Abstract
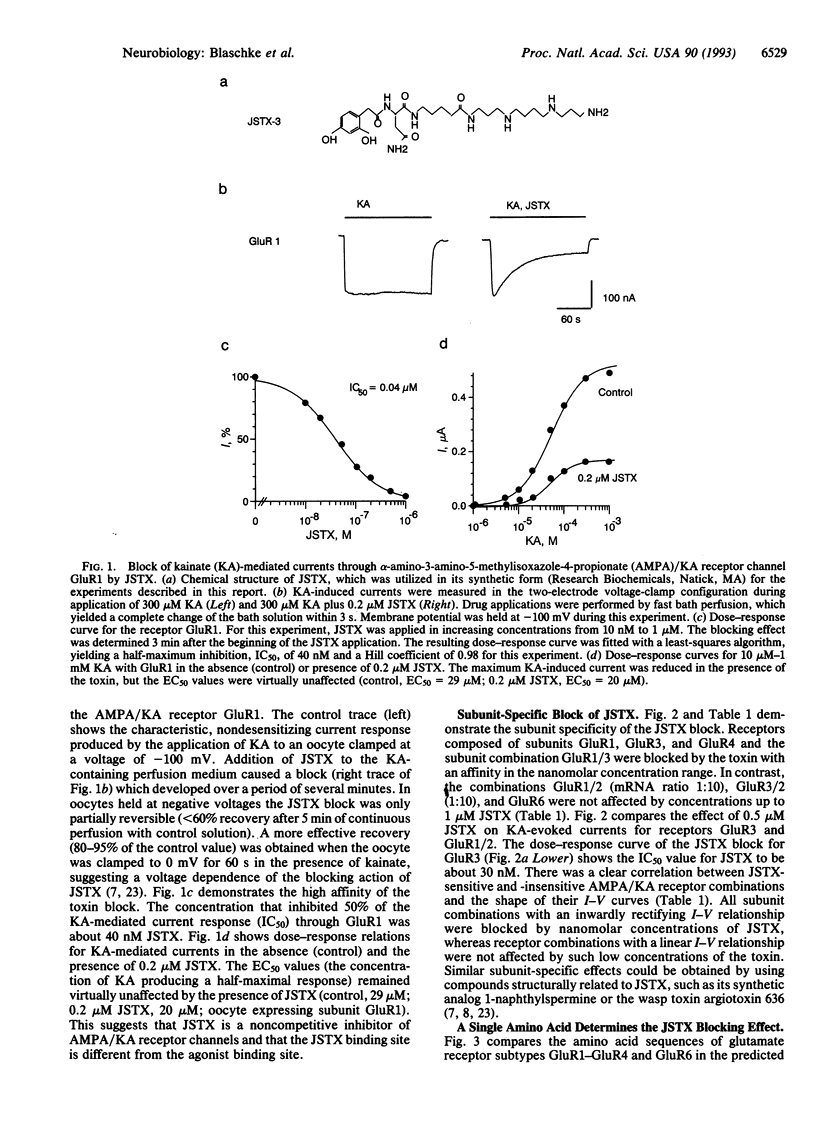
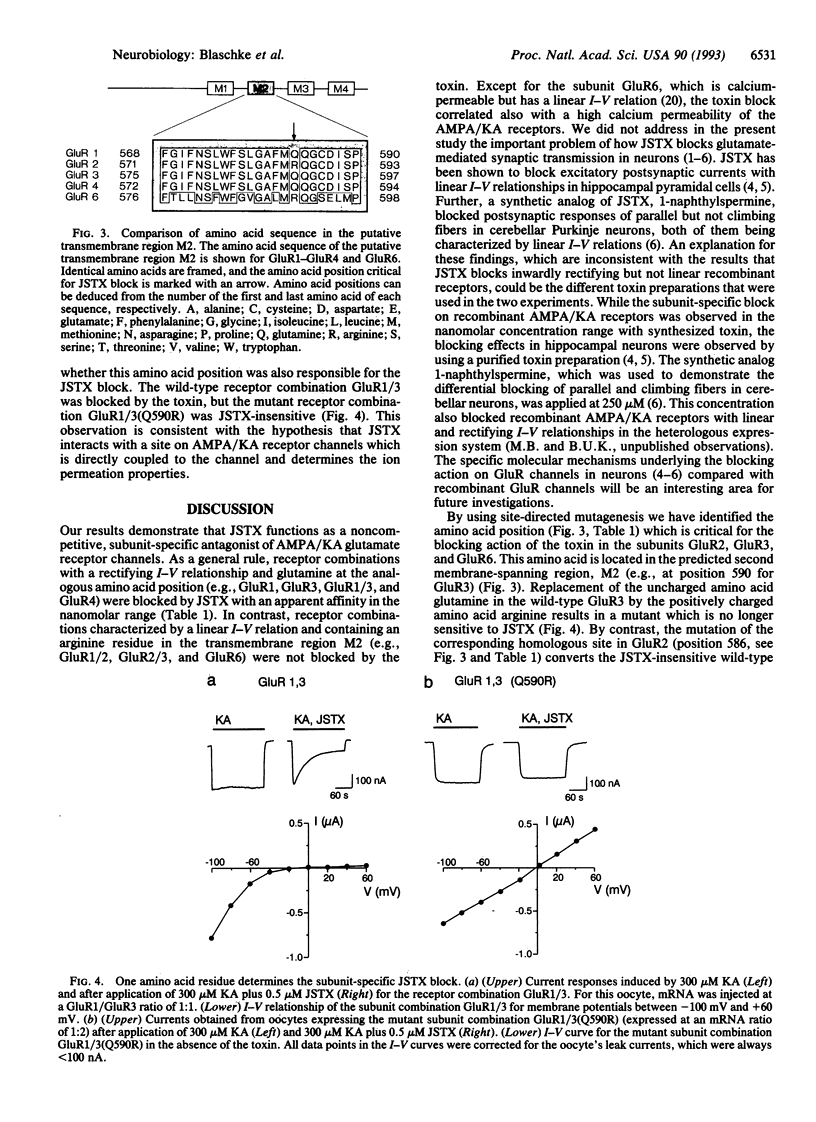
Joro spider toxin (JSTX) is one of the most potent antagonists of glutamatergic AMPA/KA (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate/kainate) receptor channels in invertebrates and vertebrates. A differential blocking effect on certain types of glutamatergic synapses--e.g., parallel and climbing fiber synaptic inputs to rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons--has been shown by using a synthetic analog of the spider toxin. By investigating the molecular basis of the JSTX action on the recombinant AMPA/KA receptors GluR1-GluR4 and GluR6 expressed in Xenopus oocytes, we found that submicromolar concentrations of JSTX exert a subunit-specific block. Thus, receptor subunits forming a receptor channel with a linear current-voltage (I-V) relationship (GluR1/2, GluR2/3, and GluR6) were not affected, while receptor subunits with rectifying I-V relationships (GluR1, GluR3, GluR4, and GluR1/3) were reversibly blocked by JSTX. By using receptor-subunit mutants obtained by site-directed mutagenesis, we have identified a single amino acid position (glutamine in the proposed second transmembrane domain) that is critical for the JSTX block. Since this site has previously been shown to control the I-V relationship of the AMPA/KA receptor channel and to participate in the regulation of the channel's permeability for calcium ions, our findings suggest that JSTX binds close to the central pore region of the channel.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajima A., Hensch T., Kado R. T., Ito M. Differential blocking action of Joro spider toxin analog on parallel fiber and climbing fiber synapses in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neurosci Res. 1991 Oct;12(1):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Kawai N., Kiskin N. I., Kljuchko E. M., Krishtal O. A., Tsyndrenko AYa Spider toxin blocks excitatory amino acid responses in isolated hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 31;79(3):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90453-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Egebjerg J., Sharma G., Pecht G., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Moll C., Stevens C. F., Heinemann S. Cloning of a putative glutamate receptor: a low affinity kainate-binding subunit. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90292-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Hartley M., Deneris E., Maron C., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1033–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2168579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Khodorova A., Jonas P., Helm P. J., Wisden W., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Calcium-permeable AMPA-kainate receptors in fusiform cerebellar glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1317970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Hume R. I., Heinemann S. F. Structural determinants of barium permeation and rectification in non-NMDA glutamate receptor channels. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4080–4087. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04080.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Heinemann S. F. Ca2+ permeability of unedited and edited versions of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Hartley M., Heinemann S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA--gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1709304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R. I., Dingledine R., Heinemann S. F. Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1028–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.1653450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson H., Usherwood P. N. Spider toxins as tools for dissecting elements of excitatory amino acid transmission. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai N., Miwa A., Saito M., Pan-Hou H. S., Yoshioka M. Spider toxin (JSTX) on the glutamate synapse. J Physiol (Paris) 1984;79(4):228–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai N., Niwa A., Abe T. Spider venom contains specific receptor blocker of glutaminergic synapses. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):169–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B. U., Blaschke M., Rivosecchi R., Hollmann M., Heinemann S. F., Konnerth A. Identification of a subunit-specific antagonist of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate/kainate receptor channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):605–609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B. U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S., Konnerth A. Calcium influx through subunits GluR1/GluR3 of kainate/AMPA receptor channels is regulated by cAMP dependent protein kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):891–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05127.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockgether T., Turski L., Honoré T., Zhang Z. M., Gash D. M., Kurlan R., Greenamyre J. T. The AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX has antiparkinsonian effects in monoamine-depleted rats and MPTP-treated monkeys. Ann Neurol. 1991 Nov;30(5):717–723. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löschmann P. A., Lange K. W., Kunow M., Rettig K. J., Jähnig P., Honoré T., Turski L., Wachtel H., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Synergism of the AMPA-antagonist NBQX and the NMDA-antagonist CPP with L-dopa in models of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect. 1991;3(3):203–213. doi: 10.1007/BF02259538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. W., Garofalo E. A., Hood T., Sackellares J. C., Gilman S., McKeever P. E., Troncoso J. C., Johnston M. V. Altered excitatory and inhibitory amino acid receptor binding in hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1991 May;29(5):529–541. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller T., Möller T., Berger T., Schnitzer J., Kettenmann H. Calcium entry through kainate receptors and resulting potassium-channel blockade in Bergmann glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1317969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N., Shneider N. A., Axel R. A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):569–581. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90212-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestley T., Woodruff G. N., Kemp J. A. Antagonism of responses to excitatory amino acids on rat cortical neurones by the spider toxin, argiotoxin636. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1315–1323. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Sahara Y., Miwa A., Shimazaki K., Nakajima T., Kawai N. Effects of a spider toxin (JSTX) on hippocampal CA1 neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 27;481(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Keinänen K., Verdoorn T. A., Wisden W., Burnashev N., Herb A., Köhler M., Takagi T., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1580–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1699275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Structural determinants of ion flow through recombinant glutamate receptor channels. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1715–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.1710829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




