Figure 7. The binding between endoglin and the PP2A/B subunit is involved in the disruption of the PP2A complex in human hemangioma specimens.
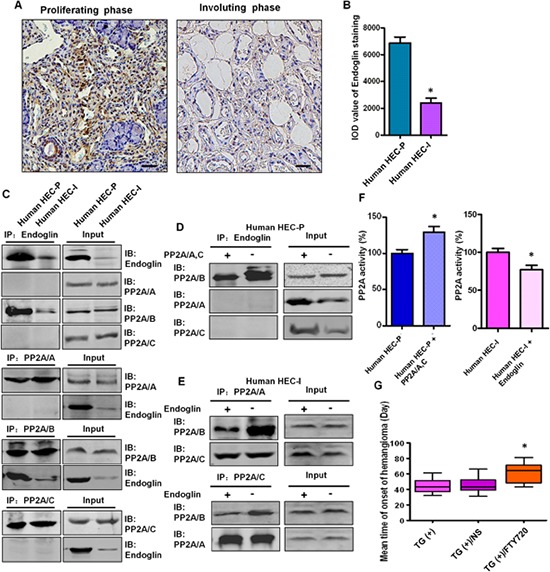
A. Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of endoglin in human proliferating phase hemangioma specimens and involuting phase hemangioma specimens. Bar = 50 μm B. Quantitative analysis of the IOD value of endoglin staining. (n = 36, t test) *P < 0.05 C. Binding between endoglin and the PP2A/B subunit in HEC-P cells and HEC-I cells was determined by immunoprecipitation and immunoblot. D. Human HEC-P cells were transiently transfected with the PP2A/A and C plasmids and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with endoglin and probed with anti-PP2A/A, B, C antibody. Competition assay results showed that ectopic expression of the PP2A/A, C subunits abolished the endoglin-PP2A/B binding. E. Human HEC-I cells were transiently transfected with the endoglin expression plasmids and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with PP2A/A, C and probed with anti-PP2A/A, B, C antibody. Competition assay results showed that ectopic expression of endoglin abolished the PP2A/B -PP2A/A, C binding. F. Phosphatase activity assay results showed that increased PP2A activity was detected when the PP2A/A, C subunits were overexpressed in HEC-P cells. In contrast, PP2A activity was decreased when endoglin was overexpressed in HEC-I cells. (n = 3/group, t test) *P < 0.05 G. There was a significant difference in the tumor-free time between the control PyMT TG(+) mice and TG(+) mice treated with PP2A activator FTY720. (n = 7/group, one-way ANOVA) *P < 0.05
