Abstract
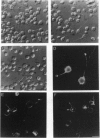
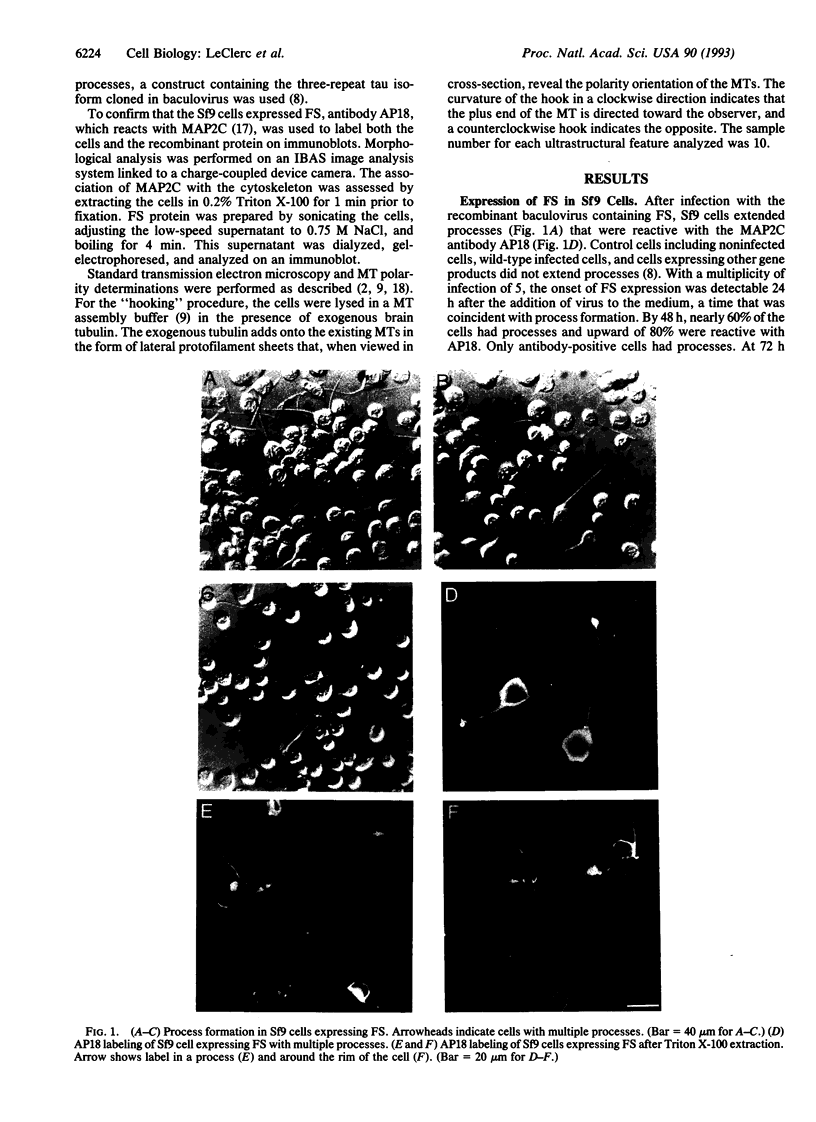
To understand the roles of various microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) in the development of axons and dendrites, we have expressed individual neuronal MAPs in normally rounded Sf9 host cells. We previously reported that expression of tau protein in these cells results in the elaboration of long processes containing dense bundles of microtubules (MTs). These bundles generally terminate in the hillock region of the cell body, and almost all of the MTs within the bundles are oriented with their plus ends distal to the cell body. Here we report the expression of a construct that approximates the MAP2C sequence and also induces the elaboration of processes with dense bundles of predominantly plus-end-distal MTs. Whereas tau generally results in a single process, there is a significantly greater tendency for the MAP2C-like construct to induce multiple processes. In contrast to the tau processes, the MT bundle in these processes extends far into the cell body. This latter observation suggests that MAP2C and tau have different effects on MT assembly and/or transport events in the cell. Although both of these MAPs can organize MTs that are competent to participate in process formation, the detailed organization of MTs induced by each of the two constructs is distinctive, and these differences may be relevant to axonal and dendritic differentiation.
Full text
PDF


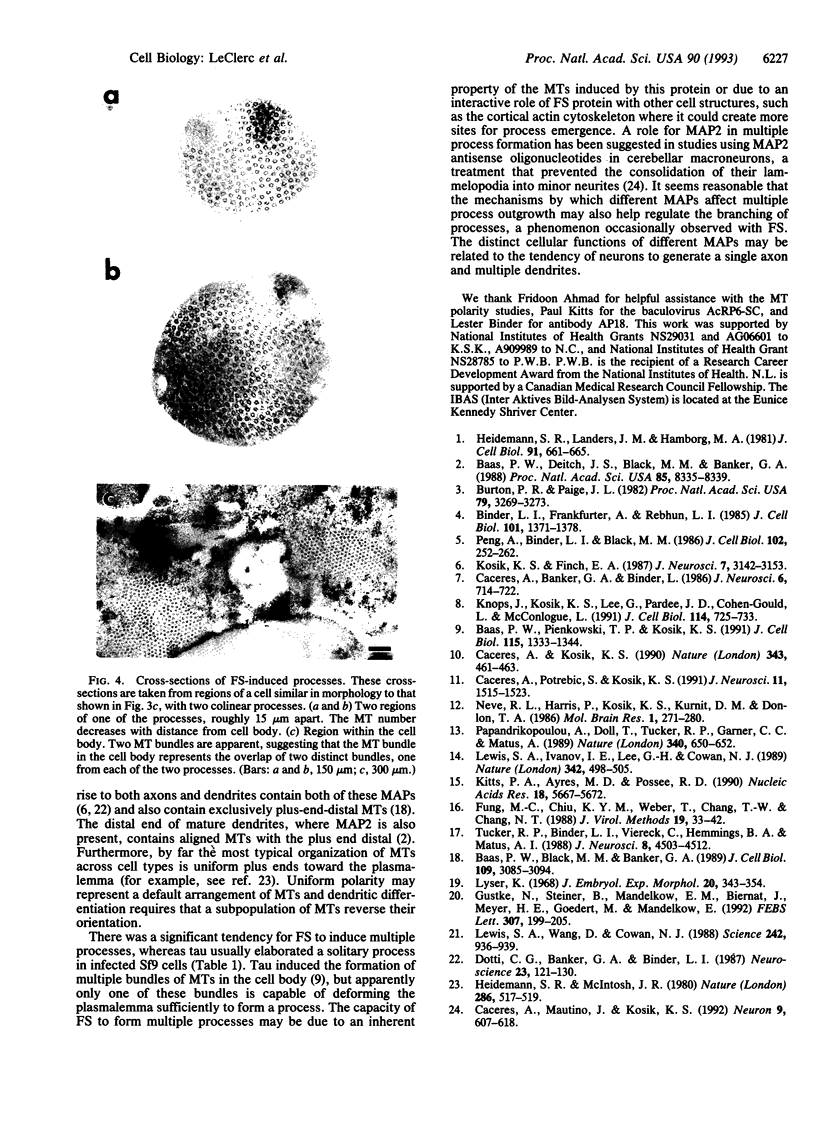
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas P. W., Black M. M., Banker G. A. Changes in microtubule polarity orientation during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3085–3094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Deitch J. S., Black M. M., Banker G. A. Polarity orientation of microtubules in hippocampal neurons: uniformity in the axon and nonuniformity in the dendrite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8335–8339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. W., Pienkowski T. P., Kosik K. S. Processes induced by tau expression in Sf9 cells have an axon-like microtubule organization. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1333–1344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Kosik K. S. Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):461–463. doi: 10.1038/343461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Mautino J., Kosik K. S. Suppression of MAP2 in cultured cerebellar macroneurons inhibits minor neurite formation. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):607–618. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Potrebic S., Kosik K. S. The effect of tau antisense oligonucleotides on neurite formation of cultured cerebellar macroneurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1515–1523. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01515.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres A., Banker G. A., Binder L. Immunocytochemical localization of tubulin and microtubule-associated protein 2 during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1986 Mar;6(3):714–722. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-03-00714.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotti C. G., Banker G. A., Binder L. I. The expression and distribution of the microtubule-associated proteins tau and microtubule-associated protein 2 in hippocampal neurons in the rat in situ and in cell culture. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Chiu K. Y., Weber T., Chang T. W., Chang N. T. Detection and purification of a recombinant human B lymphotropic virus (HHV-6) in the baculovirus expression system by limiting dilution and DNA dot-blot hybridization. J Virol Methods. 1988 Jan;19(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustke N., Steiner B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Meyer H. E., Goedert M., Mandelkow E. The Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau protein reduces microtubule binding and involves Ser-Pro and Thr-Pro motifs. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80767-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Landers J. M., Hamborg M. A. Polarity orientation of axonal microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):661–665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., McIntosh J. R. Visualization of the structural polarity of microtubules. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):517–519. doi: 10.1038/286517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Ayres M. D., Possee R. D. Linearization of baculovirus DNA enhances the recovery of recombinant virus expression vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5667–5672. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knops J., Kosik K. S., Lee G., Pardee J. D., Cohen-Gould L., McConlogue L. Overexpression of tau in a nonneuronal cell induces long cellular processes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):725–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Finch E. A. MAP2 and tau segregate into dendritic and axonal domains after the elaboration of morphologically distinct neurites: an immunocytochemical study of cultured rat cerebrum. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3142–3153. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03142.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Ivanov I. E., Lee G. H., Cowan N. J. Organization of microtubules in dendrites and axons is determined by a short hydrophobic zipper in microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and tau. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):498–505. doi: 10.1038/342498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Wang D. H., Cowan N. J. Microtubule-associated protein MAP2 shares a microtubule binding motif with tau protein. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.3142041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyser K. M. An electron-microscopic study of centrioles in differentiating motor neuroblasts. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1968 Nov;20(3):343–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Harris P., Kosik K. S., Kurnit D. M., Donlon T. A. Identification of cDNA clones for the human microtubule-associated protein tau and chromosomal localization of the genes for tau and microtubule-associated protein 2. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papandrikopoulou A., Doll T., Tucker R. P., Garner C. C., Matus A. Embryonic MAP2 lacks the cross-linking sidearm sequences and dendritic targeting signal of adult MAP2. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):650–652. doi: 10.1038/340650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng I., Binder L. I., Black M. M. Biochemical and immunological analyses of cytoskeletal domains of neurons. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):252–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. P., Binder L. I., Viereck C., Hemmings B. A., Matus A. I. The sequential appearance of low- and high-molecular-weight forms of MAP2 in the developing cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4503–4512. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04503.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]