Abstract
We have previously reported the isolation of a human retrotransposable L1 element. This element, allele L1.2B at the LRE-1 locus of chromosome 22, was shown by nucleotide sequence identity to be the direct precursor of a de novo retrotransposition event into the factor VIII gene on the X chromosome, resulting in hemophilia A in patient JH-27. We now report the isolation of the two remaining full-length members of the subfamily of L1 elements closely related to L1.2B present in the genome of the mother of JH-27. Since these elements, L1.3 and L1.4, are very similar in sequence to L1.2B and contain both open reading frames 1 and 2 intact, they are also likely to be active retrotransposable elements. This suggests that certain L1 subfamilies may contain multiple active elements.
Full text
PDF
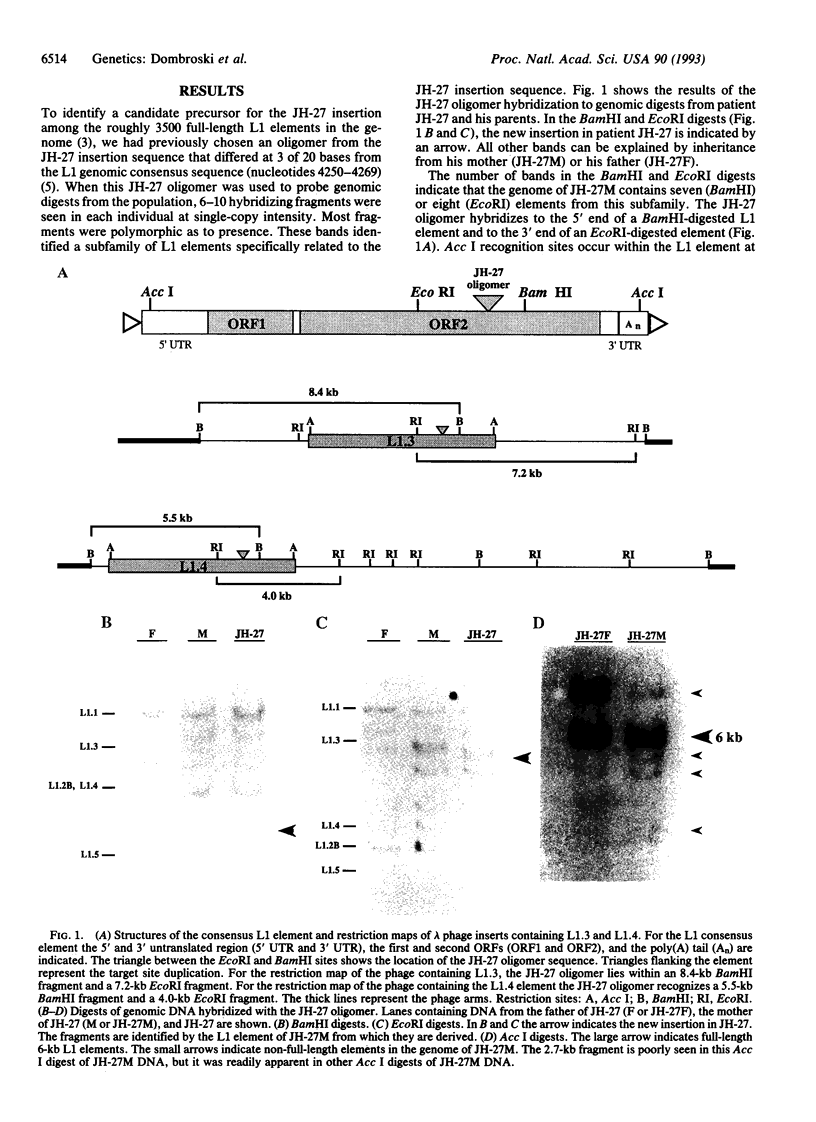

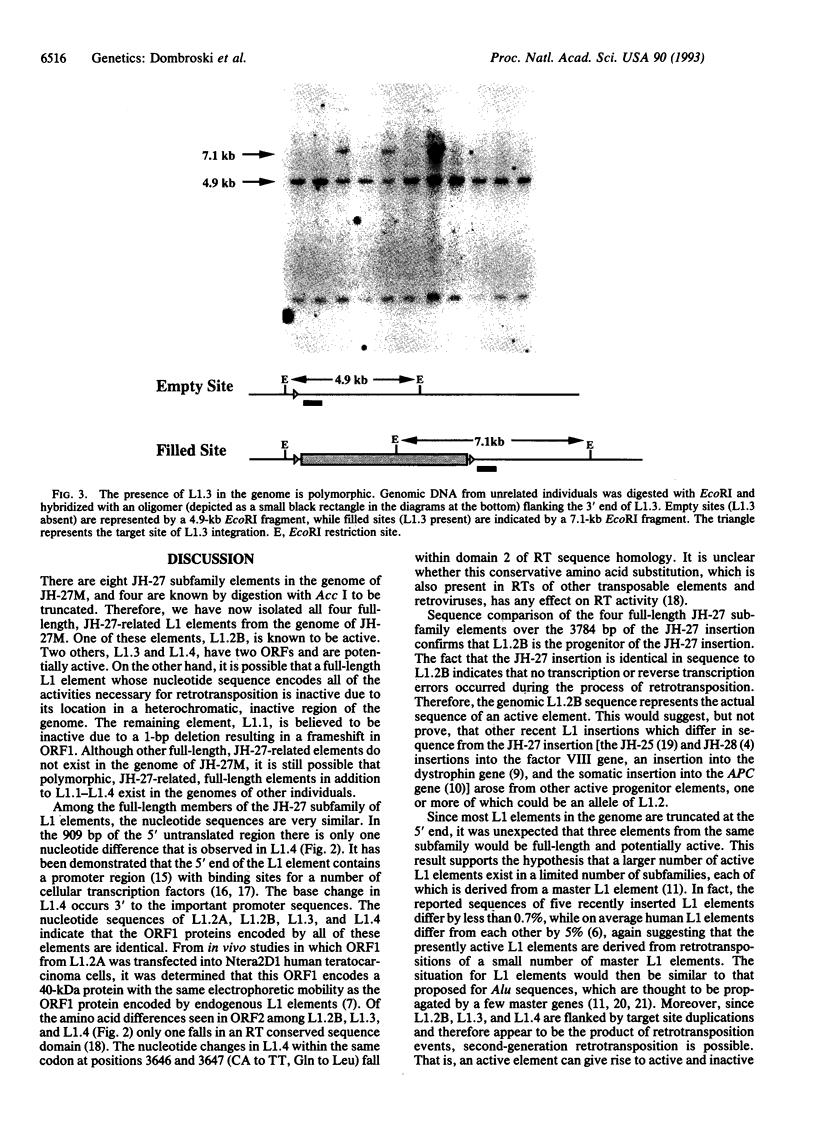

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deininger P. L., Batzer M. A., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Master genes in mammalian repetitive DNA amplification. Trends Genet. 1992 Sep;8(9):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Slagel V. K. Recently amplified Alu family members share a common parental Alu sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4566–4569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski B. A., Mathias S. L., Nanthakumar E., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr Isolation of an active human transposable element. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1805–1808. doi: 10.1126/science.1662412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of a mouse IAP sequence tagged with an indicator gene. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90217-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. E., Singer M. F., Swergold G. D. Studies on p40, the leucine zipper motif-containing protein encoded by the first open reading frame of an active human LINE-1 transposable element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19765–19768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii A., Nakatsuru S., Miyoshi Y., Ichii S., Nagase H., Kato Y., Yanagisawa A., Nakamura Y. The APC gene, responsible for familial adenomatous polyposis, is mutated in human gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 1;52(11):3231–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S., Heidmann T. An indicator gene for detection of germline retrotransposition in transgenic Drosophila demonstrates RNA-mediated transposition of the LINE I element. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1927–1937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ohta T. The age of a neutral mutant persisting in a finite population. Genetics. 1973 Sep;75(1):199–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold D. M., Swergold G. D., Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Dombroski B. A., Fanning T. G. Translation of LINE-1 DNA elements in vitro and in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6990–6994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Schmid C. W. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5424–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S. L., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boeke J. D., Gabriel A. Reverse transcriptase encoded by a human transposable element. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.1722352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S. L., Scott A. F. Promoter binding proteins of an active human L1 retrotransposon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 15;191(2):625–632. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minakami R., Kurose K., Etoh K., Furuhata Y., Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Identification of an internal cis-element essential for the human L1 transcription and a nuclear factor(s) binding to the element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3139–3145. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Torney D. C., Meyne J., Buckingham J. M., Wu J. R., Burks C., Sirotkin K. M., Goad W. B. The distribution of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the human genome. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):273–289. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90331-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muratani K., Hada T., Yamamoto Y., Kaneko T., Shigeto Y., Ohue T., Furuyama J., Higashino K. Inactivation of the cholinesterase gene by Alu insertion: possible mechanism for human gene transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11315–11319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita N., Nishio H., Kitoh Y., Ishikawa Y., Ishikawa Y., Minami R., Nakamura H., Matsuo M. Insertion of a 5' truncated L1 element into the 3' end of exon 44 of the dystrophin gene resulted in skipping of the exon during splicing in a case of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):1862–1867. doi: 10.1172/JCI116402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A., Finnegan D. J., Bucheton A. Evidence for retrotransposition of the I factor, a LINE element of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4907–4910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. F., Schmeckpeper B. J., Abdelrazik M., Comey C. T., O'Hara B., Rossiter J. P., Cooley T., Heath P., Smith K. D., Margolet L. Origin of the human L1 elements: proposed progenitor genes deduced from a consensus DNA sequence. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90003-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. The abundant LINE-1 family of repeated DNA sequences in mammals: genes and pseudogenes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):457–464. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swergold G. D. Identification, characterization, and cell specificity of a human LINE-1 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6718–6729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaud D., Vidaud M., Bahnak B. R., Siguret V., Gispert Sanchez S., Laurian Y., Meyer D., Goossens M., Lavergne J. M. Haemophilia B due to a de novo insertion of a human-specific Alu subfamily member within the coding region of the factor IX gene. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(1):30–36. doi: 10.1159/000472385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Saulino A. M., Gregory P. E., Glover T. W., Collins F. S. A de novo Alu insertion results in neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):864–866. doi: 10.1038/353864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods-Samuels P., Wong C., Mathias S. L., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E. Characterization of a nondeleterious L1 insertion in an intron of the human factor VIII gene and further evidence of open reading frames in functional L1 elements. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]