55.4%) were male. Median age was 43.6 years and 25 (18%) were >60 years of age. Forty-one patients (29.5%) died during the study follow-up and 22 (15.83%) died due to disease progression. Previous therapy included interferon in sixty-four patients (46.04%), hydroxyurea in 131 patients (94.24%) and busulfan in one patient (0.72%). Eighty-four patients (60.4%) had intervals between CML diagnosis and treatment with imatinib > 12 months. There were 128 patients with cytogenetic tests available and 79 patients with molecular tests available. Among them, 76 patients (54.7%) achieved MCR, with 67 (48%) attained a complete cytogenetic response and nine (6.7%) partial cytogenetic response; 26 patients (18.7%) achieved major molecular response (MMR). Thirty patients (21.59%) progressed to BP and five patients (3.6%) underwent HSCT.
Forty-one patients (29.5%) had CE. Among these patients, 13 had complex karyotypes, seven had trisomy of chromosome 8, three had duplication of the Philadelphia chromosome, four had chromosome 7 alterations, one had isochromosome 17q and 11 had other minor route chromosomal aberrations.14 Thirty-eight (27.34%) had splenomegaly; 28 (20.14%) had anemia; 29 (20.86%) had platelets > 1000 × 109/L or <100 × 109/L unresponsive to therapy; six (4.32%) had PB basophils ≥ 20%, ten (7.19%) had WBC > 100 × 109/L and 13 (9.35%) had PB blasts 10–29% (Table 2).
Table 2.
Characteristics of the 139 accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients.
| Variable | |
| Gender, male/female, n (%) | 77/62 (55.4/44.6) |
| Age (years), median (range) | 43.6 (10–78) |
| Previous therapy | |
| Interferon, n (%) | 64 (46.0) |
| Hydroxyurea, n (%) | 60 (43.2) |
| Others, n (%) | 15 (10.8) |
| Hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, n (%) | 28 (20.14) |
| Platelets > 1000 × 109/L or <100 × 109/L, n (%) | 29 (21.86) |
| Spleen ≥ 10 cm from left costal margin, n (%) | 38 (27.34) |
| PB blasts 10–29%, n (%) | 13 (9.35) |
| PB basophils ≥ 20%, n (%) | 6 (4.32) |
| Clonal evolution (%) | 41 (29.5) |
| WBC ≥ 100 × 109/L, n (%) | 10 (7.35) |
PB: peripheral blood; WBC: white blood cell.
Risk factors for poor survival by bivariate analysis included WBC > 100 × 109/L (p-value = 0.1496), PB blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.009), PB basophils ≥ 20% (p-value = 0.04), Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity (p-value = 0.0001), hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.033), age > 60 (p-value = 0.080), and time from CML diagnosis to treatment with imatinib > 12 months (p-value = 0.018). In forward multivariate analysis, only Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity [p-value = 0.001; odds ratio (OR) of 3.84; 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of 1.72–8.59], PB blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.023; OR of 4.21; 95% CI, 1.18–14.96) and hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.044; OR of 2.59; 95% CI, 1.03–6.54) remained significant (Table 3).
Table 3.
Factors associated with lower survival rates in 139 accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib.
| Variable | Bivariate analysis |
p-Value | Multivariate analysis |
p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |||
| PB blasts 10–29% | 4.46 | 1.31–15.13 | 0.009 | 4.21 | 1.18–14.96 | 0.023 |
| Hemoglobin < 10 g/dL | 2.51 | 1.04–6.02 | 0.033 | 2.59 | 1.03–6.54 | 0.044 |
| Grades 3 and 4 hematologic toxicity | 4.29 | 1.89–9.76 | <0.001 | 3.84 | 1.72–8.59 | 0.001 |
OR: odds ratio; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; PB: peripheral blood.
Risk factors for lack of MCR by bivariate analysis were hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.002), PB blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.006), platelets > 1000 × 109/L or <100 × 109/L (p-value = 0.088), splenomegaly (p-value = 0.128), basophils >20% (p-value = 0.032), Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity (p-value = 0.023), High Sokal score (p-value = 0.048), and previous use of interferon (p-value = 0.041). In forward multivariate analysis, only hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.001; OR of 5.27; 95% CI, 1.98–14.07), PB blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.007; OR of 6.84; 95% CI, 1.68–27.89) and previous use of interferon (p-value = 0.032; OR of 2.38; 95% CI, 1.08–5.24) were identified as significant (Table 4).
Table 4.
Risk Factors for not achieving major cytogenetic response of 139 accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib.
| Variables | Bivariate analysis |
p-Value | Multivariate analysis |
p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |||
| PB blasts 10–29% | 5.71 | 1.42–23.03 | 0.006 | 6.84 | 1.68–27.89 | 0.007 |
| Hemoglobin < 10 g/dL | 3.88 | 1.52–9.94 | 0.002 | 5.27 | 1.98–14.07 | 0.001 |
| Previous use of IFN | 2.12 | 1.01–4.42 | 0.041 | 2.38 | 1.08–5.27 | 0.032 |
OR: odds ratio; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; PB: peripheral blood; IFN: interferon.
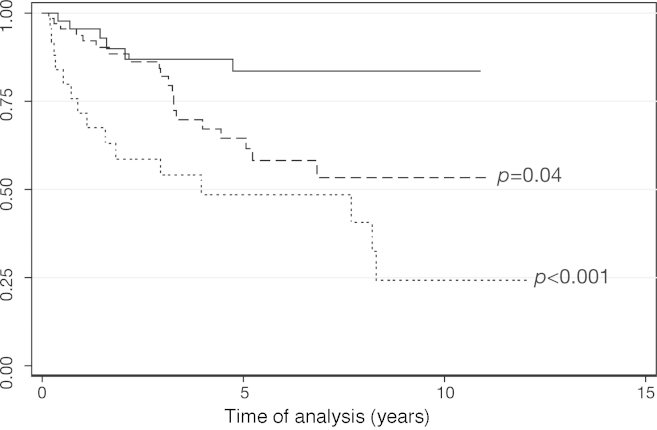
Risk factors for progression to BP by bivariate analysis were hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.003), high Sokal score (p-value = 0.064), PB blasts 10–29% (p-value = 0.052), WBC > 100 × 109/L (p-value = 0.024), time from CML diagnosis to treatment with imatinib > 12 months (p-value = 0.014), and basophils > 20% (p-value = 0.007). In forward multivariate analysis, only hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (p-value = 0.005; OR of 3.94; 95% CI, 1.53–10.15), basophils > 20% (p-value = 0.023; OR of 7.77; 95% CI, 1.32–45.62) and time from CML diagnosis to treatment with imatinib > 12 months (p-value = 0.030; OR of 3.12; 95% CI, 1.11–8.75) remained significant (Table 5). Patients with one (p-value = 0.040; hazard ratio [HR] of 2.60; 95% CI of 1.04–6.49) and two or more risk factors for progression to BP (p-value < 0.001; HR of 5.52; 95% CI, 2.14–14.25) had lower survival compared with patients who did not have any of these factors (Figure 1).
Table 5.
Factors associated with progression to blast phase in 139 accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib.
| Variables | Bivariate analysis |
p-Value | Multivariate analysis |
p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |||
| Time between CML Dx and Rx with imatinib > 12 months | 3.27 | 1.21–8.85 | 0.014 | 3.12 | 1.11–8.75 | 0.03 |
| PB basophils ≥ 20% | 8.08 | 1.33–49.18 | 0.007 | 7.77 | 1.32–45.62 | 0.023 |
| Hemoglobin < 10 g/dL | 3.79 | 1.48–9.69 | 0.003 | 3.94 | 1.53–10.15 | 0.005 |
OR: odds ratio; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; Dx: diagnosis; Rx: treatment; PB: peripheral blood.
Figure 1.
Survival estimates according to the presence of prognostic factors for progression to blast phase. Unbroken line: patients with no prognostic factors (n = 46); dashed line: patients with one prognostic factor (n = 68, Cox regression: p-value = 0.04); dotted line: patients with two or more prognostic factors (n = 25, Cox regression: p-value < 0.001).
As the PB blasts cut-off point varies in existing criteria, this study analyzed PB blasts as a continuum with death as the endpoint. The PB blast cut-off point, based on the ROC curve, was 3% with a sensitivity of 46.5% and specificity of 89.8%.
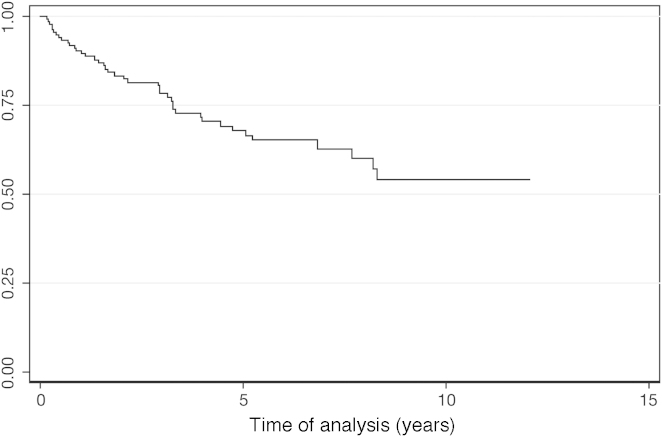
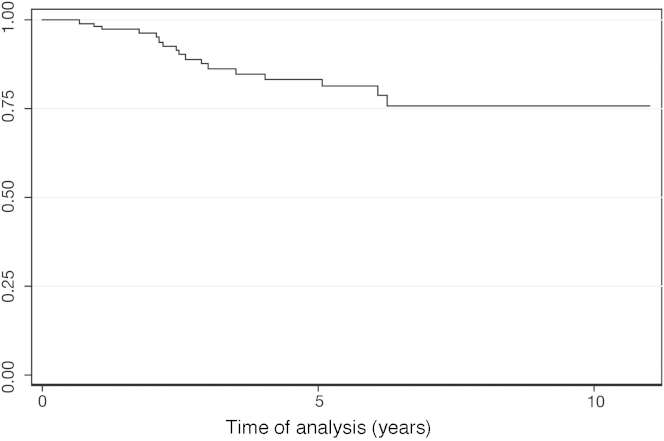
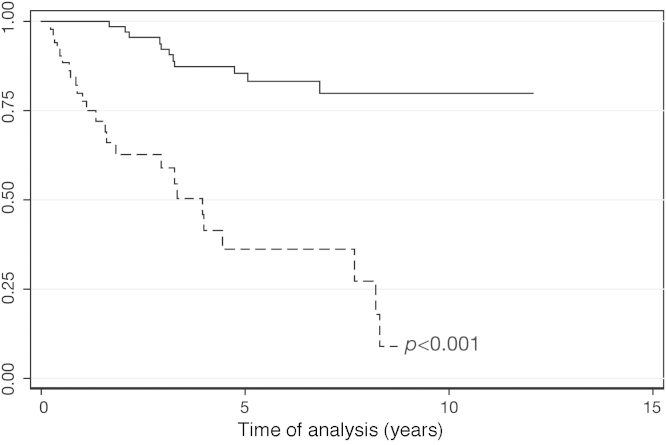
After a median follow-up of 39 months (range: 3.4–129 months), 69.23% of the patients were alive. The OS was 66% at 5 years (Figure 2). The five patients submitted to HSCT were censored in the OS. Of those five patients, four remain alive and in profound molecular response. One patient, who relapsed after transplant and received therapy with imatinib, also achieved profound molecular response. For the patients who achieved MCR, DFS was 83% at 5 years (Figure 3). MCR correlated with better OS (p-value < 0.001; HR = 7.49; 95% CI = 3.62–15.52) (Figure 4).
Figure 2.
Overall survival.
Figure 3.
Disease Free Survival.
Figure 4.
Overall survival according to major cytogenetic response (Cox regression; p-value < 0.001). Unbroken line: major cytogenetic response (n = 76); dashed line: failure to achieve major cytogenetic response (n = 52).
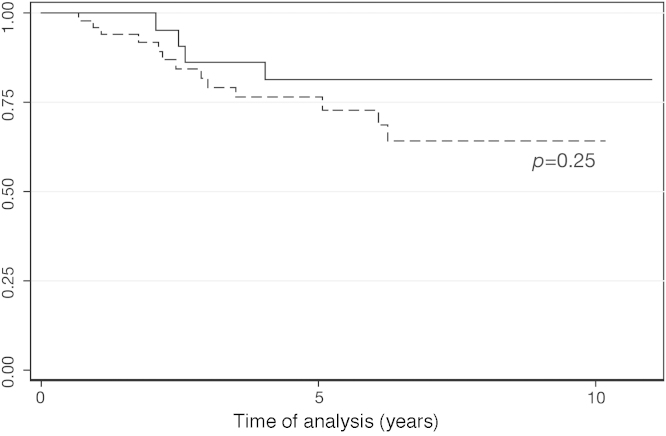
Twenty-six (18.71%) patients lost molecular response and 17 (12.23%) patients lost cytogenetic response. Patients who achieved MMR had slightly better DFS rates compared with those who did not reach MMR, but the difference did not achieve statistical significance (p-value = 0.250; HZ = 1.93; 95% CI = 0.63–5.93) (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Disease Free Survival according to major molecular response (Cox regression; p-value = 0.250). Unbroken line: Major molecular response (n = 26); dashed line: failure to achieve major molecular response (n = 53).
Discussion
As AP-CML criteria vary in the literature, the current population was studied to evaluate prognostic factors for poor survival, lack of MCR and progression to BP. Published criteria as well as other clinically relevant factors were considered.
Regarding the primary endpoint, parameters of poor survival were Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity, high blast counts, and low hemoglobin concentration. No statistical significance was found for platelets or CE. Kantarjian et al. reported pretreatment hemoglobin < 10 g/dL and a lack of cytogenetic response after three months on imatinib therapy as negative predictors of survival in AP-CML.15 Similar risk factors were identified by Jiang et al., who reported that CML duration before treatment > 12 months, hemoglobin < 10 g/dL and PB blasts > 5% were independent adverse prognostic factors for both OS and progression-free survival.16 Interestingly when the blast percentage was analyzed as a continuous variable a cut-off point of 3% in the PB was identified as a predictor of poor survival, suggesting that lower values of PB blasts can be of prognostic value.16
Hematological toxicity with imatinib is more frequent in the late stages of the disease. Severe pancytopenia developed by some patients may indicate an exhaustion of the normal clone with disease progression. Some authors had previously identified hematologic toxicity after tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy as a risk factor for survival.17, 18
Risk factors for not achieving MCR were hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, PB blasts > 5%, and previous use of interferon. As treatment with imatinib compared favorably with the results of treatment using interferon and other therapies in AP-CML patients,15 it seems that delaying the most effective therapy was the explanation that previous use of interferon was a negative factor for MCR. The Gruppo Italiano Malattie EMatologiche dell’Adulto (GIMEMA) CML Working Party found that a stable and confirmed complete cytogenetic response to imatinib constitutes an affordable surrogate marker of long-term OS and DFS, even among AP-CML patients.7
Predictors of progression to BP were hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, basophils ≥ 20%, and time from diagnosis to therapy > 12 months. The definition of BP used in this study was 30% or more blasts in order to include every patient that would be classified as in AP by at least one published criterion. The low number of patients limited the possibility of further categorizing patients by blast percentage in multivariate analysis and that is a limitation of the present study. An increased basophil count is one of the risk factors identified as significant for OS and DFS by Hoffmann et al., and it was used to calculate the European Treatment and Outcome Study (EUTOS) score.19
The rates of MCR and MMR in this study were 54.7% and 18.7%, respectively, and thus similar to previous articles6, 7, 15 (Table 6). CML duration > 12 months and hemoglobin < 10 g/dL were independent adverse predictors of DFS.16 As for the MMR, there was a small number of patients with available molecular tests, and this could explain the lack of significance of MMR on the DFS rate, although a trend was identified. The Sokal risk score has been reported to predict molecular response and OS.20 Moreover, Tripathi et al. identified a correlation between an increased total leukocyte count and poor cytogenetic response.21 However, in this study, the Sokal score and hyperleukocytosis were not associated with progression to BP.
Table 6.
Published results of imatinib therapy for accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients.
| MDACC14 | Jiang et al.15 | Palandri et al.7 | Current study | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 176 | 87 | 111 | 139 |
| MCR | 43% | 49% | 30% | 54.7% |
| MMR | – | 34.5% | – | 18.7% |
| OS | 53% (4y) | 51.4% (6y) | 43% (7y) | 66% (5y) |
MDACC: M. D. Anderson Cancer Center; MCR: major cytogenetic response; MMR: major molecular response; OS: overall survival.
CE and age were clinical factors not significantly associated with either the primary or secondary endpoints. Although some authors suggest that CE is not an important factor for achieving MMR or complete cytogenetic response with imatinib therapy,22 it is an independent poor prognostic factor for survival in both CP-CML and AP-CML according to others.23 Regarding age, older patients treated with imatinib were reported by some authors as having worse survival, but not by others.24, 25 According to Cortes et al., age was not found to be an independent poor prognostic factor for achieving cytogenetic response and for survival in AP-CML patients.26
As mentioned before, Jiang et al. demonstrated that CML duration before treatment ≥12 months, hemoglobin < 100 g/L, and PB blasts ≥ 5% were risk factors for survival among AP patients with CML. Patients were classified into low risk (if they had none of the factors), intermediate risk (if they had one factor), or high risk (for those with at least 2 factors).16 Allogeneic HSCT gives significant survival advantages only for high and intermediate-risk patients with AP-CML. For low risk patients, imatinib therapy leads to a similar outcome as HSCT.16
This study provides long-term results of survival and response of a cohort of AP-CML patients treated with imatinib. The five-year OS of 60% and DFS of 75% among those who achieved MCR are reassuring results, which indicate that patients who lack identified risk factors can achieve long-term response with imatinib.
Prospective studies are very important to define which is the best therapy for this population. Thus, identifying risk factors can allow for tailored therapy with the aim of improving survival, which is usually poor in advanced stage CML.
Conclusion
These data indicate that patients with Grades 3–4 hematologic toxicity after therapy with imatinib, PB blasts 10–29%, and hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, had worse survival than some other patients also classified as AP. Lack of MCR was associated with hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, PB blasts 10–29%, and previous use of interferon. Whereas progression to BP was correlated with hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, PB basophils ≥ 20%, and time from CML diagnosis to treatment with imatinib > 12 months. This information can allow for tailored therapy with the aim of improving results, which are usually poor in advanced stage CML.
Conflicts of interest
The authors Funke VAM and Pasquini R are speakers and/or part of the advisory board of BMS-Brazil and Novartis-Brazil.
References
- 1.Faderl S., Talpaz M., Estrov Z., O’Brien S., Kurzrock R., Kantarjian H.M. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(3):164–172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199907153410306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sawyers C.L. Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(17):1330–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199904293401706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.O’Brien S.G., Guilhot F., Larson R.A., Gathmann I., Baccarani M., Cervantes F. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(11):994–1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Druker B.J., Sawyers C.L., Kantarjian H., Resta D.J., Reese S.F., Ford J.M. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(14):1038–1042. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200104053441402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sawyers C.L., Hochhaus A., Feldman E., Goldman J.M., Miller C.B., Ottmann O.G. Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in myeloid blast crisis: results of a phase II study. Blood. 2002;99(10):3530–3539. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.10.3530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cortes J.E., Talpaz M., O’Brien S., Faderl S., Garcia-Manero G., Ferrajoli A. Staging of chronic myeloid leukemia in the imatinib era: an evaluation of the World Health Organization proposal. Cancer. 2006;106(6):1306–1315. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Palandri F., Castagnetti F., Alimena G., Testoni N., Breccia M., Luatti S. The long-term durability of cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia treated with imatinib 600 mg: the GIMEMA CML Working Party experience after a 7-year follow-up. Haematologica. 2009;94(2):205–212. doi: 10.3324/haematol.13529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Druker B.J., Talpaz M., Resta D.J., Peng B., Buchdunger E., Ford J.M. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(14):1031–1037. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200104053441401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kantarjian H., Sawyers C., Hochhaus A., Guilhot F., Schiffer C., Gambacorti-Passerini C. Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(9):645–652. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Druker B.J., Guilhot F., O’Brien S.G., Gathmann I., Kantarjian H., Gattermann N. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(23):2408–2417. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa062867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Speck B., Bortin M.M., Champlin R., Goldman J.M., Herzig R.H., McGlave P.B. Allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Lancet. 1984;1(8378):665–668. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vardiman J.W., Harris N.L., Brunning R.D. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood. 2002;100(7):2292–2302. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baccarani M., Deininger M.W., Rosti G., Hochhaus A., Soverini S., Apperley J.F. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 2013;122(6):872–884. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-501569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fabarius A., Leitner A., Hochhaus A., Müller M.C., Hanfstein B., Haferlach C. Impact of additional cytogenetic aberrations at diagnosis on prognosis of CML: long-term observation of 1151 patients from the randomized CML Study IV. Blood. 2011;118(26):6760–6768. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-373902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kantarjian H., Talpaz M., O’Brien S., Giles F., Faderl S., Verstovsek S. Survival benefit with imatinib mesylate therapy in patients with accelerated-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia – comparison with historic experience. Cancer. 2005;103(10):2099–2108. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jiang Q., Xu L.P., Liu D.H., Liu K.Y., Chen S.S., Jiang B. Imatinib mesylate versus allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in the accelerated phase. Blood. 2011;117(11):3032–3040. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-308510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Funke V.A., Medeiros C.R., Lima D.H., Setúbal D.C., Bitencourt M.A., Bonfim C.M. Therapy of chronic myeloid leukemia with imatinib mesylate in Brazil: a study of 98 cases. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2005;27(3):159–165. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sneed T.B., Kantarjian H.M., Talpaz M., O’Brien S., Rios M.B., Bekele B.N. The significance of myelosuppression during therapy with imatinib mesylate in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase. Cancer. 2004;100(1):116–121. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hoffmann V.S., Baccarani M., Lindoerfer D., Castagnetti F., Turkina A., Zaritsky A. The EUTOS prognostic score: review and validation in 1288 patients with CML treated frontline with imatinib. Leukemia. 2013;27(10):2016–2022. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hughes T.P., Kaeda J., Branford S., Rudzki Z., Hochhaus A., Hensley M.L. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(15):1423–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tripathi A.K., Kumar A., Ramaswamy A. Total leukocyte counts and the requirement of dose reduction due to cytopenias as prognostic indicators affecting response to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2011;27(1):7–13. doi: 10.1007/s12288-010-0048-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cortes J.E., Talpaz M., Giles F., O’Brien S., Rios M.B., Shan J. Prognostic significance of cytogenetic clonal evolution in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia on imatinib mesylate therapy. Blood. 2003;101(10):3794–3800. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-09-2790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.O’Dwyer M.E., Mauro M.J., Blasdel C., Farnsworth M., Kurilik G., Hsieh Y.C. Clonal evolution and lack of cytogenetic response are adverse prognostic factors for hematologic relapse of chronic phase CML patients treated with imatinib mesylate. Blood. 2004;103(2):451–455. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-02-0371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brenner H., Gondos A., Pulte D. Recent trends in long-term survival of patients with chronic myelocytic leukemia: disclosing the impact of advances in therapy on the population level. Haematologica. 2008;93(10):1544–1549. doi: 10.3324/haematol.13045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thygesen L.C., Nielsen O.J., Johansen C. Trends in adult leukemia incidence and survival in Denmark, 1943–2003. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20(9):1671–1680. doi: 10.1007/s10552-009-9417-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cortes J., Talpaz M., O’Brien S., Giles F., Beth Rios M., Shan J. Effects of age on prognosis with imatinib mesylate therapy for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer. 2003;98(6):1105–1113. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]