Abstract
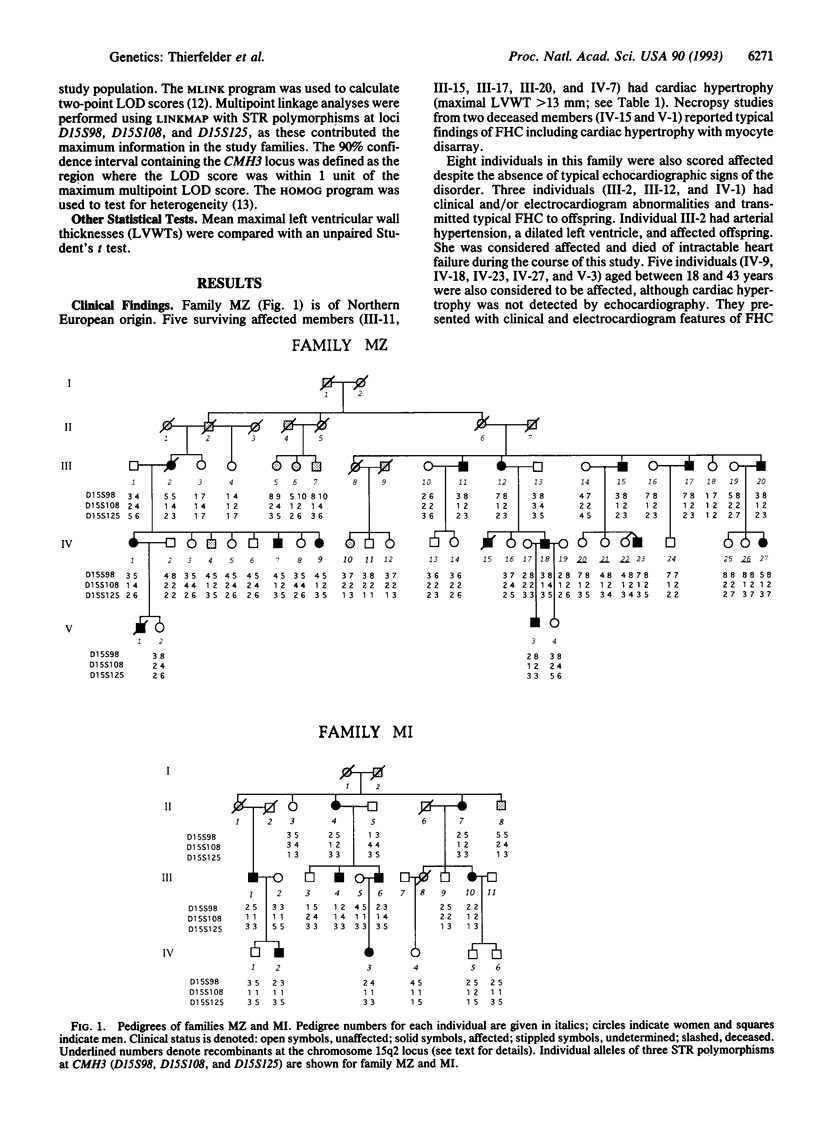
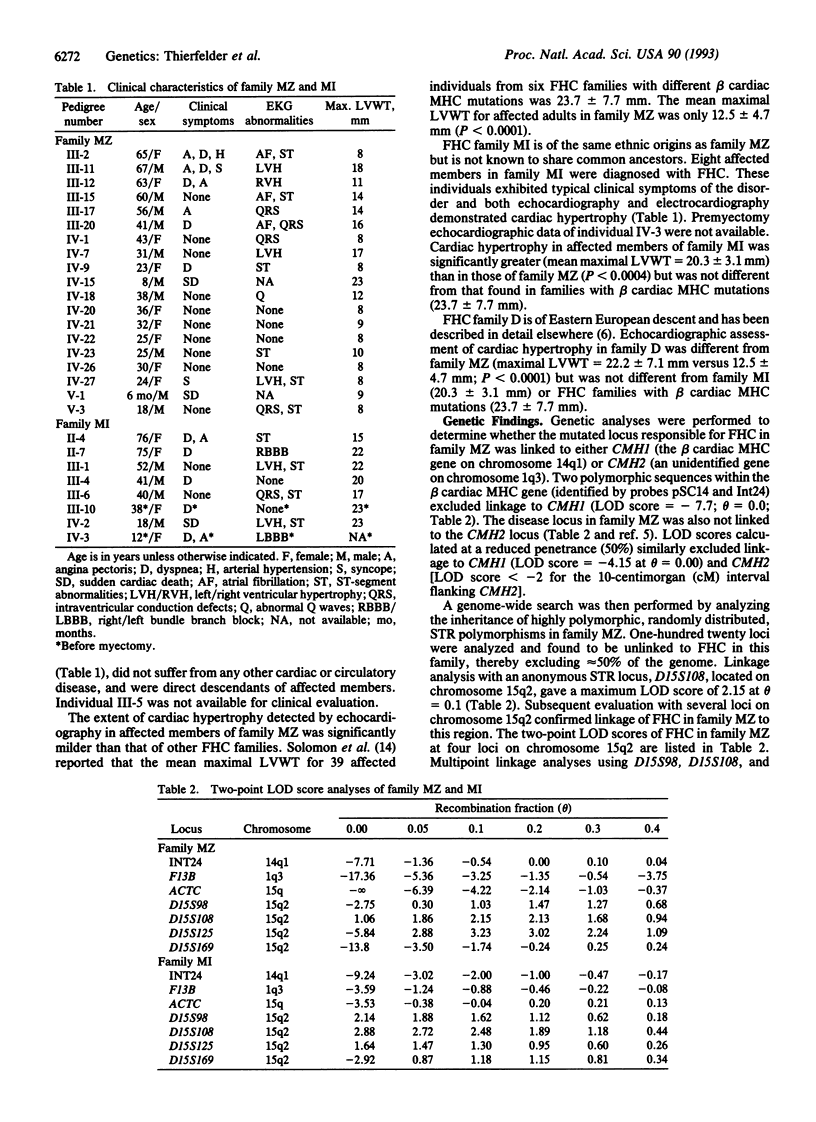
We report that a gene responsible for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC) in a kindred with a mild degree of cardiac hypertrophy maps to chromosome 15q2. The gene encoding cardiac actin, located on chromosome 15q, was analyzed and excluded as a candidate for FHC at this locus. Two additional families with typical FHC were studied and the disorder in one also maps to the chromosome 15q2 locus. The maximum combined multipoint logarithm of odds score in the two linked families is 6.02. Although these two kindreds reside in the same country, we believe that their disorder is caused by independent mutations in the 15q2 locus because of the clinical and genotypic differences between affected individuals. Mutations in at least four loci can cause FHC: chromosomes 14q1 (beta cardiac myosin heavy chain gene), 1q3, and 15q2 and another unidentified locus, suggesting substantial genetic heterogeneity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou Y. H., Brown E. M., Levi T., Crowe G., Atkinson A. B., Arnqvist H. J., Toss G., Fuleihan G. E., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. The gene responsible for familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia maps to chromosome 3q in four unrelated families. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):295–300. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N. D., Cohn G. M., Cyran F., Fananapazir L. Differences in clinical expression of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated with two distinct mutations in the beta-myosin heavy chain gene. A 908Leu----Val mutation and a 403Arg----Gln mutation. Circulation. 1992 Aug;86(2):345–352. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Kass S., Tanigawa G., Vosberg H. P., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a beta cardiac myosin heavy chain gene missense mutation. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90274-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarcho J. A., McKenna W., Pare J. A., Solomon S. D., Holcombe R. F., Dickie S., Levi T., Donis-Keller H., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Mapping a gene for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to chromosome 14q1. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1372–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. L., Luty J. A., Litt M. Regional localization of the gene for cardiac muscle actin (ACTC) on chromosome 15q. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):904–905. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90185-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Gottdiener J. S., Epstein S. E. Patterns and significance of distribution of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A wide angle, two dimensional echocardiographic study of 125 patients. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Sep;48(3):418–428. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. J., Kleinebenne A., Nihoyannopoulos P., Foale R. Echocardiographic measurement of right ventricular wall thickness in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: relation to clinical and prognostic features. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Feb;11(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. M., McKenna W. J. Distribution of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a two-dimensional echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Sep;2(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon S. D., Jarcho J. A., McKenna W., Geisterfer-Lowrance A., Germain R., Salerni R., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetically heterogeneous disease. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):993–999. doi: 10.1172/JCI114802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Jarcho J. A., Kass S., Solomon S. D., Vosberg H. P., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A molecular basis for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an alpha/beta cardiac myosin heavy chain hybrid gene. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90273-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins H., MacRae C., Thierfelder L., Chou Y. H., Frenneaux M., McKenna W., Seidman J. G., Seidman C. E. A disease locus for familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy maps to chromosome 1q3. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):333–337. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins H., Rosenzweig A., Hwang D. S., Levi T., McKenna W., Seidman C. E., Seidman J. G. Characteristics and prognostic implications of myosin missense mutations in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 23;326(17):1108–1114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204233261703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



