Abstract
Allergy diagnosis based on purified allergen molecules provides detailed information regarding the individual sensitization profile of allergic patients, allows monitoring of the development of allergic disease and of the effect of therapies on the immune response to individual allergen molecules. Allergen microarrays contain a large variety of allergen molecules and thus allow the simultaneous detection of allergic patients’ antibody reactivity profiles towards each of the allergen molecules with only minute amounts of serum. In this article we summarize recent progress in the field of allergen microarray technology and introduce the MeDALL allergen-chip which has been developed for the specific and sensitive monitoring of IgE and IgG reactivity profiles towards more than 170 allergen molecules in sera collected in European birth cohorts. MeDALL is a European research program in which allergen microarray technology is used for the monitoring of the development of allergic disease in childhood, to draw a geographic map of the recognition of clinically relevant allergens in different populations and to establish reactivity profiles which are associated with and predict certain disease manifestations. We describe technical advances of the MeDALL allergen-chip regarding specificity, sensitivity and its ability to deliver test results which are close to in vivo reactivity. In addition, the usefulness and numerous advantages of allergen microarrays for allergy research, refined allergy diagnosis, monitoring of disease, of the effects of therapies, for improving the prescription of specific immunotherapy and for prevention are discussed.
Keywords: Allergen-microarray, Sensitivity, Blocking antibodies, Allergy-diagnosis, Recombinant allergen, Immunoglobulin E, Immunoglobulin G
1. Introduction
Due to the continuing rise of the worldwide prevalence of allergic diseases the development of strategies for early diagnosis, prevention and treatment of allergic sensitizations becomes an increasingly important issue [1]. The development of IgE responses to allergen molecules, a process termed “allergic sensitization” seems to occur early in life whereas IgE-reactivity profiles of adult allergic patients do not change in a relevant manner [2,3]. This implies that there exists a period early in life during which allergic sensitization takes place and IgE-reactivity profiles are established. This period thus represents a window of opportunity for preventing allergic sensitization and early intervention strategies but the exact duration of this period of plasticity of the allergic immune response has not yet been studied in detail. Likewise, it remains to be investigated whether the development of certain clinical manifestations of allergy (e.g., asthma) and their severity [4] are linked to distinct allergen recognition profiles, levels of pathogenic (i.e., IgE) and protective (i.e., IgG) antibody responses and epitope recognition profiles which would allow early prediction of the clinical outcome. In order to address these questions the European Union-funded project MeDALL (Mechanisms for the development of allergies) (http://medall-fp7.eu/) has been established in which several birth cohorts in allergy and asthma are pooled and serum samples from mothers and children, from birth up to adolescence, are analyzed for allergen-specific IgE and IgG reactivity profiles [5].
Since the amounts of serum samples available from these birth cohorts are very limited a highly sensitive assay allowing to measure IgE and IgG reactivities to a large number of different allergen molecules with minute serum samples is needed. Allergen microarrays containing large numbers of different allergen molecules have been developed already in 2002 [6] with the goal to allow simultaneous detection of IgE reactivities to a large number of allergen molecules with small serum volumes. These allergen microarrays are comprised of chips containing spotted allergens and were suggested as tools for monitoring the development of allergic sensitization, for the establishment of comprehensive reactivity profiles and to measure eventual changes during the course of disease and various forms of treatment. Today, an allergen microarray termed ImmunoCAP ISAC (Phadia AB, Uppsala, Sweden) is already available for chip-based allergy diagnosis and can be used for determining IgE and IgG responses towards 112 allergen molecules.
The ImmunoCAP ISAC has been used in a large number of clinical studies for a number of years [7], in epidemiologic studies [8], longitudinal follow up of children [9] and to find de novo sensitizations [3]. It has many advantages and results are close but not identical to classical immunoassays [10] (WAO Position Paper, in press). However, for some allergens [11-13] and for low IgE levels [14] it may not be sufficiently sensitive. Moreover, important allergens are not included on the ImmunoCAP ISAC chip. The MeDALL allergen-chip was designed to increase the number of allergens on the chip and to improve sensitivity of the test.
We discuss specific features and advantages of allergen microarrays and describe the MeDALL allergen-chip which has been developed for the analysis of sera from birth cohorts pooled in the MeDALL project. The MeDALL allergen-chip represents a comprehensive collection of more than 170 allergen molecules for the reliable detection of allergen-specific antibody signatures. It should facilitate to study the early evolution of the allergic immune response and the generation of a European map of molecular sensitization profiles as a prerequisite for intervention and treatment strategies.
A second important aspect of this study is to demonstrate and clarify major differences between serological test results obtained by microarray and by commonly used systems for measuring quantitative IgE responses. In fact, chip-based IgE measurements provide fundamentally different information compared to quantitative IgE measurements using allergen excess and therefore cannot be directly compared. Both assays are equally sensitive and specific but measurements performed under conditions of low allergen amount allow for the estimation of the effect of allergen-specific blocking IgG on IgE binding to the allergen and thus will more closely resemble biological responses under conditions of natural exposure. These differences imply that chip-based IgE measurements should provide information of higher clinical relevance.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Design of the MeDALL allergen-chip
The development of the allergen microarray platform used for preparing the MeDALL allergen-chip has been described earlier [6]. In order to improve the diagnostic spectrum of allergens on the array and to avoid redundant markers, the allergen panel of the current version of ImmunoCAP ISAC (Phadia AB) has been modified by adding more than 70 allergen molecules and by removing cross-reactive allergens which were present in different versions on the chip (Table 1). Particular care was taken to increase the repertoire of food and respiratory allergens. One version of the MeDALL allergen-chip contained an extensive collection of bacterial superantigens whereas in another version an extended panel of food allergens was added to study hypersensitivity to wheat. For each protein/allergen, 50–200 fg, corresponding to 1–5 attomol, was spotted in triplicates onto the chip. Customized spotting of the MeDALL-array was done by Phadia Austria GmbH (Vienna, Austria). The newly added allergens are described in the following section.
Table 1.
List of allergens contained on the MeDALL allergen-chip. Allergen-sources, allergen-names according to IUIS-standard, purification from extracts (natural allergens) or production in expression systems (recombinant allergens), glycosylation and allocation to different allergen-families are shown. Proteins that were provided by collaborating groups are highlighted by coloured boxes (column “Allergen”). For wheat allergens, # indicates the number of the respective clones. Some allergen families represented on the chip by several allergen molecules are highlighted by coloured boxes (column “Function of the protein/Allergen family”). In the separate part of the list, allergens that replaced proteins from the first variant of the microarray (Proteins No. 164–176) are listed.
| Version 1 of the MeDALL-Chip | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Allergen-source | Allergen | Rec. or natural |
CCD | Route of exposure |
Function of the protein/Allergen family |
| 1 | Birch | Bet v 1 | R | inh | PR-10 | |
| 2 | Bet v 2 | R | inh | Profilin | ||
| 3 | Bet v 4 | R | inh | Polcalcin | ||
| 4 | Alder | Aln g 1 | R | inh | PR-10 | |
| 5 | Olive | Ole e 1 | R | inh | Ole e 1-related protein | |
| 6 | Ole e 7 | N | inh | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 7 | Ole e 9 | R | inh | Glucanase | ||
| 8 | Japanese cedar | Cry j 1 | N | CCD | inh | Pectate lyase |
| 9 | Cypress | Cup a 1 | N | CCD | inh | Pectate lyase |
| 10 | Plane tree | Pla a 1 | R | inh | Invertase Inhibitor | |
| 11 | Pla a 2 | N | CCD | inh | Polygalacturonases | |
| 12 | Pla a 3 | R | inh | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 13 | Timothy grass | Phl p 1 | R | inh | Grass group 1 (Beta-Expansin) | |
| 14 | Phl p 2 | R | inh | Grass group 2/3 | ||
| 15 | Phl p 4 | N | CCD | inh | Grass group 4 (Berberine bridge enzyme) | |
| 16 | Phl p 5b | R | inh | Grass group 5 | ||
| 17 | Phl p 6 | R | inh | Grass group 5/6 | ||
| 18 | Phl p 7 | R | inh | Calcium-binding proteins (Polcalcin) | ||
| 19 | Phl p 11 | R | inh | Ole e 1-related protein | ||
| 20 | Phl p 12 | R | inh | Profilin | ||
| 21 | Bermuda grass | Cyn d 1 | N | CCD | inh | Grass group 1 (Beta-Expansin) |
| 22 | Ragweed | Amb a 1 | N | inh | Pectate lyase | |
| 23 | Mugwort | Art v 1 | N | inh | Defensin-like protein | |
| 24 | Art v 3 | N | inh | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 25 | Goosefoot | Che a 1 | R | inh | Ole e 1-related protein | |
| 26 | Annual mercury | Mer a 1 | R | inh | Profilin | |
| 27 | Plantain | Pla l 1 | R | inh | Ole e 1-related protein | |
| 28 | Wall pellitory | Par j 2 | R | inh | nsLTP, type 1 | |
| 29 | Saltwort | Sal k 1 | N | inh | Pectin methylesterase | |
| 30 | Latex | Hev b 1 | R | inh, skin | Rubber elongation factor | |
| 31 | Hev b 3 | R | inh, skin | Small rubber particle protein | ||
| 32 | Hev b 5 | R | inh, skin | Acidic protein | ||
| 33 | Hev b 6.01 | R | inh, skin | Hevein (Prohevein) | ||
| 34 | Hev b 8 | R | inh, skin | Profilin | ||
| 35 | Alternaria | Alt a 1 | R | inh | Acidic glycoprotein | |
| 36 | Alt a 6 | R | inh | Enolase | ||
| 37 | Aspergillus | Asp f 1 | R | inh | Mitogillin family (Ribonuclease) | |
| 38 | Asp f 3 | R | inh | Peroxysomal protein | ||
| 39 | Asp f 6 | R | inh | Mn superoxide dismutase | ||
| 40 | Cladosporium | Cla h 8 | R | inh | Mannitol dehydrogenase | |
| 41 | House dust mite | Der p 1 | N | inh | Group 1 mite allergens (Cysteine protease) | |
| 42 | Der f 1 | N | inh | Group 1 mite allergens (Cysteine protease) | ||
| 43 | Der p 2 | R | inh | Group 2 mite allergens (NPC2 family) | ||
| 44 | Der f 2 | R | inh | Group 2 mite allergens (NPC2 family) | ||
| 45 | Der p 4 | R | inh | Group 4 mite allergens (Alpha-amylase) | ||
| 46 | Der p 5 | R | inh | Group 5 mite allergens | ||
| 47 | Der p 7 | R | inh | Group 7 mite allergens | ||
| 48 | Der p 10 | R | inh | Group 10 mite allergens (Tropomyosin) | ||
| 49 | Der p 11 | R | inh | Group 11 mite allergens (Paramyosin) | ||
| 50 | Der p 14 | R | inh | Vitellogenin (Apolipophorins) | ||
| 51 | Der p 15 | R | inh | Chitin-binding domain | ||
| 52 | Der p 18 | R | inh | Chitin-binding domain | ||
| 53 | Der p 21 | R | inh | Group 21 mite allergens | ||
| 54 | Der p 23 | R | inh | Chitin-binding domain | ||
| 55 | clone 16 | R | inh | Chitin-binding domain | ||
| 56 | Storage mite | Lep d 2 | R | inh | Group 2 mite allergens (NPC2 family) | |
| 57 | Blomia tropicalis | Blo t 5 | R | inh | Group 5 mite allergens | |
| 58 | Cockroach | Bla g 1 | R | inh | Cockroach group 1 | |
| 59 | Bla g 2 | R | inh | Aspartic protease | ||
| 60 | Bla g 5 | R | inh | Glutathione S-transferase | ||
| 61 | Bla g 7 | N | inh | Tropomyosin | ||
| 62 | Anisakis | Ani s 1 | R | f | Serine protease inhibitor | |
| 63 | Ani s 3 | R | f | Tropomyosin | ||
| 64 | Cat | Fel d 1 | R | inh | Uteroglobin | |
| 65 | Fel d 2 | N | inh | Serum Albumin | ||
| 66 | Fel d 4 | R | inh | Lipocalin | ||
| 67 | Dog | Can f 1 | R | inh | Lipocalin | |
| 68 | Can f 2 | R | inh | Lipocalin | ||
| 69 | Can f 3 | N | inh | Serum Albumin | ||
| 70 | Can f 4 | R | inh | Lipocalin (Odorant-binding protein) | ||
| 71 | Can f 5 | R | inh | Arginine Esterase (Trypsin-like serine protease) | ||
| 72 | Can f 5 | R | inh | Arginine Esterase (Trypsin-like serine protease) | ||
| 73 | Can f 6 | R | inh | Lipocalin | ||
| 74 | Horse | Equ c 1 | R | inh | Lipocalin | |
| 75 | Equ c 3 | N | inh | Serum Albumin | ||
| 76 | Mouse | Mus m 1 | N | inh | Lipocalin | |
| 77 | Peanut | Ara h 1 | N | f | Storage protein, 7S globulin (Vicilins) | |
| 78 | Ara h 1 | R | f | Storage protein, 7S globulin (Vicilins) | ||
| 79 | Ara h 2 | R | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | ||
| 80 | Ara h 3 | N | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 81 | Ara h 3 | R | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 82 | Ara h 6 | N | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | ||
| 83 | Ara h 6 | N | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | ||
| 84 | Ara h 8 | R | f | PR-10 | ||
| 85 | Ara h 9 | R | f | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 86 | Hazelnut | Cor a 1.0401 | R | f, inh | PR-10 | |
| 87 | Cor a 8 | R | f | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 88 | Cor a 9 | N | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 89 | Walnut | Jug r 1 | R | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | |
| 90 | Jug r 2 | N | CCD | f | Storage protein, 7S globulin (Vicilins) | |
| 91 | Jug r 3 | R | f | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 92 | Almond | Pru du 3 | R | f | nsLTP, type 1 | |
| 93 | Pru du 4 | R | f | Profilin | ||
| 94 | Pru du 6 | N | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 95 | Pru du 6.01 | R | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 96 | Pru du 6.02 | R | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 97 | Cashew nut | Ana o 1 | R | f | Storage protein, 7S globulin (Vicilins) | |
| 98 | Ana o 2 | R | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 99 | Ana o 2 | N | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 100 | Ana o 2 | R | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 101 | Ana o 3 | R | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | ||
| 102 | Pistachio | Pis v 3 | R | f | Storage protein, 7S globulin (Vicilins) | |
| 103 | Brazil nut | Ber e 1 | R | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | |
| 104 | Sesame | Ses i 1 | N | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | |
| 105 | Soy | Gly m 4 | R | f | PR-10 | |
| 106 | Gly m 5 | N | f | Storage protein, 7S globulin (Vicilins) | ||
| 107 | Gly m 6 | N | f | Storage protein, 11S globulin (Legumins) | ||
| 108 | Wheat | Tri a 14 | R | f, inh | nsLTP, type 1 | |
| 109 | Tri a 14 | R | f, inh | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 110 | Tri a 19.0101 | R | f | Storage protein, Omega 5 gliadin | ||
| 111 | Tri a aA TI | N | f, inh | Alpha-Amylase / Trypsin Inhibitors | ||
| 112 | m43 | R | f | Fragment of HMW Glutenin Bx7 | ||
| 113 | m82 | R | f | Fragment of HMW Glutenin Bx7 | ||
| 114 | Tri a 36 (191-369) | R | f, inh | Fragment of LMW Glutenin | ||
| 115 | Tri a 36 | R | f, inh | LMW Glutenin | ||
| 116 | Tri a 37 | R | f | Thionins (Alpha-purothionin) | ||
| 117 | Tri a 39 (#10) | R | inh | Serine protease inhibitors | ||
| 118 | Tri a Trx (#37) | R | inh | Oxidoreductases (Thioredoxin) | ||
| 119 | Tri a GST (#38) | R | inh | Glutathione S-transferases | ||
| 120 | Tri a 32 (#112) | R | inh | Peroxiredoxins (1-Cys-peroxiredoxin) | ||
| 121 | Tri a 12 (#123) | R | f, inh | Profilin | ||
| 122 | Tri a DH (#126) | R | inh | Dehydrins | ||
| 123 | Buckwheat | Fag e 2 | N | f | Storage protein, 2S albumin | |
| 124 | Kiwi | Act d 1 | N | f | Cysteine protease | |
| 125 | Act d 2 | N | f | Thaumatin-like protein | ||
| 126 | Act d 5 | N | f | Kiwellin | ||
| 127 | Act d 8 | R | f | PR-10 | ||
| 128 | Apple | Mal d 1 | R | f | PR-10 | |
| 129 | Peach | Pru p 1 | R | f | PR-10 | |
| 130 | Pru p 3 | R | f, skin | nsLTP, type 1 | ||
| 131 | Celery | Api g 1 | R | f | PR-10 | |
| 132 | Pineapple | Ana c 2.0101 | N | CCD | f, inh | Bromelain ( MUXF3, CCD-Marker) |
| 133 | Cow’s Milk | Bos d 4 | N | f | Alpha-lactalbumin | |
| 134 | Bos d 5 | N | f | Beta-lactoglobulin | ||
| 135 | Bos d 6 | N | f, inh | Serum Albumin | ||
| 136 | Bos d 8 | N | f | Caseins | ||
| 137 | Bos d Lactoferrin | N | f | Transferrin | ||
| 138 | Bos d 4 | N | f | Alpha-lactalbumin | ||
| 139 | Bos d 5 | N | f | Lipocalin (Beta-lactoglobulin) | ||
| 140 | Bos d 6 | N | f, inh | Serum Albumin | ||
| 141 | Bos d 8 | N | f | Caseins (α-, β-, κ-casein) | ||
| 142 | Bos d 9 | R | f | Caseins (αS1-casein) | ||
| 143 | Bos d 10 | R | f | Caseins (αS2-casein) | ||
| 144 | Bos d 11 | R | f | Caseins (β -casein) | ||
| 145 | Bos d 12 | R | f | Caseins (κ-casein) | ||
| 146 | Bos d Lactoferrin | N | f | Transferrin | ||
| 147 | Egg white | Gal d 1 | N | f | Ovomucoid | |
| 148 | Gal d 2 | N | f | Ovalbumin | ||
| 149 | Gal d 3 | N | f | Ovotransferrin (Conalbumin) | ||
| 150 | Egg yolk/chicken | Gal d 5 | N | f, inh | Serum Albumin | |
| 151 | Codfish | Gad c 1 | R | f | Parvalbumin | |
| 152 | Shrimp | Pen m 1 | N | f | Tropomyosin | |
| 153 | Pen m 2 | N | f | Arginine Kinase-like protein | ||
| 154 | Pen m 4 | N | f | Calcium-binding proteins (Sarcoplasmic) | ||
| 155 | Bee | Api m 1 | R | syst | Insect venom, Phospholipase A2 | |
| 156 | Api m 1 | R | syst | Insect venom, Phospholipase A2 | ||
| 157 | Api m 2 | R | syst | Insect venom, Hyaluronidase | ||
| 158 | Api m 4 | N | syst | Melittin | ||
| 159 | Api m 4 | N | syst | Melittin | ||
| 160 | Wasp | Ves v 1 | R | syst | Insect venom, Phospholipase A1 | |
| 161 | Ves v 5 | R | syst | Insect venom, Antigen 5 | ||
| 162 | Ves v 5 | R | syst | Insect venom, Antigen 5 | ||
| 163 | Paper wasp | Pol d 5 | R | syst | Insect venom, Antigen 5 | |
| 164 | Bacterial Toxins | Sem | R | skin, inh | ||
| 165 | SspB | R | skin, inh | |||
| 166 | Sec | R | skin, inh | |||
| 167 | HlgC | R | skin, inh | |||
| 168 | Tsst | R | skin, inh | |||
| 169 | Hlb | R | skin, inh | |||
| 170 | Plc | R | skin, inh | |||
| 171 | GlpQ | R | skin, inh | |||
| 172 | Hla | R | skin, inh | |||
| 173 | Ssl11 | R | skin, inh | |||
| 174 | Sei | R | skin, inh | |||
| 175 | Seb | R | skin, inh | |||
| 176 | Control-protein | MBP | R | - | Maltose binding protein | |
| Version 2 of the MeDALL-Chip (exchanged allergens) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 164 | Olive | Ole e 5 | R | inh | Superoxide dismutases | |
| 165 | Ole e 6 | R | inh | Oleaceae group 6 | ||
| 166 | Ole e 8 | R | inh | Calcium-binding proteins (Polcalcin) | ||
| 167 | Ole e 10 | R | inh | Glycosyl hydrolases | ||
| 168 | Wheat | Tri a gamma gliadin (GG1) | R | f | Gamma-gliadins | |
| 169 | Peptide 4 | R (peptide) | f | Peptides from gamma-gliadin 1 | ||
| 170 | Peptide 18 | R (peptide) | f | Peptides from gamma-gliadin 1 | ||
| 171 | Clone 79 | R | f | Gamma-gliadins | ||
| 172 | Clone 85 | R | f | Gamma-gliadins | ||
| 173 | Clone 110 | R | f | Gamma-gliadins (Fragment) | ||
| 174 | Tri a bA | R | f | beta-Amylases | ||
| 175 | Avenin-like protein | R | f | Avenin | ||
| 176 | Human | htTG2 | R | - | Human tissue transglutaminase | |
2.2. Characterization of newly added allergens
2.2.1. Peanut allergens
Natural Ara h 1, nAra h 2 and nAra h 6 were purified as described [15,16].
2.2.2. Almond, cashew and pistachio allergens
nPru du 6 (prunin) was purified from aqueous almond extract by column chromatography [17] and natural Ana o 2 was purified from aqueous cashew nut protein extract [18] as previously described. Recombinant allergens were generated as previously described for Ana o 1 [19], Ana o 2 [20], Ana o 3 [21], Pru du 4 [22], Pru du 6 [23] and Pis v 3 [24].
Recombinant Pru du 3 was amplified directly from the almond cDNA library (library generation described in detail [23]). The sequence for the lipid transfer protein from almond (Prunus dulcis) was available in the NCBI database, accession number CAA65477. The LTP-encoding cDNA was ligated into the pMAL-c4X expression vector, transformed into Rosetta gamiB(DE3)pLysS cells (Novagen/EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA), expressed, and purified as described in detail for Ana o 1 [19].
2.2.3. Cow’s milk allergens
nBos d 4, nBos d 5, nBos d 8, recombinant αS1-casein, rαS2-casein, rκ-casein, rβ-casein, transferrin and natural BSA were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA) or expressed in Escherichia coli as described [25-27].
2.2.4. Wheat allergens
A wheat cDNA library was screened with sera from wheat food allergic patients as described [28]. Recombinant Tri a 36 and Tri a 36 fragment (amino acids 191–369) [29], clones 37 (thioredoxin h), 38 (glutathione transferase), 112 (1-Cys-peroxiredoxin), 123 (profilin) and 126 (dehydrin) as well as clone 10 (serine proteinase inhibitor) were cloned, expressed and characterized as described[28,30]. cDNA-sequences of IgE-reactive clones 79, 85 and 110 that showed partial sequence identities to gamma gliadins, respectively, cDNAs coding for Tri a 37, LTP, beta amylases and avenin-like protein were codon optimized for E. coli expression and cloned with an additional sequence coding for a hexa-histidine tag into the expression vector pET17b (Novagen). Proteins were expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA), purified by nickel affinity chromatography (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and refolded by dialysis against 10 mM NaH2PO4, pH 4 (all proteins except LTP, pH 6, and beta amylases, pH 7). Using the same methodology, cDNAs of clones m43 and m82 that showed partial sequence identities to the high molecular weight glutenin x-type subunit Bx7 precursor were cloned into expression vector pMAL-c4X. Proteins were purified and dialyzed against 10 mM Na-Acetate, pH 4 (m43 and m82) as described above.
All purified proteins were tested for IgE-reactivity by non-denaturing, RAST-based IgE dot-blotting.
2.2.5. Antigens important for celiac disease
The cDNA sequence of gamma gliadin 1 (rGG1) was cloned into pET27b vector (Novagen). The rGG1-protein was expressed with a hexa-histidine tag in E. coli BL21 (DE3) (Stratagene) and purified by nickel affinity chromatography (Qiagen). Purified proteins were dialyzed against 50 mM acetic acid and stored at −20 °C (manuscript in preparation). rGG1 derived peptides 4 and 18 were synthesized and purified as described [31]. Tissue transglutaminase protein (expressed in Baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) was purchased from DIARECT AG (Freiburg, Germany).
2.2.6. Olive pollen allergens
cDNAs coding for Ole e 5, Ole e 6, Ole e 8 and Ole e 10 were codon-optimized for expression in E. coli and ligated into the pET17b vector (Novagen) with a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag. Proteins were expressed in BL21 (DE3) cells (Stratagene), purified by nickel affinity chromatography under native conditions and stored in 10 mM NaH2PO4 (pH 8). IgE-reactivity was assessed by ELISA using sera from patients allergic to olive pollen.
2.2.7. Mite allergens
Recombinant Der p 5 (Genbank accession number, S76337), rDer p 7 (U37044), rDer p 21 (DQ354124), rDer p 23 (EU414751) and the clone 16-derived allergen (Vrtala, unpublished) were expressed in E. coli as soluble, non-fusion proteins using the pET17 expression system. rDer p 5, rDer p 21 and rDer p 23 were purified as previously described [32-34]. Recombinant Der p 7 was purified by hydrophobic interaction chromatography and hydroxyapatite chromatography while the clone 16-derived protein was purified by anion and cation exchange chromatography. rDer p 4 (AF144060), rDer p 11 (AY189697), rDer p 14 (AF373221), rDer p 15 (DQ078740) and rDer p 18 (DQ078739) were expressed as hexa-histidine-tagged proteins in the inclusion body fraction of E. coli extracts and purified by nickel affinity chromatography.
IgE-reactivity was tested for all recombinant HDM allergens with sera from HDM-allergic patients in dot-blot experiments and the allergenic activity was evaluated with basophil activation (CD203c up-regulation) experiments.
2.2.8. Dog allergens
Genes coding for the mature forms of Can f 4 (ACY38525.1), Can f 5 (P09582) and Can f 6 (E2QYS2) were inserted into expression vector pET-27b (Novagen). All three genes contained sequences coding for a hexa-histidine tag at the C terminus of the protein and the gene sequences were optimized for E. coli expression [35]. Proteins were expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) (Stratagene), purified by nickel affinity chromatography (Qiagen) and refolded by dialysis against 10 mM Tris–HCl (pH 9), followed by dialysis against 50 mM bicarbonate buffer (pH 9.6). Protein fold was determined by circular dichroism on a JASCO (Tokyo, Japan) J-810 spectropolarimeter.
2.2.9. Insect venom allergens
Recombinant Api m 1, rApi m 2 and rVes v 5 were cloned as described [36] and expressed in E. coli. Melittin (Api m 4) was purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). The cDNA coding for Ves v 1 with a 3′ sequence coding for a hexa-histidine tag was codon-optimized for the expression in E. coli and inserted into plasmid pET17b (Novagen). Recombinant Ves v 1 was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells (Stratagene) and purified from inclusion bodies by nickel affinity chromatography (Qiagen). After dialysis, IgE-reactivity of rVes v 1 was assessed by dot-blot assays using sera from wasp-venom allergic patients.
2.2.10. Staphylococcus aureus toxins
Sequences encoding S. aureus toxins were ligated into expression vector pPR-IBA1 (IBA, Göttingen, Germany) and expressed with a C-terminal Strep-Tag in E. coli strain BL21. Cells were lysed by ultrasound and proteins were purified by affinity chromatography using Strep-Tactin columns (IBA). Purified proteins were stored in 0.5× PBS.
2.2.11. Maltose binding protein (MBP)
The sequence encoding MBP was ligated into pMAL-c4x vector (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), transfected and expressed in E. coli.
2.3. Calibration of the MeDALL allergen-chip for different isotypes
Serum pools were analyzed for reactivity to several different allergens on the microarray which were also available as ImmunoCAP tests in order to cover a broad spectrum of antibody specificities and fluorescence intensities. The respective allergen-specific antibodies of the isotype for which the calibration curve was generated were quantified by ImmunoCAP and calibration-curves – fluorescence intensities on the MeDALL allergen-chip versus antibody levels as detected by ImmunoCAP – were established.
2.4. Analysis of serum samples on the MeDALL allergen-chip
The microarrays were washed in washing buffer (Phadia AB) for 1 min by stirring. After drying the chips by centrifugation at 1000g for 1 min, aliquots of 35 μl per serum sample that have been centrifuged for one minute were applied and incubated for 2 h at gentle rocking. For detection of IgE, sera were applied undiluted, for detection of IgG and IgG4, samples were diluted 1:50 in sample diluent (Phadia AB), the dilution factor for IgA-detection was 1:10. After rinsing the arrays using a spray bottle, another washing step was done as described above, followed by drying by centrifugation. Thirty-five μl of detection antibody were then applied and incubated for 30 min at gentle rocking. After rinsing, washing and drying the chips as described above, the arrays were scanned using a confocal laser scanner (LuxScan-10 K microarray scanner, Capital-Bio, Beijing, People’s Republic of China) and evaluated by Microarray Image Analyzer v3.1.2 software (Phadia AB). All incubation steps were performed at room temperature. For calibration and detection of background signals a calibrator serum and sample diluent (Phadia AB), respectively, were included in each run of serum analysis.
2.5. Sensitivity of the microarray as determined with monoclonal Bet v 1-specific human IgE and effects of blocking IgG on IgE-binding
Bip1, a Bet v 1-specific monoclonal mouse IgG1 antibody [37], and chimeric Bip1, a chimeric monoclonal antibody that consists of the variable domains of Bip1 and a human Fce-portion [38] have been described elsewhere.
First, a series of dilutions of chimeric Bip1 was prepared in sample diluent, comprising concentrations of 640, 320, 32, 3.2, 1.6, 0.8, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1 and 0.05 ng/ml of antibody. Each dilution was measured on the MeDALL allergen-chip in triplicates. To study the effects of blocking IgG on IgE-signals, 3 different concentrations of chimeric Bet v 1-specific IgE, i.e., 312.5, 6.25 and 0.8 ng/ml, were prepared and mixed only with buffer, a 1-, 10-, 100-, 1000-, 10,000-fold (for 6.25 and 0.8 ng/ml IgE) and a 100,000-fold (for 0.8 ng/ml IgE) amount of Bip1. In fact, Bip1 binds to the very same epitope on Bet v 1 with the same affinity as the chimeric IgE. Again, IgE binding of each mixture to Bet v 1 was measured in triplicates using the MeDALL allergen-chip.
Control experiments were performed by mixing Bet v 1-specific IgE at a concentration of 312.5 ng/ml with an excess of two monoclonal IgG1 antibodies specific for two distinct Bet v 1-peptide epitopes (peptide 2 and peptide 6, respectively) [39], or with an excess of an antibody specific for an unrelated allergen (i.e., anti-Phl p 2 IgG1).
The same series of experiments was done with the ImmunoCAP system (Phadia AB) for detection of Bet v 1-specific IgE by testing a dilution series comprising 312.5, 39.1, 19.5, 7.8, 3.9, 2, 1, 0.5 and 0.2 ng/ml of chimeric IgE. Likewise, measurement of Bet v 1-specific chimeric IgE was performed at two different concentrations (312.5 and 20 ng/ml) in the presence of only buffer, 1-fold up to 1000-fold (both for 312.5 and 20 ng/ml of IgE) or 10,000-fold (only for 20 ng/ml IgE) amount of Bip1 using the Bet v 1-ImmunoCAP.
2.6. Sensitivity and specificity of IgG measurements exemplified with a monoclonal Phl p 2-specific human IgG1
The human monoclonal Phl p 2-specific IgG1 was described[40,41]. Such as for IgE, a dilution series of 1 μg/ml, 500 ng/ml, 100, 10, 1, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2 and 0.1 ng/ml was prepared of the monoclonal Phl p 2-specific IgG1 and measured in triplicates using the MeDALL allergen-chip. An IgG-specific detection antibody conjugate was used that binds to each of the human IgG subclasses.
2.7. Importance of using protein-containing diluents for highly diluted antibodies
In order to investigate the possible binding of highly diluted antibodies to plastic tubes and/or the surface of the chip affecting sensitivity, chimeric Bip1 was diluted to a concentration of 6.25 ng/ml by either using PBS without any proteins or blocking agents or sample diluent containing additives which block non-specific interactions. IgE reactivities of these samples were measured in triplicates on the MeDALL allergen-chip.
2.8. Examples of detecting early allergen-specific IgE responses in samples from children of two different birth cohorts
The usefulness of the MeDALL allergen-chip for the evaluation of the development of allergic sensitizations in children is exemplified for sera from two population based birth cohorts, BAMSE from Sweden [42] and ECA from Norway [43]. In the BAMSE cohort, serum samples were analyzed from the age 4, 8 and 16 years, in the ECA cohort at 10 and 16 years.
3. Results
3.1. The MeDALL allergen-chip contains a large number of clinically relevant allergen molecules
Table 1 provides an overview of the molecules contained on the MeDALL allergen-chip and information regarding allergen-sources, if proteins were purified from extracts (natural allergens) or produced in expression systems (recombinant), if they are glycosylated and to which protein family they belong. Two versions of the chip have been made, one which contains a collection of enterotoxins from Staphylococcus aureus involved in respiratory allergies [44] and another comprising an extended panel of antigens relevant for hypersensitivity to wheat [29,30,45-47]. Considering the poor quality of natural house dust mite allergen extracts, we aimed to implement a panel of purified house dust mite allergens that is as complete as possible [48-50]. Furthermore, several cockroach allergens were included [51,52]. The panel of pollen allergens contained allergens useful for the identification of the genuine sensitizing pollen species as well as cross-reactive allergens [53,54]. Furthermore, attempts were made to include relevant food allergens from, e.g., nuts, peanuts, milk and several other allergen sources [55-59]. Column “CCD” (cross-reactive carbohydrate determinants) in Table 1 indicates glycosylated allergen molecules with confirmed reactivity to CCD-specific IgE.
3.2. Technical features of the MeDALL allergen-chip
3.2.1. Calibration for IgE, IgG, IgG4 and IgA
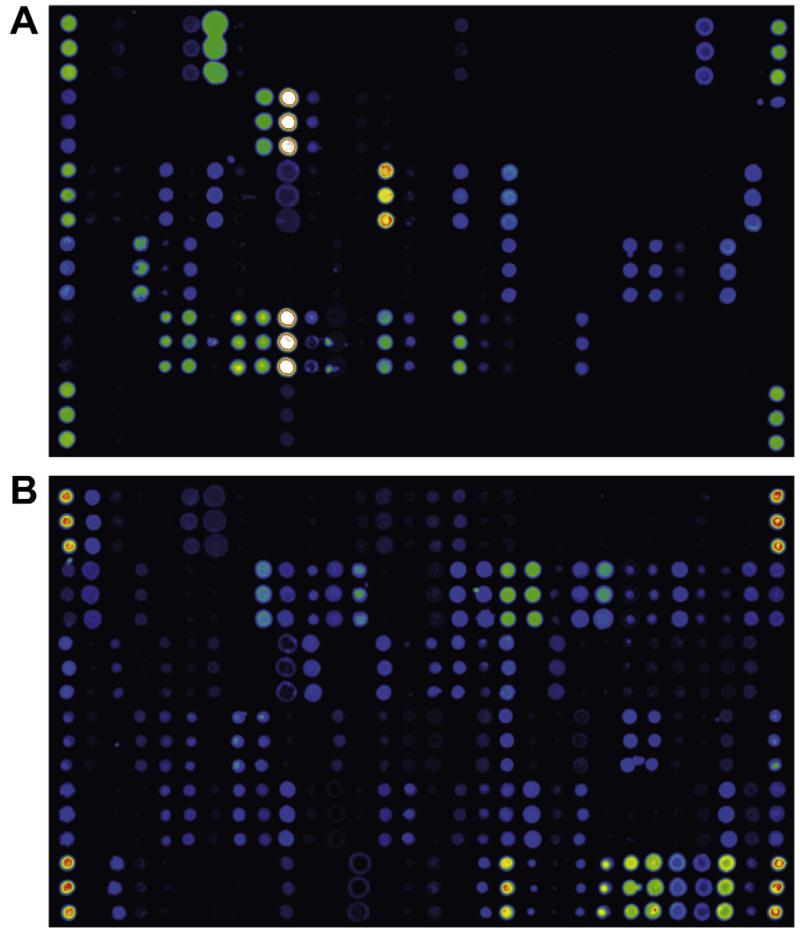
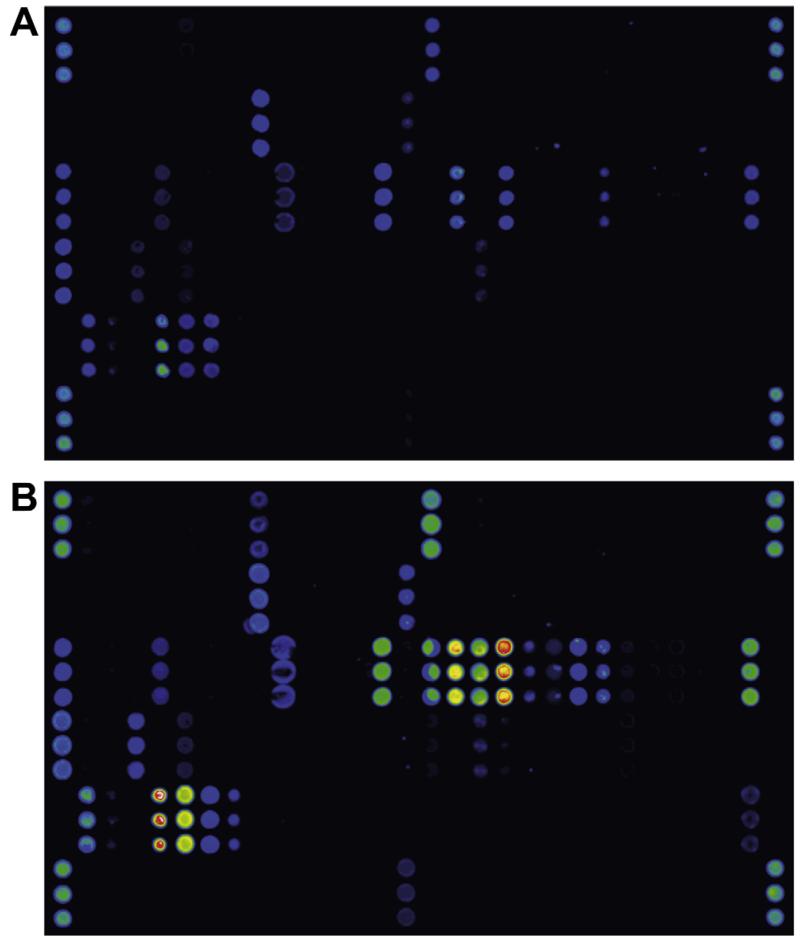
Calibration for IgE, IgG, IgG4 and IgA has been established for the MeDALL allergen-chip by relating antibody levels to several allergens detected by microarray with the respective results from ImmunoCAP measurements. Screenshots showing the detection of allergen-specific IgE and IgG in the same serum sample illustrate the specificity of the detection systems as demonstrated by distinct reactivity patterns (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Detection of allergen-specific IgE and IgG by the MeDALL allergen-chip. A serum sample from an allergic individual was tested for the presence of allergen-specific IgE (A) and IgG (B) using the MeDALL allergen-chip. Each of the allergen molecules on the chip was spotted in triplicates (groups of three dots aligned vertically), signal strength is visualized in false colours with increasing fluorescence intensities from blue to red/white.
3.2.2. Background, cut-off and inter-assay variation of the MeDALL allergen-chip for IgE in comparison to ImmunoCAP, and for IgG-detection
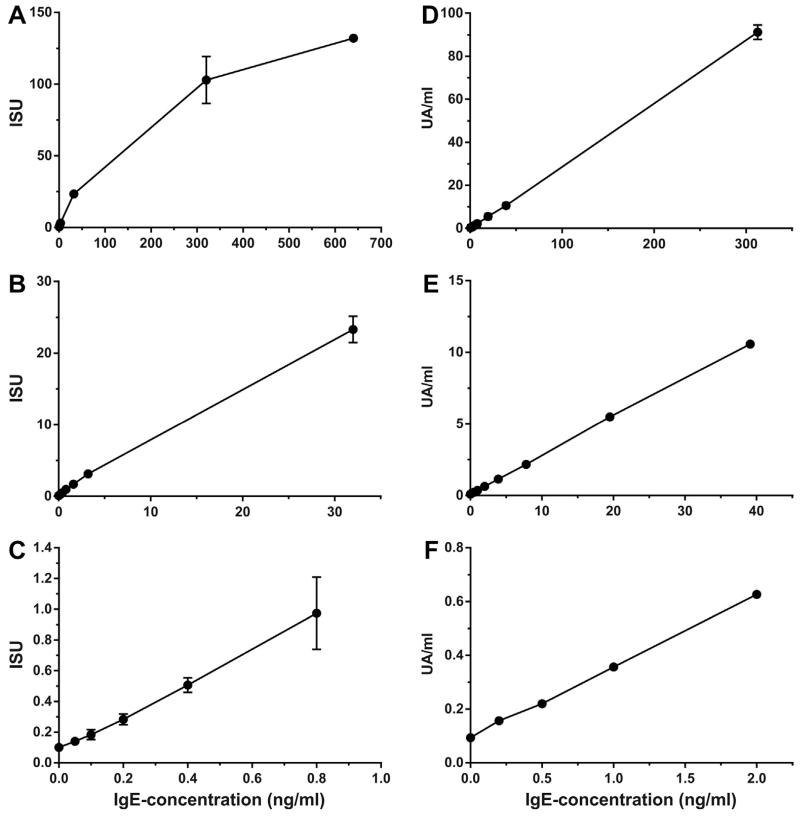
Triplicates of a serial dilution of a monoclonal human IgE antibody specific to Bet v 1 were measured on the MeDALL allergen-chip, starting from 640 ng/ml down to 0.05 ng/ml (Fig. 2A–C). An IgE-concentration of 2.42 ng/ml corresponds approximately to 1UA/ml in the ImmunoCAP [60]. Up to a concentration of 32 ng/ml of the mAb (23.3ISU), a linear correlation between Ab-concentration in ng/ml and the signal displayed in ISU was found (Fig. 2B and C). At concentrations higher than 30 ng/ml the curve begins to approach saturation (Fig. 2A). However, high IgE-levels were measured with high reproducibility (mean signal at 640 ng/ml = 132.02ISU, SD = 2.26ISU, CV = 1.7%, Table 2). The mean signal detected at the lowest IgE concentration (0.05 ng/ml) was 0.14ISU (SD = 0.01ISU) with a signal-to-noise ratio of 14. The mean background signal detected with sample diluent alone that was used for dilution of the monoclonal IgE was 0.1ISU (SD = 0.01ISU). Table 2 summarizes results for each of the applied concentrations.
Fig. 2.
Measurement of monoclonal human Bet v 1-specific IgE antibody levels using the MeDALL allergen-chip and by ImmunoCAP. Different concentrations of a monoclonal human IgE antibody specific to Bet v 1 (x-axes) were tested. Bet v 1-specific IgE-levels measured by the MeDALL allergen-chip (A–C) are shown on the y-axes in ISAC standardized units (ISU). Bet v 1-specific IgE-levels measured by Bet v 1-ImmunoCAP (D–F) are shown in units antigen per milliliter (UA/ml). Mean levels +/− standard deviations of triplicate measurements are shown.
Table 2.
Results of the detection of dilution series of monoclonal IgE and IgG1. Dilution series of a monoclonal human IgE specific to Bet v 1 were tested by the MeDALL allergen-chip (left top) or Bet v 1-ImmunoCAP (right). A dilution series of a monoclonal human IgG1 specific to Phl p 2 was tested by the MeDALL allergen-chip (left bottom). Mean results and standard deviations of triplicate measurements are shown in ISU and ISU-G, respectively, for the microarray and in UA/ml for ImmunoCAP. For each dilution, variation coefficients (%CV) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) are shown. Orange boxes at the bottom of every table display results obtained for the sample diluent used for diluting the monoclonal antibodies.
| MeDALL-chip | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bet v 1-specific monoclonal IgE | ||||||||
| IgE-conc. (ng/ml) |
ISU | %CV | mean %CV |
SD %CV |
SNR | mean SNR |
SD SNR |
|
| Mean | SD | |||||||
| 640 | 132.02 | 2.26 | 1.7 | 7.7 | 5.5 | 58.5 | 22.7 | 21.2 |
| 320 | 102.88 | 16.36 | 15.9 | 6.3 | ||||
| 32 | 23.30 | 1.83 | 7.9 | 12.7 | ||||
| 3.2 | 3.12 | 0.29 | 9.3 | 10.8 | ||||
| 1.6 | 1.67 | 0.07 | 4.0 | 25.1 | ||||
| 0.8 | 0.97 | 0.24 | 24.1 | 14.1 | 6.8 | 4.1 | 8.5 | 3.9 |
| 0.4 | 0.51 | 0.05 | 9.3 | 10.7 | ||||
| 0.2 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 12.4 | 8.1 | ||||
| 0.1 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 17.5 | 5.7 | ||||
| 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 7.1 | 14.0 | ||||
| 0 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 10.0 | 10.0 | ||||
| Phl p 2-specific monoclonal IgG1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG-conc. (ng/ml) |
ISU-G | %CV | mean %CV |
SD %CV |
SNR | mean SNR |
SD SNR |
|
| Mean | SD | |||||||
| 1000 | 181.22 | 15.12 | 8.3 | 14.9 | 7.9 | 12.0 | 8.1 | 3.6 |
| 500 | 161.01 | 16.26 | 10.1 | 9.9 | ||||
| 100 | 117.53 | 17.70 | 15.1 | 6.6 | ||||
| 10 | 31.61 | 8.21 | 26.0 | 3.8 | ||||
| 1 | 4.82 | 1.25 | 25.8 | 16.3 | 10.4 | 3.9 | 21.0 | 34.4 |
| 0.4 | 2.33 | 0.03 | 1.2 | 82.4 | ||||
| 0.3 | 1.64 | 0.31 | 18.6 | 5.4 | ||||
| 0.2 | 1.11 | 0.12 | 10.8 | 9.3 | ||||
| 0.1 | 0.59 | 0.15 | 25.0 | 4.0 | ||||
| 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 50.0 | 2.0 | ||||
| Bet v 1 ImmunoCAP | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bet v 1-specific monoclonal IgE | ||||||||
| IgE-conc. (ng/ml) |
UA/ml | %CV | mean %CV |
SD %CV |
SNR | mean SNR |
SD SNR |
|
| Mean | SD | |||||||
| 312.5 | 91.20 | 3.35 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 27.3 | 50.1 | 33.6 |
| 39.1 | 10.57 | 0.29 | 2.7 | 36.6 | ||||
| 19.5 | 5.49 | 0.26 | 4.7 | 21.4 | ||||
| 7.8 | 2.16 | 0.05 | 2.1 | 47.1 | ||||
| 3.9 | 1.14 | 0.01 | 0.9 | 114.0 | ||||
| 2.0 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 1.8 | 54.3 | ||||
| 1.0 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 30.9 | 29.0 | 2.7 |
| 0.5 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.0 | - | ||||
| 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 3.7 | 27.1 | ||||
| 0 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 6.2 | 16.2 | ||||
To determine background signals for all allergens on the chip, sample diluent was applied as negative control, yielding relevant background signals only for the bacterial toxin Plc (Table 1), i.e., 0.22ISU (SD = 0.28ISU) calculated after 32 measurements of sample diluent.
For comparison, a dilution series of the same monoclonal human IgE specific to Bet v 1 was measured by ImmunoCAP (Fig. 2D-F, Table 2). IgE-dilutions from 0.2–312.5 ng/ml were tested in triplicates. A linear correlation between IgE concentration in ng/ml and UA/ml was demonstrated up to the highest IgE concentration (312.5 ng/ml) applied (Fig. 2D). At levels higher than 100UA/ml the calibration-curve begins to approach saturation-level (calibration-curve not shown). The mean background signal assessed using sample diluent was 0.09UA/ml (SD = 0.01UA/ml). Signal-to-noise ratios and %CV for all dilutions applied are shown in Table 2.
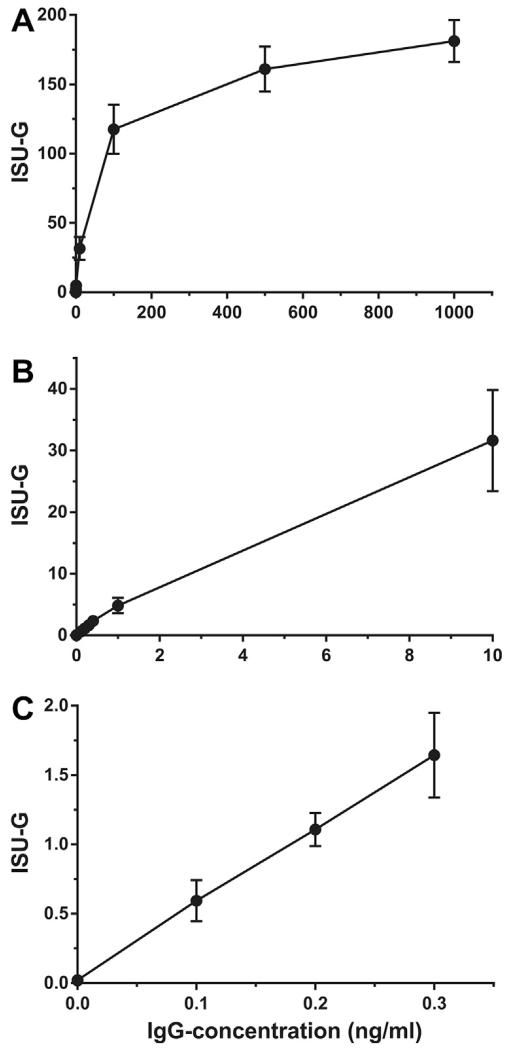
A dilution series of a monoclonal human IgG1 antibody specific to the timothy grass pollen allergen Phl p 2 with a concentration range from 0.1 ng/ml to 1 μg/ml was also measured in triplicates on the MeDALL allergen-chip (Fig. 3A–C, Table 2). From 0 to 10 ng/ml of the mAb a linear correlation between Ab-concentration in ng/ml and in ISU-G was found (Fig. 3B and C). At higher concentrations, the curve approached saturation-level. At the lowest concentration measured (i.e., 0.1 ng/ml) the signal-to-noise ratio was 4, indicating that even very low IgG-concentrations can be reliably measured by the MeDALL allergen-chip. The mean background signal was 0.02ISU-G (SD = 0.01ISU-G). Results for all dilutions tested are shown in Table 2.
Fig. 3.
Measurement of different concentrations of a monoclonal human Phl p 2-specific IgG1 antibody. Different concentrations of a monoclonal human IgG1 antibody specific to Phl p 2 (x-axes) were measured and are shown on the y-axes in ISAC standardized units for IgG (ISU-G). Graphs for IgG-concentrations of 0–1 μg/ml (A), 0–10 ng/ml (B) and 0–0.3 ng/ml (C) are shown. Error bars indicate mean levels +/− standard deviations of triplicate measurements.
Next, mean variation coefficients and signal-to-noise ratios were calculated for results from triplicate-measurements of IgE- and (only for the microarray) IgG-dilutions up to 1 ng/ml or greater than 1 ng/ml (Table 2). Microarrays and ImmunoCAPs from the same lot were used for testing antibody dilutions. The results for IgE-detection using the MeDALL allergen-chip show higher CVs for low concentrations (mean CV for concentrations up to 1 ng/ml = 14.1%, SD = 6.8%) than for higher concentrations (mean CV = 7.7%, SD = 5.5%), but the mean signal-to-noise ratio for low concentrations was sufficient (mean SNR = 8.5; SD = 3.9) to obtain reliable results even for very low IgE concentrations such as 0.05 ng/ml. For IgG detection by the MeDALL allergen-chip, both for high and for low antibody-concentrations, mean %CVs of 14.9% or 16.3% (SD = 7.9% or 10.4%), respectively, were calculated. Signal-to-noise ratios for the two intervals were 8.1 or 21, hence, also for IgG reliable results were obtained both for high and for low antibody concentrations.
Detection of the monoclonal Bet v 1-specific IgE-antibody was also performed by ImmunoCAP for concentrations from 0.2 to 312.5 ng/ml. At the lowest concentration tested (0.2 ng/ml), signals (0.16 UA/ml) were already close to the background level (0.09 UA/ml) whereas with the MeDALL allergen-chip IgE concentrations down to 0.05 ng/ml could be reliably detected. However, in ImmunoCAP, variation coefficients of 2.7% and 2.3% (SD = 1.4% and 2%) were calculated for high (i.e., greater than 1 ng/ml) and for low (i.e., up to 1 ng/ml) IgE-concentrations. Likewise, mean signal-to-noise ratios were 50.1 (SD = 33.6) for concentrations higher than 1 ng/ml and 29 (SD = 2.7) for concentrations up to 1 ng/ml (Table 2, right part).
3.2.3. Simultaneous presence of blocking IgG antibodies inhibits IgE binding to allergens on the chip but not in the ImmunoCAP
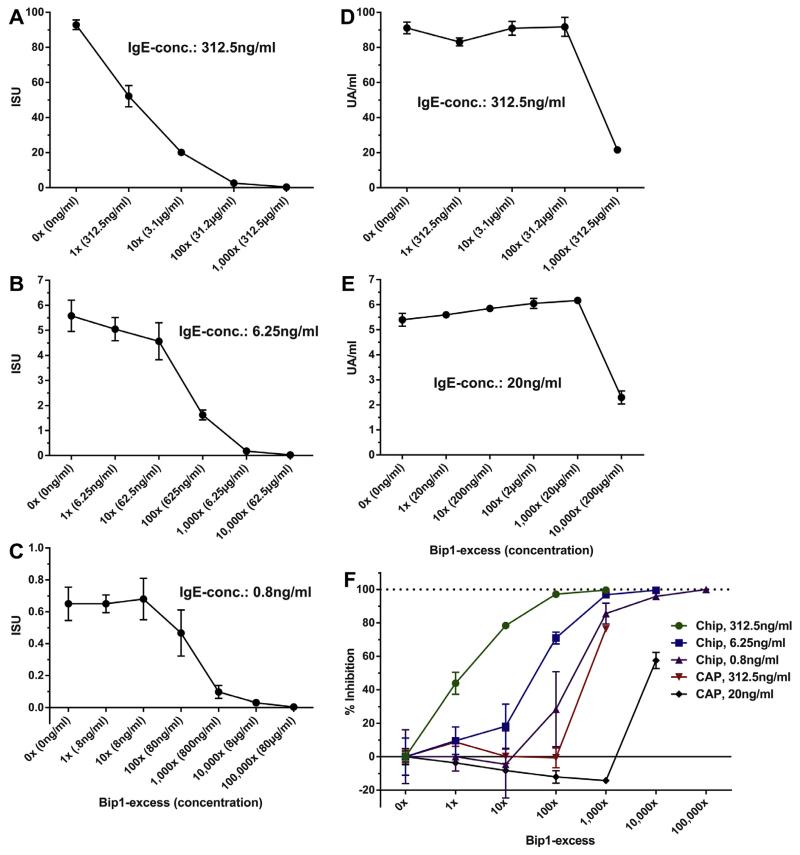
In order to test the influence of IgG antibodies on IgE binding to allergens in chip-based and ImmunoCAP assays, we used a monoclonal IgE antibody specific for the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 and an IgG antibody recognizing the very same epitope with similar affinity. This experimental set up allowed for a comparison of the effects of blocking IgG on allergen-specific IgE binding for the two technologies. For the MeDALL allergen-chip, three different concentrations of monoclonal Bet v 1-specific human IgE (312.5 ng/ml, 6.25 ng/ml, 0.8 ng/ml) were mixed with the monoclonal IgG1 (Bip1) that contains the same variable domains as the IgE-antibody and hence binds to the same epitope of Bet v 1. The respective IgE-dilutions were incubated with increasing concentrations of Bip1, ranging from a 1:1 ratio of IgE to IgG1 up to a 1000-fold (for 312.5 ng/ml IgE), 10,000-fold (for 6.25 ng/ml IgE) or a 100,000-fold (for 0.8 ng/ml IgE) excess of Bip1 as compared to the IgE antibody (Fig. 4A–C). At the highest IgE-concentration (312.5 ng/ml) a strong inhibition of the signal was found already at a 1:1 ratio of IgE and IgG (mean inhibition 43.8%, SD = 6.6%), increasing to an almost complete blocking of IgE-binding at a 100-fold and 1000-fold excess of Bip1 (Fig. 4A, Table 3). For lower IgE-concentrations we observed up to a 10-fold excess of Bip1 only a moderate (18.2% for 6.25 ng/ml IgE) or no (for 0.8 ng/ml) decrease of IgE binding (Fig. 4B and C). From a 100-fold excess of competitive IgG on, strong inhibition of the IgE-signal was observed (−71% for 6.25 ng/ml IgE, −28.3% for 0.8 ng/ml IgE) that increased to almost 100% inhibition at 1000- or 10,000-fold excess of Bip1, respectively. However, for the complete range of IgE concentrations applied, Bet v 1-specific IgE could be measured at more than 100-fold excess of competitive IgG (Table 3).
Fig. 4.
Simultaneous presence of blocking IgG reduces detected Bet v 1-specific IgE-levels. Relative excess of Bip1 compared to the respective IgE concentration and (in parenthesis) absolute concentration of Bip1 in ng/ml or μg/ml is shown on the x-axes. Bet v 1-specific IgE-levels detected by the MeDALL allergen-chip (A–C) or by ImmunoCAP (D–E) are displayed on the y-axes in ISU or in UA/ml after subtraction of background signals. IgE-concentrations applied are mentioned in the respective diagrams. Relative inhibition (F) of IgE-signals (y-axis) is plotted against levels of relative Bip1-excess (x-axis). The respective IgE-concentrations applied for detection by MeDALL allergen-chip or ImmunoCAP are displayed in the legend. Mean results of triplicates +/− standard deviations are shown.
Table 3.
Inhibition of IgE binding as measured by microarray and by ImmunoCAP after addition of blocking IgG. Different concentrations of monoclonal human Bet v 1-specific IgE (chim.IgE; concentrations indicated in coloured boxes) were incubated with increasing concentrations of blocking IgG (relative excess compared to IgE and, in parentheses, absolute concentrations of IgG indicated in the left columns) and measured by microarray (left tables) or ImmunoCAP (right tables). Absolute responses after subtraction of background signals are indicated in ISU for the MeDALL allergen-chip and in UA/ml for ImmunoCAP. Relative inhibition was calculated for every IgE-concentration applied (baseline responses indicated in red numbers).
| MeDALL-chip | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| chim. IgE → | 312.5 ng/ml |
|||
| Absolute response | % Inhibition | |||
| Blocking IgG ↓ | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| 0× (0 ng/ml) | 92.86 | 2.72 | 0.00 | 2.92 |
|
| ||||
| 1× (312.5 ng/ml) | 52.15 | 6.13 | 43.84 | 6.60 |
|
| ||||
| 10× (3.1 μg/ml) | 20.05 | 1.39 | 78.41 | 1.50 |
|
| ||||
| 100× (31.2 μg/ml) | 2.60 | 0.42 | 97.20 | 0.46 |
|
| ||||
| 1000× (312.5 μg/ml) | 0.32 | 0.02 | 99.66 | 0.02 |
| chim. IgE → | 6.25 ng/ml |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute response | % Inhibition | |||
| Blocking IgG ↓ | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| 0× (0 ng/ml) | 5.58 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 11.17 |
|
| ||||
| 1× (6.25 ng/ml) | 5.04 | 0.46 | 9.56 | 8.28 |
|
| ||||
| 10× (62.5 ng/ml) | 4.56 | 0.74 | 18.23 | 13.27 |
|
| ||||
| 100× (625 ng/ml) | 1.62 | 0.20 | 70.95 | 3.52 |
|
| ||||
| 1000× (6.25 μg/ml) | 0.18 | 0.03 | 96.83 | 0.62 |
|
| ||||
| 10,000× (62.5 μg/ml) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 99.58 | 0.27 |
| chim. IgE → | 0.8 ng/ml |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute response | % Inhibition | |||
| Blocking IgG ↓ | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| 0× (0 ng/ml) | 0.65 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 16.14 |
|
| ||||
| 1× (0.8 ng/ml) | 0.65 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 8.61 |
|
| ||||
| 10× (8 ng/ml) | 0.68 | 0.13 | −4.64 | 20.10 |
|
| ||||
| 100× (80 ng/ml) | 0.46 | 0.14 | 28.35 | 22.37 |
|
| ||||
| 1000× (800 ng/ml) | 0.09 | 0.04 | 85.57 | 6.25 |
|
| ||||
| 10,000× (8 μg/ml) | 0.03 | 0.00 | 95.88 | 0.00 |
|
| ||||
| 100,000× (80 μg/ml) | 0.00 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 0.89 |
| Bet v 1 ImmunoCAP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| chim. IgE → | 312.5 ng/ml |
|||
| Absolute response | % Inhibition | |||
| Blocking IgG ↓ | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| 0× (0 ng/ml) | 91.11 | 3.35 | 0.00 | 3.67 |
|
| ||||
| 1× (312.5 ng/ml) | 83.14 | 2.30 | 8.74 | 2.53 |
|
| ||||
| 10× (3.1 μg/ml) | 90.91 | 3.95 | 0.22 | 4.34 |
|
| ||||
| 100× (31.2 μg/ml) | 91.74 | 5.41 | −0.70 | 5.94 |
|
| ||||
| 1000× (312.5 μg/ml) | 21.54 | 1.16 | 76.36 | 1.27 |
| chim. IgE → | 20 ng/ml |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute response | % Inhibition | |||
| Blocking IgG ↓ | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| 0× (0 ng/ml) | 5.39 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 4.76 |
|
| ||||
| 1× (20 ng/ml) | 5.59 | 0.10 | −3.71 | 1.90 |
|
| ||||
| 10× (200 ng/ml) | 5.84 | 0.06 | −8.34 | 1.02 |
|
| ||||
| 100× (2 μg/ml) | 6.05 | 0.20 | −12.11 | 3.75 |
|
| ||||
| 1000× (20 μg/ml) | 6.17 | 0.08 | −14.34 | 1.52 |
|
| ||||
| 10,000× (200 μg/ml) | 2.29 | 0.26 | 57.48 | 4.83 |
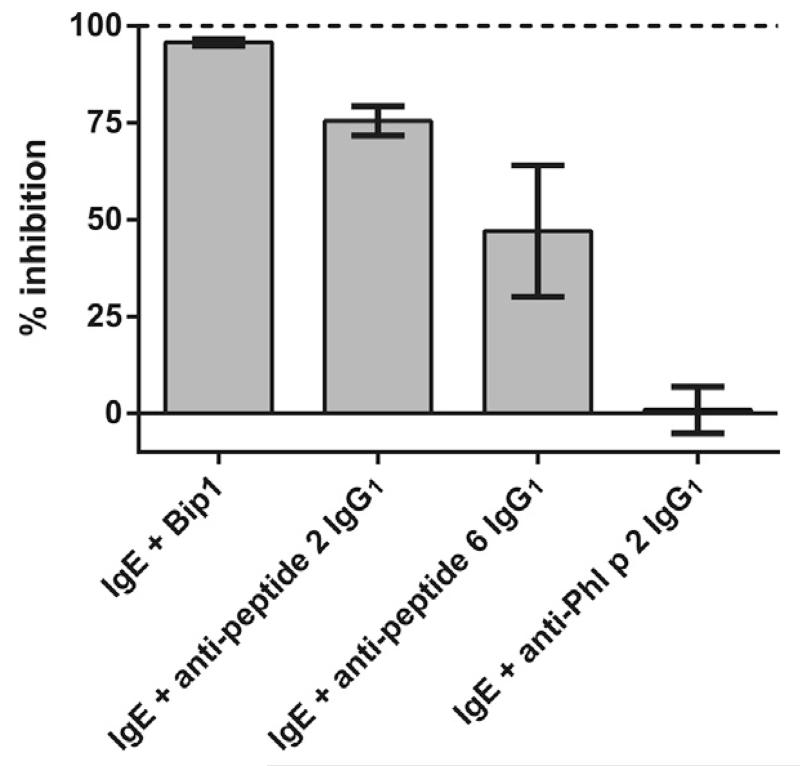
When control experiments were performed by incubating Bet v 1-specific IgE with an excess of an antibody specific for an unrelated allergen (i.e., anti-Phl p 2 IgG1) no inhibition of IgE binding was found, whereas mixing with an excess of two monoclonal IgG1 antibodies specific for two distinct Bet v 1-peptide epitopes (peptide 2 and peptide 6, respectively) gave different levels of inhibition (Fig. 5). Monoclonal IgG1 specific to Bet v 1-peptide 2 caused 75.5% inhibition, whereas inhibition by the antibody specific for peptide 6 was 47.1% (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
Bet v 1-specific IgE (312.5 ng/ml) was co-incubated with an excess of two different monoclonal antibodies binding to two distinct Bet v 1-peptides, or of a monoclonal antibody specific for the grass pollen allergen Phl p 2 (x-axis). Degree of inhibition of IgE-binding to chip-coupled Bet v 1 is shown on the y-axis. Bars show mean values of triplicates +/− standard deviation.
The same inhibitions were performed using the ImmunoCAP system by mixing two different IgE-dilutions (312.5 ng/ml, 20 ng/ml) with up to a 1000-fold (for 312.5 ng/ml IgE) or 10,000-fold (for 20 ng/ml IgE) excess of Bip1. Levels of Bet v 1-specific IgE were then measured using the Bet v 1 ImmunoCAP (Fig. 4 D-E). At high IgE concentrations (312.5 ng/ml), up to a 100-fold excess of Bip1 did not result in detectable inhibition and at low concentrations (20 ng/ml), even 1000-fold excess did not inhibit. At the highest IgG to IgE-ratios applied, an inhibition of 76% (for 312.5 ng/ml IgE) or 57% (for 20 ng/ml IgE) of IgE binding was observed (Table 3). An overlay plot of relative inhibitions of IgE binding as detected by the MeDALL allergen-chip and by ImmunoCAP is shown in Fig. 4F. The levels of inhibition are displayed in Table 3 and show that the MeDALL allergen-chip is much more sensitive (>100-fold) in detecting blocking IgG antibodies than the ImmunoCAP.
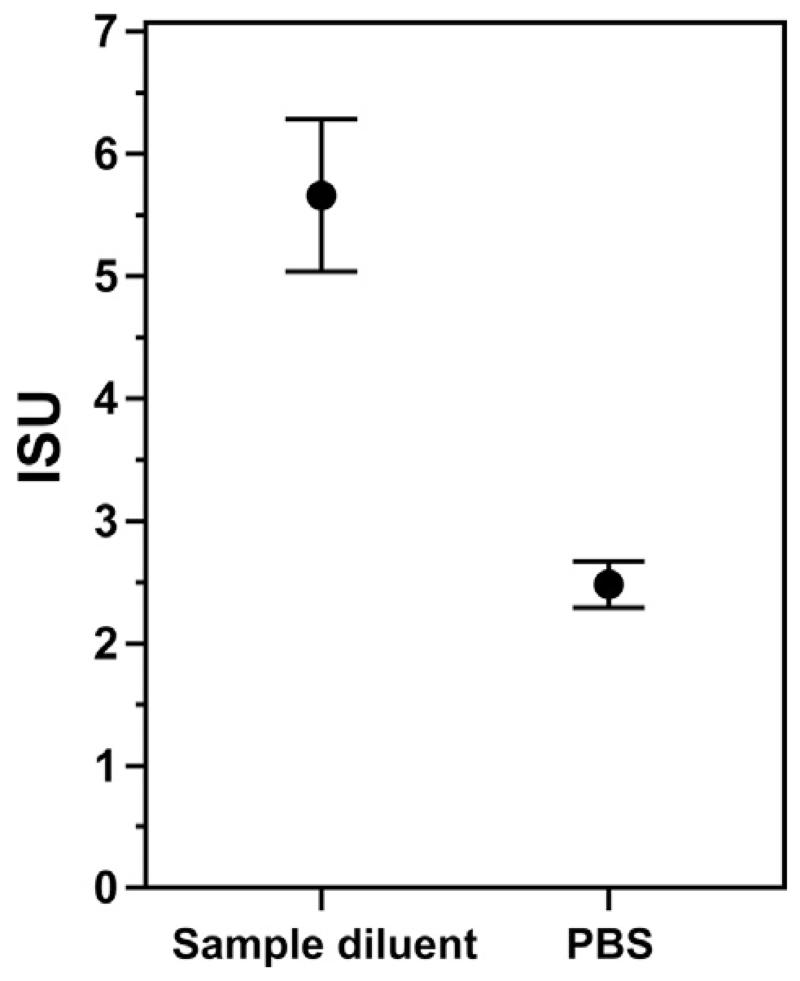
Fig. 6 illustrates an important detail when it comes to measuring low concentrations of highly diluted antibodies. Purified monoclonal human Bet v 1-specific IgE was diluted in a sample diluent which contains additives that block non-specific interaction of the antibody with the surfaces of the test tube and of the microarray, or in PBS, respectively, to a concentration of 6.25 ng/ml. Then, Bet v 1-specific IgE levels were measured by the MeDALL allergen-chip. Using sample diluent containing blocking reagents, a mean IgE-level of 5.66ISU (SD = 0.62ISU) was measured, whereas using PBS without blocking reagents, 2.48ISU (SD = 0.19ISU), i.e., a 56.1% lower level was measured. This result shows that non-specific binding to plastic or other surfaces decreases the availability of antibodies for binding to their specific target. Such adsorption effects may be misinterpreted as instability of the purified reactant and can influence results in all types of assays where highly diluted purified reactants are used (e.g., skin prick testing, cellular assays).
Fig. 6.
Effect of different diluents on detected IgE-levels. Monoclonal Bet v 1-specific IgE was diluted to a concentration of 6.25 ng/ml in a sample diluent containing blocking agents or in PBS (x-axis) and measured by the MeDALL allergen-chip. IgE-levels are displayed in ISU (y-axis). Mean results of triplicate determinations +/− standard deviations are shown.
3.2.4. Examples of different progression patterns of allergic sensitization
Table 4 shows examples for the development of IgE reactivities during early childhood as detected in serum samples from children of the BAMSE cohort from Sweden [42] at the age of 4, 8 and 16 years. Displayed are patterns of IgE responses towards respiratory and food allergens which are detectable early in life, i.e., before the age of 4 years (BAMSE 1), IgE responses which become detectable between 4 and 8 years (BAMSE 2), later, i.e., between 8 and 16 years (BAMSE 3 and 4) and mixed patterns of IgE responses appearing early and late in the same child (BAMSE 5).
Table 4.
Detection of early and late sensitization patterns in birth cohorts. IgE-reactivity profiles of five children from the BAMSE-cohort at the age of 4, 8 and 16years, assessed by the MeDALL allergen-chip are displayed. White boxes show IgE-levels below 0.3ISU, green boxes display IgE-levels ≥ 0.3 and <1ISU, ≥ 1 and ≤10ISU or higher than 10ISU (from bright to dark green). The first column shows codes of study participants.
| Individual | Allergen | IgE detected at | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 years | 8 years | 16 years | ||
| BAMSE 1 | Bet v 1 | 8.35 | 34.7 | 59.44 |
| Act d 8 | 0 | 0.73 | 0.46 | |
| Aln g 1 | 4.28 | 0 | 1.63 | |
| Ara h 8 | 0.22 | 2.55 | 1.82 | |
| Cor a 1.0401 | 15.9 | 11.12 | 4.04 | |
| Cor a1.01 | 1.23 | 6.61 | 1.56 | |
| Mal d 1 | 23.42 | 15.3 | 11.83 | |
| Pru p 1 | 0.97 | 3.12 | 4.2 | |
| Cyn d 1 | 37.14 | 97.66 | 101.27 | |
| Cup a 1 | 0 | 2.38 | 2.15 | |
| Phl p 1 | 81.63 | 96.09 | 106.65 | |
| Phl p 2 | 0 | 4.19 | 15.91 | |
| Phl p 4 | 4.8 | 30.31 | 4.03 | |
| Phl p 5 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 16.43 | |
| Can f 2 | 3.22 | 2 | 1.17 | |
| BAMSE 2 | Bet v 1 | 0 | 38.61 | 161.55 |
| Act d 8 | 0 | 0.27 | 2.75 | |
| Aln g 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.85 | |
| Api g 1 | 0 | 0 | 9.53 | |
| Ara h 8 | 0 | 0.72 | 23.78 | |
| Cor a 1.0401 | 0 | 6.96 | 77.46 | |
| Cor a1.01 | 0 | 20.11 | ||
| Mal d 1 | 0 | 11.73 | 144.86 | |
| Pru p 1 | 0 | 0 | 8.43 | |
| Bet v 2 | 0 | 3.39 | 3.62 | |
| Phl p 12 | 0 | 1.37 | 1.24 | |
| Hev b 8 | 0 | 7.05 | 16.08 | |
| Mer a 1 | 0 | 6.29 | 2.69 | |
| Pru du 4 | 0 | 2.3 | 8.41 | |
| Tri a 12 | 0 | 1.45 | 4.29 | |
| Can f 5 | 0 | 1.53 | 61.3 | |
| Can f 5 | 0 | 0.36 | 3.6 | |
| Can f 6 | 0 | 0 | 44.24 | |
| Cyn d 1 | 0 | 25.94 | 51.17 | |
| Phl p 1 | 0 | 60.17 | 151.32 | |
| Phl p 2 | 0 | 3.54 | 8.2 | |
| Phl p 4 | 0 | 0.36 | 3.79 | |
| Cup a 1 | 0 | 0.57 | 0.65 | |
| Equ c 1 | 0 | 0 | 17.53 | |
| Fel d 1 | 0 | 77.94 | 26.9 | |
| Fel d 2 | 0 | 0.98 | 1.5 | |
| Fel d 4 | 0 | 0 | 22.19 | |
| Mus m 1 | 0 | 0 | 2.99 | |
| BAMSE 3 | Bet v 1 | 0 | 0.15 | 7.08 |
| Ara h 8 | 0 | 0 | 1.02 | |
| Cor a 1.0401 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.01 | |
| Mal d 1 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.08 | |
| Gly m 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.49 | |
| Cyn d 1 | 0 | 0.11 | 3.9 | |
| Phl p 1 | 0 | 0.99 | 27.78 | |
| Equ c 1 | 0 | 0 | 3.09 | |
| Can f 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.97 | |
| Can f 6 | 0 | 0.15 | 5.03 | |
| Fel d 1 | 0 | 0 | 14.51 | |
| Fel d 4 | 0 | 0.13 | 29.79 | |
| Mus m 1 | 0 | 0 | 8.79 | |
| BAMSE 4 | Cyn d 1 | 0 | 0.17 | 47.92 |
| Phl p 1 | 0 | 0.19 | 129.4 | |
| Phl p 4 | 0 | 0.11 | 25.78 | |
| Phl p 5 | 0 | 0 | 74.52 | |
| Phl p 6 | 0 | 0 | 16.13 | |
| BAMSE 5 | Bet v 1 | 0 | 0 | 10.85 |
| Cor a 1.0401 | 0 | 0 | 5.31 | |
| Cyn d 1 | 2.71 | 51.41 | 14.89 | |
| Phl p 1 | 16.61 | 52.08 | 28.42 | |
| Phl p 2 | 0 | 1.58 | 3.66 | |
| Phl p 5 | 0 | 21.06 | 11.85 | |
| Fel d 1 | 0 | 0.14 | 4.81 | |
Screenshots of IgE detection by microarray in serum samples obtained from one study participant of the Norwegian birth cohort ECA [43] at the age of 10 and 16 years are shown in Fig. 7. At 16 years, the serum sample exhibits reactivities to some additional allergen components, mainly from the same allergen source and IgE levels were higher as illustrated by “warmer” colours (yellow to red).
Fig. 7.
Screenshots illustrating the evolution of an IgE-reactivity profile over time. Serum samples from a study participant of the Norwegian birth cohort ECA, obtained at (A) 10 years and (B) 16 years, were analyzed for IgE-reactivities using the MeDALL allergen-chip. Every allergen-molecule was spotted in triplicates (groups of three dots aligned vertically), signal strength is visualized in false colours with increasing fluorescence intensities from blue to red/white.
4. Discussion and conclusions
In the present study we demonstrated recent advances in allergen microarray technology using the MeDALL allergen-chip as a model. The MeDALL allergen-chip is a more developed version of the ImmunoCAP ISAC platform in that it contains an expanded repertoire of allergens that can be used for the detection of allergen-specific IgE as well as other immunoglobulin isotypes. The MeDALL allergen-chip has been developed as a research tool for the sensitive detection of IgE-reactivities in samples from children of different birth cohorts of various European countries to study the evolution of the allergen-specific antibody responses in childhood. The MeDALL allergen-chip allows the sensitive detection of allergen-specific IgE towards a large number of clinically relevant allergen molecules as has been demonstrated by IgE titration experiments and comparison with one of the most sensitive tools for measuring allergen-specific IgE, the ImmunoCAP assay. To establish a large panel of clinically relevant allergens on the chip we assembled purified recombinant and natural allergen molecules from different respiratory and food allergen sources, such as house dust mite, peanut and wheat, to complement the allergen panel of ImmunoCAP ISAC (Table 1). Certain molecules were spotted as recombinant, others as natural proteins purified from allergen extracts. In addition to IgE, calibration for IgG, IgG4 and IgA has been established for the MeDALL allergen-chip and specific detection of other isotypes is being developed. This allows us not only to study IgE reactivities in children’s sera but should also assess the eventual protective effects of maternal allergen-specific IgG transferred to the child or of spontaneously developing IgG responses in study subjects.
A series of experiments was performed using well defined monoclonal antibodies with known specificities to different allergens. In some of these experiments measurements were done with the MeDALL allergen-chip and by ImmunoCAP in parallel in order to study characteristics and special features of these two systems. The ImmunoCAP system was chosen as a reference because it has been widely used by clinicians for measuring allergen-specific IgE responses in the birth cohorts. Both, ImmunoCAP and the MeDALL allergen-chip were found to have almost equal background signals for IgE detection, which are in the range of 0.1 (SD = 0.01) ISU or UA/ml, respectively. At the lowest IgE-concentrations applied, i.e., 0.05 ng/ml for the MeDALL allergen-chip and 0.2 ng/ml for ImmunoCAP, signal-to-noise ratios were 14 and 27.1, relative variation coefficients were 7.1% and 3.7%, respectively. These results imply that with both technologies, low IgE-concentrations can be reliably measured, and, with the MeDALL allergen-chip, even at higher sensitivity (Table 2). When detecting IgG using the microarray, almost no relevant background signal (0.02ISU-G, SD = 0.01ISU-G) and a sufficiently high SNR (4 for 0.1 ng/ml IgG) were observed, allowing detection of IgG-concentrations even lower than the smallest concentration tested in the present series. Likewise, when looking at higher concentrations of IgE or IgG, low inter-assay variations were observed (Table 2). However, Fig. 2A demonstrates that at IgE concentrations higher than approximately 30 ng/ml, the linear relation between antibody concentration and ISU is no longer observed. Therefore, IgE levels higher than 30ISU measured with the chip correspond to increasingly higher concentrations of IgE in ng/ml (Fig. 2A). In the ImmunoCAP there is still a linear relation between antibody concentration in ng/ml and UA/ml up to 300 ng/ml of IgE (Fig. 2D). This difference between the two systems is due to the fact that on the microarray, only 50–200 fg of protein are immobilized per spot whereas in ImmunoCAP, 1–2 μg of protein, i.e., 10,000,000 times more, are coupled. Consequently, the quality of the protein preparations used and the assessment of antibody-binding capacity to the allergen spots are critically important issues for microarray technology since signal intensities decrease in relation to the proportion of spotted allergen molecules that are denatured.
Apart from the detection of IgE reactivities to defined allergen molecules for diagnosis of allergic sensitization, the measurement of blocking IgG, or antibodies of any other isotype than IgE, is an important aspect, e.g., for the assessment of the immunological efficacy of specific immunotherapy or of potentially protective effects of maternal IgG that are transferred to the child via the placenta or through breast milk or of spontaneously developing allergen-specific IgG responses. Quantification of IgG that binds to a given allergen does not provide information as to whether it inhibits IgE binding to the same allergen. In order to study how different systems for measuring allergen-specific IgE (i.e., microarray versus ImmunoCAP) can provide information regarding the presence of blocking IgG, IgE responses were detected before and after addition of competing IgG. Using ImmunoCAP, at 312.5 ng/ml of Bet v 1-specific IgE, no effect was observed on detected allergen-specific IgE-levels with up to a 100-fold excess of blocking IgG (Fig. 4D). This is due to the fact that a relative excess of allergen is used and therefore, all antibody isotypes specific for Bet v 1 can bind independently from each other. Therefore, the potential therapeutic effect of allergen-specific IgG cannot be judged by using ImmunoCAP, neither by measuring IgE before and after induction of IgG, nor by direct assessment of IgG. Performing the same experiment using the MeDALL allergen-chip, a 1:1 ratio of IgE (312.5 ng/ml) and competing IgG showed a decrease of the IgE-signal of 44% (Fig. 4A, Table 3). This means that the allergen microarray integrates all antibodies binding to the same epitope into a net IgE value (or value of any other isotype detected). Since blocking IgE from binding to allergen reduces the allergic reaction, it may be assumed that IgE levels measured by microarray should better reflect the potency of IgE to mediate an allergic reaction upon allergen contact. However, the allergen-specific IgE signal is completely abolished only at a 1000-fold or higher excess of blocking antibodies, depending on the absolute allergen-specific IgE level. Relative inhibition of IgE signals detected for all IgE-concentrations investigated and for both CAP and MeDALL allergen-chip are plotted in Fig. 4F showing that at an IgE-concentration of 0.8 ng/ml (microarray) or 312.5 ng/ml (ImmunoCAP), similar findings are obtained for both systems. Moreover, the figure illustrates that at higher IgE concentrations, IgE levels measured are more strongly decreased by the presence of blocking IgG (regarding the relative excess of IgG) than at lower concentrations. This observation becomes clear when considering that, assuming a given number of epitopes available for antibody-binding, at high antibody-concentrations, the saturation-level is approached, especially when the number of epitopes is restricted as in the microarray.
The results obtained in this study illustrate that there is a fundamental difference between allergen microarrays and the ImmunoCAP system for detecting and measuring allergen-specific IgE. In the traditionally used system for detection of allergen-specific IgE, the ImmunoCAP system, there is a relative excess of allergen molecules (1–2 μg of the respective allergen molecule) as compared to the average concentrations of allergen-specific IgE antibodies in serum. Since there is a large amount of allergen coupled to a large surface, antibodies of all isotypes can bind simultaneously. By contrast, allergen microarrays contain only approximately 5 attomol of protein per spot, corresponding to, e.g., 100 fg in case of a protein of 20 kDa. This means that, compared to ImmunoCAP, one spot of the microarray contains 10,000,000 times less protein.
This difference in immobilized allergen amounts between the two test systems has an important impact on the test results and must be considered for their interpretation. As long as antibody levels are relatively low, both systems yield comparable results but as soon as allergen-specific antibody levels rise, the relatively limited number of epitopes present per spot on the microarray prevents the binding of some of the antibodies that are specific to the respective allergen. As a consequence, in the microarray saturation levels are already reached at lower antibody concentrations which may get close to the in vivo situation of allergic patients where only a part of the circulating IgE is bound to the effector cells of the allergic reaction (e.g., mast cells, basophils, antigen presenting cells) via their specific receptors. This assumption needs to be confirmed in clinical studies comparing chip results with in vivo sensitivity in patients (e.g., titrated skin tests). Importantly, in case allergen-specific antibodies other than IgE are simultaneously present in serum samples or other biological fluids (e.g., tears, breast milk), competition between IgE and other isotypes will become detectable as a reduction of IgE binding when these isotypes represent true blocking antibodies recognizing the same epitope or affect IgE binding by other mechanisms such as steric hindrance. On the microarray, like in the in vivo situation where only small amounts of allergen enter the body, several parameters will determine which isotype will bind better to the allergen, among them concentration and affinity of the respective antibodies. Regarding allergy diagnosis, it is thus reasonable to assume that the microarray will more closely reflect the biological situation in the patient after incorporation of allergen. Likewise, for successful specific immunotherapy (SIT), higher titers of allergen-specific IgG, rather than IgE antibodies will be induced, and therefore IgG will occupy more epitopes on the allergen molecule than the corresponding IgE. If allergen-specific antibodies in such patients are measured by microarray, one will observe increases of allergen-specific IgG levels and, in those cases where these allergen-specific IgG antibodies can block IgE binding to the allergen, a reduction of IgE binding will be detectable (Lupinek & Valenta, unpublished). Therefore, allergen-microarrays may be useful for the measurement of the successful induction of therapeutically active IgG by SIT and should eventually become a new surrogate marker for therapeutic success of SIT, provided that clinical studies confirm the theoretical assumption based on the in vitro results. Test systems such as the ImmunoCAP, which, due to the presence of large amounts of allergen on the solid phase, can accommodate the simultaneous binding of IgE and other isotypes and therefore do not mimic the biological situation (i.e., clinical sensitivity of the patient upon allergen encounter). Yet, they offer the possibility to quantify allergen-specific antibodies which allows, e.g., IgE quantification in order to assess the effect of allergen avoidance or therapeutic IgE depletion on allergen-specific IgE levels.
Acknowledgments
Funding sources
This work was supported by the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme under grant agreement No. 261357 and in part by project F4605 of the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) and the Christian Doppler Research Association, Austria.
Abbreviations
- CV
variation coefficient
- HDM
house dust mite
- IgE
immunoglobulin E
- IgG
immunoglobulin G
- ISU
ISAC standardized units (for IgE-detection)
- ISU-G
ISAC standardized units (for IgG-detection)
- MeDALL
mechanisms for the development of allergies
- SNR
signal-to-noise ratio
- UA/ml
units antigen per milliliter
References
- [1].Wuthrich B, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Schindler C, Imboden M, Bircher A, Zemp E, Probst-Hensch N. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;162:143–148. doi: 10.1159/000351416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Kulig M, Bergmann R, Klettke U, Wahn V, Tacke U, Wahn U. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999;103:1173–1179. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Lupinek C, Marth K, Niederberger V, Valenta R. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;130:1418–1420. e1414. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].W.H.O.C.C.f. Asthma, Rhinitis. Bousquet J, Anto JM, Demoly P, Schunemann HJ, Togias A, Akdis M, Auffray C, Bachert C, Bieber T, Bousquet PJ, Carlsen KH, Casale TB, Cruz AA, Keil T, Lødrup Carlsen KC, Maurer M, Ohta K, Papadopoulos NG, Roman Rodriguez M, Samolinski B, Agache I, Andrianarisoa A, Ang CS, Annesi-Maesano I, Ballester F, Baena-Cagnani CE, Basagana X, Bateman ED, Bel EH, Bedbrook A, Beghe B, Beji M, Ben Kheder A, Benet M, Bennoor KS, Bergmann KC, Berrissoul F, Bindslev Jensen C, Bleecker ER, Bonini S, Boner AL, Boulet LP, Brightling CE, Brozek JL, Bush A, Busse WW, Camargos PA, Canonica GW, Carr W, Cesario A, Chen YZ, Chiriac AM, Costa DJ, Cox L, Custovic A, Dahl R, Darsow U, Didi T, Dolen WK, Douagui H, Dubakiene R, El-Meziane A, Fonseca JA, Fokkens WJ, Fthenou E, Gamkrelidze A, Garcia-Aymerich J, Gerth van Wijk R, Gimeno-Santos E, Guerra S, Haahtela T, Haddad H, Hellings PW, Hellquist-Dahl B, Hohmann C, Howarth P, Hourihane JO, Humbert M, Jacquemin B, Just J, Kalayci O, Kaliner MA, Kauffmann F, Kerkhof M, Khayat G, Koffi N’Goran B, Kogevinas M, Koppelman GH, Kowalski ML, Kull I, Kuna P, Larenas D, Lavi I, Le LT, Lieberman P, Lipworth B, Mahboub B, Makela MJ, Martin F, Martinez FD, Marshall GD, Mazon A, Melen E, Meltzer EO, Mihaltan F, Mohammad Y, Mohammadi A, Momas I, Morais-Almeida M, Mullol J, Muraro A, Naclerio R, Nafti S, Namazova-Baranova L, Nawijn MC, Nyembue TD, Oddie S, O’Hehir RE, Okamoto Y, Orru MP, Ozdemir C, Ouedraogo GS, Palkonen S, Panzner P, Passalacqua G, Pawankar R, Pigearias B, Pin I, Pinart M, Pison C, Popov TA, Porta D, Postma DS, Price D, Rabe KF, Ratomaharo J, Reitamo S, Rezagui D, Ring J, Roberts R, Roca J, Rogala B, Romano A, Rosado-Pinto J, Ryan D, Sanchez-Borges M, Scadding GK, Sheikh A, Simons FE, Siroux V, Schmid-Grendelmeier PD, Smit HA, Sooronbaev T, Stein RT, Sterk PJ, Sunyer J, Terreehorst I, Toskala E, Tremblay Y, Valenta R, Valeyre D, Vandenplas O, van Weel C, Vassilaki M, Varraso R, Viegi G, Wang DY, Wickman M, Williams D, Wohrl S, Wright J, Yorgancioglu A, Yusuf OM, Zar HJ, Zernotti ME, Zidarn M, Zhong N, Zuberbier T. Severe chronic allergic (and related) diseases: a uniform approach–a MeDALL–GA2LEN–ARIA position paper. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012;158:216–231. doi: 10.1159/000332924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Bousquet J, Anto J, Sunyer J, Nieuwenhuijsen M, Vrijheid M, Keil T, Me DSG, C.S. Group. E.S. Group. G.S. Group Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;161:1–10. doi: 10.1159/000343018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Hiller R, Laffer S, Harwanegg C, Huber M, Schmidt WM, Twardosz A, Barletta B, Becker WM, Blaser K, Breiteneder H, Chapman M, Crameri R, Duchene M, Ferreira F, Fiebig H, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, King TP, Kleber-Janke T, Kurup VP, Lehrer SB, Lidholm J, Muller U, Pini C, Reese G, Scheiner O, Scheynius A, Shen HD, Spitzauer S, Suck R, Swoboda I, Thomas W, Tinghino R, Van Hage-Hamsten M, Virtanen T, Kraft D, Muller MW, Valenta R. FASEB J. 2002;16:414–416. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0711fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Patelis A, Gunnbjornsdottir M, Malinovschi A, Matsson P, Onell A, Hogman M, Alving K, Janson C. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;130:397–402. e392. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Onell A, Hjalle L, Borres MP. Clin. Transl. Allergy. 2012;2:24. doi: 10.1186/2045-7022-2-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Cabrera-Freitag P, Goikoetxea MJ, Beorlegui C, Gamboa P, Gastaminza G, Fernandez-Benitez M, Ferrer M, Blanca M, Sanz ML. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2011;41:1440–1446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Canonica GW, Ansotegui IJ, Pawankar R, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, van Hage M, Baena-Cagnani CE, Melioli G, Nunes C, Passalacqua G, Rosenwasser L, Sampson H, Sastre J, Bousquet J, Zuberbier T, WAO-ARIA-GA2LEN Task Force. Allen K, Asero R, Bohle B, Cox L, de Blay F, Ebisawa M, Maximiliano-Gomez R, Gonzalez-Diaz S, Haahtela T, Holgate S, Jakob T, Larche M, Matricardi PM, Oppenheimer J, Poulsen LK, Renz HE, Rosario Ne., Rothenberg M, Sanchez-Borges M, Scala E, Valenta R. World Allergy Organ J. 2013;6:17. doi: 10.1186/1939-4551-6-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Javaloyes G, Goikoetxea MJ, Garcia Nunez I, Sanz ML, Blanca M, Scheurer S, Vieths S, Ferrer M. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2012;22:508–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Gadisseur R, Chapelle JP, Cavalier E. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011;49:277–280. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Asarnoj A, Moverare R, Ostblom E, Poorafshar M, Lilja G, Hedlin G, van Hage M, Ahlstedt S, Wickman M. Allergy. 2010;65:1189–1195. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Melioli G, Bonifazi F, Bonini S, Maggi E, Mussap M, Passalacqua G, Rossi ER, Vacca A, Canonica GW, I. Italian Board Clin. Biochem. 2011;44:1005–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Marsh J, Rigby N, Wellner K, Reese G, Knulst A, Akkerdaas J, van Ree R, Radauer C, Lovegrove A, Sancho A, Mills C, Vieths S, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Shewry PR. Mol. Nut. Food Res. 2008;52(Suppl. 2):S272–285. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Koppelman SJ, de Jong GA, Laaper-Ertmann M, Peeters KA, Knulst AC, Hefle SL, Knol EF. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2005;35:490–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Sathe SK, Wolf WJ, Roux KH, Teuber SS, Venkatachalam M, Sze-Tao KW. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002;50:4333–4341. doi: 10.1021/jf020007v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Sathe SK, Sze-Tao KW, Wolf WJ, Hamaker BR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997;45:2854–2860. [Google Scholar]
- [19].Wang F, Robotham JM, Teuber SS, Tawde P, Sathe SK, Roux KH. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002;110:160–166. doi: 10.1067/mai.2002.125208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Wang F, Robotham JM, Teuber SS, Sathe SK, Roux KH. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003;132:27–39. doi: 10.1159/000073262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Robotham JM, Wang F, Seamon V, Teuber SS, Sathe SK, Sampson HA, Beyer K, Seavy M, Roux KH. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;115:1284–1290. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.02.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Tawde P, Venkatesh YP, Wang F, Teuber SS, Sathe SK, Roux KH. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006;118:915–922. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Willison LN, Tripathi P, Sharma G, Teuber SS, Sathe SK, Roux KH. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011;156:267–281. doi: 10.1159/000323887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Willison LN, Tawde P, Robotham JM. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2008;38:1229–1238. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.02998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Hochwallner H, Schulmeister U, Swoboda I, Balic N, Geller B, Nystrand M, Harlin A, Thalhamer J, Scheiblhofer S, Niggemann B, Quirce S, Ebner C, Mari A, Pauli G, Herz U, van Tol EA, Valenta R, Spitzauer S. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2010;40:1809–1818. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Hochwallner H, Schulmeister U, Swoboda I, Twaroch TE, Vogelsang H, Kazemi-Shirazi L, Kundi M, Balic N, Quirce S, Rumpold H, Froschl R, Horak F, Tichatschek B, Stefanescu CL, Szepfalusi Z, Papadopoulos NG, Mari A, Ebner C, Pauli G, Valenta R, Spitzauer S. Allergy. 2011;66:1201–1207. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Schulmeister U, Hochwallner H, Swoboda I, Focke-Tejkl M, Geller B, Nystrand M, Harlin A, Thalhamer J, Scheiblhofer S, Keller W, Niggemann B, Quirce S, Ebner C, Mari A, Pauli G, Herz U, Valenta R, Spitzauer S. J. Immunol. 2009;182:7019–7029. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0712366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Constantin C, Quirce S, Grote M, Touraev A, Swoboda I, Stoecklinger A, Mari A, Thalhamer J, Heberle-Bors E, Valenta R. J. Immunol. 2008;180:7451–7460. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.11.7451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Baar A, Pahr S, Constantin C, Scheiblhofer S, Thalhamer J, Giavi S, Papadopoulos NG, Ebner C, Mari A, Vrtala S, Valenta R. J. Immunol. 2012;189:3018–3025. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Pahr S, Constantin C, Mari A, Scheiblhofer S, Thalhamer J, Ebner C, Vrtala S, Mittermann I, Valenta R. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2012;42:597–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2012.03961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Focke M, Linhart B, Hartl A, Wiedermann U, Sperr WR, Valent P, Thalhamer J, Kraft D, Valenta R. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2004;34:1525–1533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Weghofer M, Dall’Antonia Y, Grote M, Stocklinger A, Kneidinger M, Balic N, Krauth MT, Fernandez-Caldas E, Thomas WR, van Hage M, Vieths S, Spitzauer S, Horak F, Svergun DI, Konarev PV, Valent P, Thalhamer J, Keller W, Valenta R, Vrtala S. Allergy. 2008;63:758–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Weghofer M, Grote M, Resch Y, Casset A, Kneidinger M, Kopec J, Thomas WR, Fernandez-Caldas E, Kabesch M, Ferrara R, Mari A, Purohit A, Pauli G, Horak F, Keller W, Valent P, Valenta R, Vrtala S. J. Immunol. 2013;190:3059–3067. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Weghofer M, Grote M, Dall’Antonia Y, Fernandez-Caldas E, Krauth MT, van Hage M, Horak F, Thomas WR, Valent P, Keller W, Valenta R, Vrtala S. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2008;147:101–109. doi: 10.1159/000135696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Curin M, Swoboda I, Wollmann E, Lupinek C, Spitzauer S, van Hage M, Valenta R. Micro-arrayed dog, cat and horse allergens show weak correlation between allergen-specific IgE and IgG responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.10.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Mittermann I, Zidarn M, Silar M, Markovic-Housley Z, Aberer W, Korosec P, Kosnik M, Valenta R. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:1300–1307. e1303. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Laffer S, Vangelista L, Steinberger P, Kraft D, Pastore A, Valenta R. J. Immunol. 1996;157:4953–4962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Laffer S, Hogbom E, Roux KH, Sperr WR, Valent P, Bankl HC, Vangelista L, Kricek F, Kraft D, Gronlund H, Valenta R. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001;108:409–416. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.117593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Gieras A, Cejka P, Blatt K, Focke-Tejkl M, Linhart B, Flicker S, Stoecklinger A, Marth K, Drescher A, Thalhamer J, Valent P, Majdic O, Valenta R. J. Immunol. 2011;186:5333–5344. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Flicker S, Steinberger P, Norderhaug L, Sperr WR, Majlesi Y, Valent P, Kraft D, Valenta R. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002;32:2156–2162. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200208)32:8<2156::AID-IMMU2156>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Padavattan S, Flicker S, Schirmer T, Madritsch C, Randow S, Reese G, Vieths S, Lupinek C, Ebner C, Valenta R, Markovic-Housley Z. J. Immunol. 2009;182:2141–2151. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Wickman M, Kull I, Pershagen G, Nordvall SL. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2002;13(Suppl. 15):11–13. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3038.13.s.15.10.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Hovland V, Riiser A, Mowinckel P, Carlsen KH, Lødrup KC. Eur. Respir. J. 2013;41:838–845. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00071512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Huvenne W, Hellings PW, Bachert C. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;161:304–314. doi: 10.1159/000350329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Pahr S, Constantin C, Papadopoulos NG, Giavi S, Makela M, Pelkonen A, Ebner C, Mari A, Scheiblhofer S, Thalhamer J, Kundi M, Vrtala S, Mittermann I, Valenta R. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013 doi: 10.1111/all.12464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Srinivasan B, Focke-Tejkl M, Swoboda I, Constantin C, Mittermann I, Pahr S, Vogelsang H, Huber WD, Valenta R. Amino Acids. 2013 doi: 10.1007/s00726-013-1537-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Ebisawa M, Shibata R, Sato S, Borres MP, Ito K. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012;158:71–76. doi: 10.1159/000330661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Casset A, Mari A, Purohit A, Weghofer M, Ferrara R, Thomas WR, Alessandri C, Chen K-W, De Blay F, Valenta R, Vrtala S. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012 doi: 10.1159/000337654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Vrtala S, Huber H, Thomas WR. Methods. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [50].Hales BJ, Elliot CE, Chai LY, Pearce LJ, Tipayanon T, Hazell L, Stone S, Piboonpocanun S, Thomas WR, Smith WA. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;160:233–240. doi: 10.1159/000339760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Barbosa MC, Santos AB, Ferriani VP, Pomes A, Chapman MD, Arruda LK. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;161:213–219. doi: 10.1159/000346318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Pomes A, Arruda LK. Methods. 2013 [Google Scholar]
- [53].Douladiris N, Savvatianos S, Roumpedaki I, Skevaki C, Mitsias D, Papadopoulos NG. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;162:163–172. doi: 10.1159/000353113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Villalba M, Rodriguez R, Batanero E. Methods. 2013 [Google Scholar]
- [55].Willison LN, Sathe SK, Roux KH. Methods. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [56].Asarnoj A, Glaumann S, Elfstrom L, Lilja G, Lidholm J, Nilsson C, Wickman M. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012;159:209–212. doi: 10.1159/000336027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [57].Berneder M, Bublin M, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Hawranek T, Lang R. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013;161:229–233. doi: 10.1159/000345970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [58].Hochwallner H, Schulmeister U, Swoboda I, Spitzauer S, Valenta R. Methods. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [59].Caballero ML, Umpierrez A, Perez-Pinar T, Moneo I, de Burgos C, Asturias JA, Rodriguez-Perez R. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012;158:232–240. doi: 10.1159/000331581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [60].Bazaral M, Hamburger RN. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1972;49:189–191. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]