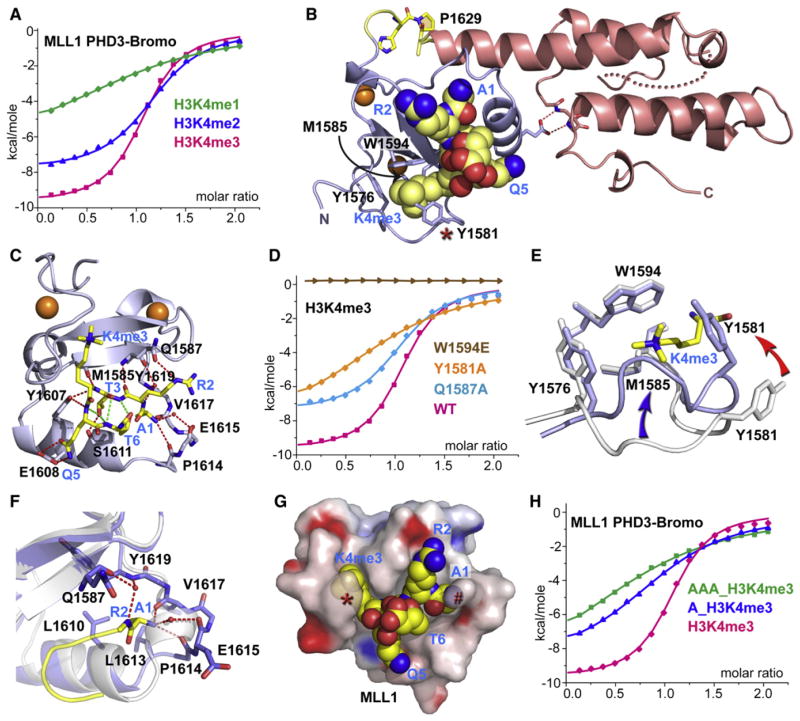
Figure 2. Crystal Structure of MLL1 PHD3-Bromo Cassette Bound to H3K4me3/2-Containing Peptides, Together with Binding Data on Wild-Type and Mutant PHD3.
(A) ITC binding curves of MLL1 PHD3-Bromo cassette with H3K4me-containing peptides.
(B) A ribbon view of the crystal structure of MLL1 PHD3-Bromo cassette in complex with H3(1-9)K4me3 peptide. cis-configured Pro1629 and pocket residues for trimethyl-lysine recognition are labeled accordingly.
(C) A view of the hydrogen bonding interactions between MLL1 PHD3 (blue) and bound H3K4me3 peptide (yellow) in the crystal structure of the complex.
(D) ITC profiles for the binding of H3(1-15)K4me3 peptide to wild-type (WT) MLL1 PHD3-Bromo and its W1594E, Y1581A, and Q1587A mutants.
(E) A view of the superimposed structures of the K4me3 binding pocket of MLL1 PHD3 in the free (silver) and H3K4me3-bound (blue) states. The blue and red arrows highlight the conformational changes in the loop spanning Tyr1576-Met1585 segment and involving Tyr1581, respectively, on complex formation.
(F) A view of the superimposed structures of the peptide N terminus binding pocket of MLL1 PHD3 in the free (silver) and H3K4me3-bound (blue) states. The Pro1614-Val1617 segment adopts an α helix (silver) in the free state but changes into a turn fold (blue) in the bound state.
(G) Surface electrostatic view of MLL1 PHD3 with bound H3(1-6)K4me3 peptide in a space-filling representation. Note that access is blocked to both the trime-thylammonium group of H3K4me3 (indicated by red asterisk) and the N terminus (indicated by red pound symbol) in this complex.
(H) ITC profiles for the binding of MLL1 PHD3-Bromo to wild-type and two modified H3K4me3 peptides containing one or three additional Ala residues added to the N terminus.
See also Figure S2.