Abstract
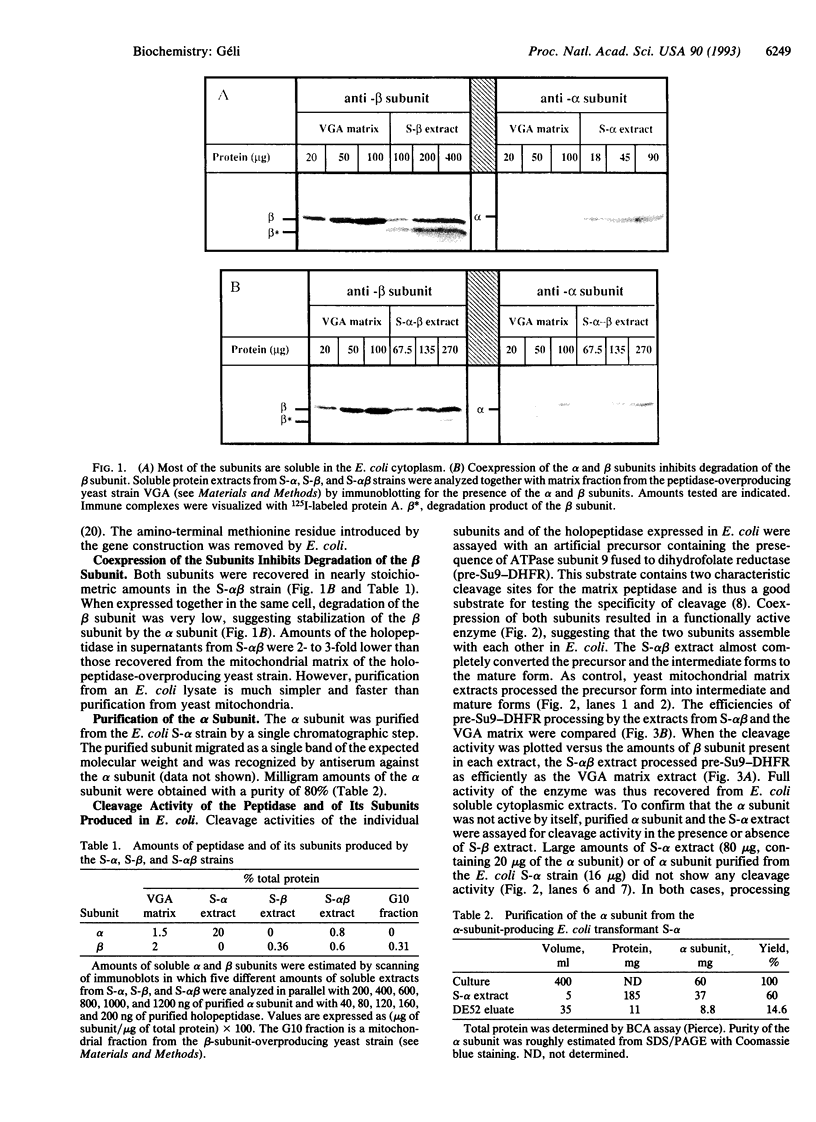
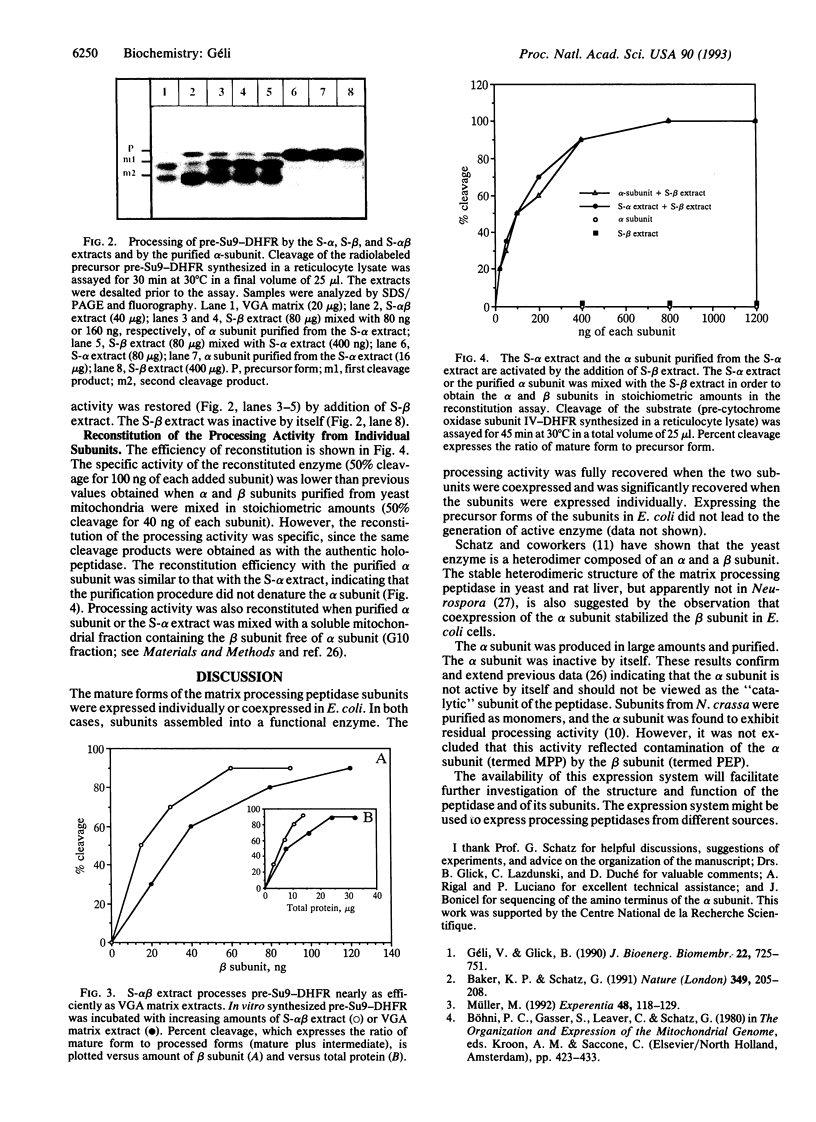
The matrix processing peptidase from yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) mitochondria was expressed in Escherichia coli via a plasmid-borne operon encoding the mature forms of the alpha and beta subunits of the enzyme. The subunits assembled into a fully active, soluble enzyme. The mature subunits were also expressed individually. The alpha subunit accumulated in large amounts and was obtained at a purity of 80% after a single chromatographic step. The beta-subunit-producing strain expressed an intact and a degraded form of the beta subunit, both of them soluble in the cytoplasm. Extract from either the alpha- or the beta-subunit-producing strain (S-alpha or S-beta extract, respectively), as well as the purified alpha subunit, was enzymatically inactive. However, precursor cleavage activity was restored by mixing either the S-alpha extract or the purified alpha subunit with the S-beta extract. The reconstituted processing activity was indistinguishable from the authentic holopeptidase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90546-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker K. P., Schatz G. Mitochondrial proteins essential for viability mediate protein import into yeast mitochondria. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):205–208. doi: 10.1038/349205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J. The MARCKS family of cellular protein kinase C substrates. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1501–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun H. P., Emmermann M., Kruft V., Schmitz U. K. The general mitochondrial processing peptidase from potato is an integral part of cytochrome c reductase of the respiratory chain. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3219–3227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Ferris C. D., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase regulatory sites. Phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C, and calcium/calmodulin protein kinase; identification of flavin and calmodulin binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10976–10981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busconi L., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase. N-terminal myristoylation determines subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8410–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhni P. C., Daum G., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Partial purification of a matrix-located protease involved in cleavage of mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4937–4943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerletti N., Böhni P. C., Suda K. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Isolated yeast mitochondria and a solubilized matrix protease correctly process cytochrome c oxidase subunit V precursor at the NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4944–4949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demolle D., Lecomte M., Boeynaems J. M. Pattern of protein phosphorylation in aortic endothelial cells. Modulation by adenine nucleotides and bradykinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18459–18465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. FASEB J. 1989 Jul;3(9):2007–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavel Y., von Heijne G. Cleavage-site motifs in mitochondrial targeting peptides. Protein Eng. 1990 Oct;4(1):33–37. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Glick B. Mitochondrial protein import. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Dec;22(6):725–751. doi: 10.1007/BF00786928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Yang M. J., Suda K., Lustig A., Schatz G. The MAS-encoded processing protease of yeast mitochondria. Overproduction and characterization of its two nonidentical subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19216–19222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawlitschek G., Schneider H., Schmidt B., Tropschug M., Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import: identification of processing peptidase and of PEP, a processing enhancing protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):795–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Sasaki Y., Tanaka T., Endo T., Ohno S., Fujii Y., Nagata T. N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, a calmodulin antagonist, inhibits cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4354–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Schatz G. The amino-terminal region of an imported mitochondrial precursor polypeptide can direct cytoplasmic dihydrofolate reductase into the mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3149–3156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber J., Kalousek F., Swaroop M., Rosenberg L. E. The general mitochondrial matrix processing protease from rat liver: structural characterization of the catalytic subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7978–7982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto T., Ito A., Omura T. Characterization of a mitochondrial matrix protease catalyzing the processing of adrenodoxin precursor. J Biochem. 1986 Jul;100(1):247–254. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Marsden P. A., Li G. K., Tempst P., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinski T., Taha Z. Nitric oxide release from a single cell measured in situ by a porphyrinic-based microsensor. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):676–678. doi: 10.1038/358676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAda P. C., Douglas M. G. A neutral metallo endoprotease involved in the processing of an F1-ATPase subunit precursor in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3177–3182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. Proteolysis in protein import and export: signal peptide processing in eu- and prokaryotes. Experientia. 1992 Feb 15;48(2):118–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01923506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu T., Suzuki H., Kiuchi K., Saitoh M., Hidaka H. Effects of myosin light-chain kinase inhibitor on catecholamine secretion from rat pheochromocytoma PC12h cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):1045–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane M., Mitchell J., Förstermann U., Murad F. Phosphorylation by calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and protein kinase C modulates the activity of nitric oxide synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1396–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou W. J., Ito A., Okazaki H., Omura T. Purification and characterization of a processing protease from rat liver mitochondria. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2605–2612. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08400.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Schmidt H. H., Nakane M., Murad F. Purification and characterization of particulate endothelium-derived relaxing factor synthase from cultured and native bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10480–10484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. A., Hartl F. U., Cheng M. Y., Ostermann J., Horwich A., Neupert W. The processing peptidase of yeast mitochondria: the two co-operating components MPP and PEP are structurally related. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3493–3500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers N. E., Ignarro L. J. Constitutive nitric oxide synthase from cerebellum is reversibly inhibited by nitric oxide formed from L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):242–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91550-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Theiler F., Horvath S. J., Tomich J. M., Richards J. H., Allison D. S., Schatz G. Amphiphilicity is essential for mitochondrial presequence function. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):649–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt B., Wachter E., Sebald W., Neupert W. Processing peptidase of Neurospora mitochondria. Two-step cleavage of imported ATPase subunit 9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Arretz M., Wachter E., Neupert W. Matrix processing peptidase of mitochondria. Structure-function relationships. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9881–9887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte U., Arretz M., Schneider H., Tropschug M., Wachter E., Neupert W., Weiss H. A family of mitochondrial proteins involved in bioenergetICS and biogenesis. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):147–149. doi: 10.1038/339147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumitsu H., Chijiwa T., Hagiwara M., Mizutani A., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. KN-62, 1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazi ne, a specific inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4315–4320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte C., Jensen R. E., Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. MAS1, a gene essential for yeast mitochondrial assembly, encodes a subunit of the mitochondrial processing protease. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1439–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. Two nuclear mutations that block mitochondrial protein import in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M. J., Geli V., Oppliger W., Suda K., James P., Schatz G. The MAS-encoded processing protease of yeast mitochondria. Interaction of the purified enzyme with signal peptides and a purified precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6416–6423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Jensen R. E., Yaffe M. P., Oppliger W., Schatz G. Import of proteins into yeast mitochondria: the purified matrix processing protease contains two subunits which are encoded by the nuclear MAS1 and MAS2 genes. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3857–3862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





