Figure 1.
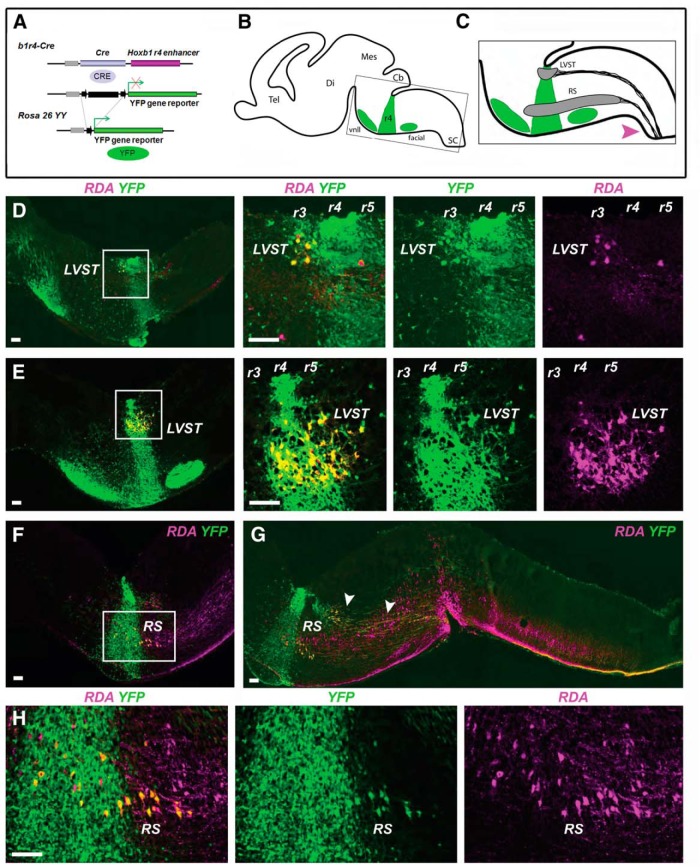
Fate mapping of LVST neurons and reticulospinal neurons. A, The b1r4-Cre line, which expresses the Cre recombinase under the control of the Hoxb1 r4 enhancer, is crossed with the ROSA26YY reporter line to label r4 derivatives by YFP expression. B, C, Schematic diagrams of E16.5 brain in the parasagittal plane illustrating the location of YFP-positive r4 and r4 derivatives (green), and the domains of the LVST group and the main population of ipsilaterally projecting reticulospinal (RS) neurons (gray). C, Magenta arrowhead indicates the tracer application site used to retrogradely label vestibulospinal and reticulospinal neurons. D, E, All LVST neurons, including those in r3 and r5, derive from r4. The first panel in each horizontal series is a low-magnification image, with a white square indicating the region shown in the subsequent images. F–H, A population of ipsilaterally projecting RS neurons in r4 and r5 derives from r4. G, Arrowheads indicate LVST axons projecting just dorsal to the RS neurons. RDA/BDA labeling is depicted by magenta, YFP immunolabeling is depicted by green, and double labeling appears as varying hues of yellow and orange. Note that in this and subsequent figures some double-labeled neurons appear to have a magenta nucleus with surrounding yellow to orange cytoplasm; this is because the RDA/BDA can partition into the nucleus where the YFP is weak. Tel, Telencephalon; Di, diencephalon; Mes, mesencephalon; Cb, cerebellum; SC, spinal cord; vnll, ventral nucleus of lateral lemniscus; facial, VIIth cranial (facial) nerve motor nucleus. Scale bars, 200 µm.