Abstract
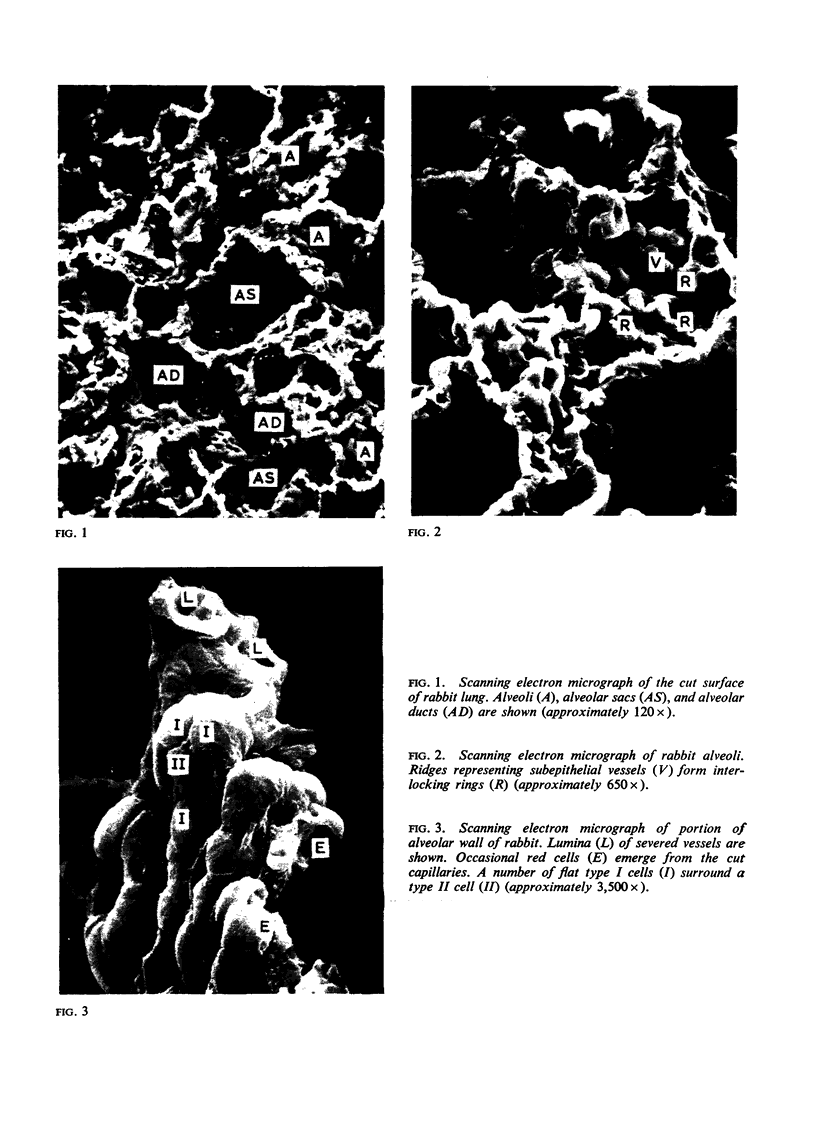
The pattern of subepithelial vessels in pulmonary alveoli of rabbits has been studied using scanning electron microscopy.
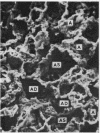
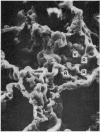
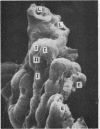
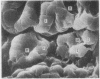
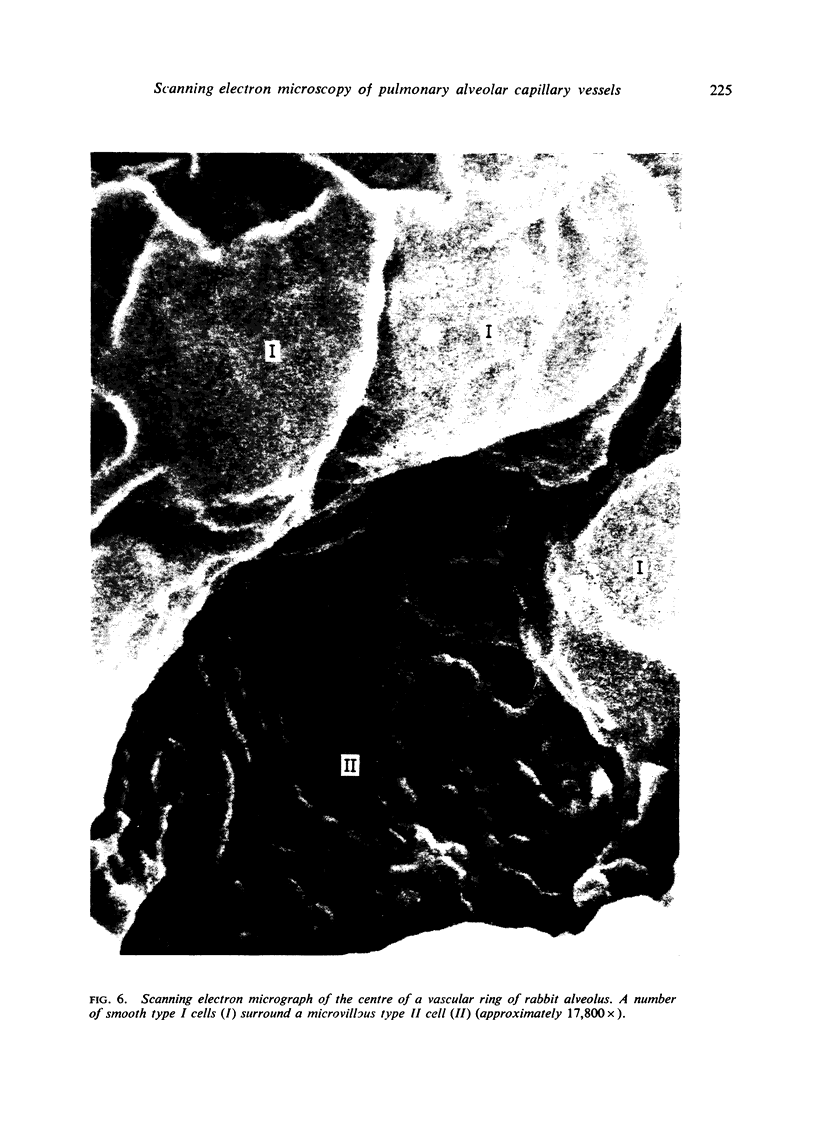
Alveolar capillaries form a network of interconnecting vascular rings, most of which surround the periphery of type II cells of the alveolar epithelium. Individual capillaries contributing to the formation of adjacent rings follow a corrugated course with angulations located on the sites of junction with other capillaries completing the rings; the capillaries are covered by type I epithelial cells which also extend into and form the alveolar lining at the peripheral area of the interstices of the capillary network. Single type II cells form the alveolar lining at the centre of vascular rings.
The pattern of pulmonary alveolar capillaries revealed by scanning electron microscopy is thus similar to that postulated by Weibel (1963) on the basis of transmission microscopic studies.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber V. C., Boyde A. Scanning electron microscopic studies of cilia. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;84(2):269–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00330870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland P. H., Schneider C. W. A simple method of preserving ocular tissue for scanning electron microscopy. Vision Res. 1969 Nov;9(11):1401–1402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C., Sobin S. S. Theory of sheet flow in lung alveoli. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Apr;26(4):472–488. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.4.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., GLAUERT R. H. Araldite as an embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Mar 25;4(2):191–194. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., 3rd, Finke E. H. The topography of the pulmonary alveolus: scanning electron microscopy using different fixations. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Jan;38(1):161–173. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The alveolar wall. Br J Dis Chest. 1970 Jul;64(3):121–140. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(70)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Schultz E. L. Pulmonary capillary length in dogs, cat and rabbit. Respir Physiol. 1968 Oct;5(3):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(68)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., GOMEZ D. M. Architecture of the human lung. Use of quantitative methods establishes fundamental relations between size and number of lung structures. Science. 1962 Aug 24;137(3530):577–585. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3530.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]