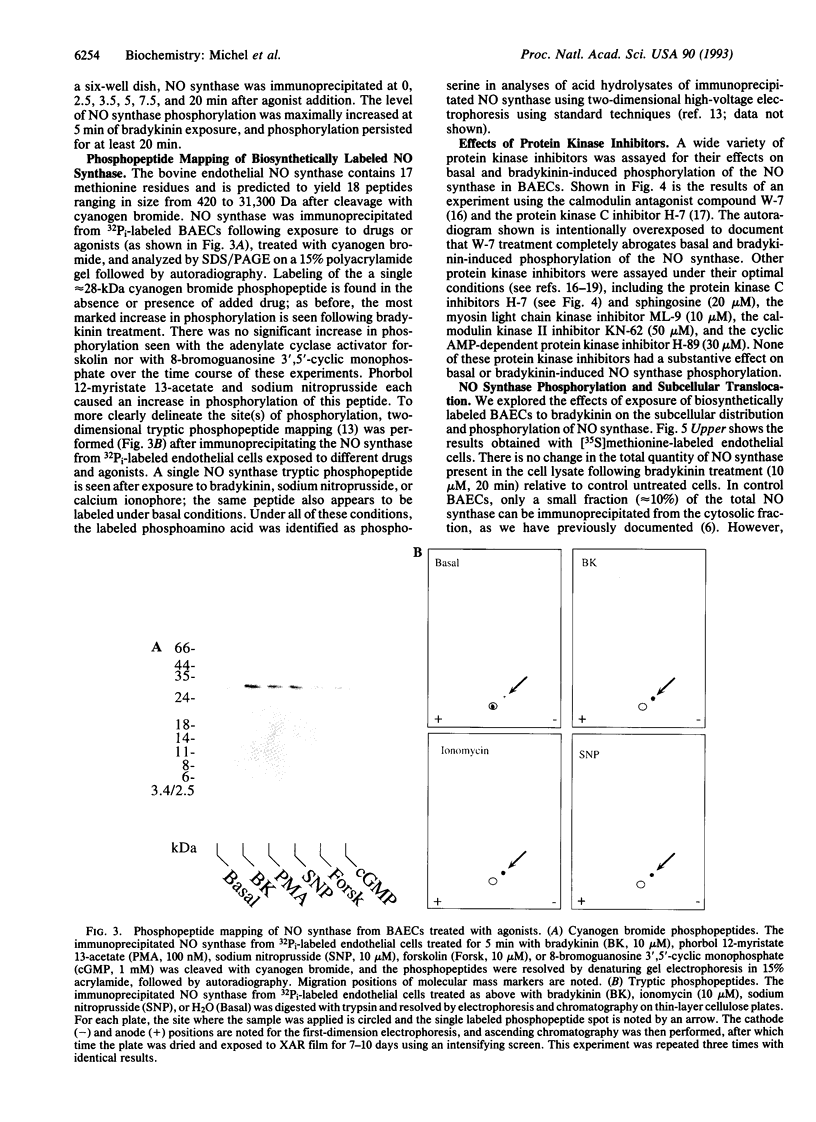
Abstract
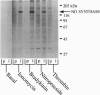
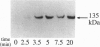
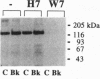
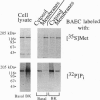
In the vascular endothelium, diverse cell surface receptors are coupled to the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent activation of nitric oxide (NO) synthase. We now report that, in intact cultured endothelial cells, several drugs and agonists are associated with increased serine phosphorylation of the endothelial NO synthase. We biosynthetically labeled bovine aortic endothelial cells with [32P]orthophosphoric acid, exposed the cells to various drugs and hormones, and then immunoprecipitated the enzyme from cell extracts using a highly specific anti-peptide antibody. The marked endothelial NO synthase phosphorylation induced by bradykinin is maximal only after 5 min of agonist exposure and is stable for at least 20 min. Basal and agonist-induced phosphorylation of the NO synthase in endothelial cells is completely inhibited by the calmodulin antagonist compound W-7. We prepared subcellular fractions of endothelial cells that had been biosynthetically labeled with [35S]methionine or [32P]orthophosphoric acid and immunoprecipitated the endothelial NO synthase from untreated (basal) and bradykinin-treated cells. In the basal state, [35S]methionine-labeled endothelial NO synthase is associated primarily with the particulate cellular fraction, but the phosphorylated enzyme is primarily cytosolic. Following exposure to bradykinin, a substantial fraction of the [35S]methionine-labeled NO synthase is now found in the cytosolic fraction, associated with a marked increase in the level of cytosolic enzyme phosphorylation. We propose that agonist-induced phosphorylation of NO synthase is associated with translocation of the enzyme from membrane to cytosol and may thereby regulate the biological effects of endothelial NO synthesis in situ.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90546-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J. The MARCKS family of cellular protein kinase C substrates. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1501–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Ferris C. D., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase regulatory sites. Phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C, and calcium/calmodulin protein kinase; identification of flavin and calmodulin binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10976–10981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busconi L., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase. N-terminal myristoylation determines subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8410–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demolle D., Lecomte M., Boeynaems J. M. Pattern of protein phosphorylation in aortic endothelial cells. Modulation by adenine nucleotides and bradykinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18459–18465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. FASEB J. 1989 Jul;3(9):2007–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Sasaki Y., Tanaka T., Endo T., Ohno S., Fujii Y., Nagata T. N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, a calmodulin antagonist, inhibits cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4354–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Marsden P. A., Li G. K., Tempst P., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinski T., Taha Z. Nitric oxide release from a single cell measured in situ by a porphyrinic-based microsensor. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):676–678. doi: 10.1038/358676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu T., Suzuki H., Kiuchi K., Saitoh M., Hidaka H. Effects of myosin light-chain kinase inhibitor on catecholamine secretion from rat pheochromocytoma PC12h cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):1045–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane M., Mitchell J., Förstermann U., Murad F. Phosphorylation by calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and protein kinase C modulates the activity of nitric oxide synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1396–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Schmidt H. H., Nakane M., Murad F. Purification and characterization of particulate endothelium-derived relaxing factor synthase from cultured and native bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10480–10484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers N. E., Ignarro L. J. Constitutive nitric oxide synthase from cerebellum is reversibly inhibited by nitric oxide formed from L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):242–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91550-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumitsu H., Chijiwa T., Hagiwara M., Mizutani A., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. KN-62, 1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazi ne, a specific inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4315–4320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]