Abstract
A convenient synthetic method is described for the preparation of peptide-methotrexate (MTX) conjugates in which MTX is coupled selectively through the gamma-carboxyl group of its glutamic acid moiety to a free amino group in peptide analogs. The syntheses of a somatostatin analog-MTX conjugate (MTX-D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys-Thr-NH2) (AN-51) and two conjugates of analogs of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) with MTX [Glp-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-D-Lys(MTX)-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2] (AJ-04) and [Ac-Ser-Tyr-D-Lys(MTX)-Leu-Arg-Pro-NH-Et] AJ-51 are presented as examples. Benzotriazol-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate (BOP reagent) was used in the synthesis for activation of 4-amino-4-deoxy-N10-methylpteroic acid, which reacted with the potassium salt of glutamic acid alpha-tert-butyl ester in dimethyl sulfoxide to form the suitably protected MTX derivative. This synthesis provides an example of the high suitability of BOP reagent for the salt-coupling method. The selectively protected MTX derivative was then coupled to the different peptide carriers and deprotected under relatively mild conditions by trifluoroacetic acid. The conjugates of MTX with hormonal analogs are suitable for targeting to various tumors that possess receptors for the peptide moieties.
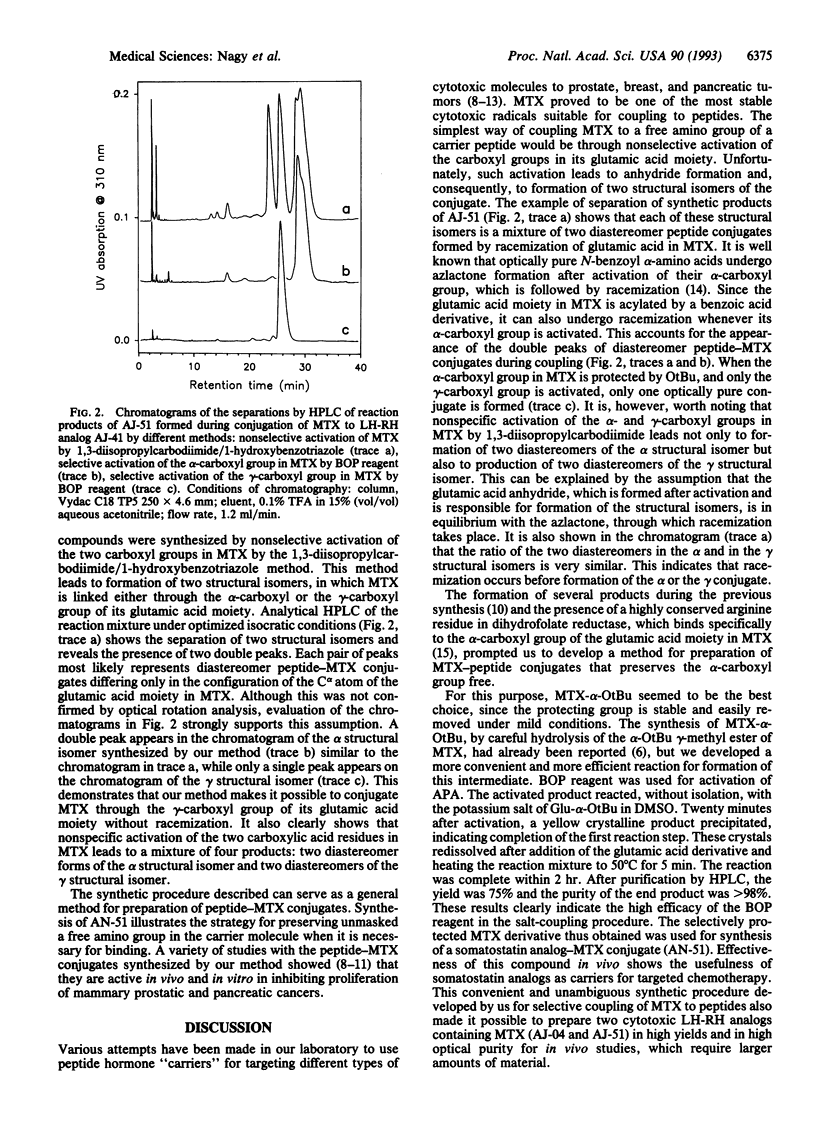
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajusz S., Janaky T., Csernus V. J., Bokser L., Fekete M., Srkalovic G., Redding T. W., Schally A. V. Highly potent analogues of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone containing D-phenylalanine nitrogen mustard in position 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6318–6322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajusz S., Janaky T., Csernus V. J., Bokser L., Fekete M., Srkalovic G., Redding T. W., Schally A. V. Highly potent metallopeptide analogues of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6313–6317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin J. T., Filman D. J., Matthews D. A., Hamlin R. C., Kraut J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 A resolution. I. General features and binding of methotrexate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13650–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai R. Z., Szoke B., Lu R., Fu D., Redding T. W., Schally A. V. Synthesis and biological activity of highly potent octapeptide analogs of somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janáky T., Juhász A., Bajusz S., Csernus V., Srkalovic G., Bokser L., Milovanovic S., Redding T. W., Rékási Z., Nagy A. Analogues of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone containing cytotoxic groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):972–976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janáky T., Juhász A., Rékási Z., Serfözö P., Pinski J., Bokser L., Srkalovic G., Milovanovic S., Redding T. W., Halmos G. Short-chain analogs of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone containing cytotoxic moieties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10203–10207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kralovec J., Spencer G., Blair A. H., Mammen M., Singh M., Ghose T. Synthesis of methotrexate-antibody conjugates by regiospecific coupling and assessment of drug and antitumor activities. J Med Chem. 1989 Nov;32(11):2426–2431. doi: 10.1021/jm00131a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radulovic S., Cai R. Z., Serfozo P., Groot K., Redding T. W., Pinski J., Schally A. V. Biological effects and receptor binding affinities of new pseudononapeptide bombesin/GRP receptor antagonists with N-terminal D-Trp or D-Tpi. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Dec;38(6):593–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radulovic S., Nagy A., Szoke B., Schally A. V. Cytotoxic analog of somatostatin containing methotrexate inhibits growth of MIA PaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Lett. 1992 Mar 15;62(3):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosowsky A., Forsch R., Uren J., Wick M. Methotrexate analogues. 14. Synthesis of new gamma-substituted derivatives as dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors and potential anticancer agents. J Med Chem. 1981 Dec;24(12):1450–1455. doi: 10.1021/jm00144a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Srkalovic G., Szende B., Redding T. W., Janaky T., Juhasz A., Korkut E., Cai R. Z., Szepeshazi K., Radulovic S. Antitumor effects of analogs of LH-RH and somatostatin: experimental and clinical studies. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;37(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(90)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srkalovic G., Cai R. Z., Schally A. V. Evaluation of receptors for somatostatin in various tumors using different analogs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Mar;70(3):661–669. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-3-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szepeshazi K., Schally A. V., Juhasz A., Nagy A., Janaky T. Effect of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs containing cytotoxic radicals on growth of estrogen-independent MXT mouse mammary carcinoma in vivo. Anticancer Drugs. 1992 Apr;3(2):109–116. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199204000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



