Abstract
CreBC is a highly conserved two-component regulatory system (TCS) in several gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Aeromonas spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. CreD is a conserved gene that encodes a predicted inner-membrane protein and is located near the creBC loci. Activation of CreBC increases creD expression; therefore, creD expression is generally used as a measure of CreBC activation in E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa systems. In this article, we aim to elucidate the expression of creD and further to investigate its functions in S. maltophilia. In spite of a short intergenic region of 81 bp between creBC and creD, creD is expressed separately from the adjacent creBC operon and from a promoter immediately upstream of creD (P creD) in S. maltophilia. We found that the promoter activity of P creD is negatively regulated by the creBC TCS, positively regulated by the bacterial culture density, and not affected by β-lactams. Furthermore, creD expression is not significantly altered in the presence of the phosphor-mimic variant of CreB, CreB(D55E), which mimics activated CreB. The functions of CreD of S. maltophilia were assessed by comparison among the following: wild-type KJ; the creD isogenic mutant, KJΔCreD; and the complementary strain, KJΔCreD(pCreD). The mutant lacking creD had cell division defects and aberrations in cell envelope integrity, which then triggered the σE-mediated envelope stress response. Thus, the results indicated that CreD plays a critical role in the maintenance of envelope integrity.
Introduction
Two-component regulatory systems (TCSs) are basic stimulus-response coupling mechanisms that allow organisms to sense and respond to changes in environmental conditions. TCSs consist of an inner membrane-spanning sensor histidine kinase (HK) and a cognate cytoplasmic response regulator protein (RR) [1]. Extracellular stimuli are sensed by HK, and HK is modulated by autophosphorylation. The HK transfers a phosphoryl group to the RR, which activates or represses the expression of an array of genes called the TCS regulon. To characterize a TCS, both the stimulus and response must be considered. Therefore, TCS activation is commonly evaluated by assessing gene expression of the responsive regulon. Some TCSs are highly conserved in different microorganisms; for example, the PhoP/PhoQ system is found in Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [2]. These TCS homologues in different microorganisms likely share same or similar activation stimuli and responsive regulons.
CreBC/BlrAB TCS, consisting of a sensor kinase (CreC/BlrB) and a response regulator (CreB/BlrA), exists in many gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa (S1 Fig). In spite of the high conservation of the CreBC TCS in different gram-negative bacteria, the conditions known to activate CreBC vary in different microorganisms. In E. coli, creBC is activated under fermentative growth conditions using glycolytic carbon sources and under aerobic conditions with low-molecular-weight fermentation products as substrates, such as formate or pyruvate [3]. However, the activation of blrAB and creBC in Aeromonas spp. and P. aeruginosa is triggered by the loss of function of penicillin-binding protein 4 (PBP4) [4, 5]. Collectively, CreBC/BlrAB responds to metabolic signals or peptidoglycan stress. The CreBC/BlrAB regulon members in E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa have been previously reported [6–8]. A common tightly controlled cre regulon gene is creD, which is located near creBC and is part of the creABCD cluster of E. coli, the blrABD cluster of Aeromonas spp., and the creBCD cluster of P. aeruginosa (S1 Fig). CreD expression is positively regulated by activated CreBC in E. coli and P. aeruginosa [3, 5] and by activated BlrAB in Aeromonas spp. [9]. A cre/blr tag sequence, TTCACN6TTCAC, is upstream of the creD gene and is critical for binding activated CreB/BlrA transcription regulators [6]. Therefore, increased expression of creD is an indicator for creBC TCS activation in E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa systems. However, there is little published paper addressing the physiological function of CreD.
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a gram-negative, genetically versatile, and environmentally ubiquitous bacterial species [10]. S. maltophilia can survive in a variety of animal and plant hosts and environmental niches. Moreover, S. maltophilia causes opportunistic infections, especially in patients with cystic fibrosis or who are immune compromised. For survival in different environmental niches, S. maltophilia has developed an array of TCSs to coordinate the expression of genes involved in adaptation. Based on its sequenced genome [11], S. maltophilia harbors at least 43 sets of TCSs. Of these, only SmeSR and CreBC have been investigated [12, 13]. However, little is understood about stimuli that activate these TCSs and gene regulons that are regulated by these TCSs.
Like E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa, S. maltophilia harbors the CreBC TCS. The creD homologue is conserved and located downstream of creBC in S. maltophilia (Fig 1A). Furthermore, a putative cre/blr tag sequence homologue, TTCACACTCGCTTCAA, is located around -80 to -65 bp relative to the start codon of creD (Fig 1B). These observations suggest that the regulatory circuit of CreBC-CreD in S. maltophilia is similar to that in E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa. Nevertheless, we recently observed that the creD transcript has a 3.83 ± 0.33-fold increase when creBC is inactivated [14], which suggests that the regulatory circuit of creD expression in S. maltophilia is distinct and perhaps more complicated than that in E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa. In this article, we aim to further elucidate the factors that regulate creD expression and the physiological functions of CreD in S. maltophilia.
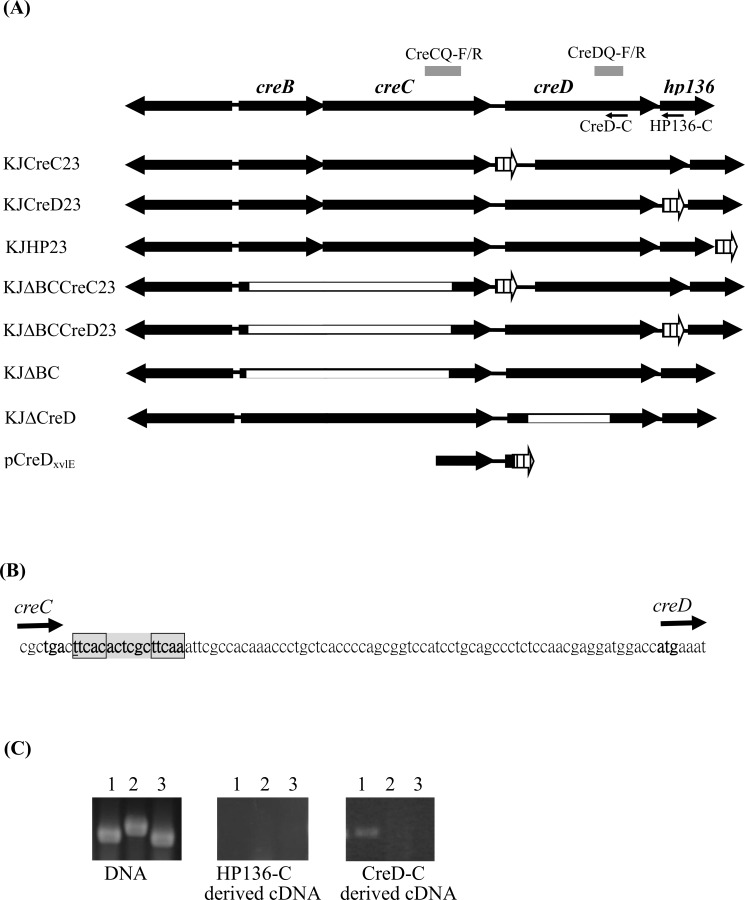
Fig 1. Schematic organization and operon verification of the creBCD-hp136 cluster of S. maltophilia KJ.
(A) Genomic organization of the creBCD-hp136 cluster and the structure of chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion constructs, mutants, and recombinant plasmids. The creBC operon forms a two-component regulatory system. CreD encodes a putative inner membrane protein. The small arrows indicate the primer HP136-C and CreD-C for the reverse transcription. The gray bar indicates the PCR amplicons using the CreDQ-F/R and CreCQ-F/R as the primer sets. The orientation of gene is indicated by the arrow. The white box indicates the deleted region for each deletion mutant construct. The crosshatched arrows represent the xylE cassette. (B) The 81-bp DNA sequence of intergenic region between creC and creD. A homologue of so-called cre/blr tag sequence (TTCACnnnnnnTTCAA) is marked in gray, at around -80 to -65 bp relative to the start codon of creD. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR). The cDNAs of S. maltophilia KJ were obtained by RT-PCR using the primers HP136-C and CreD-C respectively, and then PCR was performed using different primer sets. The S. maltophilia KJ chromosome DNA was used as a control for the primers reliability. Lane 1, primers CreDQ-F and CreDQ-R; Lane 2, primers CreCQ-F and CreCQ-R; Lane 3, primers SmeXQ-F and SmeXQ-R. SmeX gene, which is intrinsically unexpressed in strain KJ, is used as a control for the DNA contamination during cDNA preparation.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains and culture conditions
A complete list of strains, plasmids, and primers used in this study is shown in S1 Table S. maltophilia KJ served as the parental wild-type strain [15]. Cells were grown at 37°C in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth or Mueller-Hinton (MH) medium unless specified otherwise.
Construction of chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion constructs KJCreC23, KJCreD23, KJHP23, KJΔBCCreC23, and KJΔBCCreD23
The chromosomal creC-xylE, creD-xylE, and hp136-xylE transcription fusion constructs were constructed by double crossover homologous recombination. Recombinant plasmids pCreC23, pCreD23, and pHP23 were prepared as follows: two DNA fragments containing the upstream and downstream region of the inserted site were obtained by PCR using specifically designed primer sets and subsequently cloned into pEX18Tc. A xylE cassette retrieved from pTxylE [15] was inserted between the two DNA fragments, yielding plasmids pCreC23, pCreD23, and pHP23. The primer sets used were CreC23N-F/CreC23N-R and CreC23C-F/CreC23C-R for pCreC23, CreD23N-F/CreD23N-R and CreD23C-F/CreD23C-R for pCreD23, and HP23N-F/HP23N-R and HP23C-F/HP23C-R for pHP23 (S1 Table). Plasmid mobilization and xylE-transcription fusion construct selection were performed as described previously [16]. The xylE gene in these recombinant plasmids was inserted into the targeted insertion site without disrupting any gene, generating chromosomal transcription fusion constructs KJCreC23, KJCreD23, and KJHP23 (Fig 1). The expression of xylE in these constructs represents expression of creC, creD, and hp136, respectively. The KJΔBCCreC23 and KJΔBCCreD23 constructs were obtained by inserting xylE downstream of the creC and creD genes of KJΔBC, respectively, through the same procedure.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was isolated from exponential-growth bacterial cultures with the Pure LinkTM Total RNA Purification System (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and RNase-free DNase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) as described previously [16]. cDNA were synthesized from total RNA by using the MMLV Reverse Transcriptase 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Epicentre Biotechnologies, Taiwan). QRT-PCR was performed with appropriate primer sets (S1 Table), cDNA, and the Smart Quant Green Master Mix (Protech Technology Enterprise Co., Ltd.), using a programmed ABI Prism 7000 Sequence Detection System (PE Applied Biosystems). The 16S rRNA gene was used as the normalizing gene. For relative gene expression analysis, a comparative cycle threshold method (ΔΔCt) was used [17].
Construction of transcription fusion plasmid pCreDxylE
The 472-bp DNA fragment upstream of creD was obtained by PCR using primers CreD5-F and CreD5-R (S1 Table). The PCR amplicon was ligated into the promoter-less xylE reporter plasmid pRKXylE [18], generating pCreDxylE.
Catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (C23O) activity assay
Catechol-2,3-dioxygenase is encoded by the xylE gene and its activity can be measured as the rate of increase in A 375nm following the addition of 100 mM catechol, as described previously [19]. The rate of hydrolysis is calculated by using 44,000 M-1·cm-1 as the extinction coefficient. One unit of enzyme activity (Uc) is defined as the amount of enzyme that converts 1 nmol of substrate per minute. The specific activity is expressed as Uc/OD450 nm.
Site-directed mutagenesis of creB gene, yielding creB(D55E)
To generate a creB(D55E) allele in which amino acid 55 in CreB is switched from aspartate to glutamate, we used site-directed mutagenesis by primer extension PCR. Two PCR amplicons were obtained by PCR using the primer pairs CreB-F/CreB(D/E)N-R and CreB(D/E)C-F/CreB-R (S1 Table). The mutated nucleotide was introduced into the primers of CreB(D/E)N-R and CreB(D/E)C-F. Two PCR amplicons were mixed with the primer pair CreB-F/CreB-R for a second round of PCR. We checked the mutated creB(D55E) allele by DNA sequencing.
Overexpression of creB(D55E) by a fusaric acid-inducible system
Our previous study described a fuaABC operon whose expression is inducible by fusaric acid [20]. Herein, we utilized the fuaABC operon to develop a fusaric acid-inducible overexpression system in S. maltophilia. First, vector pYW2 was constructed for cloning creB(D55E). Two PCR amplicons of 382 bp and 370 bp, corresponding to the C-terminus of fuaC gene and downstream of the fuaC gene, respectively, were obtained by PCR, using primer sets YW2N-F/YW2N-R and YW2C-F/YW2C-R (S1 Table), respectively. The two PCR amplicons were sequentially cloned into pEX18Tc, resulting in plasmid pYW2. The creB(D55E) allele was cloned into pYW2 by inserting creB(D55E) between the two PCR amplicons, yielding pYW2CreB(D55E). Plasmid pYW2CreB(D55E) was mobilized from E. coli S17-1 into KJCreD23 by conjugation, and the correct double-crossover mutant, KJCreD23Fua::CreB(D55E), was selected and checked as previously described [16]. In strain KJCreD23Fua::CreB(D55E), the creB(D55E) allele was inserted downstream of the fuaABC operon without disruption of any gene, and the orientation of the creB(D55E) allele coincided with the transcription of the fuaABC operon.
Construction of the deletion mutant KJΔCreD
The intact creD gene was amplified using the primers CreD-F and CreD-R (S1 Table) and cloned into pRK415 and pEX18Tc, yielding pCreD and pEXCreD, respectively. Plasmid pEXCreD was digested by StuI and then self-ligated to generate pΔCreD, in which the internal 519-bp StuI-StuI fragment of creD was deleted. Plasmid pΔCreD mobilization and mutant KJΔCreD selection were performed as described previously [16]. The correctness of deletion mutants was confirmed by PCR and DNA sequencing.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
The bacterial strains tested were grown to an OD450nm of 1.0 and collected by centrifugation. Cells were washed three times with PBS, pH 7.4, and pre-fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4) on glass coverslips. After the cells were fixed, they were washed, post-fixed with 1% osmium tetraoxide (OsO4), dehydrated by treatment with a graded ethanol series, dried to the critical point, and coated with gold particles. Then, the samples were examined using a high-resolution FEI Inspect S scanning electron microscope.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) survival analysis
Overnight cultures of the tested strains were diluted to an A 450nm of 0.15 with LB broth. This was followed by another 15-h culture, following which the cell cultures were adjusted to an A 450nm of 1.0 with the same broth. The cells were then treated with 0.01% SDS or were not treated. CFU analysis was performed after 5 min of incubation without shaking. The percentage of survival was defined as the CFU ratio of the SDS-additive group to the SDS-free counterpart.
1-N-phenylanphthylamine (NPN) uptake assay
Overnight cultures were subcultured into fresh LB broth and grown for 15 h. The cells were centrifuged and washed with 5 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.2), and the optical density of the suspension was adjusted to an OD450nm of 0.5 with the same buffer. Aliquots (100 μl) of the cell suspension were pipetted into 96-well microtiter plates, and NPN was then added at a final concentration of 15 μM. Fluorescence was monitored after 5-min incubation from three parallel wells per sample with a fluorescence spectrophotometer at excitation and emission wavelengths of 355 nm and 402 nm, respectively.
Vancomycin susceptibility test
Susceptibility to vancomycin was assessed by E-test according to the manufacturer’s instructions. E-test strips were obtained from AB Biodisk (Solna, Sweden) and stored at −20°C until the tests were performed. The concentrations used ranged from 0.016 to 256 μg/ml for vancomycin. The MH plate was streaked with a cotton swab soaked in S. maltophilia cell suspension (107 cells/ml), and an E-test strip was applied. The plates were incubated at 37°C, and the results were read after 24 h.
Results
Analysis of creBCD cluster in S. maltophilia
Fig 1A shows the genetic organization of creD in S. maltophilia KJ cells. There is an 81-bp intergenic region (IG) between creC and creD. Hp136, ten base pairs downstream of creD, encodes a predicted 136-aa hypothetical protein (HP136) (Fig 1A). The genetic organization of the four genes strongly suggests that creB, creC, creD, and hp136 genes are organized into an operon.
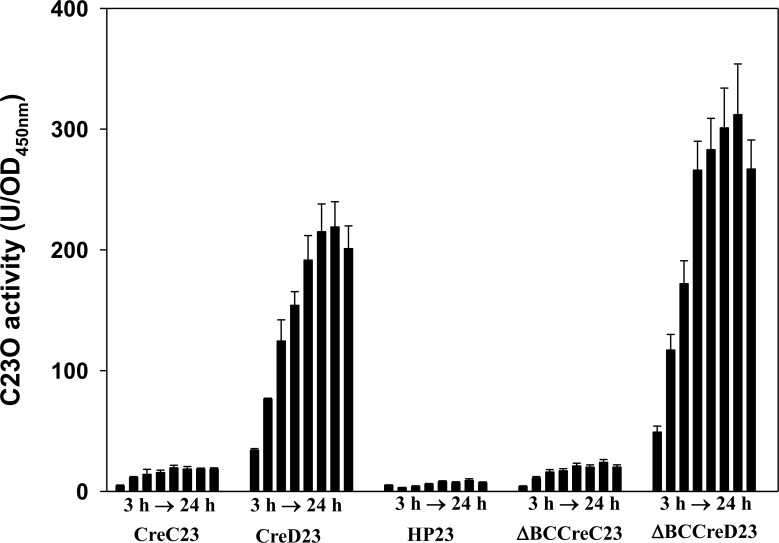
We used a chromosomal in situ xylE-transcription fusion assay and reverse transcription-PCR to verify the possibility of creBCD or creBCD-hp136 operons. The xylE gene was inserted downstream of creC, creD, and hp136 genes, yielding three chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion constructs, KJCreC23, KJCreD23, and KJHP23, respectively (Fig 1A). The C23O activities detected from KJCreC23, KJCreD23, and KJHP23 represent the amount of creC, creD, and hp136 transcripts, respectively. Additionally, C23O activities reflect the promoter activity of P creB, P creD and P hp136, if present, and could identify either creBCD or creBCD-hp136 operons. The C23O activities determined from KJCreC23, KJCreD23, and KJHP23 cells are shown in Fig 2. The C23O expression in KJCreD23 increased with growth, KJCreC23 exhibited a moderate-level of C23O expression, and KJHP23 had no significant C23O activity. These results suggest that creBCDsm-hp136 is not an operon, that the promoter of creBC TCS is intrinsically moderately active, and that creD has its own promoter, which is active in the laboratory cultured condition.
Fig 2. The C23O activity expressed by the chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion constructs of S. maltophilia KJ.
Overnight cultures of S. maltophilia strains assayed were inoculated into the fresh LB to the A 450 of 0.15. Cells were grown aerobically, and the A 450 and C23O activity were measured every 3 h.
Primers CreD-C and HP136-C, which target the internal sequences of creD and hp136, respectively, were used to produce cDNAs from total RNA (Fig 1A, S1 Table). The cDNA was PCR amplified using primer sets CreCQ-F/R and CreDQ-F/R (Fig 1A, S1 Table), which target the creC and creD genes, respectively. The PCR amplicons with an expected size of 275 and 226 bps were observed only if the creBCD or creBCD-hp136 transcripts were present. We did not detect the expected PCR amplicons in the HP136-C-derived cDNA group (Fig 1C), further ruling out the possibility of a creBCD-hp136 operon. Furthermore, we did not detect the 275-bp amplicon in the CreD-C-derived cDNA (Fig 1C), indicating that no detectable creBCD transcript exists in KJ cells. The results of the chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion assay and RT-PCR indicated that creBCD is not an operon and that the promoter of creD in wild-type KJ cells is active in the laboratory cultured condition.
CreBC TCS negatively regulates the promoter activity of creD (P creD)
To elucidate whether creD is regulated by the creBC TCS, a plasmid-borne promoter transcription fusion, pCreDxylE (Fig 1A), was introduced into wild-type KJ and KJΔBC [14] and the C23O activity was measured. To our surprise, the C23O activity in KJ(pCreDxylE) was lower and did not increase with growth (S2 Fig). The inconsistency in results of the plasmid transcription fusion construct (KJ(pCreDxylE)) and the chromosomal transcription fusion construct (KJCreD23) indicates that there are some underlying regulatory mechanisms involved in the promoter activity of the creD gene, which requires further elucidation. To verify which assay best reflects creD expression, the creD transcript of wild-type KJ was determined by qRT-PCR. The creD transcript in KJ cells after 21 h of growth increased approximately 5.3 fold compared to the transcript levels after 6 h of growth, which is consistent with the results of KJCreD23. Therefore using the plasmid-borne promoter assay to assess the promoter activity of creD is infeasible. To elucidate the underlying regulatory mechanism in the creBCD cluster, we constructed four chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion constructs: KJCreC23, KJCreD23, KJΔBCCreC23, and KJΔBCCreD23 (Fig 1A).
The growth and C23O activities of these chromosomal xylE-transcription fusion constructs were monitored every 3 h. We made several conclusions by comparing the C23O activities among different pairwise combinations (Fig 2). First, the deletion of creBC did not affect creBC expression (KJCreC23 vs. KJΔBCCreC23), indicating that creBC TCS does not autoregulate. In addition, the CreBC TCS negatively regulated the expression of creD, as evidenced by comparing the C23O activities of strains KJΔBCCreD23 and KJCreD23. Finally, the P creD activity was higher than P creBC, and both promoter activities increased with culture density.
P creD activity is regulated by bacterial culture density
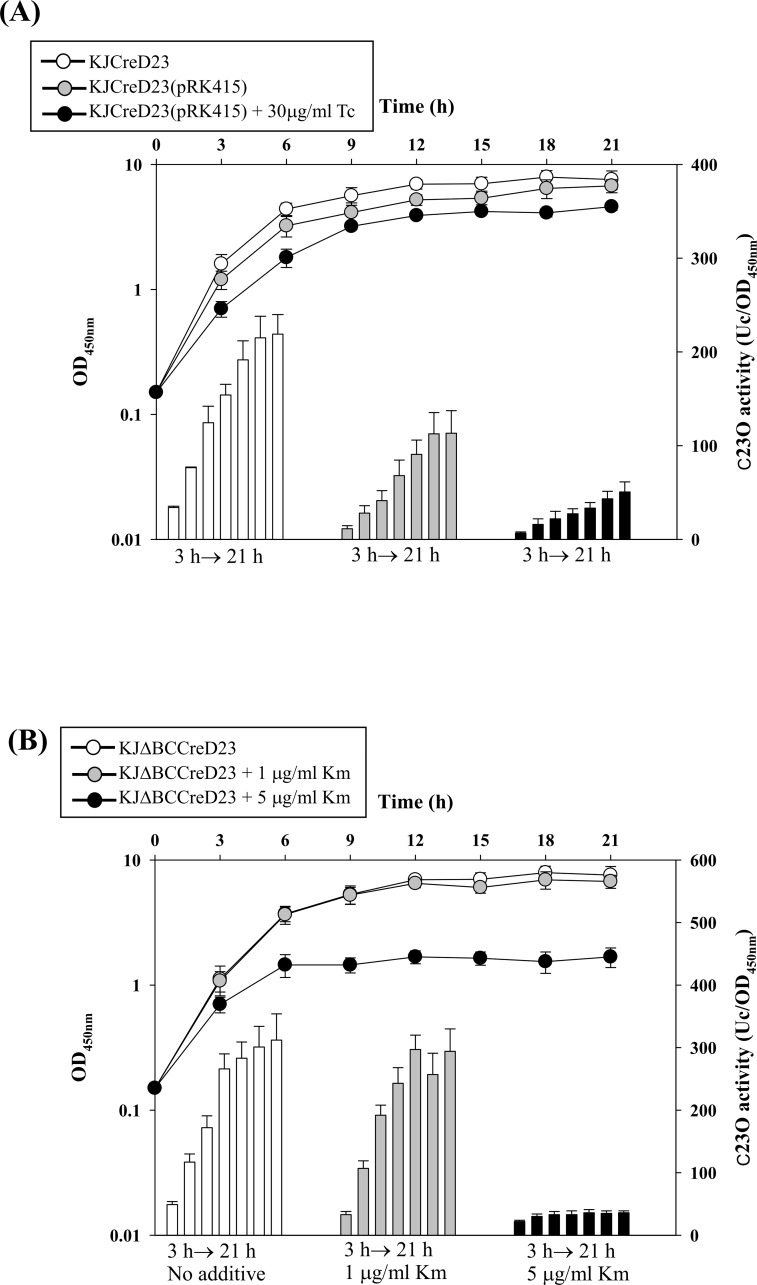
Given the inconsistency of the aforementioned results of the plasmid transcription fusion construct (KJ(pCreDxylE)) and the chromosomal transcription fusion construct (KJCreD23) (S2 Fig), we wondered whether the presence of the plasmid or the addition of tetracycline for plasmid maintenance during plasmid-borne promoter assay caused the bias. We compared the C23O activities of KJCreD23(pRK415) in the absence and presence of tetracycline (30 μg/ml) at a concentration to maintain the plasmid pRK415. The presence of plasmid pRK415 and the addition of tetracycline compromised bacterial growth and creD expression was attenuated (Fig 3A). Furthermore, the degree of attenuation of creD expression was correlated with the decrease in bacterial growth. Therefore, we assumed that the P creD activity is in response to the culture density. To test this, we determined the bacterial growth and the P creD promoter activity in different conditions. To avoid the impact of CreBC TCS on the P creD activity, we determined the C23O activities expressed from KJΔBCCreD23, which represents the P creD activity without the influence of the CreBC TCS. The KJΔBCCreD23 cells were inoculated into fresh LB at an initial OD450nm of 0.15. The cells were exposed to stressors and the cell growth (OD450nm) and P creD activity (C23O activity) were simultaneously recorded. The tested stresses included antibiotics (kanamycin), oxidative stress (menadione), and detergent (benzalkonium chloride). We categorized the outcome of the stress tests as either affecting bacterial growth or not. As shown in Fig 3B–3D, a reduced P creD activity was associated with a corresponding decrease in culture density. These results suggest that this phenotype is not a consequence of stress but is due to the decrease in bacterial culture density. If the stresses minimally affect the bacterial culture density, the C23O activity expressed by KJΔBCCreD23 is as high as that of the non-treated culture. This observation provides a reasonable explanation for the aforementioned discrepancy in the promoter activity assay between strains KJCreD23 and KJ(pCreDxylE) (S2 Fig). In the plasmid transcription fusion assay system KJ(pCreDxylE), the plasmid and tetracycline compromise the bacterial growth and influence the P creD activity. The advantage of using the chromosomal transcription fusion constructs is that the plasmids and tetracycline are avoided.
Fig 3. The promoter activity of creD gene was regulated by the bacterial culture density.
(A) The impact of plasmid and tetracycline on the bacterial growth and C23O expression of strain KJCreD23. Plasmid pRK415 was transported into KJCreD23 by conjugation. The bacterial growth (by recording the OD450nm) and C23O activity expressed from KJCreD23, KJCreD23(pRK415), and KJCreD23(pRK415) with 30 μg/ml tetracycline were monitored every 3 h. (B) The impact of kanamycin (Km) on the bacterial growth and C23O expression of strain KJΔBCCreD23. The bacterial growth (by recording the OD450nm) and C23O activity of KJΔBCCreD23 in the absence and presence of kanamycin (1 or 5 μg/ml) were monitored every 3 h. (C) The impact of menadione (K3) on the bacterial growth and C23O expression of strain KJΔBCCreD23. The bacterial growth (by recording the OD450nm) and C23O activity of KJΔBCCreD23 in the absence and presence of K3 (2 or 30 μg/ml) were monitored every 3 h. (D) The impact of benzalkonium chloride (BC) on the bacterial growth and C23O expression of strain KJΔBCCreD23. The bacterial growth (by recording the OD450nm) and C23O activity of KJΔBCCreD23 in the absence and presence of BC (1 or 5 μg/ml) were monitored every 3 h.
P creD activity is not affected in the presence of phosphor-mimic variant of CreB, CreB(D55E)
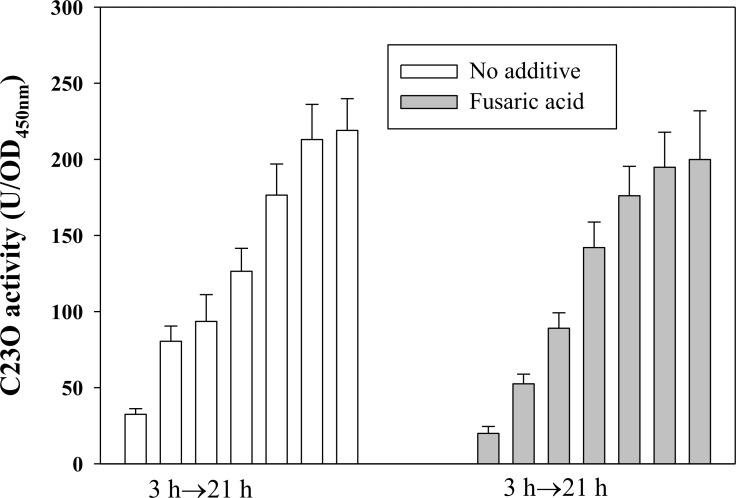
Given the evidence that the loss of function of CreBC increases the creD expression in wild-type KJ (Fig 2), we next tested whether extra activated CreB can affect the expression of creD. In other microorganisms, a mutation converting the conserved aspartate to glutamate at the site of phosphorylation constitutively activates the response regulator [21]. Since the stimuli for CreBC activation is unknown, we generated the phosphor-mimic variant of CreB, CreB(D55E), by site-directed mutagenesis. To determine the effect of CreB(D55E) on creD expression, strain KJCreD23Fua::CreB(D55E) was constructed in which creB(D55E) is inducibly expressed by fusaric acid treatment. First, we assessed the concentration of fusaric acid at which the expression of creB(D55E) can be triggered, but bacterial growth is minimally affected. We found that 30 μg/ml of fusaric acid is ideal (S3 Fig). The growth and C23O activities of KJCreD23Fua::CreB(D55E) were comparatively determined in the absence and presence of fusaric acid (30 μg/ml). Fig 4 demonstrates that the C23O activity expressed by KJCreD23Fua::CreB(D55E) was not affected in the presence of fusaric acid, although it was slightly attenuated at the time points of 3 and 6 h.
Fig 4. The impact of phosphor-mimic variant of CreB, CreB(D55E), on the promoter activity of creD gene.
Overnight culture of strain KJCreD23Fua::CreB(D55E) was inoculated into the fresh medium to the OD450 of 0.15 in the absence and presence of fusaric acid (30 μg/ml). Cells were grown aerobically and the C23O activity were measured every 3 h.
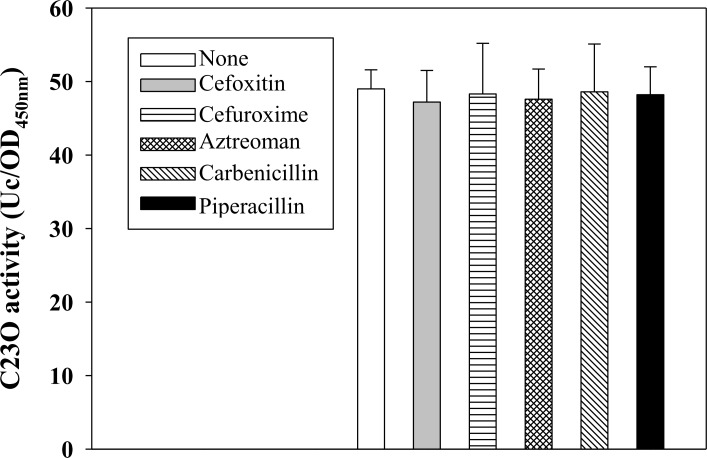
P creD activity is minimally affected by β-lactams challenge
Zamorano et al. report that the presence of β-lactams (such as imipenem or cefoxitin), which can interact with PBP4, activate the CreBC system and increase creD expression in P. aeruginosa [8]. Herein, we investigated whether β-lactams affect the promoter activity of P creD. We tested the effect of 50 μg/ml of β-lactam and found no influence on bacterial growth. The presence of β-lactams did not affect the C23O activity of KJΔBCCreD23 (Fig 5).
Fig 5. The impact of β-lactam on the promoter activity of creD gene.
Overnight culture of KJΔBCCreD23 was inoculated into the fresh medium to the OD450 of 0.15. After 30-min culture, the β-lactam as indicated was added and the culture was further incubated for 3 h. The OD450 and C23O activity were measured.
CreD deletion mutant displayed a filamentous morphology
The deletion mutant, KJΔCreD, and the complementary strain, KJΔCreD(pCreD), were used to determine the physiologic significance of CreD.
First, the growth of KJ, KJΔCreD, and KJΔCreD(pCreD) was assessed by monitoring the OD450nm every 3 h. The strains had the same growth rates at 30°C, 37°C, and 40°C (S4 Fig).
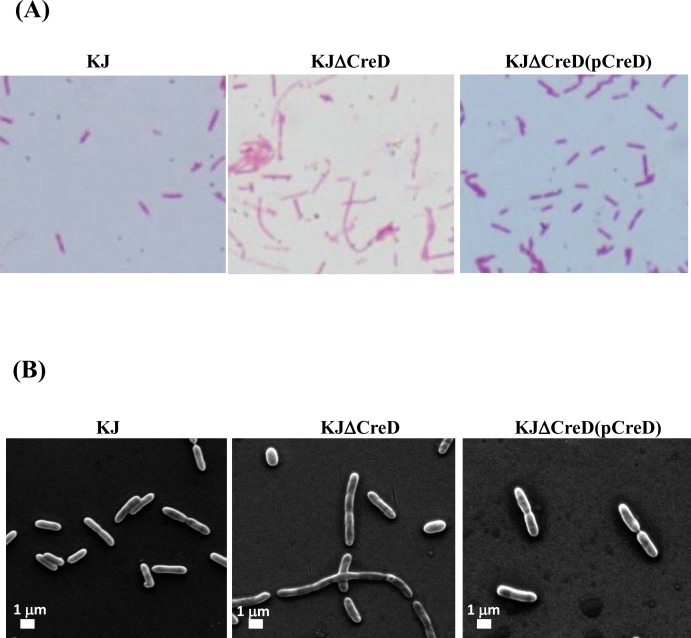
The effect of creD inactivation on cell morphology was examined by light microscopy and SEM. Inactivation of creD led to a striking phenotype of filamentous cells. In KJΔCreD cells, constriction appeared to begin at the septal ring but could not be completed, indicating a defect in constriction and separation. However, a fraction of KJΔCreD cells still seemed to maintain morphology similar to that of wild-type KJ cells. The aberrations in the morphology of KJΔCreD could be largely restored by complementation with an intact creD gene (Fig 6).
Fig 6. The impact of CreD on bacterial morphology.
(A) Bacterial cells were stained with Gram stain and examined by light microscopy. (B) Scanning electron microscopy was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Images are representative of different fields of bacteria from exponentially growing cultures at 37°C.
Cell envelope integrity of the creD deletion mutant was compromised
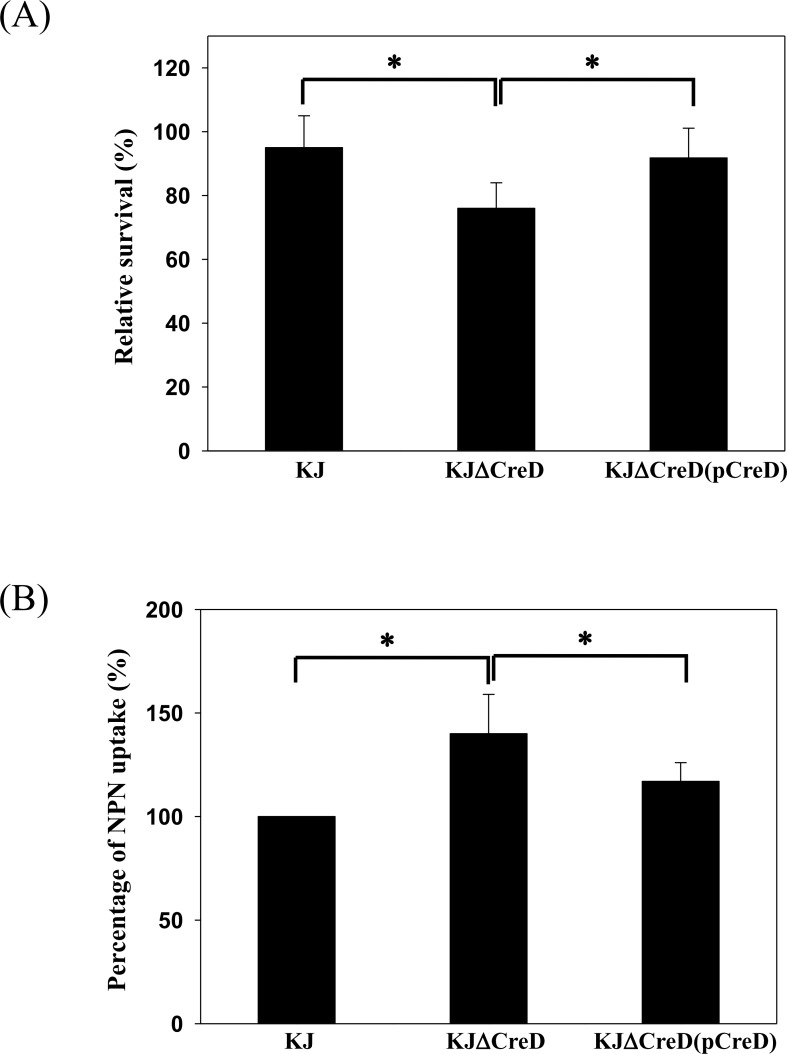
Given that inactivation of creD caused alterations in morphology, it seems probable that CreD can participate in the maintenance of cell envelope integrity. The cell envelope integrity of KJΔCreD cells was therefore assessed by an SDS sensitivity assay. Upon 5-min challenge with 0.01% SDS, the survival rate of KJΔCreD was found to be lower than that of wild-type KJ, and the complemented strain, KJΔCreD(pCreD), showed restoration of the survival rate (Fig 7A). Subsequently, the outer membrane permeability of KJΔCreD cells was assessed with the N-phenyl-1-napthylamine (NPN) uptake assay and the susceptibility test for vancomycin. KJΔCreD cells had a higher tendency for NPN uptake than wild-type KJ, and this defect could be partially restored by complementation with a creD gene (Fig 7B), indicating that the outer membrane of KJΔCreD cells had a higher tendency for cationic compound uptake than the outer membrane of wild-type KJ. In addition, the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria is generally a barrier for high-molecular-weight antibiotics such as vancomycin. Therefore, vancomycin susceptibility can be used as an indicator for evaluating the outer membrane permeability of gram-negative bacteria for high-molecular-weight substances. The susceptibility of KJ, KJΔCreD, and KJΔCreD(pCreD) to vancomycin was tested by the E-test. The MICs of KJ, KJΔCreD, and KJΔCreD(pCreD) cells for vancomycin were >256, 128, and >256 μg/ml, respectively (detection limit of the E-test strip for vancomycin, 256 μg/ml). Collectively, this evidence leads to the conclusion that CreD plays a critical role in envelope homeostasis. Loss of CreD increased the membrane susceptibility to SDS and altered the outer membrane permeability, which increased the outer membrane uptake efficiency for cationic compounds and permeability for high-molecular-weight substances.
Fig 7. The impact of CreD on cell envelope integrity.
Each bar represents the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the average deviation. *, p≤0.05 significance calculated by s Student’s t-test. (A) Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) survival analysis. The survival of KJ, KJΔCreD, and KJΔCreD(pCreD) in LB broth without or with 0.01% SDS was determined by colony forming units (CFUs) counting. The percentage of survival was defined as the CFUs ratio of the SDS-additive group to the SDS-free counterpart. (B) N-phenylanphthylamine (NPN) uptake assay. Each microtiter well was inoculated with 100 μl of the OD450 0.5 bacterial culture and 15 μM NPN, and incubated for 5 min. Fluorescence was monitored by fluorescence spectrophotometer at excitation and emission wavelengths of 355 nm and 402 nm, respectively.
Inactivation of creD triggered the σE-mediated envelope stress response
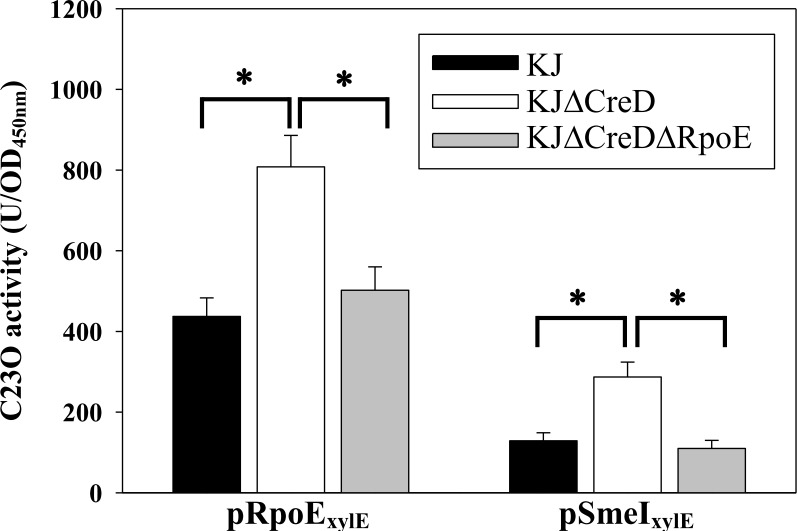
When the cell envelope integrity is compromised, bacterial cells generally trigger a variety of envelope stress response (ESRs) to alleviate the envelope stresses. Of the known ESRs, σE-mediated ESR is the most common mechanism in gram-negative bacteria [22]. Recently, σE-mediated ESR has been reported for S. maltophilia; it was found that σE itself and the smeIJK operon are members of the σE regulon [18]. Considering the effect of creD inactivation on cell envelope integrity and outer membrane permeability (Fig 7), we speculated whether loss of CreD induces activation of the σE pathway. To determine this, the expression of σE and the smeIJK operon for wild-type KJ and KJΔCreD was compared using the promoter transcription fusion assay. As shown in Fig 8, deletion of creD increased the expression of σE and smeIJK by a factor of 1.85-fold and 2.23-fold, respectively, and this upregulation was reverted when rpoE was inactivated, supporting that the loss of the inner membrane protein CreD triggers σE-mediated ESR in S. maltophilia.
Fig 8. The linkage between creD inactivation and σE-mediated envelope stress response.
The promoter transcriptional fusion constructs of rpoE and smeI genes, pRpoExylE and pSmeIxylE, were transferred into KJ, KJΔCreD, and KJΔCreDΔRpoE cells and the expressed C23O activities were determined, respectively. Each bar represents the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate the average deviation. *, p≤0.01 significance calculated by s Student’s t-test.
Discussion
S1 Fig shows the comparisons of creBCD clusters between S. maltophilia, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and Aeromonas spp. CreD of E. coli is part of the creABCD operon and has its own promoter [23]. The creD of S. maltophilia and Aeromonas spp. is a one-gene transcript. In this study, we investigated the regulatory role of the creBC TCS in creD expression. CreD of S. maltophilia is downregulated by CreBC, since creD expression increases when creBC is inactivated (Fig 2), which is not consistent with the P. aeruginosa model in which deletion of creBC does not change creD expression [5]. These results indicate that the CreBC system of S. maltophilia is active in laboratory cultured condition.
Since the exact stimuli for CreBC activation of S. maltophilia are unknown, we used an overexpressing phosphor-mimic variant of CreB, CreB(D55E), to monitor the effect of CreBC activation on creD expression. We found no significant alteration in the creD expression when CreB(D55E) is overexpressed (Fig 4), which suggests that either CreB(D55E) is not a functional transcription regulator that affects expression of the CreBC regulon or CreBC TCS is fully activated in the S. maltophilia isolate KJ and the presence of CreB(D55E) cannot further activate the CreBC TCS. In this second scenario, the activated CreB of S. maltophilia plays a negative regulatory role in the expression of creD, which is opposite of its role in E. coli, Aeromonas spp., and P. aeruginosa [3–5].
Based on the known regulatory circuit of creBC and creD, increased expression of creD is as an indicator of creBC TCS activation in E. coli and P. aeruginosa systems [3,5]. However, this is not true in S. maltophilia. Our results suggest that the expression of creD is regulated by CreBC TCS and bacterial culture density. Some intrinsic physiologic responses or external stimuli that are not related to CreBC activation can alter the bacterial growth rate and culture density, which, in turn, affects the creD expression. Therefore, the expression of creD is not an optimal indicator of creBC activation in S. maltophilia.
The cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria consists of two distinct membranes, the inner membrane (IM) and the outer membrane (OM), which are separated by an aqueous compartment, the periplasm. Approximately a quarter of all genes in the E. coli genome encode integral inner membrane proteins, whereas the inner membrane lipid bilayer occupies less than 4% of the total bacterial volume [24]. Therefore, the expression of inner membrane proteins should be tightly regulated to maintain envelope integrity. Herein, we demonstrated that CreD is constitutively expressed and that its expression gradually increases in proportion to bacterial culture density (Fig 2). Furthermore, we found that inactivation of creD causes morphological aberrations (Fig 6), compromises envelope integrity, and increases outer membrane permeability (Fig 7), which then trigger the σE-mediated envelope stress response (Fig 8). Therefore, we propose two possible roles of CreD in the maintenance of envelope integrity; the two possibilities are not mutually exclusive: (i) CreD appears to act as an architectural frame (a structural component) of the inner membrane and play a critical role in the maintenance of envelope integrity. When the bacterial culture density increases, the expression of CreD is synchronously increased to meet the requirement of cell membrane expansion, thus exquisitely maintaining the balance between bacterial growth and CreD biological function. (ii) CreD may function as a channel for extrusion of noxious metabolites that are produced during bacterial growth. Therefore, the expression of creD is proportional to active bacterial growth. If the CreD expression is impaired, the accumulated noxious metabolites may compromise envelope integrity and trigger ESR.
Supporting Information
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant MOST 104-2320-B-010-023-MY3 from Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan and grant 40419001 from Professor Tsuei-Chu Mong Merit Scholarship.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by grant MOST 104-2320-B-010-023-MY3 from Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan and grant 40419001 from Professor Tsuei-Chu Mong Merit Scholarship. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN. Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000; 69: 183–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Olaitan AO, Morand S, Rolain JM. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front Microbiol. 2014; 26: 643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Avison MB, Horton RE, Walsh TR, Bennett PM. Escherichia coli CreBC is a global regulator of gene expression that responds to growth in minimal media. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276: 26955–26961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Tayler AE, Ayala JA, Niumsup P, Westphal K, Baker JA, Zhang L, et al. Induction of β-lactamase production in Aeromonas hydrophila is responsive to β-lactam-mediated changes in peptidoglycan composition. Microbiology. 2010; 156: 2327–2325. 10.1099/mic.0.035220-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Moya B, Dotsch A, Juan C, Blazquez J, Zamorano L, Haussler S, et al. β-Lactam resistance response triggered by inactivation of a nonessential penicillin-binding protein. PLoS Pathog. 2009; 5: e1000353 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Cariss SJ, Tayler AE, Avison MB. Defining the growth conditions and promoter-proximal DNA sequences required for activation of gene expression by CreBC in Escherichia coli . J Bacteriol. 2008; 190: 3930–3939. 10.1128/JB.00108-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Alksne LE, Rasmussen BA. Expression of the AsbA1, OXA-12, and AsbM1 beta-lactamases in Aeromonas jandaei AER 14 is coordinated by a two-component regulon. J Bacteriol. 1996; 179: 2006–2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Zamorano L, Moya B, Juan C, Mulet X, Blazquez J, Oliver A. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa CreBC two-component system plays a major role in the response to β-lactams, fitness, biofilm growth, and global regulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58: 5084–5095. 10.1128/AAC.02556-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Niumsup PA, Simm M, Nurmahomed K, Walsh TR, Bennett PM, Avison MB. Genetic linkage of the penicillinase gene, amp, and blrAB, encoding the regulator of β-lactamase expression in Aeromonas Spp. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003; 51: 1351–1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Brooke JS. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25: 2–41. 10.1128/CMR.00019-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Crossman LC, Gould VC, Dow JM, Vernikos GS, Okazaki A, Sebaihia M, et al. The complete genome, comparative and functional analysis of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia reveals an organism heavily shielded by drug resistance determinants. Genome Biol. 2008; 17: R74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Li XZ, Zhang L, Poole K. SmeC, an outer membrane multidrug efflux protein of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002; 46: 333–343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lin CW, Lin HC, Huang YW, Chung TC, Yang TC. Inactivation of mrcA gene derepresses the basal-level expression of L1 and L2 β-lactamases in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66: 2033–2037. 10.1093/jac/dkr276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Huang YW, Wu CJ, Hu RM, Lin YT, Yang TC. An interplay among membrane-bound lytic transglycosylase D1, CreBC two-component regulatory system, AmpNG-AmpDI-NagZ-AmpR regulatory circuit, and L1/L2 β-lactamases expression in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. (Accepted). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hu RM, Huang KJ, Wu LT, Hsiao YJ, Yang TC. Induction of L1 and L2 β-lactamases of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52: 1198–1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yang TC, Huang YW, Hu RM, Huang SC, Lin YT. AmpDI is involved in expression of the chromosomal L1 and L2 β-lactamases of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53: 2902–2907. 10.1128/AAC.01513-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-(Delta DeltaC(T)) Method. Methods. 2001; 25: 402–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Huang YW, Liou RS, Lin YT, Huang HH, Yang TC. A linkage between SmeIJK efflux pump, cell envelope integrity, and σE-mediated envelope stress response in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . PLoS ONE. 2014; 9: e111784 10.1371/journal.pone.0111784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Lin CW, Huang YW, Hu RM, Chiang KH, Yang TC. The role of AmpR in the regulation of L1 and L2 β-lactamases in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . Res Microbiol. 2009; 160: 152–158. 10.1016/j.resmic.2008.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hu RM, Liao ST, Huang CC, Huang YW, Yang TC. An inducible fusaric acid tripartitle efflux pump contributes to the fusaric acid resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia . PLoS ONE. 2012; 7: e51053 10.1371/journal.pone.0051053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Klose KE, Weiss DS, Kustu S. Glutamate at the site of phosphorylation of nitrogen-regulatory protein NTRC mimics aspartyl-phosphate and activates the protein. J Mol Biol. 1993; 232:67–78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hayden JD, Ades SE. The extracytoplasmic stress factor, σE, is required to maintain cell envelope integrity in Escherichia coli . PLoS ONE. 2008; 3: e1573 10.1371/journal.pone.0001573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Drury LS, Buxton RS. Identification and sequencing of the Escherichia coli cet gene which codes for an inner membrane protein, mutation of which causes tolerance to colicin E2. Mol Microbiol. 1998; 2: 109–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Elofsson A, von Heijne G. Membrane protein structure: prediction versus reality. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007; 76: 125–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.