Abstract
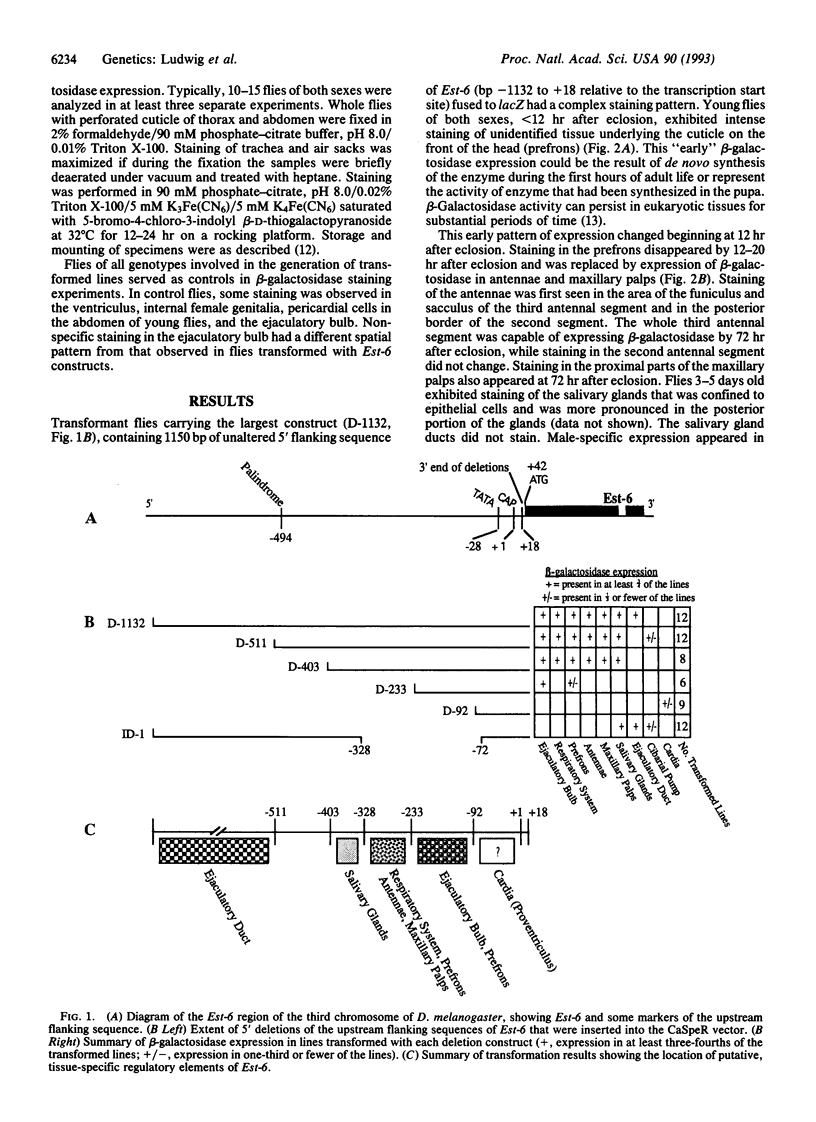
The esterase 6 gene (Est-6) of Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in a variety of tissues that differ between larval and adult stages and among related species. Variability in the level of expression of this locus among different species and strains and its species- and tissue-specific patterns of expression make it a useful system for studying the evolution of gene regulation in Drosophila. We have begun to determine the location of the regulatory regions of Est-6 by constructing deletion mutants of the 5' regions of the gene and transforming them back into flies. Deletion mutants of the putative 5' promoter regions of Est-6 were fused to the bacterial beta-galactosidase gene (lacZ) and assayed for their ability to direct tissue-specific expression in transformed D. melanogaster adults. We have identified four independently acting Est-6 regulatory regions that direct the expression of lacZ in (i) the ejaculatory duct; (ii) the adult salivary glands; (iii) the respiratory system, prefrons, antennae, and maxillary palps; and (iv) the ejaculatory bulb and prefrons. We also found a region near the start of transcription that directed expression of Est-6 in the cardia or proventriculus in some transformed lines.
Full text
PDF
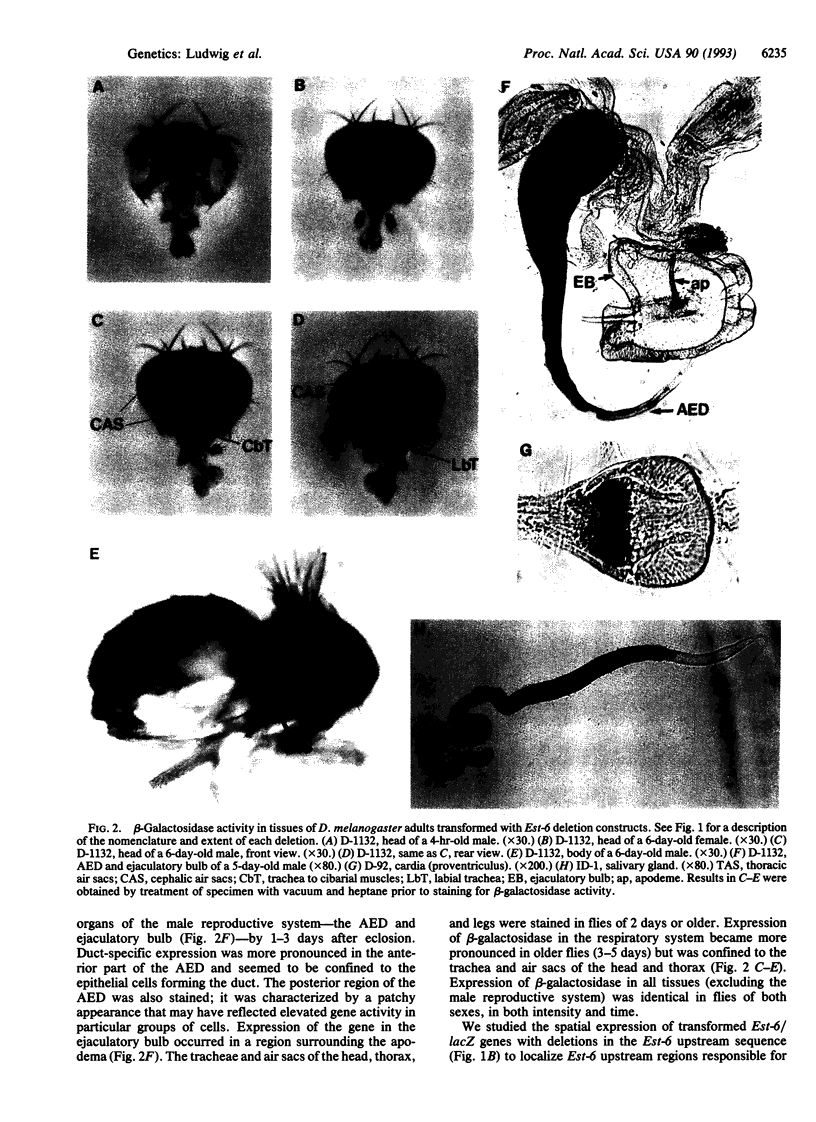


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronshtam A. A., Kuzin B. A. Stanovlenie polovogo dimorfizma po vyrazheniiu gena Est-6 v ontogeneze Drosophila melanogaster i Drosophila simulans. Zh Obshch Biol. 1974 Nov-Dec;35(6):926–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. P., Richmond R. C. Molecular analysis of evolutionary changes in the expression of Drosophila esterases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8217–8221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. P., Richmond R. C., Oakeshott J. G. Cloning of the esterase-5 locus from Drosophila pseudoobscura and comparison with its homologue in D. melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol. 1990 Nov;7(6):525–546. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Transgenic animal studies on the evolution of genetic regulatory circuitries. Bioessays. 1992 Apr;14(4):237–244. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collet C., Nielsen K. M., Russell R. J., Karl M., Oakeshott J. G., Richmond R. C. Molecular analysis of duplicated esterase genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol. 1990 Jan;7(1):9–28. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson W. J. On the architecture of regulatory systems: evolutionary insights and implications. Bioessays. 1988 Jun;8(6):204–208. doi: 10.1002/bies.950080608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game A. Y., Oakeshott J. G. Associations between restriction site polymorphism and enzyme activity variation for esterase 6 in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):1021–1031. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., O'Kane C. Neural enhancer-like elements as specific cell markers in Drosophila. Development. 1989 Jan;105(1):35–52. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould S. J., Lewontin R. C. The spandrels of San Marco and the Panglossian paradigm: a critique of the adaptationist programme. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Sep 21;205(1161):581–598. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy M. J., Dumancic M. M., Oakeshott J. G. Biochemical and physiological studies of soluble esterases from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1991 Aug;29(7-8):365–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00554144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. G. Cellular organization and peritrophic membrane formation in the cardia (proventriculus) of Drosophila melanogaster. J Morphol. 1988 Jun;196(3):253–282. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051960302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mane S. D., Tepper C. S., Richmond R. C. Studies of esterase 6 in Drosophila melanogaster. XIII. Purification and characterization of the two major isozymes. Biochem Genet. 1983 Oct;21(9-10):1019–1040. doi: 10.1007/BF00483957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakeshott J. G., Collet C., Phillis R. W., Nielsen K. M., Russell R. J., Chambers G. K., Ross V., Richmond R. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of esterase-6, a serine hydrolase of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3359–3363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J., Wistow G. J. Enzyme/crystallins: gene sharing as an evolutionary strategy. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90956-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]