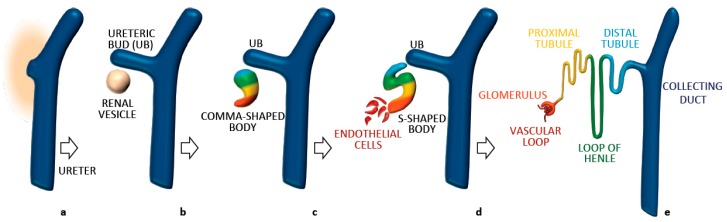
Figure 2.
Main developmental steps of the renal nephron. Branching of the ureter generates ureteric buds (UB), surrounded by mesenchymal tissue (a); their interaction induces a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and generates the renal vescicle (b); that develops in a patterned comma-shaped body (c); subsequently extending in a tubular S-shaped body (d). On one side the S-shaped body makes contact with the ureter, on the other side it connects with migrating endothelial cells that will form the vascular loop within the glomerulus. The patterned expression of specific transcription factors in each tract of the S-shaped body generates the different structures of the mature nephron (see color code (e)).