Abstract
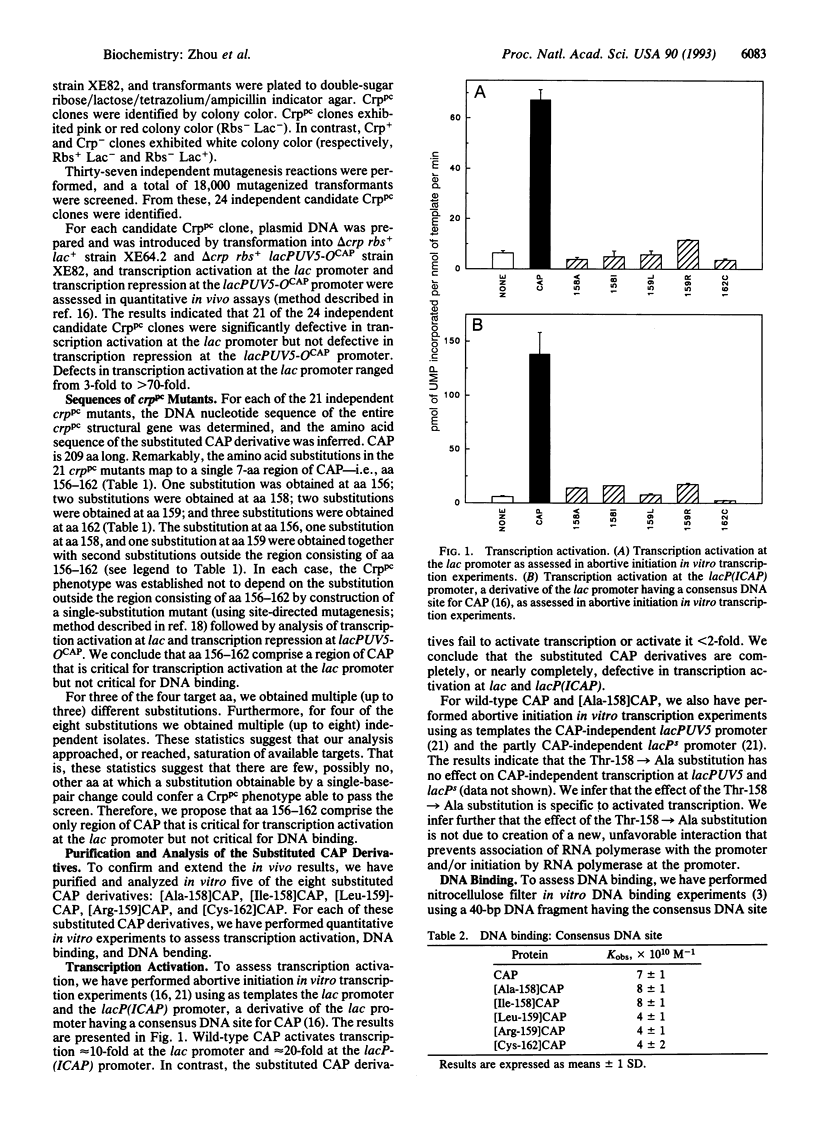
We have isolated 21 mutants of catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) defective in transcription activation at the lac promoter but not defective in DNA binding. The amino acid substitutions in the mutants map to a single region of CAP: amino acids 156-162. As assessed in vitro, the substituted CAP variants are nearly completely unable to activate transcription at the lac promoter but bind to DNA with the same affinity and bend DNA to the same extent as wild-type CAP. Our results establish that amino acids 156-162 are critical for transcription activation at the lac promoter but not for DNA binding and DNA bending. In the structure of CAP, amino acids 156-162 are part of a surface loop. We propose that this surface loop makes a direct protein-protein contact with RNA polymerase at the lac promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antosiewicz J., Porschke D. Turn of promotor DNA by cAMP receptor protein characterized by bead model simulation of rotational diffusion. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Feb;5(4):819–837. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A. W., Buckel S. D., Groarke J. M., Hope J. N., Kingsley D. H., Hermodson M. A. The nucleotide sequences of the rbsD, rbsA, and rbsC genes of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7652–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A., Gaston K., Williams R., Chapman K., Kolb A., Buc H., Minchin S., Williams J., Busby S. Mutations that alter the ability of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to activate transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7243–7250. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenlauer A. C., Reznikoff W. S. Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein mutants defective in positive control of lac operon transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5024–5029. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5024-5029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekera A., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. DNA sequence determinants for binding of the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14713–14720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyduk T., Lee J. C. Solution studies on the structure of bent DNA in the cAMP receptor protein-lac DNA complex. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 9;31(22):5165–5171. doi: 10.1021/bi00137a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin N., Ptashne M. Mutants of the catabolite activator protein of Escherichia coli that are specifically deficient in the gene-activation function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8315–8319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandecki W., Caruthers M. H. Mutants of the lac promoter with large insertions and deletions between the CAP binding site and the -35 region. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschke D., Hillen W., Takahashi M. The change of DNA structure by specific binding of the cAMP receptor protein from rotation diffusion and dichroism measurements. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2873–2878. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y. L., Garges S., Adhya S., Krakow J. S. Cooperative DNA binding of heterologous proteins: evidence for contact between the cyclic AMP receptor protein and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S. Catabolite gene activator protein activation of lac transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):655–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.655-658.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Straney S. B., Crothers D. M. Synergy between Escherichia coli CAP protein and RNA polymerase in the lac promoter open complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. P., Gunasekera A., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Derivatives of CAP having no solvent-accessible cysteine residues, or having a unique solvent-accessible cysteine residue at amino acid 2 of the helix-turn-helix motif. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Dec;9(3):463–473. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Zhou Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) is not an "acidic activating region" transcription activator protein. Negatively charged amino acids of CAP that are solvent-accessible in the CAP-DNA complex play no role in transcription activation at the lac promoter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8136–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. H., Zhang X. P., Ebright R. H. Random mutagenesis of gene-sized DNA molecules by use of PCR with Taq DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):6052–6052. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.6052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Comparative gel electrophoresis measurement of the DNA bend angle induced by the catabolite activator protein. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]