Abstract
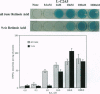
We have assessed whether retinoic acid (RA) comes from local sources or is available widely to activate gene expression in embryos. We used an RA-responsive indicator cell line, L-C2A5, to localize RA sources. In these cells, an RA-sensitive promoter/lacZ reporter construct used previously by us to produce indicator transgenic mice is induced globally by RA in medium or locally by RA released at physiological concentrations (1 nM) from AG-1X2 resin beads. Furthermore, the cells are differentially responsive to the 9-cis and all-trans isomers of RA at low concentrations. Indicator transgenic mice with the same promoter/reporter construct were used to identify regions of RA-mediated gene activation. There are distinct domains of lacZ expression in the cervical and lumbar spinal cords of embryonic indicator mice. This pattern might reflect localized RA sources or restricted spatial and temporal expression of RA receptors, binding proteins, or other factors. To resolve this issue we compared the pattern of transgene activation in indicator cell monolayers cocultured with normal embryonic spinal cords with that in transgenic spinal cords. The explants induced reporter gene expression in L-C2A5 monolayers in a pattern identical to that in transgenic mice: alar regions of the cervical and lumbar cord were positive whereas those in the thoracic and sacral regions were not. We conclude that restricted sources of RA in the developing spinal cord mediate the local activation of RA-inducible genes. Thus, region-specific gene activation in embryos can be mediated by precisely localized sources of inductive molecules like RA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allenby G., Bocquel M. T., Saunders M., Kazmer S., Speck J., Rosenberger M., Lovey A., Kastner P., Grippo J. F., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):30–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkan W., Colbert M., Bock C., Linney E. Transgenic indicator mice for studying activated retinoic acid receptors during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3347–3351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenstam A., Vivanco Ruiz M. M., Barettino D., Horikoshi M., Stunnenberg H. G. Cooperativity in transactivation between retinoic acid receptor and TFIID requires an activity analogous to E1A. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90443-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Huang L., Russo A. F., Solursh M. Retinoic acid is enriched in Hensen's node and is developmentally regulated in the early chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10056–10059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Leroy P., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. I. A systematic study of their differential pattern of transcription during mouse organogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1133–1151. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espeseth A. S., Murphy S. P., Linney E. Retinoic acid receptor expression vector inhibits differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1647–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Jahroudi N., Varshney U., Gedamu L. Structure and expression of the human metallothionein-IG gene. Differential promoter activity of two linked metallothionein-I genes in response to heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11528–11535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornbruch A., Wolpert L. Positional signalling by Hensen's node when grafted to the chick limb bud. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986 Jun;94:257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., McGuire W. L. Estrogen control of progesterone receptor in human breast cancer. Correlation with nuclear processing of estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Chen D. T., Hoar R. M., Agnish N. D., Benke P. J., Braun J. T., Curry C. J., Fernhoff P. M., Grix A. W., Jr, Lott I. T. Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):837–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E. Retinoic acid receptors: transcription factors modulating gene regulation, development, and differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1992;27:309–350. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60538-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall H., Nonchev S., Sham M. H., Muchamore I., Lumsden A., Krumlauf R. Retinoic acid alters hindbrain Hox code and induces transformation of rhombomeres 2/3 into a 4/5 identity. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):737–741. doi: 10.1038/360737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffery P., Lee M. O., Wagner M. A., Sladek N. E., Dräger U. C. Asymmetrical retinoic acid synthesis in the dorsoventral axis of the retina. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):371–382. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Ruberte E., LeMeur M., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Developmental analysis of the retinoic acid-inducible RAR-beta 2 promoter in transgenic animals. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):723–734. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morriss-Kay G. M., Murphy P., Hill R. E., Davidson D. R. Effects of retinoic acid excess on expression of Hox-2.9 and Krox-20 and on morphological segmentation in the hindbrain of mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2985–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds K., Mezey E., Zimmer A. Activity of the beta-retinoic acid receptor promoter in transgenic mice. Mech Dev. 1991 Dec;36(1-2):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90068-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossant J., Zirngibl R., Cado D., Shago M., Giguère V. Expression of a retinoic acid response element-hsplacZ transgene defines specific domains of transcriptional activity during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1333–1344. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):45–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Jessell T. M. Retinoic acid modifies the pattern of cell differentiation in the central nervous system of neurula stage Xenopus embryos. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):945–958. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satre M. A., Kochhar D. M. Elevations in the endogenous levels of the putative morphogen retinoic acid in embryonic mouse limb-buds associated with limb dysmorphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1989 Jun;133(2):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Summerbell D., Wolpert L. Positional signalling and specification of digits in chick limb morphogenesis. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):199–202. doi: 10.1038/254199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran P., Zhang X. K., Salbert G., Hermann T., Lehmann J. M., Pfahl M. COUP orphan receptors are negative regulators of retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4666–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Han B., Jessell T. M. Regional differences in retinoid release from embryonic neural tissue detected by an in vitro reporter assay. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):55–66. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Thaller C., Jessell T., Eichele G. Polarizing activity and retinoid synthesis in the floor plate of the neural tube. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):819–822. doi: 10.1038/345819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]