Abstract
The first enantioselective carbonyl crotylations through direct use of alkynes as chiral allylmetal equivalents are described. Chiral ruthenium(II) complexes modified by Josiphos (SL-J009-1) catalyze the C-C coupling of TIPS-protected propargyl ether 1a with primary alcohols 2a-2o to form products of carbonyl siloxy-crotylation 3a-3o, which upon silyl deprotection-reduction deliver 1,4-diols 5a-5o with excellent control of regio-, anti-diastereo- and enantioselectivity. Structurally related propargyl ethers 1b and 1c bearing ethyl- and phenyl-substituents engage in diastereo- and enantioselective coupling, as illustrated in the formation of adducts 5p and 5q, respectively. Selective mono-tosylation of diols 5a, 5c, 5e, 5f, 5k and 5m is accompanied by spontaneous cyclization to deliver the trans-2,3-disubstituted furans 6a, 6c, 6e, 6f, 6k and 6m, respectively. Primary alcohols 2a, 2l and 2p were converted to the siloxy-crotylation products 3a, 3l and 3p, which upon silyl deprotection-lactol oxidation were transformed to the trans-4,5-disubstituted γ-butyrolactones 7a, 7l and 7p. The formation of 7p represents a total synthesis of (+)-trans-whisky lactone. Unlike closely related ruthenium catalyzed alkyne-alcohol C-C couplings, deuterium labeling studies provide clear evidence of a novel 1,2-hydride shift mechanism that converts metal-bound alkynes to π-allyls in the absence of intervening allenes.
Introduction
Polyketides and their semi-synthetic congeners are used extensively in human medicine.1 With one exception,2 all commercial polyketides derive from soil bacteria, yet less than 5% of soil bacteria are amenable to culture with many phyla having eluded culture entirely.3 As techniques for bacterial culture improve, the number of medicinally relevant polyketides is anticipated to expand. Presently, all polyketides used in human medicine, again with one exception,3 are prepared via fermentation or through modification of fermentation products.1 Although de novo chemical synthesis offers a gateway to otherwise inaccessible structural variants, conceptual advances beyond the first-generation lexicon of synthetic methods are required for the design of more efficient, cost-effective routes to these important secondary metabolites.1d
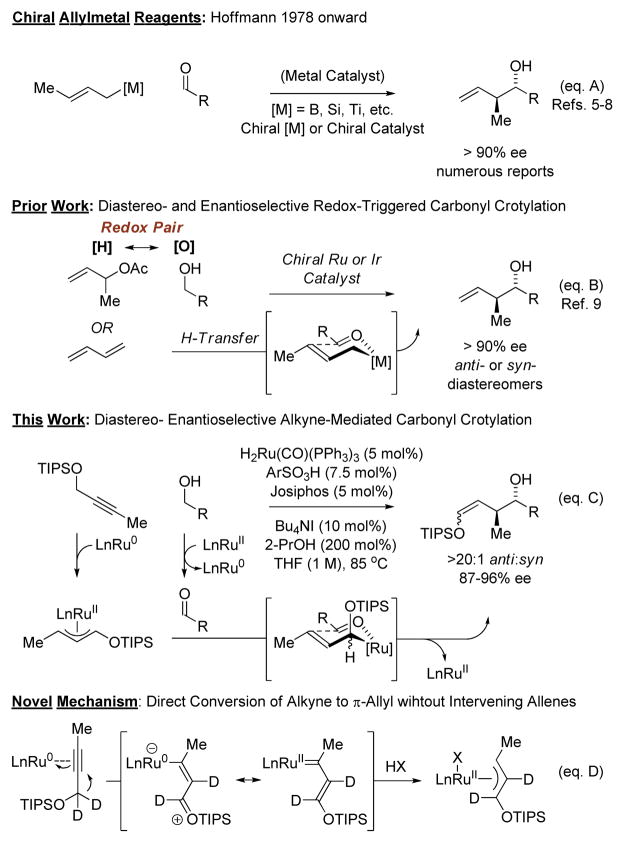
Among methods for de novo polyketide construction,4 dia-stereo- and enantioselective carbonyl crotylation has proven especially effective (Figure 1).5 Beginning with the pioneering studies of Hoffmann,6 the majority of asymmetric crotylation protocols employ crotylmetal reagents that incorporate chiral modifiers (Figure 1, eq. A).5 Catalytic enantioselective crotylations, including umpoled reactions of crotyl halides or carboxylates,7,8 were subsequently developed. These too rely on the use of stoichiometric metals, specifically, crotylmetal reagents5 or metallic terminal reductants.7,8 In a significant departure from prior art, we have introduced the concept of engaging alcohols and π-unsaturated reactants as redox pairs for the generation of carbonyl-organometal pairs en route to products of carbonyl addition.5k Based on this concept of “redox-triggered carbonyl addition,” reactions of primary alcohols with α-methyl allyl acetate9a–c or butadiene9d–f to form products of carbonyl crotylation were developed (Figure 1, eq. B). In this account, we report the first direct alkyne mediated carbonyl crotylations (Figure 1, eq. C).10 These transformations display high levels of anti-diastereo- and enantioselectivity and operate through a novel mechanism wherein metal-bound alkynes are converted to π-allylmetal species in the absence of intervening allenes (Figure 1, eq. D).
Figure 1.
Overview of methods for carbonyl crotylation and the discovery of alkyne mediated crotylation.
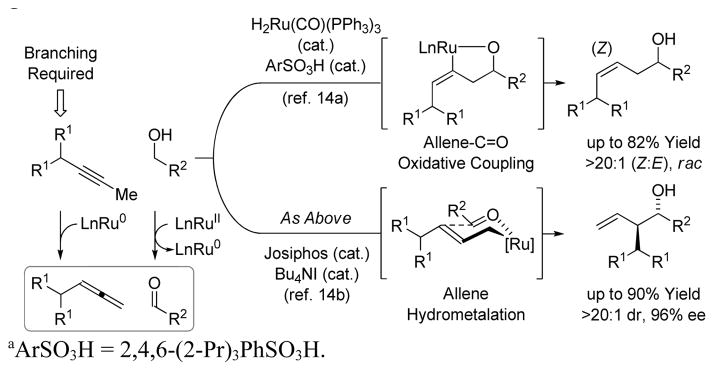
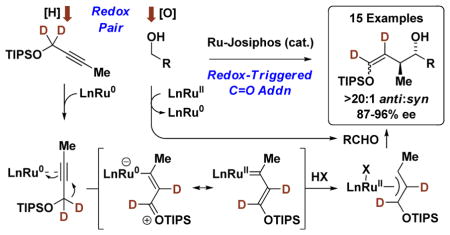
In recent work from our laboratory, ruthenium catalysts were found to promote the redox-triggered coupling of primary alcohols with allenes to form homoallylic alcohols.11,12 During these studies, Obora and Ishii described the iridium catalyzed coupling primary alcohols with aryl propynes to form products of (α-aryl)allylation.13 This work suggested the feasibility of a dual ruthenium-based catalytic cycle wherein alkyne-to-allene isomerization occurs in tandem with redox-triggered carbonyl addition. Two key modifications to our previously reported ruthenium(II) based catalyst fulfilled efforts toward this goal (Scheme 1). First, using the catalyst generated in situ upon acid base reaction of H2Ru(CO)(PPh3)3 and 2,4,6-(2-Pr)3PhSO3H,9e ruthenium(0) species became accessible via H-X (X = ArSO3) reductive elimination, enabling alkyne-to- allene isomerization via ruthenium(0) mediated propargyl C-H oxidative addition-reductive elimination pathways. Allenes generated under these conditions engage in ruthenium(0) mediated oxidative coupling with carbonyl partners to form linear (Z)-homoallylic alcohols.14a A second key modification to the catalyst involves the introduction of iodide and an electron rich chelating phosphine ligand, which suppresses oxidative coupling, while maintaining catalytic alkyne-to-allene isomerization. Allenes generated under these conditions participate in hydrometallative pathways en route to branched homoallylic allylic alcohols.14b It should be emphasized that in both cases isotopic labelling studies and other experiments corroborate intervention of allenes as discrete intermediates.14
Scheme 1.
Dual ruthenium-based catalytic cycles wherein al-kyne-to-allene isomerization occurs in tandem with redox-triggered C-C bond formation.a
aArSO3H = 2,4,6-(2-Pr)3PhSO3H.
Research Design and Methods
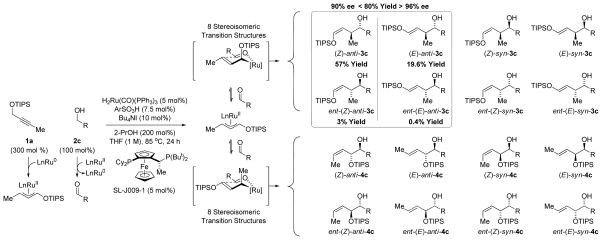
For hydrometallative pathways en route to branched homoallylic allylic alcohols, the 2-alkyne must be branched at propargylic position to suppress numerous side-reactions. However, the TIPS-protected propargyl ether 1a was not subject to this constraint. Exposure of propargyl ether 1a to p-bromobenzyl alcohol 2c under conditions used in the asymmetric couplings of 4-methyl-2-pentyne14b delivered the product of “siloxy-crotylation” 3c with complete control of regio- and dia-stereoselectivity as a 3:1 (Z:E) mixture of olefin geometrical isomers in 70% isolated yield. The (Z)- and (E)-alkenes each displayed high levels of enantiomeric enrichment: 87% ee and 94% ee, respectively. This result was surprising given the large number of regio- and stereoisomers potentially formed in this transformation. Further optimization was undertaken.15 Although (Z)- and (E)-selectivity was insensitive to variation of ether substituent, reactions conducted at lower temperatures and slightly higher loadings of 2,4,6-(2-Pr)3PhSO3H delivered (Z)- and (E)-anti-3c in 80% isolated yield and 90% ee and 96% ee, respectively (Scheme 2). The (Z)- and (E)- selectivity is inconsequential, as fluoride assisted cleavage of the enol in the presence of NaBH4 enabled convergence of (Z)- and (E)-anti-3c to diol 5c in quantitative yield and 92% ee.16 The requirement of 2-propanol merits discussion. In the absence of 2-propanol, un-reacted aldehyde accumulates due to competing transfer hydrogenation of propargyl ether 1a. As the allylruthenium-aldehyde intermediates are generated in a pairwise manner, introduction of 2-propanol returns the aldehyde to the alcohol oxidation level, enabling reentry into the catalytic C-C coupling pathway.
Scheme 2.
Regio-, diastereo- and enantioselectivity in the redox-triggered C-C coupling of propargyl ether 1a and p-bromobenzyl alcohols 2c.a
aArSO3H = 2,4,6-(2-Pr)3PhSO3H. R = p-BrPh. Yield refers to a mixture (Z)-anti-3c and (E)-anti-3c and their enantiomers isolated by silica gel chromatography. See Supporting Information for further experimental details.
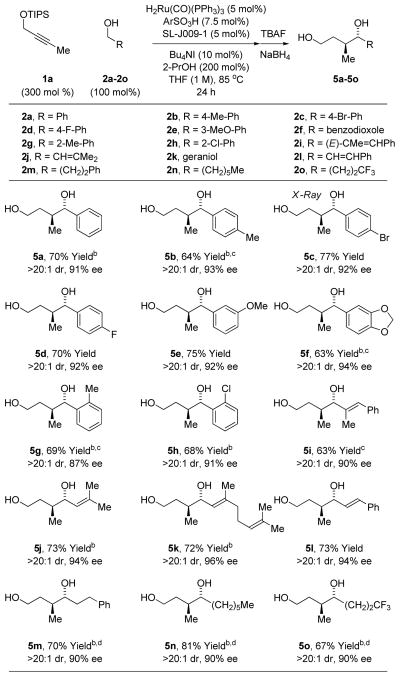
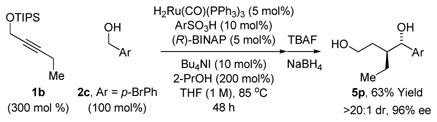
Under these optimal conditions, propargyl ether 1a was exposed to benzylic alcohols 2a-2h, allylic alcohols 2i-2l and aliphatic alcohols 2m-2o (Table 1). The respective enol silanes 3a-3o were converted diols 5a-5o, which were formed with complete levels of regio- and anti-diastereoselectivity and uniformly high levels of enantioselectivity (87–96% ee). The stere-ochemical assignment of diols 5a-5o was made in analogy to that determined for compound 5c by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Both TBS and TBDPS ethers participate in coupling, but isolated yields were lower by roughly 20%. Application of these conditions to alkyl ethers led to complex mixtures. Diminished levels of asymmetric induction were observed in attempted reactions of nitrogen bearing heterocycles. To evaluate the scope of the alkyne partner, the coupling of pro-pargyl alcohols 1b and 1c, bearing ethyl and phenyl groups, respectively, was explored. Use of the ruthenium catalysts modified by JOSIPHOS ligands such as SL-J009-1 led to inseparable mixtures of constitutionally isomeric products, as corroborated by 1H NMR and mass spectroscopic analysis. Eventually, it was found that BINAP modified ruthenium catalysts promote the
Table 1.
Regio-, anti-diastereo- and enantioselective coupling of alkyne 1a with alcohols 2a-2o to form diols 5a-5o.a
Yields are of material isolated by silica gel chromatography.
48 h. See Supporting Information for further details.
H2Ru(CO)(PPh3)3 (6 mol%), SL-J009-1 (6 mol%), ArSO3H (9 mol%), Bu4NI (12 mol%).
2-PrOH was omitted.
 |
(eq. 1) |
 |
(eq. 2) |
desired transformations (eq. 1, 2). Although longer reaction times (48 h) are required, adducts 5p and 5q are obtained in highly enantiomerically enriched form.
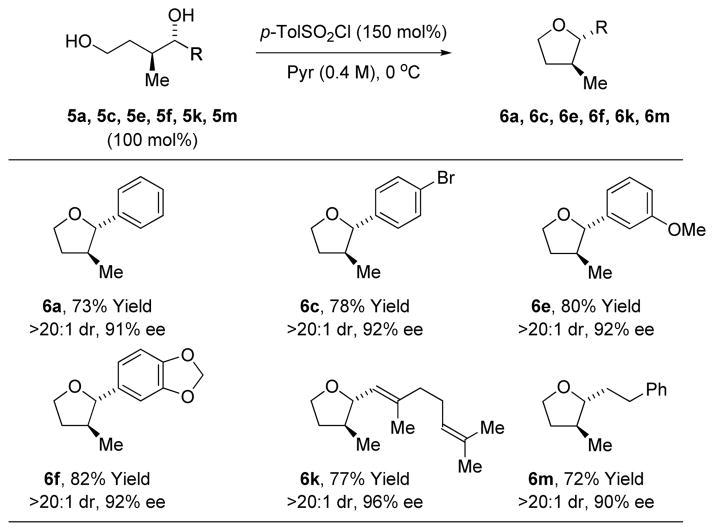
To illustrate the utility of this methodology, diols 5a, 5c, 5e, 5f, 5k and 5m were exposed to p-toluenesulfonyl chloride in pyridine solvent, resulting in highly chemoselective mono-to-sylation of the primary alcohol and spontaneous cyclization to form the corresponding trans-2,3-disubstituted furans 6a, 6c, 6e, 6f, 6k and 6m (Table 2). Only in the formation of 6f was any erosion in enantiomeric purity observed. Notably, 2,3-di-substituted furans that incorporate 3-methyl substituents appear frequently as substructures in type I polyketide natural products.17 Coupling of primary alcohols 2a, 2l and 2p under
Table 2.
Conversion of adducts 5a, 5c, 5e, 5f, 5k and 5m to trans-2,3-disubstituted furans 6a, 6c, 6e, 6f, 6k and 6m.a
Yields are of material isolated by silica gel chromatography. See Supporting Information for further details.
 |
(eq. 3) |
 |
(eq. 4) |
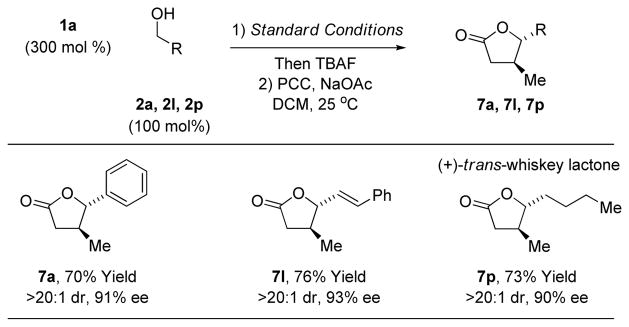
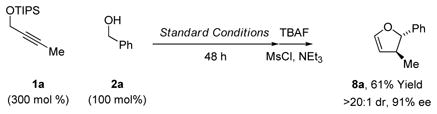
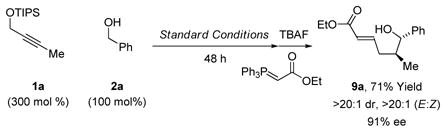
standard conditions followed by exposure to TBAF led to crude hemiacetals, which upon treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) delivered the trans-4,5-disubstituted γ-butyrolac-tones 7a, 7l and 7p (Table 3). The formation of 7p represents a total synthesis of (+)-trans-whisky lactone.18 Similarly, crude hemiacetals obtained in the aforesaid manner can be treated with mesyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine to form trans-4,5-disubstituted-2,3-dehydrofurans, as illustrated in the formation of 8a (eq. 3). Finally, crude hemiacetal can be treated with the indicated stabilized Wittig reagent to deliver the enoate 9a with complete alkene (E)-stereoselectivity (eq. 4).
Table 3.
Conversion of alcohols 2a, 2l and 2p to trans-4,5-di-substituted γ-butyrolactones 7a, 7l and 7p.a
Yields are of material isolated by silica gel chromatography over the two-step sequence. See Supporting Information for further details.
Mechanism
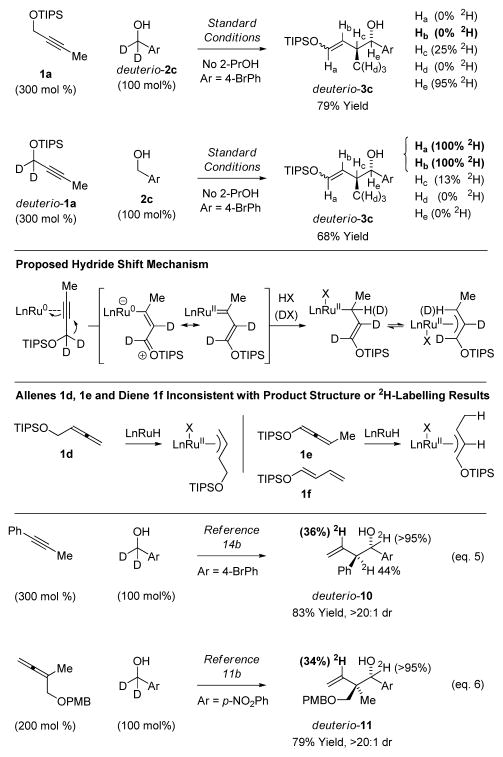
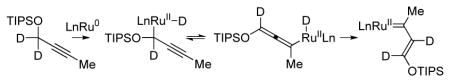
Unlike the asymmetric couplings of 4-methyl-2-pentyne,14b the products obtained in reactions of propargyl ether 1a are inconsistent with the intervention of a terminal allene, such as 1d. Initially, it was assumed that siloxy-crotylation proceeded by way of the internal 1,3-disubstituted allene 1e or diene 1f. However, deuterium labelling studies exclude allene 1e or diene 1f as intermediates (Scheme 3).19 If allene 1e or diene 1f were discrete intermediates, the reaction of propargyl ether 1a should result in deuterium incorporation at Hb or Hd of adduct deuterio-3c, respectively, but it does not. Rather, the reaction of deuterio-1a with alcohol 2c results in deuterium transfer to Ha and Hb of adduct deuterio-3c. These data clearly corroborate the indicated 1,2-hydride shift mechanism.20,21,22 To our knowledge, direct conversion of metal-bound alkynes to π-allyls via 1,2-hydride shift is unique.
Scheme 3.
Deuterium labelling studies exclude allenes as discrete intermediates and are consistent with a hydride shift mechanism.a
aYields are of material isolated by silica gel chromatography. See Supporting Information for further details.
The question as to whether the 1,2-hydride shift mechanism is at all operative in related asymmetric alkyne-alcohol C-C couplings14b merits consideration. Here, it is instructive to consider the respective patterns of deuterium incorporation observed upon use of d2-benzylic alcohols. For the related asymmetric alkyne-alcohol C-C couplings (eq. 5),14b wherein hydro-metalation of a discrete allene intermediate is proposed to generate a nucleophilic allylruthenium species, the pattern of deuterium closely resembles that observed in the parent allene-alcohol C-C couplings (eq. 6).11b For the analogous isotopic labelling experiment using propargyl ether 1a does not result in deuterium incorporation at the interior vinylic position. These data exclude allene hydrometalation in the present couplings of propargyl ether 1a, and suggest the 1,2-hydride shift mechanism is likely inoperative in the previously developed alkyne-alcohol C-C couplings.23
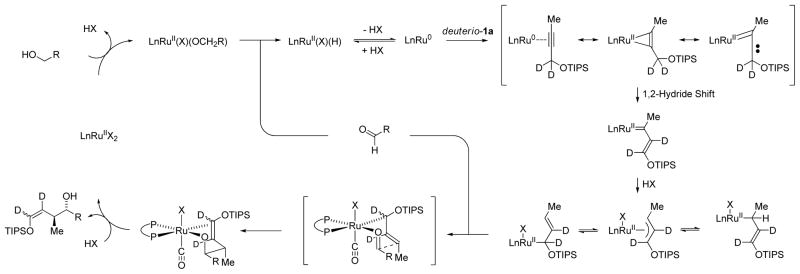
Based on this novel pattern of reactivity, a general catalytic mechanism for asymmetric ruthenium catalyzed siloxy-crotylation via redox-triggered carbonyl addition was proposed (Scheme 4). A ruthenium(II) complex mediates alcohol dehydrogenation to form aldehyde and LnRu(II)HX. Elimination of HX delivers a zero-valent ruthenium complex that binds the π-acidic alkyne. A high degree of π-backbonding between ruthenium(0) and the bound alkyne promotes metallacyclopropene or carbenoid character which induces 1,2-hydride shift to form a vinyl carbene. The n→σ* interaction between the oxygen lone pair and the propargylic C-H bond appears to important in terms of promoting 1,2-hydride shift, as in the absence of the silyl ether alkyne-to-allene isomerization is observed.14 Protonation of the vinyl carbene delivers a nucleophilic siloxy-substituted allylruthenium(II) complex. Aldehyde addition occurs by way of a Zimmerman-Traxler type transition structure from the σ-bound allylruthenium haptomer wherein ruthenium resides at the oxygen-bearing carbon atom. This haptomeric preference is presumably due to the negative inductive effect of oxygen. Protonolytic cleavage of the resulting homoallylic ruthenium(II) alkoxide releases the product and regenerates the starting ruthenium(II) complex.
Scheme 4.
General catalytic mechanism as corroborated by deuterium labeling experiments.
Conclusions
In summary, we report a direct alkyne-mediated carbonyl (siloxy)crotylation via redox-triggered carbonyl addition that is enabled through a unique 1,2-hydride-shift mechanism. This method directly converts primary alcohols to secondary alcohols bearing a propionate-based monoketide structural motif. Complete levels of regio- and anti-diastereoselectivity are accompanied by uniformly high levels of enantioselectivity using a Josiphos (SL-J009-1) modified ruthenium(II) catalyst. Deuterium labelling studies corroborate a novel catalytic mechanism wherein 1,2-hydride migration of a ruthenium-bound alkyne forms an α,β-unsaturated carbene, which upon protonation delivers a 1,3-disbustituted π-allylruthenium complex. Thus, metal-bound alkynes are directly converted to chiral allylmetal species in the absence of intervening allenes. The present transformation contributes to a growing body of redox-neutral catalytic C-C bond formations that merge the characteristics of carbonyl addition transfer hydrogenation.5k
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The Robert A. Welch Foundation (F-0038) and the NIH-NIGMS (RO1-GM069445) and the Center for Green Chemistry and Catalysis for partial support of this research.
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
Supporting Information. Experimental procedures and spectroscopic data for all new compounds (1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, HRMS), including images of NMR spectra. Single crystal x-ray diffraction data for 5c. This material is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org
References
- 1.Selected reviews: O’Hagan D. The Polyketide Metabolites. Ellis Horwood; Chichester: 1991. Rohr J. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2000;39:2847. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20000818)39:16<2847::aid-anie2847>3.0.co;2-0.Rimando AM, Baerson SR. ACS Symp Ser. 2007;955:1.Itoh T, Dechert-Schmitt AMR, Schmitt DC, Gao X, Krische MJ. Nat Prod Rep. 2014;31:504. doi: 10.1039/c3np70076c.
- 2.Eribulin mesylate, a truncated derivative of the marine polyether macrolide halichondrin B, is the only commercial polyketide prepared through de novo chemical synthesis: Yu MJ, Zheng W, Seletsky BM. Nat Prod Rep. 2013;30:1158. doi: 10.1039/c3np70051h.
- 3.Sait M, Hugenholtz P, Janssen PH. Environ Microbiol. 2002;4:654. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00352.x. and references cited therein. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.For a review on the use of the aldol reaction in polyketide construction, see: Schetter B, Mahrwald R. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2006;45:7506. doi: 10.1002/anie.200602780.
- 5.For selected reviews on enantioselective carbonyl allylation and crotylation, see: Yamamoto Y, Asao N. Chem Rev. 1993;93:2207.Ramachandran PV. Aldrichim Acta. 2002;35:23.Kennedy JWJ, Hall DG. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2003;42:4732. doi: 10.1002/anie.200301632.Denmark SE, Fu J. Chem Rev. 2003;103:2763. doi: 10.1021/cr020050h.Yu CM, Youn J, Jung HK. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2006;27:463.Marek I, Sklute G. Chem Commun. 2007:1683. doi: 10.1039/b615042j.Hall DG. Synlett. 2007:1644.Li J, Menche D. Synthesis. 2009:2293.Leighton JL. Aldrichim Acta. 2010;43:3.Yus M, González-Gómez JC, Foubelo F. Chem Rev. 2011;111:7774. doi: 10.1021/cr1004474.Ketcham JM, Shin I, Montgomery TP, Krische MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2014;53:9142. doi: 10.1002/anie.201403873.
- 6.(a) Herold T, Hoffmann RW. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1978;17:768. [Google Scholar]; (b) Hoffmann RW, Ladner W. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979;20:4653. [Google Scholar]
- 7.For selected reviews on catalytic enantioselective Nozaki-Hiyama-Kishi reactions, see: Avalos M, Babiano R, Cintas P, Jiménez JL, Palacios JC. Chem Soc Rev. 1999;28:169.Bandini M, Cozzi PG, Umani-Ronchi A. Chem Commun. 2002:919. doi: 10.1039/b109945k.Hargaden GC, Guiry PJ. Adv Synth Catal. 2007;349:2407.
- 8.For selected reviews on carbonyl allylation via umpoled reactions of allylic carboxylates, see: Masuyama Y. In: Advances in Metal-Organic Chemistry. Liebeskind LS, editor. Vol. 3. JAI Press; Greenwich: 1994. p. 255.Tamaru Y. In: In Handbook of Organopalladium Chemistry for Organic Synthesis. Negishi E-i, de Meijere A., editors. Vol. 2. Wiley; New York: 2002. p. 1917.Tamaru Y. In: In Perspectives in Organopalladium Chemistry for the XXI Century. Tsuji J, editor. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1999. p. 215.Kondo T, Mitsudo TA. Curr Org Chem. 2002;6:1163.Tamaru Y. Eur J Org Chem. 2005:2647.Zanoni G, Pontiroli A, Marchetti A, Vidari G. Eur J Org Chem. 2007:3599.
- 9.For catalytic diastereo- and enantioselective redox-triggered carbonyl crotylation using α-methyl allyl acetate or butadiene pronucleophiles, see: Kim IS, Han SB, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:2514. doi: 10.1021/ja808857w.Gao X, Townsend IA, Krische MJ. J Org Chem. 2011;76:2350. doi: 10.1021/jo200068q.Gao X, Han H, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:12795. doi: 10.1021/ja204570w.Zbieg JR, Moran J, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:10582. doi: 10.1021/ja2046028.Zbieg JR, Yamaguchi E, McInturff EL, Krische MJ. Science. 2012;336:324. doi: 10.1126/science.1219274.McInturff EL, Yamaguchi E, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:20628. doi: 10.1021/ja311208a.
- 10.Indirect use of 1-alkynes in carbonyl allylation is achieved through their conversion to allylboron reagents via tandem alkyne hydroboration-alkene isomerization, see: Miura T, Nishida Y, Murakami M. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:6223. doi: 10.1021/ja502169d.Miura T, Nishida Y, Morimoto M, Murakami M. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:11497. doi: 10.1021/ja405790t.
- 11.For ruthenium catalyzed C-C coupling of alcohols and allenes via transfer hydrogenation, see: Zbieg JR, McInturff EL, Krische MJ. Org Lett. 2010;12:2514. doi: 10.1021/ol1007235.Zbieg JR, McInturff EL, Leung JC, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:1141. doi: 10.1021/ja1104156.Sam B, Luong T, Krische MJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2015;54:5465. doi: 10.1002/anie.201500238.
- 12.For iridium catalyzed C-C coupling of alcohols and allenes via transfer hydrogenation, see: Skucas E, Bower JF, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:12678. doi: 10.1021/ja075971u.Han SB, Kim IS, Han H, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:6916. doi: 10.1021/ja902437k.Moran J, Preetz A, Mesch RA, Krische MJ. Nature Chem. 2011;3:287. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1001.
- 13.Obora Y, Hatanaka S, Ishii Y. Org Lett. 2009;11:3510. doi: 10.1021/ol901366q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.(a) Park BY, Nguyen KD, Chaulagain MR, Komanduri V, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:11902. doi: 10.1021/ja505962w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Liang T, Nguyen KD, Zhang W, Krische MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:3161. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.See Supporting Information for further optimization experiments, including results obtained under standard conditions with different chiral ligands.
- 16.Similar racemic products of hydroxymethyl crotylation are formed through the nickel catalyzed coupling of dienes and aldehydes mediated by B2(pin)2: Cho HY, Morken JP. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:16140. doi: 10.1021/ja806113v.
- 17.Lorente A, Lamariano-Merketegi J, Alberico F, Álvarez M. Chem Rev. 2013;113:4567. doi: 10.1021/cr3004778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.For reviews on the synthesis of γ-butyrolactones, see: Seitz M, Reiser O. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9:285. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.03.005.Burstein C, Tschan S, Xie X, Glorius F. Synthesis. 2006:2418.Gil S, Parra M, Rodriguez P, Segura J. Mini-Rev Org Chem. 2009;6:345.
- 19.Allene 1e and diene 1f were prepared and exposed to alcohol 2c under standard reaction conditions. Dehydrogenation of alcohol 2c was observed, but products of C-C coupling were not detected.
- 20.A related hydride shift was observed in the ruthenium catalyzed internal redox isomerization of propargyl alcohols to form conjugated enones: Trost BM, Livingston RC. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:11970. doi: 10.1021/ja804105m.
-
21.The indicated mechanism involving propargyl C-H oxidative addition followed by internal hydrometallation from the allenylruthenium haptomer was considered and cannot be excluded on the basis of the isotopic labelling studies. However, such internal hydrometallations of allenic species dos not appear geometrically feasible.
- 22.For rhodium catalyzed isomerization of 1-alkynes to allenes, which are then converted to electrophilic π-allyls, see: Lumbroso A, Koschker P, Vautravers NR, Breit B. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:2386. doi: 10.1021/ja1108613.Xu K, Khakyzadeh V, Bury T, Breit B. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:16124. doi: 10.1021/ja509383r.Koschker P, Kähny M, Breit B. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:3131. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b01131.
- 23.In these isoptopic labelling studies, it should be noted that protons from the reactant alcohol or adventitious water may contribute to diminished levels of deuterium incorporation: Tse SKS, Xue P, Lin Z, Jia G. Adv Synth Catal. 2010;352:1512.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.