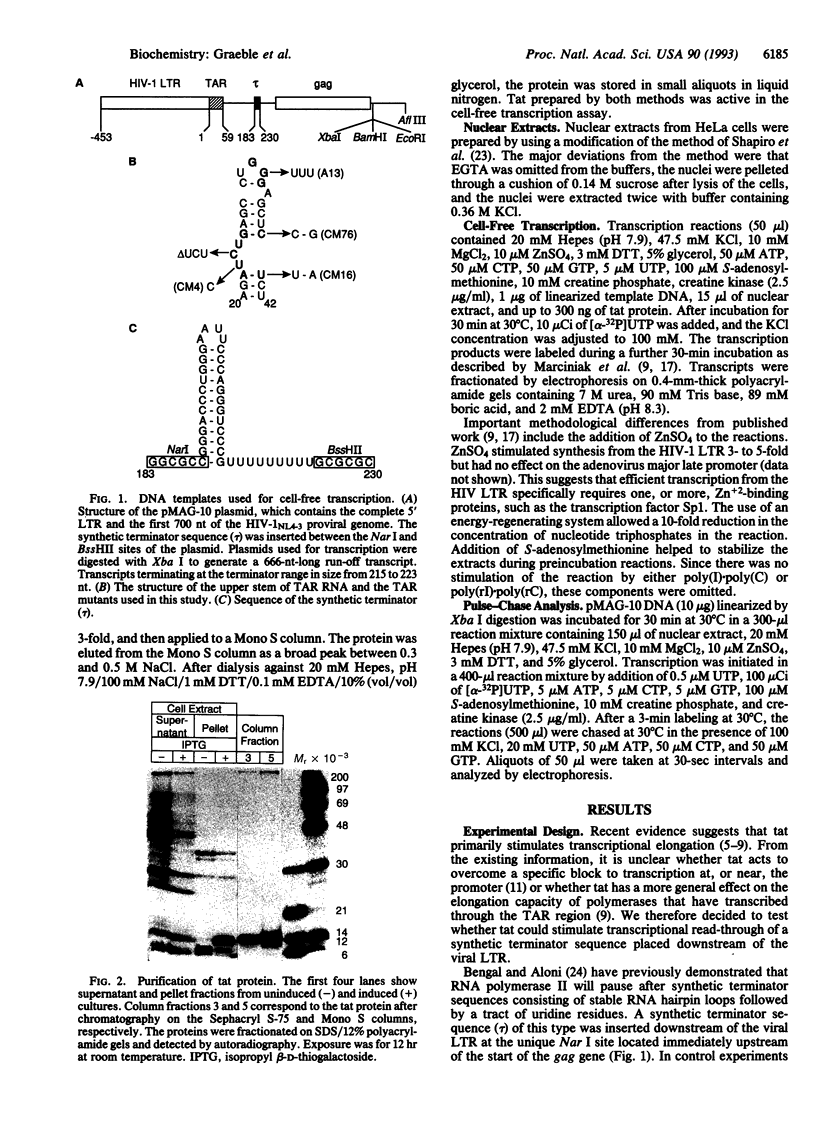
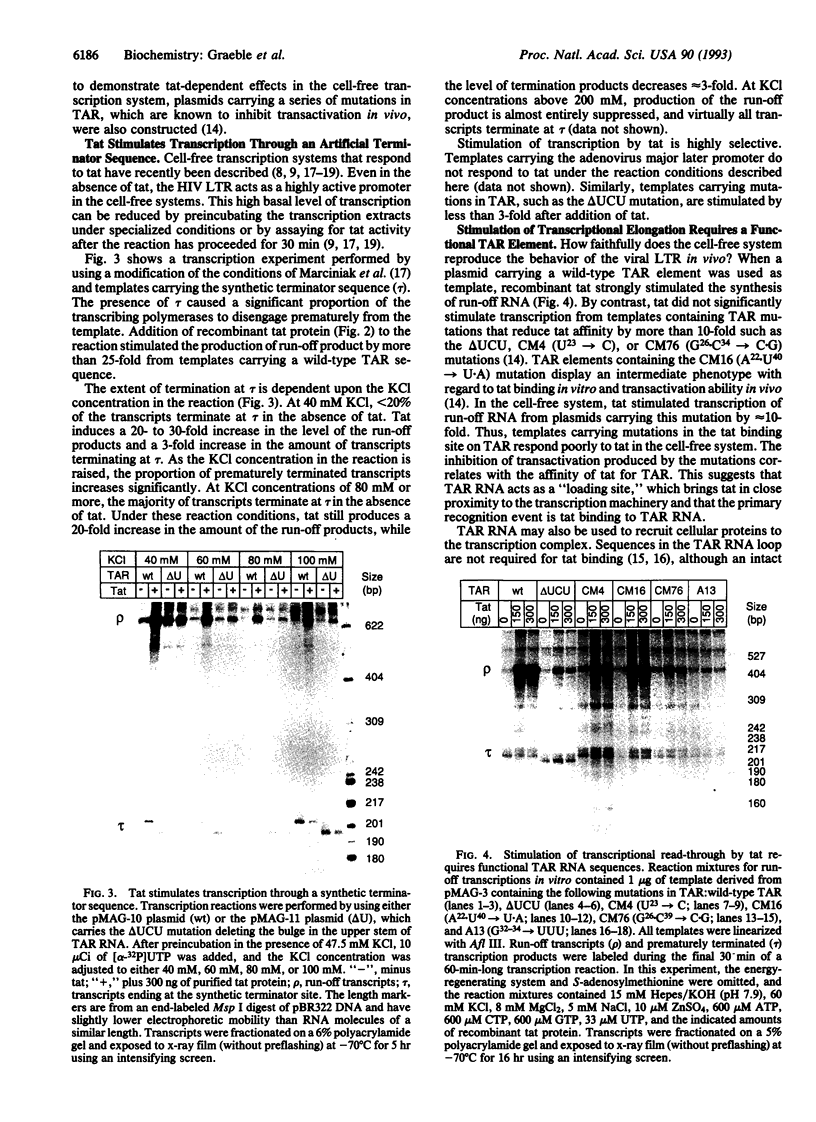
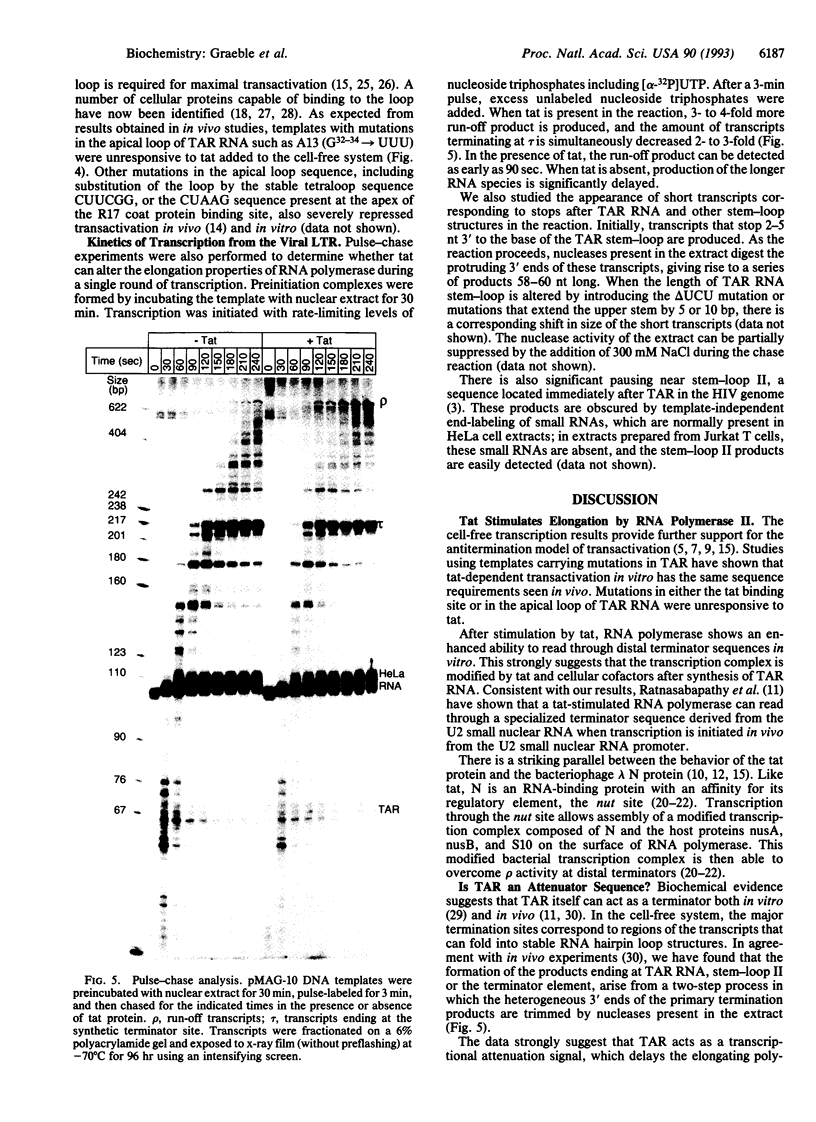
Abstract
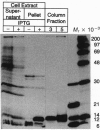
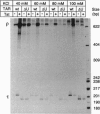
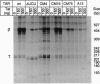
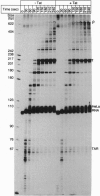
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivator protein, tat, specifically stimulates transcription from the viral long terminal repeat. We used cell-free transcription systems to test whether tat can stimulate transcriptional read-through of an artificial terminator sequence (e.g., a stable RNA stem-loop structure followed by a tract of nine uridine residues) placed downstream of the viral long terminal repeat. In the absence of tat, RNA polymerases are prematurely released from the template at the terminator sequence. Recombinant tat protein purified from Escherichia coli increased the synthesis of full-length transcripts approximately 25-fold and decreased the amount of transcripts ending at the terminator sequence. The reaction is strictly dependent upon the presence of a functional transactivation-responsive region (TAR) sequence. Mutations in the tat binding site on TAR RNA and mutations in the TAR RNA loop block transactivation in vivo. Neither type of mutation is able to respond to tat in vitro. These results strongly suggest that after transcription through the TAR region, tat modifies the transcription complex to increase its elongation capacity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barik S., Ghosh B., Whalen W., Lazinski D., Das A. An antitermination protein engages the elongating transcription apparatus at a promoter-proximal recognition site. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):885–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Aloni Y. A block of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II at synthetic sites in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9791–9798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Aloni Y. Transcriptional elongation by purified RNA polymerase II is blocked at the trans-activation-responsive region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4910–4918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4910-4918.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Rabson A. B., Jeang K. T. TAR-independent activation of the HIV-1 LTR: evidence that tat requires specific regions of the promoter. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher M. J., Lamont C., Hamy F., Dingwall C., Green S. M., Lowe A. D., Butler J. G., Gait M. J., Karn J. High affinity binding of TAR RNA by the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat protein requires base-pairs in the RNA stem and amino acid residues flanking the basic region. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):90–110. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 tat protein stimulates transcription by binding to a U-rich bulge in the stem of the TAR RNA structure. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4145–4153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M., Mathews M. B. Premature termination and processing of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-promoted transcripts. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4488–4496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4488-4496.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. Synergy between HIV-1 Tat and adenovirus E1A is principally due to stabilization of transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2397–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein trans-activates transcription in vitro. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):791–802. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Sharp P. A. Identification and characterization of a HeLa nuclear protein that specifically binds to the trans-activation-response (TAR) element of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4189–4196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nodwell J. R., Greenblatt J. The nut site of bacteriophage lambda is made of RNA and is bound by transcription antitermination factors on the surface of RNA polymerase. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2141–2151. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Rosen C. A. Contribution of the TATA motif to Tat-mediated transcriptional activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5594–5597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5594-5597.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Walker M. D. Elevated levels of mRNA can account for the trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9734–9738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasabapathy R., Sheldon M., Johal L., Hernandez N. The HIV-1 long terminal repeat contains an unusual element that induces the synthesis of short RNAs from various mRNA and snRNA promoters. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2061–2074. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Parkin N. T., Rosen C., Itovitch J., Sonenberg N. Structural requirements for trans activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat-directed gene expression by tat: importance of base pairing, loop sequence, and bulges in the tat-responsive sequence. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1402–1406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1402-1406.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheline C. T., Milocco L. H., Jones K. A. Two distinct nuclear transcription factors recognize loop and bulge residues of the HIV-1 TAR RNA hairpin. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2508–2520. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. Location of the trans-activating region on the genome of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2990041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Jones K. A. In vitro formation of short RNA polymerase II transcripts that terminate within the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoter-proximal downstream regions. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):265–282. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F., Garcia J., Sigman D., Gaynor R. tat regulates binding of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-activating region RNA loop-binding protein TRP-185. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2128–2140. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]